Every person strives to move up the career ladder. To do this, he tries to cope well with his work responsibilities, and can also combine several positions at once. But sometimes citizens have to face demotion. This is possible only if there are compelling reasons, as well as with proper documentation on the part of the employer. A person is demoted from his position if he cannot cope with his duties or his health condition worsens.
Slide concept
Demotion of an employee is represented by a process in which a citizen is transferred to a lower position, for which a lower position is selected. This process is accompanied by a negative reaction from the employee. Even business managers react poorly to the demotion of employees, since the process takes a long time and requires the preparation of numerous documents.
Most often, this procedure is implemented when there are really compelling reasons for which it is impossible to keep the employee working in his previous position.
Reasons for implementation
Article 81 of the Labor Code contains information about the reasons for which an employee may be demoted from his position. The employer must make sure that the reason is valid and that the employee’s labor rights are not violated in any way, otherwise he will have to face the negative consequences of his illegal decision.
The most popular grounds for demotion are the following:
- Replacing another specialist who goes on long unpaid leave or maternity leave, and such a demotion is temporary, so after a certain period of time the citizen returns to his previous place of work, and can also count on a promotion.
- Suspension of the activities of the company in which the citizen works, so if the enterprise is in a state of downtime, then the manager has the right to transfer employees to lower positions, which is indicated in Art. 72 TK.
- According to Art. 74 of the Labor Code, a demotion is permitted if an employee, without good reason, refuses to fulfill his labor duties based on his position, for example, if the employer legally increases the workload, therefore, with such a refusal, a transfer to a lower position with easy working conditions is proposed in writing.
- Based on Art. 81 of the Labor Code, the demotion of any specialist is allowed as part of a reduction in staff or position, for example, another position is offered to a citizen who has a preferential right to remain in the company, but the position he occupies is completely removed from the staffing table.
- As a result of the certification, it is established that the citizen’s knowledge and skills are not enough to easily cope with the main tasks of the position held, and the verification of the professional suitability of employees is usually carried out through examinations and tests, so if a person cannot score the required number of points, the director can issue order to demote such an employee.
- The transfer is due to medical indications, so if a person’s health deteriorates, which leads to the inability to fulfill the employer’s requirements, then he may be demoted, and the citizen must agree to receive a new appointment.
- A pregnant employee is demoted if, while working in her previous position, the health of the employee and her fetus is adversely affected.
Another significant reason is any violation detected by the employer during the performance of the citizen’s official duties. Managers often resort to demotion as punishment. This is possible even in government agencies, where employees abuse their powers or simply deliberately refuse to perform official duties.
Document flow when transferring an employee to a lower position
Application for transfer. As we noted above, sometimes a transfer to a lower position is carried out on the initiative of the employee (in particular, for family reasons). In such a case, he will be required to submit a statement in any form. An example of it is shown on the right.
Translation proposal. If the transfer initiative comes from an individual entrepreneur, he must obtain the employee’s consent to the transfer. To do this, the employee is sent a corresponding proposal drawn up in any form.
This document justifies the need for his transfer to a lower position and indicates a list of all available positions that the employee can occupy in accordance with his qualifications. The document also provides information on official salaries corresponding to vacant positions.
If an employee is temporarily or permanently transferred to a lower position on the basis of a medical report, the transfer proposal must indicate the number and date of such report.
The employee's consent to a demotion is also made in writing. For this purpose, a special column can be provided in the proposal for transfer to another job.
In addition, the employee can submit an application to the individual entrepreneur and inform him of his decision. Please note that the labor legislation does not establish a deadline for withdrawing an employee’s application for transfer to another job. That is, before signing an additional agreement to the employment contract, the employee has the right to contact the individual entrepreneur with a statement indicating refusal to transfer to a lower position.
Additional agreement. If the employee does not object to being transferred to a lower position, an additional agreement to the employment contract is concluded with him. It specifies all the conditions for the transfer: the employee’s new job function, the structural unit in which he will work, the terms of remuneration and the deadline for the transfer.
When an employee is temporarily transferred to another job, the terms of the employment contract are changed for a certain period. The duration of temporary transfer to a lower position is established by agreement of the parties. For example, if an individual entrepreneur temporarily demotes an employee due to deprivation of a special right, the document must reflect the exact date of the employee’s return to his previous place of work. If it is unknown, you can make a note: “Until the day of restoration of special rights.”
Please note: an employee can be temporarily transferred to another position for a period of up to one year (Part 1, Article 72.2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). If the transfer was carried out while replacing an absent employee whose job is retained, its term ends on the day the employee returns to work. That is, in such a situation, the period of transfer to a lower position may exceed a year.
