Not guilty until proven otherwise. If the employer’s position in the final report of the internal audit turns out to be insufficiently reasoned, the court may subsequently side with the employee. Legally accurate and paperwork-wise preparation of documents at different stages of the investigation will help you make an informed decision and calmly defend the interests of the company in the future.
An internal investigation (internal audit) is a serious procedure. It is not used to prove minor violations. Often it is enough to have a preventive conversation with a corporate troublemaker. If there are suspicions that an employee has caused significant material damage to the organization or used his official powers for personal gain, then it is worth taking strict measures. The fact of absenteeism is also confirmed by the results of the internal investigation.
In addition, disciplinary violations that a special commission will undertake to review include evasion of a medical examination (for workers of certain professions) and of undergoing special training and exams on labor protection, safety precautions and operating rules during working hours, as well as refusal of a conclusion agreement on full financial liability, if this is the main job function of the employee.
Russian legislation does not contain the concept of an official investigation as such. It can be considered part of disciplinary proceedings, which describes in detail the procedure for bringing to responsibility for a disciplinary offense. An internal investigation in a particular organization is regulated by internal labor regulations and internal regulations (instructions, regulations).
It is important to know that conducting an internal investigation is an internal event. The employer can summon the perpetrator, eyewitnesses of the incident and other employees for “interrogation,” but only within the framework of his organization, department, institution, etc. Since the procedure is voluntary, employees have the right to refuse to participate. Employees cannot be forced to undergo a polygraph test or searches and personal searches must be carried out without their consent. If an official matter requires an expert opinion, it is allowed to involve third parties (auditors, appraisers, medical workers, engineers, etc.) on a contractual basis. The law also allows you to send requests necessary for investigation to government agencies and other organizations.
Where does an internal investigation begin?
The main task of the employer when conducting an internal investigation is to prove the fact of a disciplinary offense, to establish the employee’s guilt and its degree, the nature and extent of the harm caused. Additionally, the reasons and motives for committing a disciplinary offense, mitigating and/or aggravating circumstances, the employer’s ability to eliminate and prevent such violations of labor discipline, and measures to hold persons accountable are determined.
Before starting the official procedure, it is necessary to ensure that the fact of the misconduct is documented. It is this document that serves as the basis for subsequent verification. This may be a memo from the head of a unit, department and/or immediate superior. As a rule, it is drawn up in paper form (see Sample 1), but can also be issued in the form of an electronic document.
The memo must be accepted for execution and registered. From the moment when the incoming number according to the internal document flow log and the date of acceptance are placed on it, the countdown begins for the investigation. In addition to the memo, the basis for verification may be:
- statement from the employee himself;
- counterparty claim or consumer complaint;
- act of discovery of a shortage of goods;
- auditor's conclusion, inventory report;
- written and oral appeals from citizens, representatives of organizations containing information about the employee committing an offense, etc.
One of these documents is enough to launch an internal investigation procedure. The starting shot for him is an order from the manager to conduct an inspection or from another authorized person responsible for making personnel decisions.
https://youtu.be/LUt2z8DQAio
On refusal to familiarize yourself with the official investigation report
We, the undersigned, have drawn up this act stating that the ward nurse Ivanova M.I., in respect of whom an official investigation was carried out, in our presence refused to certify with her signature the fact of familiarization with the act of the official investigation. She did not motivate her refusal in any way.
The contents of the official investigation report conducted against the ward nurse of the general department, Ivanova M.I., was read to the ward nurse Ivanova M.I. aloud.
Deputy Director for Medical Unit “___” ____ 20___ ____________ Ivanov N.N. Paramedic “___” ____ 20___ ____________ Sidorova V.V. Senior nurse “___” ____ 20___ ____________ Petrova N.N.
Who is involved in the internal investigation?
Typically, the internal audit is carried out by the security service and/or the internal audit department. In small companies, these functions are often taken over by the HR department. As mentioned above, third-party specialists (lawyers, accountants, etc.) can also be involved in an internal investigation. The investigation must involve the immediate supervisor of the employee in respect of whom it is being conducted. At the same time, it is important to know that for the objectivity of the audit, the immediate superior cannot be a member of the special commission. This requirement also applies to the managers of the organization who make decisions on imposing disciplinary sanctions. Thus, the commission may include security and personnel officers, as well as trade union officials. As a rule, it consists of at least three people, headed by the head of the security service.
