A probationary period is understood as a period of work during which the head of the organization takes a closer look at the newly hired employee, evaluates the quality of his work and the compliance of his professional skills with the position held. For the employee, this time is characterized by the opportunity to figure out whether this place and working conditions are suitable for him. Sometimes, for various reasons, the employer does not have time to understand the employee’s professional qualities during this period, and then the probation period increases. In this article we will look at when an employer has the right to extend the probationary period and how to document it.
What is the length of the probationary period?
The advantage of establishing a probationary period belongs to the employer. It can only be applied to a newly hired employee, and not to someone transferred from other departments of the enterprise. An exception is established for civil servants transferred to management positions. It is established only if an employment contract is drawn up, since it does not matter whether the employee is hired on a probationary basis or without it, employment must be formalized according to all the rules. And if the employment agreement does not contain clear information about this period, then the employee is considered hired without a probationary period.
| Category | Maximum test period |
| Head of the enterprise, his deputy | Six months |
| Chief accountant, his deputy | Six months |
| An employee with whom an employment agreement has been concluded for a period of 2 weeks to six months | 14 days |
| Other categories | 3 months |
The duration of the probationary period is limited by law (Article 70 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). In standard cases, it does not exceed 3 months.
| ★ Best-selling book “Accounting from scratch” for dummies (understand how to do accounting in 72 hours) > 8,000 books purchased |
Questions
Is unilateral action allowed without notice to the employee?
Current legislation provides the right to change an employment contract unilaterally. The employer has the right to do this if the technological and organizational working conditions have changed.
With proper legal registration, the employer theoretically has the opportunity to change the duration of the probationary period. For example, additions are made to the job description, establishing a longer probationary period for the employee.
At the same time, Rostrud made it clear that the test period is assigned only at the time of applying for a job. Therefore, it is not possible to extend the inspection period of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Thus, given the controversial nature of this situation, it is advisable to set the maximum possible period of testing when hiring; extending the test may cause problems in the future.
Is it possible for a period longer than 3 months?
Most positions have a probationary period of three months. For a number of specialists it is established within six months (managers and chief accountant). In the civil service, extended periods range from three months to a year.
Consequently, establishing a verification period of more than three months is permitted only in cases strictly stipulated by law.
As you can see, the legislator has determined the maximum terms for conducting testing when applying for a job.
The inspection should be extended only if it was interrupted due to the employee’s absence from the workplace.
Situations where the probationary period was initially set less than acceptable and the employer later wants to increase it are considered controversial. It is recommended to adhere to the position of Rostrud.
https://youtu.be/2UF25gOtlRQ
- Due to frequent changes in legislation, information sometimes becomes outdated faster than we can update it on the website.
- All cases are very individual and depend on many factors. Basic information does not guarantee a solution to your specific problems.
That's why FREE expert consultants work for you around the clock!
- via the form (below), or via online chat
- Call the hotline:
- Moscow and the Region –
- St. Petersburg and region –
- Regions –
Who cannot have a probationary period when hiring?
It is prohibited to employ the following categories of citizens under probationary conditions:
- pregnant women;
- women whose children have not reached the age of 1.5 years;
- workers finding employment for the first time after graduating from university in the first year;
- persons under 18 years of age;
- employees arriving on transfer terms;
- persons undergoing alternative service;
- employees with whom a fixed-term employment contract is concluded for a period of less than 2 months;
- other employees reflected in Article 70 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
| ★ Best-selling book “Accounting from scratch” for dummies (understand how to do accounting in 72 hours) > 8,000 books purchased |
Extension of probationary period: analysis of reasons
In the process of work, under the influence of various circumstances, the employer may need to extend the test period. However, not every case of increasing such a period is legal.
| Reason for extending the probationary period | Employer's actions in relation to the law |
| During the trial, the employer did not finally understand whether the employee he hired was suitable for the position held | Not legal |
| An employee was absent from work due to illness | Legal |
| The employee was absent from work due to forced downtime of the enterprise | Legal |
| The employee was absent from work due to being in a training session | Legal |
| The employee was absent from work because he was taking time off. | Legal |
Thus, it will be legal to extend the probationary period for the time that the employee was not at his workplace for valid reasons and could not perform his professional duties. During this period, the employer did not have the opportunity to objectively assess the employee’s capabilities. All other reasons for extending probation will be unlawful, even if the employee does not object, and may be subsequently challenged in court.
