Legislative position
Under current laws, extensions of contracts limited in duration are possible under certain circumstances. They are prescribed in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (Article 59):
- Employment in an organization created for a short period of time to perform certain work (for example, construction of a factory).
- Occupying the position of a temporarily absent worker who, due to illness or maternity leave, cannot perform his duties.
- Alternative service or internship.
- Employment at a certain time of the year or performing a specific amount of work specified by agreement.
- Providing work on a competitive basis. This approach is typical for representatives of the teaching staff.
After agreeing on the terms of the contract, the latter can be concluded with the following persons:
- Recipients of old-age pensions.
- Citizens who have health problems and are unable to work on a regular basis.
- Elected persons.
- Employees employed in the north, which requires moving to a new location.
- Heads of enterprises.
The validity period of the agreement may vary (depending on the specifics of the work). As a rule, the document is issued for a period from 2-3 months to 5 years. During this period, the participants fulfill the obligations assumed under the fixed-term contract. The document must specify the reason why the employment relationship is implemented on a temporary basis.
Is extension allowed and when is it possible?
The law does not provide for the extension of a fixed-term employment contract for a new term. But sometimes this is possible, including under the terms of the law. In particular, a fixed-term agreement between an employer and an employee is allowed to be extended in the following circumstances:
- A pregnant woman cannot be fired before giving birth and the end of maternity leave.
- The validity period ends shortly before the age limit (typical for teaching staff). This feature, as a rule, concerns rectors and vice-rectors, and the features are prescribed in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (Article 332).
- The employee who replaced another employee and was hired to fulfill obligations did not start work on the specified date. This situation is relevant when maternity leave is extended from 1.5 to 3 years.
- A person temporarily changes his place of employment, after which he remains with the new employer. In this case, the head of this company has the right to change the period of validity of the agreement by extending it for the period of interest to him. The Labor Code of the Russian Federation applies here (Article 348.4).
Taking into account judicial practice, the extension of a fixed-term contract with an employee is possible in a number of additional situations:
- Within the maximum permissible term of the agreement. There is a limit of five years (if agreed upon by the parties).
- If an employee replacing another employee is hired, but does not show up to perform his duties on a certain date.
- Failure to complete the pre-planned scope of work.
Approaches to solving the issue
Paradoxically, the problem of the possibility or impossibility of changing the term of a fixed-term employment contract is still controversial not only in the professional environment of personnel specialists.
On the issue of applicability of the provisions of Art. 72 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation regarding the extension of such an agreement for a long time there was no consensus, including among the courts. At the moment, many personnel service employees firmly take the position that extensions are not allowed as a general rule. And if the parties wish to continue the relationship on the same terms, the parties should terminate the agreement, the term of which has expired, and enter into a new one for the same or a different period of time. This position is based on the idea that a fixed-term employment contract is a special type of agreement, and the determining term of the term differs from the ordinary terms of the contract, which can be changed by agreement of the parties.
In the specialized literature, one can find the position that the continuation of work beyond the initially established period should be understood as work in a situation where none of the parties demanded termination of the agreement due to the expiration of its term, and therefore, the existing agreement between the parties is no longer urgent, but indefinite (part 4 of article 58 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Arbitrage practice
Until recently, the courts, when establishing the fact of extending the term of the agreement, believing that this violates the rights of the employee (Part 6 of Article 58 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), decided to consider such an agreement concluded for an indefinite period.
At the same time, to understand the deadlock of this approach, one should keep in mind the explanations given in the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated March 17, 2004 No. 2 “On the application by the courts of the Russian Federation of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation” on the issue of termination of an existing fixed-term contract due to the expiration of the term (p. 2 part 1 article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) and the conclusion of a new agreement: “if it is established during the trial that the fact of multiple conclusions of fixed-term employment contracts for a short period for the performance of the same labor function, the court has the right, taking into account the circumstances of each case, to recognize the employment contract imprisoned for an indefinite period." That is, such behavior of the employer is by default understood as a violation of the requirements of Part 6 of Art. 58 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which prohibits the conclusion of fixed-term contracts in order to evade the provision of rights and guarantees provided for employees with whom an agreement is concluded for an indefinite period. Illegal motives and intent to evade providing the employee with rights and guarantees in this case are apparently presumed.
The practice on the issue of extending the term of a fixed-term employment contract, which has currently developed in the courts of general jurisdiction, is uniform and consistent. Perhaps it is precisely this fact that is associated with the absence, after 2014, of a changed opinion expressed by the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation regarding the possibility of extending the terms of fixed-term employment contracts (the courts correctly apply the rule, there is nothing to correct them).
