Working hours
Companies have recently practiced slightly reducing working hours for women on maternity leave. However, the Social Insurance Fund insisted that such a reduction is not considered part-time work. The courts sided with the Social Insurance Fund and confirmed that despite the fact that the legislation does not contain certain limits on time reduction, many employers reduce working hours by only a few minutes in order to receive benefits from the Social Insurance Fund in the form of additional income, and not as compensation for lost earnings.
Currently, an employer does not have the right to set a young mother a certain number of hours of work under part-time conditions. Employers are required to negotiate with the employee about “safe” working hours according to the rules established by the FSS (Letter of the FSS of Russia No. 02-03-13/08-2498). You can offer an employee who worked a 40-hour week before maternity leave to reduce her working day by 1 hour.
Important! It will be safe for the employer to reduce the working day by no less than 1 hour, and the week – by no less than 1 day.
Thus, the FSS insists that the working day established for a young mother should be shortened not by a few minutes, but by hours. Moreover, such a reduction in working hours must occur on every working day of the week. It is also permissible to reduce the number of days in the working week, but leave the length of the working day the same.
The employer has no right to set requirements for an employee; a young mother has the right to refuse such working conditions (
https://youtu.be/U0yhVOlUz98
Working conditions
As noted above, the employee can choose for herself how much her working day will be reduced. If desired, it can be set up for either a part-time or a part-time work week. It is also possible to work part-time with part-time work, i.e. not 5 days a week for 8 hours a day, but, for example, only 4 days for 7 hours a day.
Often both the employee and the employer himself have a question: what should be understood by part-time work? Based on the explanations of Rostrud on this issue (letter of Rostrud dated 06/08/2007 No. 1619-6), part-time working time should be considered that time, the duration of which is less than the normal working time.
Normal working hours, according to Art. 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, is 40 hours per week and should not exceed the established norm. Consequently, if you reduce the standard working time for an employee even by 1 hour per week, then such work will already be considered part-time. However, this right cannot be abused.
The legislation of the Russian Federation does not establish clear limits for the amount of time by which the working day can be reduced in order to consider it not full. That is, it can be reduced by an arbitrary number of hours.
Therefore, some employers allow themselves the practice of reducing the working hours of an employee on maternity leave by just a few minutes a day. Such actions are not approved by the Social Insurance Fund, and in the event of litigation, the court, as a rule, sides with the Social Insurance Fund.
We advise the employer to adhere to the rules established by the Social Insurance Fund (letter of the Federal Social Insurance Fund of Russia No. 02-03-13/08-2498) and agree with the employee to reduce the length of her working day by at least 1 hour. Otherwise, the Social Insurance Fund may stop paying child care benefits or reimbursing them to the employer.
In order not to attract the attention of the FSS and to avoid possible proceedings in court, it is undesirable for the employer to reduce the working day by less than 1 hour, and the working week by less than 1 day (letter of the FSS of Russia No. 02-03-13/08-2498).
Salary rate
There is no such concept as a rate in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. In the staffing table there is the term “staffing unit”. In this case, it is meant that the employee will work part-time and his payment will be in direct proportion to the time he worked.
An employee can work at a fraction of the full rate (0.75; 0.5; 0.25, etc.) depending on the number of working hours established for him, and this reduction will mean the establishment of part-time work for him. The salary will decrease according to the reduction in working hours. That is, at a rate of 0.5, the employee’s earnings will be 50% of his standard earnings.
To introduce these rules, you need to sign an additional agreement with the employee, stipulating part-time work (indicate the specific agreed mode) and including in the agreement the wording “Wages are calculated in proportion to the time worked.”
Benefit payment
While working on maternity leave, in the event of a reduction in working hours, a woman continues to receive a monthly care allowance for up to 1.5 years. The benefit is paid at the expense of the Social Insurance Fund. The payment amount is 40% of the average monthly earnings for the 2 years preceding the birth of the child, and should not be lower than the minimum established by law.