There are cases when an employee is transferred to a lower position temporarily, but as a result, work in the new place becomes permanent for him. This is possible if, at the end of the transfer period, the employee is not given his previous job, and he himself does not require it and continues to work.
Please note that an additional agreement to the employment contract, which implies a demotion, must be signed by both the employer and the employee. If an employee refuses to sign it and does not return to work in a new position, in the event of a trial, the servants of Themis will take his side (Determination of the Moscow City Court dated 08/03/2010 N 33-23228).
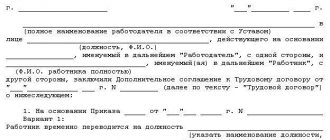
Order. Based on the additional agreement, an order is prepared for the employment contract using one of the unified forms - N T-5 or T-5a (approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated January 5, 2004 N 1). The individual entrepreneur must familiarize the employee with this order against signature.
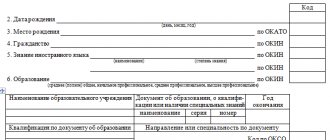
Marks on your personal card. The fact of transfer to a lower position for an individual entrepreneur must be reflected in the employee’s personal card (form N T-2, approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated January 5, 2004 N 1). In Section III “Hiring and transfers to another job” the following should be indicated:
— date of transfer;
- structural subdivision;
— position (specialty, profession), rank, class (category) of qualifications;
— tariff rate (salary) and bonus;
- basis for translation.
Please note: the individual entrepreneur is obliged to familiarize the employee with each entry made on the basis of an order to transfer to another job, against signature.
Process Rules
According to Art. 74 and 81 of the Labor Code, the demotion of an employee should only be carried out taking into account certain legal requirements. Therefore, the following rules are taken into account:
- if the company has changed its manager or the latest technological equipment has been introduced into the production process, then the new director can revise the provisions of labor contracts concluded with different employees, and the process is carried out without obtaining consent from the employees;
- an employee of the enterprise must be notified of the reasons and features of changes in the employment agreement two months before making adjustments;
- employees are notified of changes solely through written notification;
- if a person does not agree with the changes being made, then he may be offered a lower level job;
- if the employee does not want to move to another job, then the employment relationship with him is terminated.
Can they be demoted without the employee's consent? If the employer really has good reasons for this, then he may not ask the hired specialist for consent.
Transfer to a lower paid job at the initiative of the employer
Many people are interested in whether it is possible to temporarily transfer to another job, and even with lower pay, initiated directly by the employer?
Here it is important to understand what exactly should be understood by the employer’s initiative. If he offers the employee to terminate the existing employment contract (or, by mutual consent, change the conditions reflected in it) and the employee is satisfied with such an offer (including a reduction in salary), then the transfer is possible and does not create any problems for either one or the other sides. If the employee does not express a desire to move to a lower-paid job, then he has the right to refuse the employer’s offer and continue to perform the job duties specified in his employment contract.
A transfer to a lower-paid job is possible, for example, if the employee’s position is subject to reduction in the manner prescribed by Russian labor legislation. In such a situation, after notification of a layoff, the employer must offer the employee other available vacancies (including those with lower wages). And if the latter is satisfied with the proposed position, then he can accept the offer and continue to perform labor functions for this employer, even despite the lower level of remuneration.
Is the employee's consent required?
Demotion is an unpleasant event for every person, since almost all citizens want to climb the career ladder. But if the employer really has good reasons for making such a decision, then the citizen will not be able to take any measures to change such a decision.
If there are good reasons, it is not necessary to obtain prior consent for a demotion from the direct employee. He may not agree with this process, which leads to termination of the employment contract.
Documenting
Article 81 of the Labor Code contains rules that employers who wish to demote any employee must follow. This includes the need to prepare certain official documentation, without which the process can easily be challenged in court.
When demoting an employee, the following documents must be prepared:
- a new employment contract, which specifies the labor responsibilities that the employee has based on the new position he occupies;
- It is often enough to draw up an additional agreement to the existing contract if the changes are not too significant;
- if the process is implemented as a result of the fact that a person cannot cope with his job responsibilities, then an official note from the immediate supervisor is required;
- if the demotion is due to medical indications, then an appropriate medical certificate containing information about the employee’s health status is required;
- if staff reduction is made, then notification is required to be given to employees two months before this procedure;
- Additionally, when transferring a person to a new position, an order must be issued by the head of the company.
Only correct documentation will make it possible in the future to protect against unfounded claims from employees, who often go to court to challenge demotion or dismissal.
Procedure
When transferring to another position, the employer is obliged to ensure correct documentation of all changes, as well as compliance with mandatory procedures and actions required by law.