In court decisions, the possibility of extending the terms of fixed-term employment contracts, as a rule, is justified by the absence of contradictions between Art. , , 79 Labor Code of the Russian Federation and Art. 72 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Federal Service for Labor and Employment (Rostrud)
It is worth noting that the relevant executive body - Rostrud (namely, personnel workers en masse rely on its letters when the law is unclear) - was not consistent in its understanding of the possibility or impossibility of extending the period. In Letter No. 4413-6 dated October 31, 2007, Rostrud reacted quite calmly and positively to the possibility of extending the term of a fixed-term employment contract and recommended changing the term of the employment contract by concluding an additional agreement to it.
However, a little more than a year later, Rostrud changed its opinion to the exact opposite. In Letter No. 2742-6-1 dated December 8, 2008, Rostrud indicated that there are no legal grounds for extending a fixed-term employment contract for a new term without terminating it. In the same Letter, Rostrud also indicated that an exception to this rule is established by law only for certain categories of workers (in particular, for pregnant women and teachers - part 2 of article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and part 8, part 9 of article 332 of the Labor Code RF, respectively).
And on October 24, 2018, Rostrud once again changed its opinion to the opposite and spoke out about the possibility and legality of extending a fixed-term employment contract, provided that the basis on which the fixed-term employment contract was concluded is preserved (does not change), and also if the total term of the employment contract does not exceed 5 years.
This approach cannot be considered successful, since it goes against the established practice of the courts and is based on the vicious basis “what is not permitted is prohibited,” not allowing the employee and employer to act freely, based on their interests and economic needs. Acceptance of the changes proposed by the Ministry of Labor to the text of Art. 58 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, in our opinion, will most likely lead to an increase in abuses on the part of the employer during dismissal in a situation where the term of the current contract goes beyond the scope of the need for a given employee. This need, especially at the micro-enterprise level, is difficult to accurately predict. And in the conditions of the possibility of only a one-time extension, the validity period of the concluded or extended contract will be set with a “reserve” (the issue of changing the contract term downwards is ignored both in the text of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and in the text of the draft of the Ministry of Labor).
When extension is prohibited
The current regulations do not stipulate when the extension of an agreement with a limited period of validity is prohibited. For this reason, conflict situations and violations arise in this area. For example, if the contract states that the employee is employed to perform seasonal work, he will not be able to be involved in cooperation for 12 months of the year.
A similar situation occurs with people selected to occupy a particular position. The work of such an employee under the terms of the contract extension is excluded, because after the expiration of the document, he must be fired. In any case, each situation is considered individually, and when deciding on an extension, one must proceed from the specifics of employment and logic.
How to prepare documents
When hiring on a fixed-term contract, a person indicates in the application that his work will be temporary. For example, he uses the wording “during the absence of the main employee” or “I ask to be hired on a fixed-term contract.”
The main thing is to reflect in the application that the employee is informed about the temporary nature of the employment. Otherwise, the sample application remains standard and includes traditional details: position and name of the head of the organization, full name of the applicant, name of the vacant position, date of preparation and signature.
Now let's look at how to renew if the contract has expired. The simplest way would be to sign an additional agreement between the employee and the employer and indicate in it the period during which the contract is extended with the following wording: “the term of this contract is extended by ... months (years).”
A sample order to extend a fixed-term employment contract can be easily found on the Internet. This document can be adopted in free form or in accordance with the standards adopted by the organization. The main thing is to indicate:
- title “on extension of the employment contract”;
- date and registration number;
- number and date of the renewed document;
- reason (for example, the need to complete work).
In order for the extension to be legal, all wording in the documents must be extremely clear and precise, with an exact indication of the dates and numbers of previous acts. It is important to remember that contract extension is possible only by mutual agreement . Therefore, if the employee does not intend to continue cooperation, he may refuse the extension, even if the work for which he was hired has not been completed.
Nuances of drawing up fixed-term contracts with pregnant women
A fixed-term employment contract with a pregnant woman cannot be terminated even after the expiration of the term. In this case, the employer signs an order to extend the contract, indicating a medical certificate from the antenatal clinic as a basis. The employee must provide such a certificate upon request of the employer every three months.
The exception is situations where the contract stipulates that the employee is hired during the absence of the main employee. If the employer does not have a vacancy to which a pregnant employee agrees to transfer, the parties do not renew the contract by mutual agreement.
The contract with such an employee can be terminated only after the end of pregnancy. Managers and personnel of organizations should take into account that in cases when it comes to litigation, the court almost always takes the side of the pregnant woman.