The procedure for paying benefits when going on a shortened day will not change, but the Social Insurance Fund will need to submit a copy of the woman’s application and the order to transfer to part-time work during parental leave.
In addition, a working mother has the right to a tax deduction for each of her children until they reach 18 years of age. To provide a deduction, you need to take an application from the woman. This deduction is taken into account immediately when calculating personal income tax.
A woman working part-time who is on maternity leave for a child under 3 years old is entitled to a standard tax deduction in the amount of 1,400 rubles. for the first child and 3,000 rubles. for each next one. It is by this amount that her monthly income will be reduced to deduct tax at a rate of 13%.
Now, in many regions of the Russian Federation, a pilot FSS project called “Direct Payments” has begun to operate. This means that all the benefits listed above will be paid not by the employer himself, who may delay payments due to lack of funds at the enterprise, but directly by the Social Insurance Fund to the bank account of the young mother.
If a woman goes to work part-time, the Social Insurance Fund will continue to pay benefits. The employer must submit documents confirming the woman’s right to maintain payments, in the form of a copy of the application and order, to the Social Insurance Fund.
Feeding breaks
If a mother who is breastfeeding a child goes to work, she is given breaks to feed the child. They must be paid, last at least 30 minutes each and be provided at least every 3 hours (Article 258 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). If a woman has more than one child under the age of 1.5 years, then the duration of each of these breaks increases and is at least 1 hour.
Since this right is directly provided for by the Labor Code, a woman cannot be denied such breaks. A woman can add them to the lunch break and move them to the beginning or end of the working day, reducing it. To do this, she needs to write a corresponding statement.
After this, you need to conclude an additional agreement with her and issue an order to provide such breaks (Part 2 of Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Annual holiday
A young mother cannot go on annual paid leave if at the same time she works and is on maternity leave, since she simultaneously receives child care benefits - clause 20 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation dated January 28, 2014 No. 1 ( read more about whether and when you can take annual leave after maternity leave).
To use it, the employee must interrupt maternity leave (read about how to draw up and submit an application to interrupt maternity leave for a child under 3 years old, and from this article you will learn how to apply for early leave from maternity leave). She will have to do the same if she decides to exercise her right to study leave.
Sick leave
If a maternity leaver falls ill while working part-time, she will be paid sick leave. The law provided for the possibility of simultaneously receiving two benefits for a woman working part-time and on maternity leave: a child care benefit and a temporary disability benefit. Sickness benefits compensate for lost earnings. Since it exists, the benefit must be paid.
It is interesting that in the event of a child’s illness, the employee must be issued a certificate of temporary disability to care for a sick family member, despite the fact that she already receives benefits for caring for the same child.
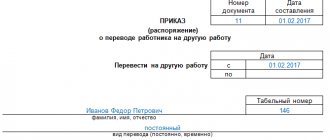
Procedure for registering for part-time work
Before an employee is allowed to return to work, it is necessary to agree on working conditions with her. To return to work, the employee will need to write a statement in which she will indicate the desired mode of work.
Important! A young mother can go to work at any time during her vacation.
The employer reviews the employee’s conditions specified in the application and adjusts them if they contradict the production conditions established in the company. For example, the production process in a company starts at 9:00 a.m., and the employee in her application indicates working hours from 12:00 p.m.
Having approved the working hours, you will need to draw up an additional agreement to the employment contract. It specifies the duration of such working conditions. They may end with the end of the young mother’s vacation (from the moment the child turns 3 years old), or if the employee herself decides to change her working conditions part-time. The additional agreement specifies the employee’s work schedule and payment procedure, which is made depending on the time worked.
After this, an order is issued to work on a part-time basis.
About interruption of maternity leave in general
An employee on maternity leave can return to work at any time she wishes. It doesn’t matter how much time has passed since the birth of the child. But early exit can only occur at the request of the employee. The employer, for its part, must provide full leave and benefits, and does not have the right to demand that the employee start work earlier.
