Why are provisions on structural divisions needed?
Let's start by noting two important details:
- Writing regulations is relevant if there is a real division of the organization into these same divisions.
- The presence of the provisions in question is not mandatory for the organization.
A structural unit of an organization is a part of the enterprise that is allocated in the prescribed manner, but does not have the characteristics of a legal entity and is not separate, and is assigned independent tasks, functions and responsibilities.
The main criterion for separating a part of an enterprise (employees) into a separate structure is the assignment of special tasks and functions to it, as well as the assignment of special powers necessary to solve these problems.
Management practice shows that it is possible to effectively organize work and exercise control if no more than 8-10 employees are directly subordinate to one manager. Therefore, it is desirable to divide large divisions into smaller structural units:
- management - departments, services;
- workshops - sectors, sections;
- departments - departments, sectors, sections.
This is important to know: Where to submit 6 personal income taxes for a closed separate division
The most important part of the provisions is the delimitation of areas of responsibility and the streamlining of relationships between departments. Try to connect your existing “rectangles” (structural divisions) with lines indicating their connections. The result will be a picture resembling a spider's web. And if you analyze the range of issues on which interaction takes place, then I am sure that you will find a lot of “empty” (information is simply not needed by the department where it is received) and duplicating each other. But the organizational structure and, in particular, the provisions being developed are aimed precisely at streamlining these information flows, reducing the time they pass from the performer to the manager and back, and ultimately increasing the quality and speed of decision-making.
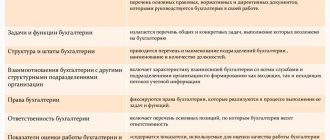
Department functions
A sample regulation on the personnel department and other structural divisions must contain a complete list of the functions of a specific department with the distribution of which powers are assigned only to the specified entity, and which powers are vested in the unit together with other departments.
If any functions are of a general nature, the section indicates in what form this or that department is involved in the process of exercising powers. If there is an internal structure, the names of each subdepartment and its functional responsibilities are written down.
https://youtu.be/fZweSjUk_SY
Development of regulations on a structural unit
First , determine the tasks for which a structural unit is being created. The tasks set before him must be real, even if they seem impossible at this stage, but feasible in principle. In the future, in the process of staffing this department with employees, you will evaluate people for their ability to solve assigned tasks, determine whether there is a need to attract outside specialists or whether your own human resource is sufficient, and also plan personnel training.
Secondly , determine the functions (actions) that the department must perform to solve the assigned tasks.
Thirdly , group similar functions into separate areas, determine the number of required personnel by distributing functions among virtual workers and calculating time standards for their implementation (or in another way), analyze the possibility of control by the head of the unit over the implementation of all functions assigned to the unit and determine Is there a need to create smaller structural units within the division?
Next, insert a “building block” into the existing structure and define service relationships with other departments.
After completing this work, submit the draft “Regulations” for approval to the interested departments (they were determined at the previous stage of work). Collect comments and suggestions. Analyze them, if they are significant and constructive (be careful, because you are taking away some of the powers from other managers, which can deprive them of their indispensability status), then assemble a so-called “conciliation commission” and resolve all differences in content.
Submit it to the legal department to check compliance with current legislation and, after receiving a positive response, approve the document with the manager.
In some organizations, most often this is typical for state and municipal bodies or budgetary institutions, the procedure for developing and approving Regulations is fixed in a separate document “Instructions on the procedure for drawing up, agreeing and approving Regulations on structural divisions.”
When developing the Regulations, you can take a different, simpler route. And take as a basis the “Qualification Directory of Positions of Managers, Specialists and Other Employees,” since the main tasks and functions of a department may be derived from the job responsibilities of the corresponding managers and specialists, and vice versa. At the same time, the tasks and functions of the structural unit must be clarified and supplemented in relation to your organization. For example, the functions of the marketing and advertising department will be determined by combining the job responsibilities of the heads of the marketing and advertising department, in accordance with the tasks assigned to this department, and taking into account the specifics of the structural structure and activities of this enterprise.
The main thing is an informal approach to developing the Regulations. Excessive bureaucracy and the use of standard, stamped formulations will lead to the fact that once an employee has read such a document when applying for a job, he will never refer to it again and, accordingly, will not rely on it in the future in his work.
The responsibility for developing Regulations on structural divisions is usually assigned to the organization and remuneration department, and in its absence, to the personnel department or legal department.
The regulations must define: the procedure for creating and the legal status of the unit in the ionization structure of the enterprise; the structure of the unit and its staffing levels; tasks, functions, rights and responsibilities, as well as the procedure for interaction of the unit with other structures of the organization.
This is important to know: Documents for the reconstruction of a private house with an increase in the area of the property: how to obtain permission
As follows from the definition, the Regulations may consist of the following sections:
- General provisions.
- Structure and staffing.
- Tasks.
- Functions.
- Rights.
- Interaction.
- Responsibility.
The following document structure is recommended. In practice, there may be more sections in the Regulations (the following may be added: property and funds (budget), terms of remuneration, organization of work, procedure for approving and making changes, etc.) or fewer.
Typical sample
The General Provisions specify:
- Purpose of the document. As a rule, there is the following phrase: “These regulations determine the order...”.
- Scope of action. The regulation may apply to workers or facilities.
- Regulatory documents in accordance with which the act was developed.
- Rules for approval, adjustment, cancellation of regulations.