How to renew?
As already mentioned, the extension of the test occurs on the basis of an order from the head of the enterprise if there are circumstances that give the right to do so.
Decor
Employers often have questions about how to properly arrange a probationary period. Here it is necessary to adhere to the provisions of labor legislation, according to which the condition for the application of a probationary period must be included in the employment contract. The form and content of the agreement are established by Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The contract clause can be written as follows: “By agreement of the parties, the employee is given a trial period of n months.”
In parallel with the agreement, an order for employment is issued with the display of a probationary period. As for the execution of the extension of the inspection, in this case the manager must issue a corresponding order. However, a situation may arise when, during the probationary period, it is discovered that the employee is pregnant, then in this case the manager urgently needs to issue an order to terminate the trial early.
Employee notification
The procedure for notifying an employee depends on the procedure with which the notification is associated.
If considering the issue of prolongation of the trial, the employer must notify the employee after the order is issued.
Upon dismissal, the employer is required to notify the employee three days before the event occurs.
See sample notification here:
Notice of dismissal for failure to complete the probationary period
Extension of probationary period: registration
If the need to increase the duration of the test does arise, and the employer has the legal right to do this, then it is important to correctly formalize the action. The main document that confirms the extension of the trial period is an order issued in accordance with established requirements.
This document must necessarily contain the following details:
- Business name;
- order number and subject;
- specific reasons that prompted the employer to increase the probationary period;
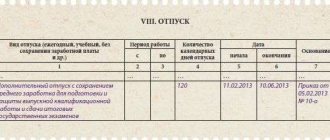
- the period for which the trial is extended ( no more than the time during which the employee was absent from work in the previous trial period );
- FULL NAME. and the employee’s personnel number;
- link to documents confirming the employee’s absence from work, on the basis of which the probationary period is extended.
All documents confirming the legality of the extension of the trial period must be attached to the order. The order is brought to the attention of the employee within 3 days from the moment it is signed by the manager, about which a written note is made.
What documents are required to formalize the extension of probation for the period of absence of an employee from the workplace?
— Business organization — Personnel — Probationary period extension
In some cases, an employer may need to extend an employee's probationary period.
However, current labor legislation provides for the possibility of prosecution if this procedure is carried out incorrectly.
You can learn about how to extend the probationary period and whether it is possible to extend the probationary period when applying for a job from the standards of the Labor Code and the federal legislation of Russia.
Russian legislation provides employers with the right to establish a special probationary period when employing workers.
The legal mechanism of the probationary period greatly simplifies the dismissal of a worker for both parties to the labor relationship, which makes it possible, if necessary, without unnecessary consequences, for one party to get rid of an unsuitable employee, and for the other to start looking for a new employer or find a job in a new place without long-term work.
Legislative regulation of the probationary period, as well as the timing of its extension, if necessary, is provided primarily by the Labor Code. In particular:
- Article 57, which considers the content of the employment contract, suggests the possibility of including information about the test in the text of the document.
- Article 70 directly establishes in its provisions the definition of the test applied to employees during their employment, as well as a list of persons for whom such testing cannot be assigned.
- Article 71 establishes the specifics of the employer’s actions and the procedure for recognizing the results of the probationary period as unsatisfactory.
- Article 72 regulates issues related to changes in the terms of an employment contract, which may include an extension of the probationary period for employment.
- Article 289 contains additional restrictions prohibiting the establishment of probationary periods for employees whose fixed-term contract implies employment for less than two months.
In general, the probationary period itself provides for a special period, previously agreed upon when hiring the employee. The duration of this period is determined depending on a number of factors.
In normal situations, the maximum probationary period is three months.
If the contract is concluded with the director, chief accountant or their deputies, then its duration can be up to six months, and in the case where the contract is drawn up for a period of up to six months, the trial can last no more than two weeks.
In some cases, a probationary period cannot be assigned, and if one is actually present, the agreement and the terms thereof are legally void. It is prohibited to set this period for:
- Pregnant applicants.
- Applicants who are employed for a period of less than two months.
- Minors.
Since the above categories cannot work on a probationary period, then, accordingly, any agreements to change it will also not have legal consequences, with the exception of holding the employer liable for violation of labor laws.
The length of the probationary period does not have to correspond to the maximum period established by law. The employer has the right to set in his regulations any duration of this period within the framework and restrictions established by law.