Maternity leave can be interrupted in two ways:
- The employee refuses it completely and goes back to work full time. In this case, benefits payments to her will cease.
- An employee can go to work part-time or work remotely. In this case, she will receive salary and benefits at the same time.
In the second case, there are several nuances regarding working conditions:
- An employee cannot be forced to work overtime or asked to work on weekends;
- No business trips;
- It is prohibited to transfer an employee to another position (promotion with the consent of the employee is possible, but demotion is not);
- An employee cannot be fired (even if there are good reasons for this).
Employer's refusal to shorten the working day by a few minutes
If an employee insists on shortening her working day by just a few minutes, then the employer has no right to refuse her. It is important to maintain the payment of benefits, otherwise the State Tax Inspectorate may be fined for violation. Fear of disputes with the Social Insurance Fund is not a reason for refusing to shorten an employee’s working day by a few minutes. However, in our opinion, the employer and employee in this case must find a compromise so that there are no claims from social insurance or the labor inspectorate, and it is convenient for the young mother to carry out her work duties (
Part-time work: how maternity pay is calculated in 2020
- Women who were fired during the twelve months preceding the day they were recognized as unemployed in the prescribed manner due to:
- liquidation of organizations;
- termination by individuals of activities as individual entrepreneurs (IP);
- termination of powers by private notaries or termination of the status of a lawyer;
- termination of activities by other individuals whose professional activities in accordance with federal laws are subject to state registration and (or) licensing.
Since it exceeds the maximum amount for calculating maternity benefits in 2020, the benefit should be calculated based on the specified maximum average daily earnings - 1632.88 rubles. Minimum benefits... In practice, the average earnings of employees going on maternity leave per full calendar month are often less than the minimum wage. In such situations, as well as in cases where a woman has no earnings at all during the billing period, maternity benefits are calculated based on the minimum wage (Part Art. 14 of Law No. 255-FZ). Let us remind you that the minimum wage from January 1, 2020 is 5965 rubles. (Article 1 of the Law of December 1, 2014 N 408-FZ).
Accordingly, the average daily earnings for calculating maternity benefits cannot be less than 196.11 rubles. (RUB 5,965 x 24 months: 730). This norm states that in the Russian Federation the labor and health of people are protected, a guaranteed minimum wage is established, state support is provided for the family, motherhood, paternity and childhood, the disabled and elderly citizens, a system of social services is developed, state pensions, benefits and other guarantees are established. social protection. However, representatives of the Supreme Court, as they say, did not hear the arguments of the employer-individual entrepreneur. “Bonus for young people In conclusion, we note that maternity benefits are also calculated in a special manner in the case where the employee’s insurance period at the time of the insured event is less than 6 months. We are talking, for example, about young specialists who, after graduating from the relevant educational institution, are just starting their career. In accordance with part. To begin with, we calculate the SDZ from the minimum wage using the formula, taking into account the regional coefficient: Minimum wage × 1.5 × 24 / 730 = SDZ earnings for 2 years SDZ = 11,163 × 1.5 × 24 / 730 = 550.50 rubles .
Then we calculate the amount of maternity benefit using the formula: SDZ × 140 (sick leave days) = maternity benefit. Maternity benefit: 550, 50 × 140 = 77,070 rubles. Calculation of maternity benefits according to the minimum wage in 2020, if the length of service is less than six months. As mentioned above, a maternity leave worker who has been working for a total of less than 6 months is entitled to maternity benefits in an amount not exceeding the minimum wage. In this case, the calculation of maternity benefits will be different.
To calculate benefits, it is necessary to compare the average daily benefit for a maternity leave, determined for the billing period from the minimum wage, through the SDZ according to the minimum wage. You should know that when several children are born at the same time, the above are carried out for each child (first, second and subsequent ones). The condition for receipt is the presentation to the accounting department at the place of work of a birth certificate (original) received at the registry office, as well as a certificate from the place of work of the second parent about non-receipt of a one-time and monthly allowance.
