Suspension and dismissal: what's the difference?
A distinction should be made between “suspension” and “dismissal” in advance, since both terms are used in the law. The first concept means temporary exclusion of an employee from performing his official functions. A person retains his work relationships, his place, length of service, certain rights, and guarantees.
Dismissal involves the complete exclusion of the employee from the staff, issuing him a work book, where an entry is made reflecting the reason for this action. At the same time, it presupposes the severance of official relations and the termination of the contract. Another term used in the legislation is translation. It is carried out with the written consent of the employee, after which he begins to carry out his new functions. When transferring, the manager is obliged to re-enter into an employment agreement or make changes to the existing one.
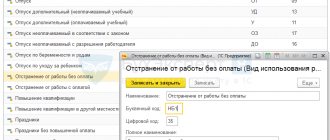
What information is reflected in the timesheet?
Special notes must be made on the report card indicating that a particular specialist did not perform his work duties during a certain period of time. The following notations are used for this:
- NB - if wages are not accrued for the entire period of inactivity.
- BUT - if the citizen retains his salary in full.
- PV - used for forced absenteeism, during which the missed days are paid by the employer.
Regardless of the reason for the suspension, employers must understand the rules for handling such a situation, otherwise they may be held liable. The reasons must be compelling and supported by official documents.
Conditions and procedure for removing employees from work
One of the powers of the employer is to release the employee from his duties, which is carried out on the basis of Article 76 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. But for this there must be compelling reasons or circumstances specified in this document.
Temporary suspension from work is considered a last resort, but does not provide for a complete termination or change in the employment relationship. It is used only to avoid paying wages to the employee. If the latter is not to blame, then forced idleness is regarded as downtime, according to which he is paid. At the same time, if there is a violation, it is possible to hold the employee accountable for a disciplinary offense in the form of dismissal.
Article 76 of the Labor Law provides for a number of provisions that provide grounds for a manager to remove his employee from work.
Appearing at work in an inappropriate manner
According to legal norms, a citizen must observe labor discipline and adhere to safety regulations. If he is seen at the workplace in a drunken state, that is, under the influence of alcohol, drugs, toxic substances, the boss must necessarily remove him from official duties.
To do this, it is necessary to write a report on the identification of the violation, certified by the signatures of at least two independent witnesses, obtain a written explanation from the employee himself, as well as a certificate provided by a doctor after a medical examination. Suspension must be immediate if it occurs during his shift and not after the end of the working day. If the above documents are missing, the fact of temporary release from work is considered illegal, and the citizen can appeal against the illegal actions of management in court.
Failed medical examination
At any enterprise or company, employees and administrative personnel are required to undergo regular medical examinations. For its part, the employer must exercise control over the implementation of this activity. Only employees should do this not on their own initiative, but in accordance with a pre-approved schedule and after concluding an agreement between the head of the enterprise and the medical institution. The administration allocates funds for routine medical examinations.
Advice! An employee has the right to refuse to undergo the procedure if he is obliged to do so at his own expense and on a day off. Otherwise, if all conditions are met, the employee’s refusal may result in legal dismissal from official duties.
Medical contraindications identified
Medical examination of personnel is carried out not only to confirm health and permission to continue to fully perform their functions at the enterprise or company. This procedure is necessary to exclude contraindications to the implementation of work that were described when signing the agreement.
Having in hand the conclusion of a medical worker, which contains recommendations to reduce workloads and change job functions, the employer has the authority to transfer the citizen to another job, guided by the provisions of Art. 73 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. If there is no vacancy that meets the recommendations given by the specialists, or the citizen refuses a temporary transfer, the manager has the right to suspend him for a period of up to four months or until he receives disability in the prescribed manner.
https://youtu.be/9rHaEgI1wnU
The employee has not passed the certification
There are some subtleties when taking action against individuals who have not been tested. At every enterprise, organization, company there is a commission that checks employees for safety rules and evaluates their qualifications. These events are regulated by a special package of documents.
Therefore, it is not possible to remove personnel from work without a valid reason. The manager is required to provide written confirmation drawn up on the basis of the training schedule, inspection protocol, and grades received. If it is missing, the removal is considered illegal.
Claims from special bodies or authorized officials
Such cases arise after the Inspectorate verifies the legality of the actions of certain categories of personnel, in particular, personnel department employees or accountants, persons whose activities are related to serving the population.
Based on the conclusion submitted in writing to the administration of the enterprise, the manager is obliged to release the employee until the circumstances are clarified or a decision is made regarding the duration of the sanctions applied. Such a situation leaves management no choice but to remove or dismiss the worker.
Temporary deprivation of special rights
The head of the enterprise is authorized to temporarily release the employee from performing labor duties if the license or other documents are suspended or expired. However, he must take into account a number of certain nuances. These measures are carried out mainly in relation to drivers who are deprived of their rights due to violation of the law and, accordingly, cannot perform their work.
At the same time, there is a special category of personnel performing specific activities. As an example, security guards who are granted permission to carry weapons, healthcare workers who are required to periodically confirm a patent that has certain time limits. In this situation, responsibility for the violation lies not with the staff, but with management, since it is obliged to check the qualifications of employees and send them for recertification.