When an order is required
An order to conduct an internal investigation is issued to conduct an internal investigation in an organization.
Internal investigations are carried out in the organization based on the results of shortages identified as a result of the inventory, theft, disclosure of commercial or official secrets and any other incidents.
In some types of offenses, conducting an investigation is the responsibility of the employer, while in other cases it is a voluntary initiative of the manager. If such an investigation is not carried out, the employee will subsequently be able to appeal the disciplinary punishment to which he was subjected.
However, the investigation procedure is quite labor-intensive and responsible, so a special commission must be appointed for it. Its main task is to clarify the circumstances of the incident, talk with the alleged culprits, establish the degree of their guilt, and calculate the damage caused to the organization.
The commission must include at least three people from different departments of the company. All of them must be sufficiently qualified and competent specialists to conduct an investigation efficiently, at the proper level, analyzing all the motives, cause-and-effect relationships and other circumstances. At the same time, you need to act extremely carefully, avoiding violation of the rights of workers. As a rule, the commission includes:
- representative of the internal security service,
- lawyer,
- accounting department employee or economist,
- technical worker, for example, engineer, etc.
The commission may also include the head of the company.
The basis for issuing an order to conduct an internal investigation is a report or presentation from the head of the department/head of the unit in which a violation was discovered.
This procedure applies to both commercial and budget organizations.
This is interesting: Sample travel plan for a Schengen visa
Time frame for the investigation
One month is the amount of time allotted by law for investigating violations of labor discipline. It is counted from the date of the decision (issuance of an order) to conduct an inspection. If the investigation is carried out on the basis of an internal memo from an employee, the inspection must be completed no later than one month from the date of filing the document (Article 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The specified period does not include the employee’s illness, his stay on vacation, as well as the time required to take into account the opinion of the representative body of employees, which in total cannot exceed six months. A disciplinary sanction cannot be applied later than six months from the date of commission of the offense, and based on the results of an audit, inspection of financial and economic activities or an audit - later than two years from the date of its commission. These time limits do not include the time of criminal proceedings.
The procedure for carrying out an internal audit
An internal audit is an investigation during which the guilt of the employee is established, as well as the circumstances of the incident.
As a rule, it is carried out within the framework of public service. However, investigations can also be performed in commercial companies. In this case, it is necessary to approve the relevant local acts. Typically, verification is carried out in large organizations. IMPORTANT! Despite the fact that the law does not set out the procedure for internal investigations in commercial structures, it is important to conduct the event correctly. All stages of verification are documented. During the investigation, solid evidence of the employee’s guilt must be found. If the basic rules are not followed, the worker against whom an investigation has been initiated may contact the labor inspectorate.
https://youtu.be/YJHtbQF2AGs
The law enshrines only the concept of verification applied to civil servants. All the nuances of the investigation are contained in Federal Law No. 79 of June 26, 2020. Regarding inspections in the bodies of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation, the order of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of March 26, 2013 No. 161 is relevant. All other features and circumstances of the inspection can be found in certain articles of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The investigation must be motivated by a specific reason. Typically, these are the following circumstances:
- The employee committed an offense, the signs of which are set out in Articles 192-193, 195 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The rationality of conducting an investigation in this case is determined by the severity of the consequences of the offense. For example, an inspection is mandatory if there is a threat of dismissal of an employee. It is relevant for employee absenteeism, petty and major theft, and disclosure of secrets.
- The worker is held financially liable. The grounds for attracting, as well as the procedure for collecting funds, are set out in articles 232-233, 238-250 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. If an employee is held accountable based on the results of an inventory, there is no need to conduct an additional investigation. It is replaced by an inspection by the relevant commission.
- The employee has committed an act that may lead to dismissal. The list of such acts is set out in Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. For example, this is an unreasonable decision by a manager that resulted in material damage to the company.
- The rules for drawing up an employment contract, which are recorded in Article 84 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, were violated. For example, this is the incompatibility of an employee’s duties with his existing medical contraindications.