Preparation of necessary documents
The list of documents that will be required for registration consists of the following items:
- notification;
- a written statement from the employee indicating his consent;
- HR documentation log;
- regulations relating to the new place of work, which the employee signs;
- job description;
- additional agreement to the employment contract or a new contract;
- work book in which the entry will be made;
- employee’s personal card, in which marks are also made.
Documents for download (free)
- Order form for transfer to another position (form T-5)
- Sample additional agreement on transfer to another position
- Transfer application form
Drawing up an order
When drawing up an order, it must reflect the following information:
- Full name of the employee who is being transferred;
- the exact date of the transfer;
- current position of the employee;
- type of transfer (whether it is temporary or carried out on a permanent basis);
- the amount of current wages plus additional payments that may be made.
Sending a notification
Sending a notification is a prerequisite for a change in position, since such actions cannot be carried out without the knowledge of the employee.
Such a proposal-notification contains information characterizing the new place of work - wages, working hours, main functions, general working conditions, which may be of interest to the employee or become decisive for him.
If necessary, in such a notification you can refer to the articles of the law on the basis of which the personnel reshuffle will be carried out.
Recording in labor
Entry into the labor record will not be made only if the nature of such an action is temporary, that is, a return to previously performed duties is expected.
If it is permanent, then data on the transfer to another position is entered. If the nature of the transfer involves an employment relationship in another organization, data on dismissal from one company and employment to another is entered.
Personnel documents
All necessary documents that must be completed in such cases must be stored in a designated place - the personnel department.
The only exception may be an order, which will be located in the internal documentation of the accounting department, and the personal file will contain only a copy of it.
How to properly process an employee transfer? The answer to the question is in the video.
https://youtu.be/I9a0hOuEGTg
Rules for writing a report
If the decision to transfer to another position with a demotion is made by the employee’s immediate supervisor, then he draws up a memorandum addressed to the general director of the company. This document contains the following information:
- personal information about the employee who needs to be demoted;
- grounds for transfer to a lower position;
- name of the department in which the hired specialist works;
- professional qualities, skills and abilities that a citizen possesses.
This document is signed by the immediate supervisor and then handed over to the employee for review. If a citizen does not agree to a legal transfer, he is offered dismissal.
What does the Law say?
The issue of transferring an employee to another position at the initiative of the employer is regulated by Articles 30, 35, 40, 73 and 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, as well as other norms of Russian Legislation.
According to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, in order for the process of transfer to another position to be considered a lawful action of the employer, it must be documented. After all, for an employee, a transfer will mean significant changes in working conditions and the nature of work. In other words, the employer will instruct the employee to perform duties that are in no way related to his current profession, position and level of qualifications.
Read about how to draw up an employment contract here.
When does earnings not decrease?
But in some situations, the employer does not have the right to reduce a specialist’s salary. This applies to the following cases:
- deterioration of the employee’s health;
- the transfer is due to the employee’s pregnancy;
- a new job is offered as a result of the fact that a citizen in his previous job suffered an injury or occupational disease while performing his job duties.
In other situations, the amount of income usually decreases. This especially applies to demotion based on certification results.
Question about salary reduction without demotion
So, the enterprise has only equivalent positions of the same profile with the same pay. Many employers are interested in whether, in this case, they have the right, without moving the employee, to only reduce wages if it is determined that his competence is not too high.
Let's figure it out.
According to Part 2 of Art. 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the amount of remuneration must be specified in the employment contract as a separate condition.
According to Art. 72 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, changing the terms of the employment contract determined by the parties, including transfer to another job, is allowed only by agreement of the parties to the employment contract, with the exception of cases provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. An agreement to change the terms of the employment contract determined by the parties is concluded in writing. Since the change in salary in this case will not be a consequence of a transfer to another job, this method of amending the employment contract cannot be used.
However, there is also the possibility of changing the terms of the employment contract unilaterally - in accordance with Art. 74 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. But in this case, the employer will have no reason to use it, because the necessary reasons for this will be absent - changes in organizational or technological working conditions (changes in equipment and production technology, structural reorganization of production, other reasons).
Conclusion:
If the results of the certification reveal that the employee is unsuitable for the position held, then by reducing his already established salary, the employer is acting illegally. In the same way, you cannot reduce the salary of an employee whose incompetence has been established by other means.
Features of demotion for medical reasons
If a person works in any difficult or specific conditions, then he needs to have good health. If he develops any health problems or illnesses, he cannot legally continue his normal work activities. Under such conditions, the employer may offer him a job that will be lower in rank.