How to calculate maternity leave in 2020 (example and online calculator) Let's consider a situation where a woman goes on maternity leave in January 2020 for a period of 140 days (normal pregnancy and childbirth without complications). These figures mean that when calculating maternity payments for 2020, you can take into account the maximum amount of income in the following amount: 1,473,000 rubles. Accordingly, the size of the maximum average daily earnings has also changed. In 2020 it is equal to 2020.81 rubles.
When assigning benefits to employees who have less than 6 months of insurance coverage, the new minimum wage must be taken into account. For 2020 it is equal to 9489 rubles. The average daily minimum wage is now 311.97 rubles. For convenience, we summarize all the numbers in a table. Taking into account all the latest changes, the amount of this benefit in 2020 will be the following indicators:
Long business trip
Whether or not she will retain the right to benefits or lose it will depend on how long the business trip on which the young mother is sent will depend.
While on a long business trip, which lasts more than 1 month, a young mother cannot care for her child. If the employer does not stop independently paying the employee benefits, then the Social Insurance Fund may refuse to pay. This rule applies only to long business trips and does not apply to business trips of several days.
It is important to inform the employee about the possibility of refusing a business trip. This must be done in the following way: the employee is sent a proposal for a business trip, which indicates its duration, goals and the possibility of refusal. This rule also applies to other persons raising a child under 5 years of age without a mother (father, guardian or other relative).
In addition, the employee must be informed that she will lose the right to receive benefits during a long trip (more than 1 month). If the employee agrees to this condition, she will need to interrupt her vacation for the duration of the trip. To do this, you need to write an application for early leave from vacation.
After this, a business trip order is issued, which indicates that the employee’s maternity leave is suspended for the period of the trip, and the payment of benefits is stopped.
Is it possible to work officially while on maternity leave?
Official legislation does not contain the concept of “maternity leave”. In practice, this term is applied to 2 periods: leave due to pregnancy and childbirth (hereinafter referred to as Maternity leave) and leave to care for a newborn minor child.
Decree on BiR
This type of maternity leave is provided on the basis of sick leave, issued at the 30th week of pregnancy (28th - in case of multiple pregnancy). However, going on maternity leave is a worker’s right, not her responsibility.
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Full and free access to the system for 2 days.
In other words, having received the opportunity to go on maternity leave due to her pregnancy, the employee may not immediately take leave and continue to work as long as her desire and health are sufficient. The courts also agree with this opinion regarding official work in late pregnancy. An example of this is the resolution of the Arbitration Court of the Eastern Military District dated October 28, 2008 in case No. A31-357/2008-7.
IMPORTANT! You should know that a woman on maternity leave cannot simultaneously count on both payment of benefits under the BiR and receipt of wages. In addition, maternity leave taken after the 30th week of sick leave is not subsequently extended for the period after childbirth (letter of the Social Insurance Fund dated October 8, 2004 No. 02-10/11-6671).
It is impossible to call a maternity leave early from leave under the BiR at the initiative of the employer (Part 3 of Article 125 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). However, a pregnant woman can go back to work, interrupting her labor and employment leave at her own request, but this requires permission from the head of the company (letter of the Federal Service for Labor and Employment dated May 24, 2013 No. 1755-TZ). In this case, it will be necessary to recalculate the B&R benefits already paid before going on vacation.
