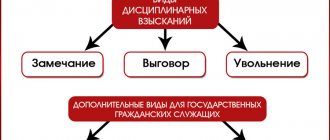
Disciplinary sanctions are special measures of liability provided for persons found to have violated labor regulations adopted at an enterprise or institution. The legislation clearly regulates the methods of punishment and allows the use only of those provided for in the relevant articles of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Who exactly imposes a disciplinary sanction on an employee directly for a sanitary offense? Let's figure it out.
Applying order
Among the responsibilities of the management of an institution or enterprise is the imposition of disciplinary sanctions on employees found to have committed a sanitary offense. In serious cases, they must exercise their right solely on the basis of a proposal issued by either the chief medical officer or his first deputy.
A penalty can only be imposed for a certain period - usually a month. The starting point is the day the offense was discovered. However, this period of time does not include:
- vacations;
- sick leave;
- periods required to obtain union consent.
In addition, disciplinary punishment cannot be used if:
- more than 6 months have passed since the violation of discipline;
- the fact was revealed during an inspection or audit 2 years later.
The time frame mentioned above should not include time spent on investigations carried out as part of criminal proceedings.
Penalty for violation of sanitary legislation - types, legal norms
The Russian legal framework provides for significant sanctions for violation of sanitary legislation. Therefore, it is necessary to initially determine the measures of responsibility for committing such offenses and crimes. Thus, the types of penalties for violation of sanitary legislation may be as follows:
- A disciplinary sanction for a sanitary offense is imposed directly on the employee of the enterprise who is guilty of committing it. At the same time, the legislation strictly defines the list of permissible disciplinary sanctions in the regulations of the Labor Code.
- An administrative penalty can be imposed both on an individual employee and on an enterprise as a whole, and most often it is expressed in the form of a direct monetary administrative fine.
- Criminal penalties are intended exclusively for application to certain individuals guilty of violating sanitary legislation and are not applied to enterprises.
- Civil liability concerns issues of compensation for damage caused to injured persons due to sanitary violations.
From a legislative point of view, the above aspects of penalties are regulated by the following regulatory documents:
- Article 192 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation defines specific existing types of disciplinary sanctions.
- Article 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation considers the procedure according to which disciplinary sanctions should be imposed by employers in the Russian Federation.
- Article 6.3 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation presupposes liability for violations of the general sanitary and epidemiological safety of the population.
- Article 6.4 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation directly regulates violations of sanitary requirements regarding the procedure for the use and operation of premises or transport.
- Article 6.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation is devoted to responsibility for ignoring legal requirements regarding drinking water.
- Article 6.6 of the Code of Administrative Offenses regulates the issues of punishment for inadequate provision of food to the population and epidemiological requirements for relevant institutions.
- Article 6.7 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation considers issues related to ensuring sanitary safety in children's health, recreational or educational institutions.
- Article 8.2 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation is devoted to issues of liability for improper waste management.
- Article 236 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation considers criminal punishment for violations of sanitary legislation if they entail consequences in the form of illness or death of a person.
Violations of requirements
For improper implementation of sanitary standards, the employer has the authority to reprimand orally or in documentary form and enter it in a personal file, make a reprimand or dismiss.
This is also important to know:
How employees are deprived of bonuses under the Labor Code of the Russian Federation: procedure and its registration
Civil punishment is punishment for damage caused to a person, property of an individual or legal entity in the field of sanitary standards. Damage must be compensated in accordance with the laws of Russia.
In situations of moral damage, compensation for damages is due. The amount of compensation for loss is decided by determining the level of guilt of the perpetrator.
Also taken into account is the information of the injured party: the levels of physical and psychological suffering suffered by the victim. The Code of Laws on administrative violations of Russia regulates the following list of offenses:
- failure to comply with legislative acts in the field of sanitary provision of the population, expressed in the form of failure to comply with hygiene standards, failure to perform preventive tasks;
- non-compliance with epidemiological tasks in relation to city and apartment buildings, city institutions, including transport;
- failure to comply with sanitary standards for drinking equipment and drinking water itself;
- failure to implement epidemiological measures in public catering establishments.
Penalties
Failure to comply with sanitary laws is subject to administrative punishment, which is characterized by the inspector making a remark or imposing an administrative fine in the amount of 110 to 3,000 rubles for individuals; from 6,000 to 200 thousand rubles for legal entities.
The inspector also has the right to stop the operation of the enterprise for up to 90 days. As for criminal punishment for failure to comply with epidemiological requirements, resulting in mass infection, in such a situation responsibility for the act comes into force, namely:
- punishment in the form of a fine in the amount of up to 90,000 rubles;
- deprivation of the right to work in a certain profession for up to three years;
- civil work lasting 190 hours;
- correctional measures lasting one year;
- limited mobility for up to three years.