Considering such strict legal regulation of the main aspects of the probationary period, changing its duration can be quite a problematic moment in the implementation of labor relations.
However, the current legislation has certain aspects that should be taken into account by both employees and HR specialists or employers.
The main standard that establishes the possibility of changing the probationary period in labor practice is Article 72 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. It allows both the employee and the employer to make changes to the text of the employment contract. This right is also confirmed by the standards of Articles 21 and 22 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, respectively. But the possibility of such a change is extremely limited.
The main principle of changing the terms of the contract, including in matters of the duration of the probationary period, is the parties reaching an agreement on this fact. That is, the employee has every right to refuse the said extension without any consequences for his work activity.
Accordingly, the employer cannot extend the probationary period without obtaining the employee's consent. In addition, under no circumstances, even with the consent of the employee, the probationary period can be extended for a duration exceeding the maximum for this category of workers.
Not only the employer, but also the employee can initiate the procedure for extending the probationary period. However, in this case, the extension can only be carried out if there is mutual agreement of the parties to such conditions.
However, current legislation provides for the possibility of changing the employment contract unilaterally - in accordance with the standards of Article 74 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer has the right to make such changes if these changes are associated with corresponding changes in technological or organizational working conditions.
- The employer makes changes to job responsibilities and internal regulations, establishing a longer probationary period for employees of a certain position. The employer can justify such changes by the need to improve the skills of workers and labor protection requirements.
- 14 days before the said changes come into force, the employer notifies all employees holding the relevant position about them.
- In accordance with changes in internal regulations and job descriptions, as well as changes in organizational character, the employer sends the employee a notice of the need to extend the testing period until the required time.
- An employee has the right to refuse to continue working for a given employer due to disagreement with the change in conditions. In this case, the employer, if there is such a refusal, is obliged to provide the employee with the opportunity to transfer to another position, if such a vacancy exists and corresponds to the qualifications and medical indications of the employee. In their absence, the employer has the right to dismiss the employee in accordance with the provisions of clause 7, part 1, article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
- The employer makes a final settlement with the employee, paying him wages for all time worked, as well as compensation for unused vacation. In addition, the employer is also obliged to issue the employee with a work book, a certificate of income and deduction of contributions to the Pension Fund on the day of dismissal. A key aspect of dismissal for this reason is also the payment of benefits to the employee in the amount of his average two-week earnings at this place of work.
Considering the complexity of dismissing an employee for this reason and the need to pay him additional compensation for severance pay, this method of extending the probationary period is unlikely to be of practical use for the employer, but it is possible. But using such a legal mechanism is permissible only if the total time of the probationary period does not exceed the limits and restrictions established by law.
The provisions of Article 70 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation also provide for other situations in which the employer is allowed to extend the employee’s probationary period without any additional restrictions. Including no restrictions on its initial total duration. However, the scope of application of these standards is quite narrow and includes:
- The length of time the employee is on sick leave.
- The length of time an employee is on unpaid leave.
- Time of actual absenteeism of the employee.
- Time of removal of the employee from position.
In this case, the above-mentioned periods are not included in the total duration of the test upon hiring, and the countdown of the probationary period is suspended for this time. For any other reason, the extension of the trial is void and illegal.
However, even with legal grounds in the form of the above reasons, the employer should document the occurrence of such circumstances and record it in the internal documentation of the enterprise in order to avoid subsequent risks during legal proceedings.
For an illegal extension of the probationary period, if any is discovered, the employer will be held liable under Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
At the same time, he can be brought to such liability either on the basis of an employee’s complaint to the labor inspectorate, or if this fact is found during an inspection by the labor inspectorate of the enterprise, or as a result of a trial with the employee.
In most cases, in practice, employees seek to challenge the illegal extension of the probationary period if they were fired due to unsatisfactory test results. (36 votes, 4.20 out of 5)Loading…
Prolongation of the trial is not allowed even by agreement of the parties. An exception may be a long-term absence of an employee from the workplace, for example, due to illness (Article 70 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, temporary loss of ability to work must be confirmed by an appropriate document. An additional reason is vacation at your own expense, study or forced downtime of the enterprise.
It is worth noting that absenteeism is not considered a valid reason and may become grounds for dismissal of an employee (81 Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
To continue the probationary period, the employer must issue an order.