Hiring employees under a fixed-term employment contract is possible only if there are objective circumstances
How to renew the agreement
An agreement issued for a limited period is more attractive for the employer (when compared with the benefit for the employee). The manager hires a person for a limited period to perform a specific job, after which he has the right to fire him. For its part, it would be more convenient for the employee to work on a permanent basis and independently make the decision to quit. That is why the extension of such contracts occurs in rare cases and upon agreement of the parties.
Features and reasons
In the issue of extending a fixed-term employment contract, only one of the parties speaks. Before drawing up a new document, the participants meet and discuss the terms of future cooperation. Based on the results of the conversation, an additional document is drawn up (to the existing agreement), and then an order is issued for the entry into force of the agreement.
It is important to take into account that an “oral” extension of a fixed-term agreement is excluded, because specific rules apply to the main document. Consequently, when specifying the validity period of the contract, there must be grounds taking into account the current legislation (Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Articles 57 and 59). That is why, at the next extension, the reasons must be stated again.
Deadlines
According to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (Article 58), fixed-term employment agreements are allowed to be drawn up for a five-year period. The presence of a restriction allows the parties to renew the agreement, taking into account the requirements of the law and within the established time interval.
Here are the following options:
- Extension for a new term. For example, if an employee received a position for 12 months, but did not manage to complete the task within the allotted period, the agreement may be extended for the period necessary to complete the work (the maximum period is limited to five years).
- Extension for an indefinite period. According to the law (Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Article 58), an agreement with a limited period can be converted into an open-ended agreement. This is possible in a situation where the manager does not require termination of the agreement, and the employee continues to work. Such situations often occur due to the banal forgetfulness of the director, who did not remember the expiration of the agreement.
Number of renewals
An equally important issue concerns the number of extensions of fixed-term employment contracts. The law specifies four cases in which this is permitted, and all of them are considered from the position of exception. That is why the issue of multiple prolongation of such contracts is not even being studied. For example, the pregnancy of a woman working at an enterprise is unlikely to continue indefinitely. If we are talking about doing a certain job, it cannot be postponed constantly.
It is worth noting that multiple extensions include signing the contract for a new term more than twice. If for any reason the employee does not have time to complete the work after the extension of the fixed-term contract, the latter is terminated and a new document is drawn up.
General information about fixed-term employment contracts
The main feature of a fixed-term employment contract is that it is concluded strictly for a specific period, at the end of which the employee is fired (with 3 days prior notice). The maximum validity period of such a document is 5 years. This option for registering labor relations seems to many entrepreneurs to be more profitable than registering employees for an indefinite period, as it allows you to reduce the number of mandatory payments and manage staff more flexibly.
On the other hand, we must not forget that the Russian Labor Code provides for only a few cases when a fixed-term contract can be concluded . All of these situations imply that the work required of the employee can be completed within a certain period (season) or during the absence of another employee. Internships and alternative service are also most often arranged in this way.
An employer should not enter into a fixed-term contract without the grounds provided for by law. If the contract does not clearly justify the reason for its “urgency,” most likely, in a controversial situation, the court will recognize the document as unlimited.
The maximum validity period of a fixed-term employment contract is 5 years
Design rules
Extension of a fixed-term employment contract does not imply great difficulties for the employer. For the legal conduct of the process, the consent of the parties and the execution of several additional papers are sufficient. But there are a number of nuances that must be taken into account by each of the parties to the agreement:
- To extend the agreement, a written application from the employee is required (as when drawing up a new contract). The Labor Code of the Russian Federation (Article 261) states that when prolonging a contract during pregnancy, the employee must fill out an application and attach a certificate from a medical institution to it.
- After agreeing on all issues, the parties enter into an additional agreement. The document specifies the conditions for extending the period of cooperation and the reasons why this became necessary. An example is the extension of a woman’s maternity leave.
- To consolidate the legality of the additional agreement, an order is issued approving this document. As a result, the agreement of the parties receives legal force.
- Upon termination of the contract, the employee must be informed of the end of cooperation 72 hours in advance. If the document is not delivered on time, the agreement can be extended automatically. As a result, the contract becomes indefinite. If the employer and employee do not plan to work together for a long time, you can extend the current one or draw up a new contract, but through dismissal. In the latter case, notification of the employee is also required.