Other cases involving a ban on performing work duties
Exemption from official functions is assumed in some other situations, but they must be provided for by law. It must be taken into account that such actions, if they have no basis and are not reflected in the relevant documents, are considered illegal and can be protested.
Based on current legislation, superiors or management must exclude the appearance at work of citizens who:
- Infectious agents were identified.
- Diseases dangerous to others have been diagnosed.
- Due to the type of activity, there is a need for contact with people of these categories.
- There is no opportunity or desire to visit a medical facility for examination or vaccination.
The basis in this situation is a certificate of incapacity for work, a certificate from the attending physician, a document from the Higher Quality Commission recognizing the person as unable to perform his official duties.
When is an employee suspended?
As noted above, the Labor Code and its Article 76, in particular, determines that the employer is obliged to remove workers from their duties if a reason established by law is identified.
The grounds for exclusion look like this:
- alcohol intoxication or drug influence;
- failure to undergo occupational safety training;
- failure to undergo a medical examination;
- presence of contraindications for health reasons;
- deprivation of special rights;
- requirement of authorized persons and bodies.
As you can see, the rules of law focus on situations dangerous to society or the worker.
We recommend you study! Follow the link:
Punishment up to and including dismissal for improper performance of official duties
The first reason - intoxication - is valid regardless of the time the worker appears at his place. The legislator proceeds from the fact that such behavior on the part of the worker is a gross violation of his obligations.
But it is important that the condition of the offending employee is properly certified and recorded. The form of confirmation is a medical examination or reliable testimony from other workers.
The medical examination is carried out in accordance with the Temporary Instructions, which is an annex to the Order of the USSR Ministry of Health 06-14/33-14 dated September 1, 1988. And for the validity of the testimony, they are drawn up in a special act. The latter is drawn up with the participation of an official representative of the trade union in which the worker is a member.
Completing training in occupational safety, safe methods of performing work, and first aid techniques is the direct responsibility of the employee in accordance with Article 214 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. As well as passing a test of the knowledge acquired in these courses and internships. At the same time, Articles 212 and 225 of the Code impose on the employer the obligation to organize all of the above activities. And the norm in question obliges the removal from activities of employees who do not comply with this requirement.
A number of articles of the Labor Code and other laws establish a requirement to undergo a mandatory medical examination and a list of medical contraindications that are an obstacle to occupying a particular position. In particular, we are talking about Art. 65, 73, 69, 97, 185, 224, 254, etc.
Mandatory preliminary and periodic medical examinations are carried out in the manner established by Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development No. 302n of April 12, 2011. Government Decree No. 695 of September 23, 2002 established the procedure for mandatory psychiatric examination for workers in certain hazardous professions. A list of contraindications that will become the basis for removal can be found in Resolution of the Council of Ministers No. 377 of April 28, 1993.
The legislation provides for a category of government bodies and officials, at the request of which, in certain situations, the employer must decide to remove certain persons.
In particular, an investigator or inquiry officer in a criminal case, with the consent of superior officials, may ask the court to issue a ruling to remove the accused or suspected of committing a crime. Carriers of infections dangerous to others are removed by decision of the chief sanitary and epidemiological doctors and their deputies.
The executive body of a joint stock company, which is of a sole nature, as the Law on Joint Stock Companies states, removes, if so stated in the charter, the board of directors or the supervisory board.
Possible time frame for elimination
Labor Code of the Russian Federation Art. 76 establishes that the restriction of an employee in the performance of his functions is carried out for the period necessary to eliminate the cause of this violation on the part of management. The maximum period is not fixed anywhere.
- If a person comes to work drunk, he is suspended only until the end of the day (shift).
- If there is no certificate of inspection, then after certification the sanction measure is canceled.
- If a person is not allowed to work at the request of officials or bodies, the decision is canceled after the charges brought are dropped.
Is it suspended due to deprivation of a driver's license?
This legislative act establishes that a worker is suspended from performing duties if his special right is suspended. The period of such suspension is determined to be up to two months.
We recommend you study! Follow the link:
Features of working under a temporary employment agreement
What special law is and under what circumstances it is suspended can be found out from the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. This term includes the right to drive a vehicle, the right to bear arms, all kinds of licenses, etc.
Suspension may occur due to:
- punishments;
- occurrence of circumstances of a different nature.
In accordance with Art. 3.8 of the Code of Administrative Offences, a special right is deprived for a certain period of time if a citizen grossly and systematically violates the rules for using it. The period of administrative penalties for related articles can range from a month to three years. But it is worth noting that if it exceeds two months, the employer dismisses the employee, and does not suspend him.
The form of execution of this punishment is the confiscation of a document indicating the existence of a right (for example, a driver’s license). It is returned to the owner after the expiration of the sentence, except in cases provided for by norms 9.3 and 32.6 of the Code of Administrative Offenses - then it is necessary to pass exams or undergo a mandatory medical examination.
It is worth noting that removal from duties due to deprivation of special rights is not automatic.
It is necessary only if.
- The employee cannot perform the duties prescribed by the employment contract.