- Circumstances in the presence of which an official investigation is stipulated in regulations. For example, these are accidents while an employee is doing his job.
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! As a rule, an internal inspection is carried out upon the fact that an employee has committed a disciplinary offense.
IMPORTANT! If the investigation is carried out in a commercial company, the grounds for its conduct must be set out in the relevant local acts.
Let's consider the main tasks of conducting an audit in a company:
- Establishing the fact of committing a guilty act on the basis of which a disciplinary sanction was imposed.
- Identification of the time and circumstances of the incident, analysis of the consequences, determination of the amount of existing damage.
- Search for an employee who has committed a disciplinary offense.
- Determining a person's guilt.
- Analysis of the motives for committing an offense, additional circumstances.
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! The head of the company is recommended to approve recommendations for carrying out preventive measures necessary to eliminate the reasons that led to the disciplinary offense.
As a rule, information about an illegal act is received first. Then the manager approves the decision to initiate an internal audit. It is recommended that this be completed within 3 days after the violation is discovered. The inspection must be completed no later than 20 days from the start date. The investigation is carried out either by a specially appointed employee or by a commission. It is carried out on the basis of an order or other administrative document, in which it is necessary to indicate a number of information:
- The reason for the investigation.
- Participants included in the commission, as well as its chairman.
- Powers of the commission.
- Time limits for verification.
- Deadlines for sending documents about the results of the investigation to the manager.
As a rule, the members of the commission are employees of the human resources department, representatives of security and finance departments. The chairman is responsible for the work of the commission.
You should not involve the guilty person, his relatives or subordinates to participate in the commission. This may lead to biased investigation results.
ATTENTION! The order to initiate an internal investigation must be signed by all members of the commission, as well as by the person whose guilt is established.
At the end of the inspection, it is required to draw up a report outlining the results of the investigation. In particular, the document contains the following information:
- Members of the commission and its chairman.
- Information about the illegal act.
- Information about the allegedly guilty person.
- Reasons for what happened.
- Information about the extent of the employee’s responsibility for the incident.
A number of documents are attached to this conclusion. This could be an order to conduct an investigation, a character reference for an employee, explanations regarding what happened, or other papers.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with it. I bought a tablet and want to return it.
Conducting an internal investigation
After the commission has been formed by order of the head, the investigation into the circumstances of the violation begins. The employee is asked for a written explanation. It is recommended to send a notification to the employee’s place of residence - by registered mail with a list of attachments or by telegram (see Sample 2).
Two days are counted from the date of receipt of the notice, during which the employee must give a written explanation. Failure to respond after this time is regarded as a refusal to cooperate with the investigation. A corresponding act is drawn up regarding the fact of refusal (see Sample 3).
The forms of these documents are not established, but it is advisable that they be signed by all members of the commission. An employee can draw up an explanatory note in free form in compliance with general office work requirements. In the explanatory note, the employee sets out his version of what happened, explains the circumstances and indicates the reasons for the offense (see Sample 4).
An explanatory note is a mandatory, but not always the only document of the investigation. The commission may require copies or originals of other documents confirming the guilt or innocence of the employee. All received documents are numbered and filed. In the final inspection document they are presented as attachments.
Absence from work
If the employee does not go to work, then for each day of absence a report on the person’s absence from the workplace is drawn up. Indirect evidence can be attached to the act, such as the fact that the employee does not have a signature in the employee logbook, information in the electronic personnel access control system, reports from co-workers and immediate superiors, etc. The requirement to report to work and provide an explanation for absenteeism is sent by registered mail. with an inventory of the attachment or a telegram at the employee’s place of residence, if he did not appear at the workplace for two days in a row. It is recommended to count the waiting period for a response from the date of receipt of the letter or telegram. The employee may send his explanations in writing. If there is confirmation that the correspondence was not received by the addressee, the employer has the right to contact the police or send inquiries to hospitals. It is important to remember that if the reasons for failure to appear for work in court are recognized as valid, the employee will be reinstated and the employer will suffer losses in the form of monetary compensation to the employee for the entire period of his absence from work.
