Features of employment of minors
In the Russian Federation, the work of minors is not prohibited, but there are a number of restrictions regarding their work activities. For example, Art. 265 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation directly prohibits the employment of teenagers in hazardous and/or hazardous industries. The list of such works is established by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated February 25, 2000 No. 63.
What other nuances are important to consider:
- Employment of persons under 18 years of age is carried out with the written consent of parents or guardians. At the same time, the potential employee must have no medical contraindications to work, and must also meet the level of education required for the position.
- In some cases, the employment of children aged 14 to 16 years may additionally require the consent of the guardianship authorities.
- Teenagers should not be asked to work at night, on weekends, or sent on business trips. Also, they cannot be part-time workers.
- Minors are provided with reduced production standards and a lighter work schedule. The duration of annual paid leave for them should not be less than 31 days. The employer also undertakes to conduct annual medical examinations at his own expense.
As can be seen from the above, minor employees enjoy greater benefits than persons over 18 years of age.
Such norms are approved by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The same applies to the dismissal of teenagers: if adult workers can be dismissed if there are grounds at the initiative of the employer without any problems, then the involvement of the commission for minors and the labor inspectorate is required (Article 269 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Requirements for dismissal of a minor
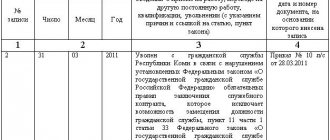
The dismissal of an employee is formalized by an order signed by the head of the organization. The dismissed employee puts his signature on the document. The day of dismissal is the last day of service. At this time the management:
- makes final payments to the employee;
- issues a work book with a record of dismissal;
- provides a certificate of average salary for the last two years;
- transmits information on accrued and paid insurance contributions for compulsory pension insurance.
The procedure for dismissing a minor employee has some peculiarities.
At the initiative of the employer
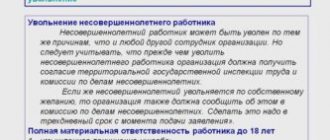
If an employer decides to fire an employee under 18 years of age, he must obtain the consent of all members of the commission for working with minors .
The commission considers the question and gives a positive or negative answer. In case of a negative decision, dismissal of a minor employee at the initiative of the employer is possible only when he crosses the threshold of his 18th birthday. The exception is situations when the company is completely liquidated and the entire workforce is fired.
Self-care
Previously, Russian legislation required mandatory notification of a special commission, even if a minor is dismissed at his own request. It was necessary to make sure that the young man decided to leave his job voluntarily, and not because of pressure or harassment from management.
In recent years, additional agreement on this issue has not been required. If a minor employee decides to leave the enterprise, this opportunity is presented to him without additional proceedings.
If a minor worked at an enterprise under a fixed-term employment contract, then at the end of the term he quits. A teenager can be hired under such a contract in the following cases:
- during maternity leave of the main employee;
- for temporary or seasonal work;
- for work related to practice or internship;
- for creative work in the media, cinematography, theater.
The dismissal of working teenagers in all cases must be carried out in compliance with all legal standards. The law protects this category of citizens and in the event of unjustified dismissal, the court will always side with the minor.
How to fire a minor employee at your own request
Several years ago, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provided for the obligation to inform the commission on cases of minors by the employer, even if the teenager was dismissed at his own request . Currently, thanks to the new amendments, this is required only when terminating the contract on the initiative of the director, with the exception of cases of liquidation of the enterprise or closure of the individual entrepreneur’s activities.
The procedure for terminating an employment contract with a minor in this case is carried out in accordance with the general procedure:
- A teenager submits a letter of resignation to his manager. He is not obliged to explain the reasons. The application indicates the date of termination of the contract. In the absence of such, the employer has the right to impose mandatory two-week work. This period is not established if the dismissal occurs due to retirement: in this case, the director is obliged to release the employee within the established time frame.
- The manager puts a resolution on the application and issues a dismissal order. The person resigning gets acquainted with the order by signing it. If desired, he may be given a copy of the document upon request.
- On the last day of work, a full payment is made to the resigning employee and all certificates are issued. This date is considered the date of dismissal and is indicated in the work book with references to the basis - the manager’s order with details (date and number).
Expert commentary
Kamensky Yuri
Lawyer
If a teenager is employed under a fixed-term contract, the employment relationship ends on the day it ends. The director is obliged to notify such an employee of the upcoming dismissal 3 days before the date.
Reasons
The basis for termination of the contract at the request of a minor employee is the application submitted by him. No additional documentation is required.
Procedure for dismissal of teenage employees
The procedure for registering the dismissal of a teenager is no different from a regular adult employee.
How to place an order
To draw up an order, the standard T-8 form is usually used (or T-8a, if several people are fired at once). In addition, the law does not prohibit drawing up an order on the organization’s letterhead; in this case, it must have mandatory details.
The Labor Code does not indicate the exact date when the order should be drawn up. But in any case, this must be done before the last working day.
You might be interested in:
Dismissal for absenteeism in 2020: step-by-step procedure-diagram with sample documents
There is no point in drawing up an order immediately after the manager has signed the resignation letter - the employee has two weeks to change his mind. In this case, if a dismissal order is already available, you will have to issue another one, which will cancel the first one.
A situation may arise that an employee will first want to take the vacation days that he has accumulated, and then quit. But this can only be done with the direct consent of the manager. In this situation, it is necessary to draw up two separate orders - one for vacation, and the second for dismissal.