Under such conditions, even written consent to the transfer from the employee is not required, since in any case he cannot remain in his previous position. If the employer does not have suitable vacancies or the citizen does not want to transfer to another job, then the employment relationship is terminated.
Possibility 2: Demotion as a result of performance appraisal
Suitable for situation:
The organization carried out certification of individual employees, and some of them showed unsatisfactory results. In accordance with this, the certification commission came to the conclusion that the positions held by these certified persons were inappropriate.
How to use:
strictly in accordance with the requirements of Part 3 of Art. 81 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Thus, dismissal on the grounds provided for in clause 3, part 1, art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (as a result of the employee’s incompatibility with the position held or the work performed due to insufficient qualifications confirmed by the results of certification), is allowed if it is impossible to transfer the employee with his written consent to another job available to the employer (either a vacant position or a job that matches the employee’s qualifications, or and a vacant lower position or lower paid job) that the employee can perform taking into account his state of health. In this case, the employer is obliged to offer the employee all vacancies available in the given area that meet the specified requirements. The employer is obliged to offer vacancies in other localities if this is provided for by the collective agreement, agreements, or employment contract.
Thus, after the certification commission decides that the employee is not suitable for the position held, and the head of the enterprise decides to dismiss the employee under clause 3 of part 1 of Art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer must first offer him a transfer to another job and only if he refuses the transfer, dismiss him on the above grounds.
The same applies to a specific category of workers – civil servants. So, clause 3 and clause 16 of Art. 48 of the Federal Law of July 27, 2004 No. 79-FZ “On the State Civil Service of the Russian Federation” provide, as one of the possible consequences of unsatisfactory certification results, the demotion of an employee to a civil service position and exclusion from the personnel reserve if he is in it. If a civil servant refuses to be transferred to another position in the civil service, the employer's representative has the right to release the civil servant from the position being filled and dismiss him from the civil service.
A similar procedure is provided for law enforcement officers and other “specific” categories of workers whose activities are regulated by special regulations.
Compliance with Law:
complies with the law if the procedure is followed.
Risk of dispute:
there is a risk of dispute regarding the legality of the certification itself, as well as the validity of its results. The dismissal procedure under clause 3, part 1, art. 81 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. However, here too, the court does not always find itself on the side of the employee: if the court determines that the certification was carried out in accordance with the internal local act (the legality of its content and the procedure for approval in these types of disputes is always verified by the court), the results are recorded in the commission act and comply with the assessment rules competence of employees, the court recognizes dismissal based on the results of certification (or transfer with demotion in accordance with Part 3 of Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) as legal and justified.
On practice.
An employee who was transferred to another position with a demotion filed a lawsuit to challenge the transfer. In support of the requirements, he indicated that the basis for the transfer was the certification, which revealed his inadequacy for the position held. He was forced to agree to a downward transfer because... I didn’t want to be fired under clause 3, part 1, art. 81 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. However, he still believes that the purpose of the certification was the dismissal of undesirable employees, among whom he found himself. The court examined both the basis for the certification and the compliance of the certification with the established procedure for its implementation and found no violations in the actions of the employer. Moreover, the court also assessed the employee’s certification sheet. The fact that the plaintiff was asked 14 questions during the certification process, and the plaintiff gave incorrect answers to 11 of them, was correctly assessed by the court as evidence of the validity of the certification commission’s conclusions about the plaintiff’s unsuitability for the position held. Taking this into account, the court came to the conclusion that the results of the certification were legal, the plaintiff’s transfer was downgraded, and the plaintiff’s claim was accordingly denied (decision of the Selivanovsky District Court of the Vladimir Region dated July 12, 2011 in case No. 2-248/2011).
On the contrary, if the court establishes the illegality of the certification, its results or the procedure, then the downward transfer may be declared illegal. Moreover, the trial may generally end quite disastrously for the employer: all subsequent actions of the employer with the specified employee “along the chain” may be declared illegal, and the employee is reinstated in his previous (the one before the certification) position, in which he is calm and will continue to work... until the next certification or dismissal for suitable reasons.
On practice.