The section “Terms, abbreviations, definitions” provides concepts used in the document. All abbreviations must be deciphered. Terms should be listed in alphabetical order. Each concept is indicated on a new line in units. h. The definition of the term is given without the word “this”, separated by a dash. The “Process Description” section provides a step-by-step description. It is advisable to introduce subparagraphs. Each of them will correspond to a specific stage. In the same section, employees involved in performing certain operations are indicated. Not only actions are described, but also their results.
Read more Get a certificate of real estate encumbrance
Regulations on the structural unit
Depending on the scale and specifics of the organization’s activities, its industry affiliation and management features, legal requirements and other factors, structural divisions may be created in the organization. Such divisions can be created both within the organization (for example, departments, services, departments, etc.) or be separate divisions. The latter includes branches and representative offices.
We will tell you in our consultation whether it is necessary to develop regulations on structural divisions and how to draw them up.
Nuances
It is important that each employee clearly understands what he needs to do and how the results achieved will affect his earnings. That is why it is necessary to discuss the regulations before their approval. The key role in drafting the document is, of course, assigned to the head of the working group (project). The tasks of this specialist include asking pressing questions. He must be able to present a clear model of the process. Each participant sees the picture with his own eyes. It is necessary to achieve a common understanding. Each participant must be explained the responsibility in creating the regulations. In most cases, teams are skeptical about the implementation of such a document. Depending on the complexity of the process, the introduction of regulations takes 4-12 months.
Read more Justification for increasing wages example
Is the Regulation on the structural divisions of an organization mandatory?
The mandatory approval of the Regulations on a structural unit depends on the type of such unit.
For example, an organization decided to create a representative office or branch. Let us recall that a representative office is a separate division of a legal entity, located outside its location, which represents the interests of the legal entity and protects them (clause 1 of Article 55 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). A branch is a separate division of a legal entity, which is located outside its location and carries out all or part of its functions, incl. functions of representation (clause 2 of article 55 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Despite the fact that representative offices and branches are not legal entities, the law indicates that they act on the basis of the provisions approved by it (Clause 3 of Article 55 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
And if an organization creates a new department or organizes a department, is it necessary to develop and approve regulations on such a structural unit? In this case, the development of regulations is left to the discretion of the organization itself. However, given that one of the goals of creating structural units is to improve the management system and increase the efficiency of the organization as a whole, the development of such provisions is considered appropriate. After all, it is in the position that one can reveal the tasks and functions of a structural unit, its subordination and the order of interaction with other units and employees of the organization, and therefore create the basis for the effective functioning of such a unit.
Application
It usually contains a graphical model of the business process. It is depicted as a diagram consisting of several blocks. Graphic images can be created using PC software. Schemes reflect a specific procedure for implementing certain tasks. Visualization is more convenient than text. The diagram clearly shows the beginning of the process and each stage, the connection between them and the final result. This model is often used by developers of regulations for interaction between company departments under 223-FZ. The diagram highlights key parameters such as outputs and inputs, participants and clients. If a beginner becomes familiar with such a model, he will immediately understand the specifics of the process and will be ready to implement a certain task.
Read more Amount of penalty for late delivery of goods
General information
The general information about the department's regulations (sample section below) contains the following information.
- The full name of the structural department (and abbreviated name if it is recorded in the statutory documents).
- An indication of the place occupied by the unit in the structure of the enterprise (organization).
- Determining the degree of economic and business independence.
- Information about who directly reports to the specified unit.
- Information about the position of the person who manages the structural department, the procedure for his appointment (dismissal) from position.
A sample regulation on the HR department of an enterprise is one of the first to be developed, since these entities are engaged in hiring new employees.
A separate paragraph of the first section of the act is a list of basic legal, regulatory, instructional, and policy documents that are taken as the basis for the activities of the unit.
If the department is divided into subdivisions or sectors, the general provisions may include a subclause on the internal structure. This subsection contains information about the internal division of the department, indicating the name (full, abbreviated), positions of the heads of each of their divisions, indicating directly subordinate persons and bodies.
The final paragraph contains information about whether the department has a separate seal. If it is present, a description of the item, purpose, and storage conditions are indicated.
Drawing up and approval of the document
The development of the Regulations is carried out by the division independently. As a rule, this task is assigned to the head of the department. First, a draft document is drawn up. It is coordinated with higher administration and interested employees. The latter, in particular, may include:
- Heads of departments with which the department interacts.
- Head of Human Resources.
- Head of Legal Department.
A specific list of coordinating units and employees is established by the boss. He also organizes familiarization of employees with the Regulations.
Department Responsibility
The section on responsibility is considered one of the most important in the act (for example, in the provision on the legal department of the organization, a sample of which was presented above). It sets out the types of administrative, disciplinary and, in exceptional cases, criminal liability.
A great responsibility lies with the employees of the procurement department (sample position below), which is directly stated in the relevant federal laws.
Often, sanction measures are applied only to the head of the relevant department if he improperly performs his assigned duties. The section must also contain precise formulations of economic responsibility in relation to the management of internal economic accounting.
Peculiarities
The document under consideration acts as an organizational and technological act. It defines:
- Place of the department in the enterprise system.
- Functional load, technological responsibility.
- Interaction with other departments.
- Regulatory documents that regulate the activities of an organization's division.
The act is drawn up directly in the department of the enterprise. His boss is responsible for this. The head of the organization must review and sign the document. An enterprise may have one department or several. The creation of divisions should be carried out on the principle of expediency. Their activities must be justified and effective.