Attention! The reason for terminating an employment agreement depends on the circumstances. If the teenager himself wrote a statement of his own free will, then it is necessary to make a reference to Art. 77 of the Labor Code, if dismissal is made for violations, then under Art. 81.
The employee must be familiarized with the order against signature. If he refuses to do this, then a commission is assembled, which draws up an act of refusal.
Making an entry in the work book
Entry in the work book is carried out on a general basis, and for adult workers. Information about the grounds for dismissal is indicated in the same way as in the order - it must contain wording in accordance with the Labor Code and a reference to Article 77 or 81.
Recording in the labor record is carried out by the person responsible for this. It may not contain the seal of the business entity. Then the employee must affix an acknowledgment signature.
If an error was made in the entry, the responsible employee bears financial responsibility for this. It is expressed in the need to pay compensation in the form of average earnings for all the days when the fired person could not get a new job due to an error.
What payments are due?
On the final day of work, the dismissed person must receive the following payments:
- Compensation for vacation days that he did not use;
- Salary for the current month;
- Benefits and compensation, if they are provided for by the company’s internal regulations.
Attention! If the employee is unable to receive payment on the last day (for example, is on sick leave), then the funds must be kept by the employer. Their payment is made the next day after receiving a written request from the employee.
How to fire a minor employee at the employer’s initiative: step-by-step instructions
Everything becomes more complicated when the head of the organization becomes the initiator of the dismissal of a teenager. In this case, the procedure is as follows:
- The director discovers grounds that give him the right to terminate the contract with the teenager. All this is recorded in the documentation. The employee is required to provide an explanatory note, which he must submit to his boss within two working days.
- The head sends written requests to the commission on juvenile affairs and the State Tax Inspectorate.
- Within 10 days, authorized representatives of government agencies hold a meeting with the participation of the employer on the issue of dismissing the child. It is this commission that decides his future fate.
- Based on the results of the meeting, a protocol is drawn up, and the director receives permission to dismiss the teenager.
- A dismissal order is drawn up. The employee must familiarize himself with it against signature. If he does not want to sign, a corresponding act is drawn up to this effect in the presence of two witnesses.
- On the date of termination of the contract, a full settlement is made and all certificates are issued.
Expert commentary
Shadrin Alexey
Lawyer
As can be seen from the above, the only difference in dismissing a teenager is the obligation to inform government authorities. Otherwise, the procedure is identical to terminating a contract with an adult employee.
Reasons
The list of grounds for termination of the contract at the request of the employer is contained in Art. 81 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Why a teenager can be fired after proceedings involving government agencies:
| Base | Explanation |
| For absenteeism | Absenteeism is considered absence from work for more than 4 hours without good reason. |
| Failure to fulfill official duties | The violation must be repeated. Dismissal occurs if the employee has already been subject to disciplinary action. |
| Being intoxicated at work | The offense is recorded in an act signed by two witnesses. A medical examination will be required. Employers have the right to deliver teenagers to institutions for testing only with the permission of their parents. |
| Committing theft at the place of work, incl. and theft of personal belongings of employees | Installed by law enforcement agencies. Until a court verdict is issued, a citizen is considered innocent, and it is impossible to dismiss him on this basis. |
| Violation of labor protection requirements resulting in serious consequences | Grave consequences mean causing significant property damage to the organization, or causing harm to the health of other employees, if the fault of the dismissed person is established |
| Providing false information or forged documents during employment | A forged document can be a certificate of education, a certificate of completion of courses, etc. |
Important! If the company is liquidated, management is obliged to inform all employees in advance. The participation of IPDN and GIT in this procedure is not required. If only staff reduction is planned, and a minor is dismissed, it is mandatory to inform the specified authorities. In addition, all employees must be notified in writing about the layoff 2 months before the expected date, and they must be offered vacant positions to replace those being laid off.
Let's consider a practical example of dismissal for negative reasons:
17-year-old Ivanov O.N. employed in a children's entertainment club as an animator. On July 15, he returned to work as scheduled. Closer to lunch, the administrator suspected that Ivanov O.N. is in a state of drug intoxication, and reported this to the club manager. The manager called Ivanov for a conversation, during which signs of drug intoxication were revealed: inappropriate behavior, lack of response to questions, sluggish speech. The manager called the teenager’s mother, who came to the club. The woman, together with the manager, went to the drug treatment clinic on her own, where a blood test was taken. As a result of the analysis, traces of a narcotic substance were found.
All documents for dismissal by the manager were collected correctly: a memo from the employee, an explanatory note taken the next day from O.N. Ivanov. The test results are also attached to the case.
The employer sent a notification to the State Tax Inspectorate and the IPD. As a result of consideration of the issue, a decision was unanimously made to dismiss O.N. Ivanov.
On the day the decision was made, the manager issued an order to dismiss the employee.
Liability for illegal dismissal
Based on Art. 392 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, an employee dismissed for no reason has the right to go to court to be reinstated in the workplace and hold the employer accountable within 1 month after receiving a copy of the order.
If it is established that the employer actually terminated the contract without reason, the claims will be satisfied, and he will be held accountable under Part 1 of Art. 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, which provides for the following sanctions:
- fine up to 5,000 rubles. for officials and individual entrepreneurs;
- fine up to 50,000 rubles. for legal entities.
The same applies to termination of an employment contract bypassing the requirement to notify the commission for minors and the territorial division of the labor safety inspectorate: the manager will have to pay a fine.