- It is impossible (with his consent) to be transferred to a position that suits his qualifications and health status, even if it is lower.
In other cases, the worker does not face any risk of deprivation of the same driver’s license.
Payment for the period of inadmissibility to work
In the comments to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Article 76, the time during which personnel remain uninvolved in production is not taken into account when calculating the amount of earnings. But there are often situations when an employee did not have the opportunity to timely undergo a medical examination, certification, refresher courses or testing not at his own request and has evidence of these actions. Innocence in this situation is confirmed, as a result of which he receives payment for the entire period of downtime.
If during the period of suspension from official duties the employee falls ill and has sick leave, then compensation is also not issued. In this case, the administration is guided by the Special Regulations on the procedure for providing benefits for pregnancy, childbirth, and disability, approved on September 30, 1997.
It is important to know! In a number of situations, a person who has been suspended from work is paid certain subsidies instead of earnings. For example, infected people, carriers of pathogens, are provided with social insurance benefits. If persons are released for some time due to procedural coercion, they receive compensation from the state equal to five monthly salaries.
What does this entail?
The main consequence of removal from work duties for a worker is non-payment of wages for this period.
Some regulations establish, however, that wages can also be paid in this case - if we are talking about a civil servant who is being subject to an internal audit or an employee who has not undergone safety training through no fault of his own. In the latter case, the work is paid in the same amount as in the case of downtime.
It is worth remembering that suspension is strictly a temporary measure and cannot last longer than is required to eliminate the circumstances that led to it. Thus, a drunk cannot be suspended for longer than the time he is drunk.
Every worker and every employer should know Article 76 of the Labor Code. Thanks to this rule, it is possible to determine under what circumstances an employee’s removal from the performance of his duties is required, and what this means. It clearly establishes the temporary nature of such a measure and protects against abuse of power by employers. Also, this article establishes that for the duration of the restriction, wages will not be paid.
Grounds for dismissal
Reasons for dismissal can be objective or subjective. The first ones are determined by the norms of the current Labor Code of the Russian Federation and are legal grounds.
The latter reflect the interpersonal relationships that were formed during the period of work between the employee and his immediate superiors and/or colleagues. This should also include the desire to change place of residence, qualifications, company (enterprise).
Since the reasons can be varied, the law provides the opportunity to clearly formulate the reason for terminating the contract. Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation reflects the provisions that are a legal reason for terminating an agreement and expelling an employee from the staff.
According to general grounds, the most common dismissal is:
- during the probationary period;
- at the personal request of the staff;
- at the suggestion of the employer;
- as a result of an agreement between both parties;
- due to the fact that the term of the employment agreement has expired;
- due to violations of official functions;
- due to a decrease in the number of personnel (staff);
- in connection with the completion of the activities of the enterprise (company, individual entrepreneur).
The employer has the authority to dismiss an employee due to his prolonged absence. To do this, daily reports are drawn up stating that the missing employee does not appear at his work place for a long time due to unknown circumstances.
Attention! If there is no news from the disappeared person for more than a year, management can, through the court, declare the citizen untimely absent and terminate the employment agreement.
https://youtu.be/RCGkLDCNFvI
Some nuances
If an employee is under the influence of alcohol or drugs, he must undergo a medical examination. Otherwise, the removal will be considered illegal. Only with a doctor’s conclusion does the manager have the right to take such an action. However, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation leaves the issue of dismissal at the discretion of the employer, since after an offense this is an optional sanction.
If there are problems with the medical report, the person is offered other positions in the enterprise. Suspension is carried out only if there is no possibility of a change of place or if the employee refuses to transfer.
For the entire period, the employee retains his first position. During the period of suspension, the employee is not paid a salary and is not accrued vacation time. The employer does not make contributions to the Social Insurance Fund and the Pension Fund.
If a person is sure that he was suspended illegally, then he has the right to challenge the decision in court. In case of a positive outcome, the employer will be obliged to pay in full for the missed days and make all payments. The length of service is also restored.
https://youtu.be/TVn-nc9-qbA
Conclusion
Article 76 of the latest edition of the Russian Labor Code makes it clear that the manager has the authority to dismiss any employee for reasons that are reflected in the provisions of the relevant legal documents. At the same time, he must provide compelling reasons for carrying out such actions, confirmed by relevant certificates. Otherwise, temporary release from official duties will be considered unauthorized, and the employee can easily challenge it in court.
Art. 76 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation with comments 2020
The norm in question establishes the level of responsibility of the employee. Moreover, in part 1 of Art. 76 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that its use is the responsibility of the employer.
Suspension is carried out until the reasons for which it was imposed on the employee are eliminated. For example, if a citizen appears drunk at an enterprise, then he is not allowed to work only for the day on which he was in this state.
Accordingly, it would be unlawful to suspend this employee in subsequent days, including, for example, before a decision is made to impose a disciplinary sanction on him.
The obligation enshrined in Art. 76 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, does not depend on the respectability or disrespectfulness of the reasons why a citizen did not undergo training, a medical examination or a knowledge test. In these cases, the citizen is removed under any circumstances.