What to write in a work book
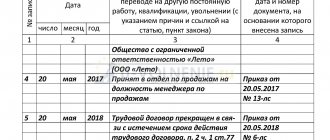
If, when concluding a fixed-term contract, information about the period of cooperation is specified in the document, then in the event of an extension, a new entry is made. In particular, the fact of prolongation of the agreement until such and such a date is indicated with an indication of the order. Sometimes HR officers do not include deadlines in the process of hiring a person. In this case, the fact of extension may not be noted.
Legal basis
The Labor Code establishes the circumstances under which a fixed-term contract can be concluded with an employee. A complete list of situations is given in Art. 59 Labor Code of the Russian Federation:
- replacing a temporarily absent employee;
- performing temporary or seasonal duties;
- performance of functions not related to the main activities of the organization;
- internship;
- part-time job
When concluding such an agreement, it should be taken into account that its repeated extension without changing production functions may be considered a violation of the employee’s rights. As a result, the contract, by court decision, will be recognized as indefinite, and the director of the enterprise will suffer administrative punishment.
The legislation does not provide for the extension of a fixed-term employment contract; such a cooperation agreement must either be extended, becoming indefinite, or terminated due to the expiration of its validity period. But some categories of workers are exceptions to this rule. Such specialists include:
- women expecting a child;
- employees of higher educational institutions;
- athletes.
According to Art.
261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, it is prohibited to terminate a fixed-term contract with a pregnant employee. The document must be extended until the end of pregnancy. In cases where a woman is employed to replace an absent specialist, she can be fired after the return of the main employee. But before terminating the temporary agreement, the employer is obliged to offer the employee another vacant position. If there is no such place or the woman does not consent to the transfer, which is confirmed by her written statement, then the dismissal is considered legal. With employees of higher educational institutions, the employment contract is extended on the basis of the provisions of Art. 332 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, but only if the specialist holds his previous position. In this case, the fixed-term contract is extended by an additional agreement without dismissal, with the condition that the total period of cooperation does not exceed five years.
In Art. 348 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes that an athlete can be temporarily transferred to another employer for a period of up to one year, but the person must agree to change the employer. The contract that was previously concluded with him is suspended without interruption, and after the athlete returns, its validity is resumed.
https://youtu.be/aPGR5HxQW-Y
Sometimes, after the temporary period has ended, a person decides to continue cooperation with a new employer. If at the same time the original fixed-term employment contract expires, then its extension upon expiration is considered legal.
There is no provision for extending the period of labor relations with such categories of employees as senior managers and retirees. They are allowed to enter into a new contract, but only after official dismissal due to the end of the previous agreement.
Subtleties of extending a fixed-term contract
The nuances of extending an agreement with a limited duration largely depend on the reasons for performing this work. Let's consider each case separately:
- Upon termination of the old contract. If the previous agreement has expired, two options are possible - extension of cooperation (transformation of the agreement into an open-ended document) or dismissal with the subsequent conclusion of a new agreement.
- When a worker is pregnant. A woman in a special position is protected by Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. This means that if there is a certificate from a gynecologist, it will not be possible to fire such an employee until the end of the contract. As a result, an extension of the document is required until the end of the burden.
- No dismissal. According to the law, prolonging a fixed-term contract more than once is a violation fraught with problems with regulatory structures. It is also necessary to follow the rules regarding indicating the grounds for continued cooperation.
- For a pensioner. If a retiree wishes to continue working, he has the same rights and obligations as other employees. Due to advanced age, a person cannot always perform duties at the same level, therefore the law allows for the execution of an agreement with a limited validity period (if agreed upon by the parties) and the possibility of extension.
- For the CEO. The Labor Code of the Russian Federation (Article 275) states that the period of validity of the agreement with the manager is determined by the constituent papers. For example, if a director is initially hired for a limited period, the contract cannot be extended - the director will have to be fired.
- For the chief accountant. According to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (Article 59), it is allowed to hire a chief accountant under a fixed-term employment contract and order of the general director. Extension is possible on the basis of Article 72 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
- For a foreigner. When employing a foreign citizen, a number of conditions must be taken into account - the availability of work permits, the period of validity of the residence permit, and so on. This means that providing space for a long period is impossible, as is extending the contract.
- With a part-time partner. If a person was hired instead of another employee (for example, during maternity leave), if he fails to complete his work, an extension of the agreement is allowed.
- For persons under 18 years of age. Such employees get jobs for short periods of time, for example, during vacations or internships. This is why extensions are often not necessary. It is worth remembering that according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (Article 92), minors can work from 12 to 17 hours a week.
If the work is not completed, and the parties plan to complete it, the contract may be extended under the conditions specified above. If the parties continue to cooperate and do not take any action, the agreement is automatically extended and becomes permanent.