Is it possible to work during maternity leave on the basis of a civil contract? Yes, this is quite acceptable, but it is important that in its form such an agreement is not similar to an employment agreement, i.e. that it does not contain the mandatory conditions prescribed in Art. 57 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. So, this may be a contract agreement drawn up on the basis of Art. 702 of the Civil Code of Russia, or a contract for the provision of paid services in accordance with Art. 779 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. Persons working under such contracts are not subject to labor legislation (Part 7, Article 11 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Child care decree
Having taken leave to care for a newborn child after completing maternity leave, the young mother/father can continue to officially work - at home or on a part-time basis. At the same time, after completing her “pregnant” sick leave, she may not go on leave to look after the child, but simply go back to work full time and not submit any applications for leave. If an employee(s) has gone on UzR leave, the employer will be able to call him back only by agreement (Part 2 of Article 125 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Thus, a maternity leaver has several options for building labor relations:
- A young mother can interrupt her vacation early and go to work for the whole working day. At the same time, the right to take maternity leave is acquired by her closest relatives: the child’s father, his working grandfather/grandmother, adult aunt/uncle. The maternity leaver herself will receive a full salary, and the care allowance can be issued by the person who will actually care for the child. The maternity leaver retains the right to go on maternity leave again at any time before the child’s 3rd birthday, but then the right to it is lost by the relative caring for the child instead of the mother.
- The employee has the right, without interrupting his vacation (while maintaining benefits), to officially go to work on a part-time basis with the consent of the employer (Clause 2 of Article 11.1 of Law No. 255-FZ of December 29, 2006). It is also possible to switch entirely to home working. There is also no need to interrupt vacation for this, but the employer has the right to refuse to provide work in this mode if the employee was not a homeworker before the maternity leave.
- While on maternity leave at his main place of work, the employee will be able to enter into an employment contract with the same or another employer and work part-time. And the number of part-time jobs can be unlimited (Part 2 of Article 282 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Another opportunity to earn extra money for a maternity leaver caring for his child while on leave from his main place of work is to perform casual work on the basis of a civil contract.
Applying for father's benefits
During a long business trip for a young mother, the benefit can be issued to another family member, for example, to the father. To do this, dad will need to apply for parental leave at his place of work. In addition, he will need to provide a certificate from his mother’s place of work stating that she does not use vacation and does not receive benefits.
For a young mother, you need to make an entry in your personal card. It indicates the start date of the business trip, its end date and the total number of days of the trip. In addition, the number and date of the order, which was the basis for the business trip, is indicated.
Important! After the end of the business trip, payment of benefits can be resumed.
Paid vacation and sick leave for part-time work on parental leave
Art. 93 of the Labor Code indicates that the duration of annual paid leave is not limited when working part-time . A worker has the right to leave, even if his working day is shorter than that of other workers.
However, parental leave is an obstacle to receiving annual paid leave in accordance with paragraph. 2 clause 20 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation No. 1 of January 28, 2014. If necessary, an employee can interrupt maternity leave and take advantage of paid leave.
Letter of the Federal Service for Labor and Employment No. PG/8139-6-1 dated 10/15/2012 gives mothers and other persons caring for children under 3 years of age this right.
The procedure is as follows:
- Interrupt maternity leave.
- Take annual paid leave.
- At the end of your vacation, write a second application for maternity leave.
To carry out each of these steps, you must write an application addressed to the employer.
Annual leave
If a young mother works on maternity leave, she has the right to annual paid leave (Rostrud letter No. PG/8139-6-1). She can use it after the end of maternity leave, since, according to labor legislation, a young mother does not have the right to use two types of leave.
If there is a need for annual leave, the employee has the right to take it, while interrupting her maternity leave. To do this, she writes a statement where, in addition to a request for annual leave, she asks to interrupt her maternity leave. Based on this application, an order is issued and a corresponding entry is made in the employee’s personal card. Payment of benefits during vacation stops and resumes when it ends.
Salary for part-time work
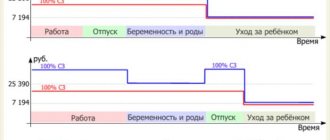
For part-time work, remuneration is made in proportion to the time or depending on the volume of work performed in accordance with paragraph. 3 tbsp. 93 TK. While on maternity leave, the mother has the right to receive both wages and benefits:
- until the child is one and a half years old - care benefits for up to 1.5 years in the amount of 40% of average earnings;
- before the age of three - care compensation equal to 50 rubles per month.