Failure to comply with sanitary requirements, which resulted in the death of the population, is punishable in the form of civil labor for up to 250 hours, correctional labor for six months or three years.
This is also important to know:
After what period is the disciplinary sanction lifted: procedure for removal
In some situations, a sentence of restriction of movement or imprisonment of up to six years is imposed. Criminal punishment is regulated in such legislative articles of the Criminal Code of Russia as:
Free legal consultation We will answer your question in 5 minutes!
Ask a Question
Free legal consultation
We will answer your question in 5 minutes!
Ask a Question
- Article 238 - sale of goods, services and work that do not meet consumer health and life safety standards;
- Article 246 - failure to comply with sanitary requirements in the field of construction work;
- Article 247 - improper handling of bacteriological, toxic substances;
- Article 248 - failure to comply with safety precautions when working with microorganisms;
- Article 254 - improper use of fertilizers during agricultural work.
For these types of acts, the following forms of punishment are prescribed, depending on the degree of aggravating circumstances:
- penalties in the amount of up to 600,000 rubles or monthly payments deducted from wages for up to four years;
- a ban on working in a certain profession or for a specific type of work for up to four years;
- restricted movement for three years;
- a prison sentence lasting ten years, also in addition to the sentence, by a court decision, they will be ordered to pay the amount of fines or may be prohibited from working in a certain specialty for up to ten years;
- corrective measures up to three years;
- civil work lasting from 130 to 250 hours.
How a penalty is imposed - procedure
The decision on punishment is made by the head of the enterprise or organization. This is usually done on the basis of a report or a report received from the violator’s immediate superiors. The date of familiarization with these documents is the moment from which the statute of limitations is calculated.
In accordance with the procedure provided for by law, the administration is obliged to request written explanations from the employee. If the latter refuses, an act is drawn up recording this circumstance.
If an explanatory note is nevertheless submitted, then management has the right to make a final decision at its own discretion, depending on the reasons given in it. If the basis for the application of sanctions is the order of the chief medical officer, then his recommendation is followed.
Next, an order is drawn up, which clearly indicates what kind of penalty will be imposed.
Disciplinary sanctions: commandments for personnel officers
What is meant by work responsibilities? According to part two of Article 21 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employee is obliged to:
- conscientiously fulfill his labor duties assigned to him by the employment contract;
- comply with the internal labor regulations of the organization;
- observe labor discipline;
- comply with established labor standards;
- comply with labor protection and occupational safety requirements;
- treat the property of the employer and other employees with care;
- immediately inform the employer or immediate supervisor about the occurrence of a situation that poses a threat to the life and health of people, the safety of the employer’s property.
A sanitary offense, in accordance with regulations, is a culpable violation of sanitary requirements and standards, if it does not entail the consequences provided for in Art. 236 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
Responsibility for violation of sanitary legislation is provided for by the law “On the sanitary and epidemiological welfare of the population” (1999).
A sanitary offense, in accordance with regulations, is a culpable violation of sanitary requirements and standards, if it does not entail the consequences provided for in Art. 236 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
Heads of enterprises and organizations are obliged to impose disciplinary sanctions on officials and workers who have committed sanitary offenses, upon the recommendation of the chief state sanitary doctor or his deputy.
Depending on the nature of the violation and the severity of the consequences, the type of prosecution is selected individually and on the basis of Article 55 of Federal Law No. 52 “On the sanitary and epidemiological welfare of the population.”
Questions for catering workers
Didn't find the answer to your question? Find out how to solve exactly your problem - call right now (Moscow, Moscow region) (St. Petersburg, Leningrad region) ext. 386 (Federal number) Consultation is free! Add a comment Free legal consultation by phone Moscow, Moscow region. +7 (499) 7034119 St. Petersburg, Leningrad region. +7 (812) 3098651 Federal number 8 (800) 333-45-16 ext. 386 Calls are free! We work seven days a week! Popular publications Free legal consultation by phone Moscow, Moscow region. Before this age, parents or guardians of the minor are involved in cases of administrative violations. The circumstances of the case and the characteristics of the person involved as the perpetrator must be considered.
Types of administrative responsibility
There are various types of administrative penalties for sanitary violations.
SanPiN 2.3.2. 1324-03
These include:
- warnings;
- fines;
- confiscation of an item used to commit an offense;
- deprivation of a right obtained specifically (for example, the right to hunt);
- administrative arrest;
- deportation (for foreigners);
- disqualification.
In each specific case, the type of punishment for the crime committed is established individually, since determining the degree of responsibility is quite difficult due to the content of the norms in different laws.
What amount can Rospotrebnadzor assign?
The most basic violations of the sanitary environment are failure to undergo a medical examination and refusal to wear a special work uniform.