Causing material damage
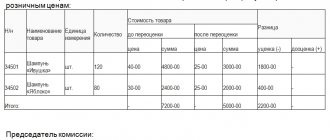
According to Federal Law No. 402-FZ “On Accounting” dated December 6, 2011, an inventory is mandatory when facts of theft, abuse or damage to property are detected. The inventory is carried out by the commission on the basis of an order from the head of the organization. Establishing the causes and extent of material damage is mandatory before making a decision on compensation for damage by specific employees. In this case, the amount of damage is determined by actual losses based on market prices prevailing in the area on the day it was caused (Article 246 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). But it cannot be lower than the value of the property according to accounting data minus depreciation charges. As a rule, to determine the size, employers invite independent appraisers or take data from the book value of the property.
Abuse of power
In order to identify the fact of abuse of power, an audit is carried out or independent auditors are involved. Their services may be needed to establish, for example, the validity of the release of goods, the transfer of property for rent at reduced prices, etc. For a joint-stock company and a limited liability company, the decision on an audit is made by the general meeting of participants (shareholders) of a legal entity in order to confirm the accuracy of the accounting documentation , financial statements and the state of current affairs of the organization.
Grounds for internal investigation
We list the most important grounds on which an internal investigation can be initiated at an enterprise:
- Absence of an employee during working hours - if an employee is not at his workplace for more than four hours, then according to the Labor Code he should be given absenteeism, the punishment for which may be a reprimand or dismissal (if the violation is not the first, or it entailed serious consequences). But in order to dismiss an employee on the basis of absenteeism, sometimes it is necessary to find out his circumstances, for which an internal investigation is carried out.
- Causing material damage to the employer by an employee. This may include damage to property or production equipment, shortage of funds in the cash register, theft of funds or property. In these cases, an investigation is also carried out, and data from the balance sheet is used to determine the amount of damage caused by the employee. Sometimes independent experts are hired to carry out assessments for this purpose.
- Abuse of position - committing actions contrary to the interests of the company or job description in order to obtain benefits. For example, such a violation would be if the person responsible for subletting in a shopping center rents out space to traders who offer lower prices than others, and at the same time receives remuneration from them. Sometimes, in order to establish how serious the damage is and to identify the entire range of persons involved in violations, an audit is carried out.
How to formalize the results of an internal investigation
The result of the internal investigation is a written conclusion or act (see Sample 5), drawn up on the basis of the collected materials. The conclusion consists of three parts: introductory, descriptive and conclusive:
- The introductory part
contains the fact of violation of labor discipline, the date of the violation, the period of the investigation and the composition of the commission. - The narrative
details the evidence from the investigation. - The operative part
is a summary: who exactly is guilty of what, and whether this employee has similar outstanding penalties.
At the end there is a list of appendices to the final act of the commission:
- memos on the discovery of a disciplinary offense, acts of absence of an employee, other documents that are the basis for an investigation;
- targeted demand to provide explanations, documents confirming the direction (delivery) of this request, an explanatory note from the employee (or an act of refusal to submit it);
- reports, official and explanatory notes of officials and eyewitnesses of the incident;
- inventory act;
- auditor's report; opinions of independent experts, as well as testimony of special technical means, etc.
The document along with attachments must be signed by all members of the commission. In office work, the final act is assigned a serial number and the date of its preparation is indicated. This marks the end of the investigation. The document is approved by the head of the organization and certified by a seal.
Responsibility for disciplinary offenses
The decision to bring an employee to disciplinary liability is made at the discretion of the employer. It must be accepted by the head of the organization within three days from the end of the investigation. Some employers limit themselves to mild measures of influence: holding conversations, expressing reproach, etc. The Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for three types of punishment: reprimand, reprimand and dismissal on appropriate grounds. Other penalties cannot be applied to the employee, with the exception of employees who are subject to special statutes and regulations on labor discipline (Part 5 of Article 189 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The heads of an organization or its structural unit or their deputies are subject to mandatory disciplinary action for violation of labor legislation and other acts containing labor law norms, the terms of a collective agreement, or agreement. If the fact of a violation was confirmed during the inspection, the official must be subject to disciplinary action up to and including dismissal (Article 195 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The decision on a disciplinary sanction is formalized by an order (see Sample 6), which identifies the guilty officials, the penalties imposed and the grounds for the decision.