The order must contain the following statements:
- name of company;
- Full name of the head;
- name and number of the order;
- a description of the reasons for extending the inspection;
- test extension period;
- Full name and position of the employee;
- links to documents that confirm the employee’s absence;
- date, manager’s signature, company seal.
How is payment made during the probationary period?
The main mistake of the employer is that, when hiring an employee on a probationary basis, he sets the salary lower than that provided for in the staffing table for a similar profession or position. The situation when an employee is offered one salary during the probationary period, and another after successfully completing it, is illegal. A person hired on a probationary period is subject to labor laws, that is, he has exactly the same rights and the same responsibilities as other employees.
For example, the staffing schedule of a trade organization provides for 2 staff positions for a salesperson-cashier. One salesperson has been working for a long time; a new employee has come to the second position with a probationary period. From the very beginning of work, a new employee, regardless of what the result of his test will be, must receive the same salary as a salesperson working without a probationary period.
In addition to wages, during the probationary period, an employee can legally count on payment for:
- bonuses;
- period of illness;
- overtime work;
- work on weekends and holidays.
Methods on the verge of legality
In rare cases, employees are forced to agree to dismissal in order to be rehired again under a probationary period. But such agreements are illegal in nature and violate the rights of the employee.
More often, business managers practice talking with an employee before the probationary period expires. During this process, he is asked to write an application with an open date. In this case, the manager promises not to dismiss the employee after the probation period and to use the signed document only in forced cases.
Please note that these requests are illegal. The recording of the conversation can be presented as evidence of a violation of labor laws. This will entail, at a minimum, an administrative fine for the employer. If the employee agrees to this option of extending the probationary period, one can expect deprivation of legal pay for the last month.
Salary during the probationary period
An employer, on completely legal grounds, can pay for the work of an employee hired on probation in a smaller amount than in the employment contract. To do this, it is necessary to reflect the salary of a newcomer to this position in the staffing table. But the employer must not forget that the salary of this employee cannot be less than the minimum amount (see → Minimum wage) established by law.
Recommendations for the employer
There are a limited number of options for legally increasing the probationary period. Its duration must be fixed in the employment agreement. Even if this condition was verbally agreed upon during employment, but there is no information about this in the contract, the employee will be enrolled without a probationary period. The employer will not be able to determine the candidate's professional level. Therefore, it is recommended to take a responsible approach to drawing up an employment contract and indicate in this document the maximum probationary period possible by law. If an applicant for a position proves himself to be a qualified specialist, he can always be laid off.
In what cases is it prohibited?
For some categories of persons, it is prohibited to establish a test when signing an employment contract.
These include:
- pregnant women going on maternity leave;
- women with children under one and a half years old;
- minors;
- young specialists who have received a diploma and have not worked anywhere before;
- disabled people of the first group;
- pensioners;
- persons elected to positions through competition;
- employees in elected positions;
- transferred from another employer;
- signed a fixed-term contract for two months.
Is there a probationary period for part-time employment? About this - here.
End of trial period
Even if the employer has a legal basis to extend the probationary period, at the end of it it is necessary to make a decision whether the employee has completed this period or not. If the employer has not taken any action and the employee continues to perform professional duties, then he has successfully passed the test.
An employee who fails to complete the probationary period is subject to dismissal. The dismissal must be formalized in accordance with all the rules, otherwise this action may be challenged in court and lead to the payment of monetary compensation.
Stages of dismissal:
- drawing up a notice that the employee has not completed the probationary period. The document must indicate the reasons for dismissal. All claims against the employee that arise during the probationary period must be documented. The notice must indicate on what date he is subject to dismissal. The document is drawn up in 2 copies;
- delivery of notice to the employee 3-4 days before the expected date of termination of the employment contract;
- obtaining the employee’s signature indicating that the document has been provided to him. If he does not want to sign the notice, then an act is drawn up in which at least 2 witnesses must sign;
- directly the dismissal itself and the final payment in accordance with labor legislation. It is necessary to take into account that the dismissal of employees who have not passed the probationary period is subject to all restrictions regarding dismissal at the initiative of the employer. For example, you cannot fire a pregnant employee or a temporarily disabled employee.
If the employee himself decides before the end of the probationary period that this job is not suitable for him, he notifies the employer 3 days in advance. He does not have to work for 2 weeks.