The employee, recognized by the results of certification as inappropriate for the position held, was transferred from the position of specialist expert to the position of senior specialist of the 1st category (with reduction) and was soon dismissed from this position due to staff reduction. By going to court, the employee demanded that the certification results be declared illegal, and that the transfer and subsequent dismissal be declared illegal as well. The court examined the procedure for conducting certification and came to the conclusion that its results were illegal due to unconfirmed circumstances indicating the low quality of the plaintiff’s work. In addition, the court came to the conclusion that the certification of the plaintiff was carried out unlawfully - without following the procedure for its conduct. Based on these findings, the court declared the certification results illegal and the demotion of the plaintiff carried out in connection with this was also illegal. Despite establishing that there were no violations in the procedure for dismissing the plaintiff due to staff reduction, the court declared the plaintiff’s dismissal on the above grounds illegal, reinstating her at work. At the same time, the court indicated that since the results of the certification and the transfer were recognized as illegal, the plaintiff was subject to reinstatement as a specialist expert. This means that she was not subject to dismissal due to staff reduction, unlike the position of senior specialist of the 1st category, which was reduced (decision of the Supreme Court of the Republic of Tatarstan dated 07/07/2011 in case No. 8430/11).
If the court recognizes the results and certification procedure as lawful, but finds only a violation of the translation procedure, it may also declare such a translation illegal.
On practice.
The court declared the transfer of the employee to a lower position illegal and reinstated him in his previously held position. As the court found, the employee filled the position of the state civil service of the legal consultant department of the legal support department of the legal department of the apparatus of the regional Duma. Based on the results of the certification of the civil servant, the certification commission decided that the employee does not correspond to the position being filled. By notification, the employee was warned about the upcoming transfer to the lower position of the state civil service proposed for replacement - a leading specialist in the general department of the apparatus of the regional Duma from <date>, and he was explained the right to refuse the transfer, as a result of which he would be dismissed from the state civil service. The employee was familiarized with this notice. By order of <date>, the legal consultant of the legal support department of the legal department of the regional Duma apparatus was transferred to a lower position in the state civil service - a leading specialist in the general department of the regional Duma apparatus. The court declared the transfer illegal taking into account the provisions of paragraph 1 of Art. 28 of the Federal Law of July 27, 2004 No. 79-FZ “On the State Civil Service of the Russian Federation” on the possibility of transferring a civil servant to another position in the civil service only with the written consent of the civil servant. According to the established facts, the transfer of the employee to a lower position was carried out without his written consent established by law (cassation ruling of the Volgograd Regional Court dated 06/01/2011 in case No. 33–7037/2011).
In practice, however, there are also small incidents: the results of certification are recognized as legal, the actions of the employer that followed as a reaction to unsatisfactory results of certification are also legal, but the dismissal of an employee is not.
On practice.
Based on the results of the certification, the maritime pilot was deprived of his pilot’s license and then dismissed under clause 9 of Art. 83 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (expiration, suspension for a period of more than two months or deprivation of an employee of a special right (license, right to drive a vehicle, the right to carry a weapon, other special right) in accordance with federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, if this entails the impossibility of the employee fulfilling his duties under the employment contract). The employee did not agree with the results of the certification, nor with the deprivation of his pilot’s license, nor with the dismissal and went to court. The court examined the specific regulations governing the work of maritime employees and came to the conclusion that the conclusions of the certification commission were legal, as well as the legality of the employer’s subsequent order to deprive the plaintiff of his pilot’s license (which was permitted by regulations governing the work of maritime pilots). At the same time, the court considered that, despite the defendant’s compliance with the general procedure for terminating the employment contract provided for in Art. 84.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the wording of the grounds for dismissal is incorrect due to the fact that it is impossible to recognize a pilot’s license as confirmation that an employee has a special right: a pilot’s license only certifies that the plaintiff holds the position of pilot and confirms his right to pilot ships in certain areas. Meanwhile, the plaintiff was dismissed on the grounds provided for in paragraph 3 of part 1 of Art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, - due to the employee’s inadequacy for the position held due to insufficient qualifications, which is confirmed by the results of certification. Due to the incorrect application of the grounds for dismissal and the inability to change the wording of the grounds for dismissal in accordance with Art. 394 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and paragraph 60 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated March 17, 2004 No. 2 “On the application by the courts of the Russian Federation of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation,” the plaintiff was reinstated at work, even without a pilot’s license (decision of the Kirovsky District Court of St. Petersburg dated 05/04/2009 in case No. 2–971/09).
Can it be used as punishment?
Often, employers use demotion in the form of disciplinary action for various violations committed by employees during the performance of their job duties. According to the law, there are only three types of penalties, represented by a reprimand, reprimand or dismissal. Therefore, demotion cannot be a way to punish a negligent employee.
Under such conditions, the employee can file a complaint with the labor inspectorate or the prosecutor's office. Based on his official statement, an investigation will be carried out. If an illegal demotion is discovered, the employer will be held administratively liable for violating the employee’s rights. This will lead to the payment of a fine of up to 5 thousand rubles, and the citizen will also be reinstated in his position. Therefore, managers of different enterprises must competently approach the reshuffling of personnel.