When Misha was one year old, his mother Elena went to work part-time (two days out of five), without interrupting maternity leave. The benefit amount is 4564 rubles per month. The salary for a full week at the enterprise is 23,000 rubles per month. In March 2020, 20 working days, of which Elena will work 8 and receive a salary of 9,200 rubles and a benefit in the amount of 4,564 rubles.
Her income in March 2020 will be 4564 + 9200 = 13764 rubles.
A grandmother, father or other family member who actually takes care of the child can also take care of leave, and any of them has the right to agree on part-time work .
The legislative framework
| Letter of the FSS of Russia No. 02-03-13/08-2498 dated 03/22/2010 | “About the part-time work schedule” |
| Article 93 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation | "Part-time work" |
| Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation | “Violation of labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms” |
| letter of Rostrud No. PG/8139-6-1 dated 10/15/2012 | “On the provision of annual basic paid leave to an employee working part-time while on parental leave” |
Rate the quality of the article. Your opinion is important to us:
Types of part-time work
Working hours shorter than the legal norm (40 hours per week) are considered incomplete. Its length is established by agreement of the parties.
Types of part-time work:
- part-time work (shift) - the number of hours that need to be spent at work is reduced;
- part-time work - the number of days present at work is reduced.
The law does not exclude a combination of these two types. In this case, the boss and subordinate agree on what days it will be necessary to go to work and for how many hours.
Is it possible to apply for maternity leave for another relative?
Today, not only the mother, but also the baby’s father and even close relatives, for example, grandparents, can go on maternity leave. This right is enshrined in Article 256 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
A guardian or relative can receive payments for the child until the child turns three years old. The amount of the benefit is calculated according to the same scheme as for mothers - it is forty percent of the average salary (however, the benefit cannot be less than the established minimum).
Arranging for such a vacation is quite simple.
The father or some other relative who will take on this function must write two applications at work: one for maternity leave, the second for payment of social benefits.- In addition, you should provide the child’s birth certificate and a certificate from the mother’s employer, which will indicate that she does not receive benefits. If the mother does not work, such a certificate is also issued by the social protection center.
IMPORTANT! If a relative does not work or is retired, he has the right to take care of the child with all payments only if the child’s parents cannot do this (for example, they died, are in prison, etc.).
Is it possible to leave later?
Is it possible to go on maternity leave later? Many are afraid that the postponement of maternity leave and sick leave will provoke the fact that the maternity leaver will be left without payments at all. This is wrong. Let's take a closer look at the situation.
Let’s assume that a woman already has a sick leave certificate in her hands, which allows her to write an application for maternity leave from today and leave work. However, if a pregnant employee does not go on maternity leave and does not want to do this, she simply does not submit an application and sick leave to the employer, but works as before.
However, it is worth informing the employer that you will work in the position for some time before you leave .
The moment you decide that it’s time to start your vacation, you submit an application to the employer, as well as a sick leave certificate. Since the deadline for taking leave is overdue, the employer issues your maternity leave later than the date indicated on the sick leave, that is, on the day you submit the application, and from this day your salary ceases to be accrued, and maternity benefits are accrued.
But the maternity leave in Article 255 70 days before childbirth and 70 days after, begins to flow not at the moment when you decide to go on maternity leave, but at the moment when your pregnancy is 30 weeks and you have been given a sick leave certificate.
This little confusion can be frightening to your employer, so if you want to continue to carry out your job function, you must inform him of your plans and work out a course of action together.
When, in this case, is it necessary to obtain sick leave for pregnancy and childbirth at the antenatal clinic?
Many people believe that since there is no desire to leave work, then at 30 weeks there is no need to receive sick leave.
This is wrong. A sick leave certificate is issued at 30 weeks for a normal pregnancy and at 28 for a multiple or complex pregnancy . You receive it immediately upon the arrival of the relevant deadline, but whether to submit the document to the employer or not is at your discretion.