In addition to citizens who hold leadership positions, legal entities, as well as ordinary citizens of the country, can be held administratively liable for violating sanitary standards. The type of punishment is determined individually based on the circumstances of the case, the subtleties of the case committed and other parameters of the offense.
If we look at Art. 3.2 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, we will see that they can be punished in different ways. It could be:
- warning;
- fine;
- confiscation of the item that served as the object of the offense;
- deprivation of a special right (for example, the right to hunt);
- administrative arrest;
- in the case of a foreigner - deportation from the country;
- disqualification.
In conclusion, it should be repeated that the act under consideration rarely constitutes a qualification under one article, since the crime/offense itself assumes that the guilty person, in most cases an official, violated not only the norms of SanPiN, but also existing local legal acts, as well as norms establishing liability for excess or abuse of official powers.
For these types of acts, the following forms of punishment are prescribed, depending on the degree of aggravating circumstances:
- penalties in the amount of up to 600,000 rubles or monthly payments deducted from wages for up to four years;
- a ban on working in a certain profession or for a specific type of work for up to four years;
- restricted movement for three years;
- a prison sentence lasting ten years, also in addition to the sentence, by a court decision, they will be ordered to pay the amount of fines or may be prohibited from working in a certain specialty for up to ten years;
- corrective measures up to three years;
- civil work lasting from 130 to 250 hours.
Depending on the offense committed, you can be brought to disciplinary, administrative or criminal liability if the current legislation establishes the appropriate composition.
Thus, the head of the state body, independently or on the basis of the recommendations of the Commission, makes the following decisions:
- imposes appropriate penalties;
- sends materials for additional internal investigation;
- does not impose a penalty.
The employee must be fully aware of his job responsibilities, including those related to compliance with sanitary legislation.
How to write a disciplinary order: sample
Before applying disciplinary action to an employee, it is necessary to establish the existence of guilt. The most common are disputes regarding lateness to work due to transport problems, bad weather conditions, which the employee is not able to foresee, even if he wishes.
Administrative punishment is the most common type of liability for violations in the field of sanitary control. Liability is determined by Article No. 6 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation and applies in the following cases:
- an organization or an individual violated the sanitary standards in force at the time of the offense or failed to take measures to prevent such violations;
- the fact of non-compliance with established sanitary standards for the use and operation of residential and non-residential premises and buildings, public buildings, and passenger transport was proven;
- facts of significant violations were revealed in the procedure for providing (supplying and supplying) drinking water to the population or an individual enterprise;
- shortcomings were identified in the organization and implementation of measures for the destruction of industrial waste (disposal of food waste), etc.;
- the conditions for organizing the supply, delivery, storage and issuance (sale) of food products to the population have not been met or have been fulfilled in violation.
The offender is given two months to pay in accordance with Art. 32.2 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation (but only from the date of entry into force of this document, which occurs within 10 days from the date of its introduction), in case of evasion of this obligation under Art. 20.25 a double sanction will be applied.
You will have to answer for rudeness in the workplace
If an employee has actually committed a disciplinary offense related to a violation of sanitary standards, then the employer, in accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, has the right to impose a disciplinary sanction on him subject to certain conditions. Thus, the employer must order an investigation, request explanations from the employee and, on their basis, determine the measure of punishment.
During the work process, the worker is obliged to obey internal regulations and perform job duties for his position (profession). By not following the rules and not fulfilling official duties, an employee commits a disciplinary offense.
A penalty is imposed for a certain period of time, which begins to take effect from the moment the offense is committed.
How long does the penalty apply?
The most basic violations of the sanitary environment are failure to undergo a medical examination and refusal to wear a special work uniform. Thus, in addition to a fine, a warning may be issued under Art. 6.3 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, it is also possible to apply suspension of activities.
To clarify all the circumstances of the commission of a disciplinary offense and determine the degree of guilt of the employee who committed the offense, the head of the organization is obliged to request a written explanation from the employee before bringing him to disciplinary liability.
It is not permitted to apply a disciplinary sanction after six months from the date of commission of the offense, and based on the results of an audit, inspection of financial and economic activities or an audit - two years from the date of its commission. The time of criminal proceedings is not included in the specified periods.
The employee must be familiarized with the order (instruction) imposing a disciplinary sanction against signature within three working days, not counting the time of his absence from work. Refusal to sign is certified by the relevant act. The order (instruction) on the application of penalties is brought to the attention of all employees of this organization.
A disciplinary sanction for a sanitary offense is imposed directly on the employee of the enterprise who is guilty of committing it.
Administrative penalties for violations are applied by state supervision and control bodies within the limits of their powers and in the manner established by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
However, employers should take into account a number of certain nuances when imposing a penalty on an employee. So, in order to hold the employee accountable, the employer is obliged to make certain efforts.