For each disciplinary offense, only one disciplinary sanction can be applied. To record official investigations and their results, a Journal of Internal Investigations is maintained in paper or electronic form (see Sample 7). It is advisable to store all investigation materials filed in separate files or in one file and place them in chronological order.
In accordance with Art. 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employee must be familiarized with the order to apply a disciplinary sanction within three working days of the day of its publication, not counting the time of his absence from work. In case of refusal of the employee, a corresponding act is drawn up. Art. 248 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes that an order to recover from the financially responsible person the amount of damage caused is issued no later than one month from the moment the employer finally establishes its amount.
ATTENTION!
It is advisable that the employee familiarize himself with the entire package of documents before signature. This may prevent the employee from filing a claim in the future, since he knew in advance the employer's reasoned position.
If, during an internal investigation, signs of a crime were discovered (for example, an employee used official authority for personal gain), it is necessary to name them and make proposals to the head of the organization to consider initiating a criminal case.
T.V. Voitsekhovich
When is an internal investigation carried out?
Labor legislation does not have a clear definition regarding investigations of an official nature.
However, in a number of cases, for example, damage to the company, such a procedure is considered mandatory. The process itself is a set of measures to identify consequences and clarify the guilt of certain individuals. It is accompanied by the preparation of the necessary documentation.
Important! Placing blame on an employee without strong, indisputable evidence is illegal. Such processes may be appealed through the judicial system.
Service review is a standard procedure in the presence of public service. In all cases, regardless of the form of the organization, that is, it can be private or budgetary, the procedure can be carried out in case of serious violations. Among them are:
- absence from work or being late;
- causing damage to the material type of the organization;
- there was an abuse of official or official position in relation to employees or third parties;
- violation of an employment or collective agreement, as well as other documentation, including job descriptions;
- violation of safety regulations of any type;
- dissemination of proprietary data, such as commercial information;
- bribe or participation in bribery;
- shortages identified during inventory or various inspections;
- receiving complaints against an employee from other employees or outsiders.
The list includes any forms of violations that could damage the organization financially. Additionally, this includes facts that reduce the reputation of the company or structure. In such cases, an inspection is also possible, based on the results of which a decision will be made. Without carrying out a full procedure, the employee should not be punished financially or with similar measures.
Disciplinary offense
An inspection may be ordered in connection with a disciplinary offense. These include:
- absenteeism or tardiness;
- violation of safety instructions or position;
- failure to complete the list of works established by the documents.
Depending on the severity of the offense that is proven during the inspection, sanctions range from warning to dismissal. It is first necessary to conduct a full investigation with documentation of all case materials. The procedure begins after receiving an act or report-type note. After the commission is created, all evidence is collected and a decision is made.
You will first need to receive an explanatory note from the employee.
Important! If there is unproven guilt, any penalty can be appealed. A positive court decision will lead to the employee’s reinstatement and payment of all due funds for the specified period. For this reason, verification is necessary to fully identify all factors of misconduct.
Causing damage
There are several cases of property damage. The most common of them:
- fact of theft;
- non-compliance with safety precautions, which led to consequences with damage;
- distribution of commercial information;
- any damage to property.
Read also: Land Code of the Russian Federation in 2020
The process begins when damage or theft is detected, for example, after an inventory. The commission is obliged to find the culprit and fully prove his guilt. The responsible person cannot receive recovery or compensation for damage if there is no evidence of his guilt.
The amount of damage is calculated during the inspection. Current market prices are used as a basis. This is recorded in Article 246 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The damage should not be below the established amounts according to accounting data. For an assessment, it is necessary to provide balance sheet data on the property or engage an independent appraiser. All these stages must have documentary evidence, since on their basis they determine the further amount of funds that will need to be compensated to the culprit.
Article 246 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation “Determination of the amount of damage caused”
Abuse of authority
Abuse of authority is a common occurrence of violations. An audit is ordered when a fact is identified, for example, after a report or data inconsistency. An example of the latter option could be an independent increase in the price of a product. In various cases, audit assistance is used if violations concern the material or financial part. In other cases, it will be necessary to bring witnesses.
Attention! Bribery is also an abuse. A full investigation should also be carried out into this case. In some situations, the information obtained may be transferred to law enforcement agencies with accompanying documentation.