Part-time work and civil law agreements
When working in several companies on a part-time basis at the same time (often found among IT specialists and accountants), the employee has the right to receive benefits from all companies in which she has been employed for at least two years. This situation is described in detail in Article 287 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Certificate for appointment of payment of maternity benefits
To provide benefits for part-time work, each institution must provide a certificate of incapacity for work received at a medical institution and a standard application form. The issuance procedure is regulated in Order of the Ministry of Health No. 624n, specific features are prescribed in employment contracts.
Important! In places of work where the average monthly income of an employee is below the minimum wage, her benefit is equal to the minimum wage. Thanks to this, the benefit for part-time work can be higher than the woman’s usual monthly income.
Labor and employment leave is issued for each place of work individually. This means that a woman can work in one place and receive benefits in another. In the absence of a submitted application for one of the places of work, the employer is obliged to register the failure to appear as an absence for unknown reasons.
Pros and cons of not taking maternity leave
According to the law, payment under the BiR is carried out in a lump sum, at the request of the woman, within six months after the end of the period. With a salary “in envelopes”, both parties may benefit from a waiver of maternity leave: the employer will not need to look for a replacement for a valuable employee, the mother will receive a salary along with benefits. Of course, this is illegal and is an attempt to deceive the FSS. The employer will be punished, and the mother will have to return the money received back.
Application for permission to return to work early
With a “white” salary and the absence of significant bonuses and bonuses, refusing a vacation without paying in advance will not give a woman anything. In any case, her vacation pay will be equal to the average salary, so by refusing maternity leave, she will work these 140 days just like that, for money that actually belongs to her.
Management does not have the right to fire a pregnant woman; any pressure or attempts to evade granting maternity leave are illegal. The state has transferred almost all the rights in the situation to the woman, so she will be able to choose in what format her vacation will take place over the next three years.
Is it possible to work during maternity leave?
The expectant mother has the right to continue working and receive payments in accordance with the employment contract (ET). Moreover, starting from the 30th week (28th in case of multiple pregnancy), she has the right to go on leave under the BiR. In a standard situation, it is provided for 140 days; deductions are paid based on average earnings for the last 2 years in a lump sum.
Let's consider several situations related to labor during the period of economic development:
the employee did not provide the manager with a sick leave certificate from the antenatal clinic, confirming the right to B&R. She continues to work and receives the salary due to her. At any time from the moment the labor and labor formally begins, the employee can change her mind and apply for leave on a certificate of incapacity for work. In this case, the benefit will be paid according to the actual number of non-working days. For example, if a woman worked for 15 days, they will not be covered by both benefits and wages. Only the salary will be paid, and benefits will begin to be deducted based on the calculation (140-15) = 125 days;
- a similar situation will occur if the employee decides to graduate from labor and employment prematurely. For example, after the birth of the child, she did not wait and immediately went to work. 30 days of the allotted vacation were spent, with another 110 left. Then 30 days already spent are covered by benefits, and for 110 days the woman is obliged to reimburse insurance contributions. The funds are not transferred to the employer personally, they go towards her salary, that is, for some time the employee can work for free in order to reimburse the costs.
Expert opinion
Irina Vasilyeva
Civil law expert
The legislation does not prohibit carrying out labor activities during the period of economic development.
Is it possible to receive benefits, does its amount change and how?
In conditions of part-time employment, the child’s mother retains the right to all required payments , namely:
- allowance for child care up to one and a half years old - paragraph 3 of Article 256 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, paragraph 2 of Article 11.1 of Law No. 255-FZ;
- compensation payment up to the age of three – paragraph 1 of Decree of the President of the Russian Federation No. 1110.
You can learn more about how to apply for benefits in this article, and find out what the size of payments depends on, as well as the calculation formula and other subtleties of applying for child care benefits here.