Basic moments
Clause 1 of part one of Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation determines the possibility of terminating a contract with an employee at almost any time. At the same time, they can be fired even during the probationary period. To carry out the procedure under consideration, it is sufficient that one of the parties expresses readiness to terminate the relationship. In other words, if the boss proposes to terminate cooperation with the employee, and the subordinate does not agree, then this is his right.
Recently, cases of dismissal without working for two weeks (2017, Article 78 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Every employee can use this right when irresolvable disagreements arise with their superiors. In this case, there is no need to give comments or conduct timely coordination with a senior manager.
Article 78 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation on termination of an employment contract by agreement of the parties can also be used by management. A common case is when, due to changes in circumstances, it is necessary to reduce employees without timely notification.
In this case, upon execution of a written agreement, the employer can pay compensation to the subordinate to compensate for lateness.
Employee initiative
Article 77, paragraph 3 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that an employee can be dismissed on his own initiative. This is based on the principles of freedom of labor and choice of place of work. At the request of the employee, the employment relationship can be terminated at any time. In addition, Article 77, paragraph 3 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation contains a reference to Article 80. Labor Code, according to which the employer must be notified of this 14 days before the date of dismissal in writing, moreover, this can be done not only during the performance of work duties, but also on vacation, during illness.
If the reason for dismissal is the impossibility of continuing work for objective reasons (study, pension, violation of labor rights by the employer, the terms of collective agreements, additional agreements), the contract must be terminated within the period specified in the application. An employee can also withdraw his resignation letter if the employer has not found a replacement for him. The contract cannot be terminated in this case.
Contract termination procedure
The accepted procedure for terminating employment contracts in paragraph 1 of Art. 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation allows you to quickly quit without the consent of management.
It is characterized as follows:
- One of the parties to the concluded employment contract expresses a desire to terminate it.
- The first step is to formalize the agreement. It should be in writing in order to eliminate consequences for unlawful actions of the employer.
- After this, the document is registered in a special journal.
- A copy of the completed document is given to the subordinate for signature.
- The accepted order is recorded in the journal.
- The employee is notified of the contents of the decree. It must also be signed.
- On the specified date, the employee is fired and the allocated funds are paid.
When considering the procedure, it is worth considering that some employees are not paid compensation. In addition, there is no need to specify the terms of payment of severance pay or other funds.
The new edition of the legal document does not provide for any design standards . This means that the director can draw up the form of the agreement himself. The manager may not sign the application until full mutual understanding has been reached between the parties, and also if the final text of the transaction has not yet been approved.
Some of these documents cannot be presented to the employee for review. An example is the case when he did not show up for work or refuses to review the drawn up contract. This point must be indicated in the text. The same paper is issued if the employee was unable to collect the intended funds or his work book.
https://youtu.be/SMviuYx6X8Q
Responsibility for violation of employee rights
Since violations by the employer during the dismissal process are far from uncommon, it is better to familiarize yourself in advance with the content of the legal norms in this area.
Know! To avoid being forced to resign at personal request, employees need to know their rights, then they will be able to prevent their violation.
The Labor Code not only regulates the procedure itself in detail, it also provides for liability for violations in the field of labor relations.
The application of sanctions is determined by more than one Labor Code of the Russian Federation; punishments for offenses in this area are also provided for in the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
Legal norms and types of sanctions:
- penalty (penalty) for delay in payment in the amount of 1/150 of the rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation (Article 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- fine or ban on holding certain positions for 1–3 years (Article 5.27 of the Administrative Code of the Russian Federation).
The amount of fines varies within the following limits:
- from 1,000 rub. up to 5,000 rub. – for officials and entrepreneurs. The latter may also, as an alternative sanction, be deprived of the right to operate for a period of up to 3 months;
- from 30,000 rub. up to 50,000 rub. - for legal entities. This type of punishment can be replaced by a ban on carrying out activities for a maximum of 90 days.
If the offense is very serious and committed by employees of state or municipal bodies, as well as by the top officials of the enterprise (manager and his deputy), a ban on holding such positions for 1 to 3 years may be applied.
The severity of the punishment depends on the seriousness of the illegal act. If a citizen was forced to resign of his own free will, he has the right to protect his interests in court. Filing a claim does not require payment of a state fee.
Watch the video. How to withdraw your resignation letter:
https://youtu.be/CZuMNl-kqO0
Dear readers of our site! Our articles talk about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is unique.
If you want to find out how to solve your specific problem, please contact the online consultant form on the right. It's fast and free! Or call us at :
+7-495-899-01-60
Moscow, Moscow region
+7-812-389-26-12
St. Petersburg, Leningrad region
8-800-511-83-47
Federal number for other regions of Russia
If your question is lengthy and it is better to ask it in writing, then at the end of the article there is a special form where you can write it and we will forward your question to a lawyer specializing specifically in your problem. Write! We will help solve your legal problem.
Payments after dismissal
Dismissal by agreement of the parties provides for the payment of compensation, which can be agreed upon in advance between the employer and the worker. If the employee does not agree with the accrued amount, Article 140 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation may come into effect. If this document was used as the basis for assigning the amount of compensation, then it cannot be challenged.
Upon termination of the contract between the employer and the hired worker, the following compensations are issued:
- In case of unused vacations for the entire period of work, they are paid in full.
- Unpaid wages for the last days of work or withheld funds for the entire period of employment.
- Compensation related to the termination of the concluded contract. This item is often indicated separately.
If the organization's regulations provide for payment to a former employee, and it was not carried out, then after dismissal he can sue his manager. The most difficulties arise in the case when vacation was not used during the year or the entire period of work.
When calculating the intended amount, the average earnings are taken into account.
Duration of the voluntary dismissal procedure
The dismissal process, like any other, takes some time. In this case, this period cannot exceed 14 days from the date of submission of the application.
If an employee leaves the probationary period, the period lasts only 3 days.
In certain cases, the parties can agree and reduce the working period by a couple of days. It is impossible to obtain such an agreement regarding the extension of the contract, since this is contrary to the law and entails liability.
Payroll preparation
The average monthly salary is used as the basis for calculating various compensations, the payment of which is provided for when using clause 1 of Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation at the time of dismissal.
To obtain the correct result, vacation days, sick leave and days off are deducted. The calculation procedure is as follows:
- The number of days that a person worked in the organization is determined.
- All salaries add up.
- The result obtained is divided by the number of days worked.
After determining the average salary, compensation calculations can be carried out. You can carry out such calculations yourself to determine the amount due.
Base 1
According to the first paragraph of Article 77 of the Code, dismissal is carried out by agreement of the parties. In this case, the employment relationship is terminated at the initiative of the employee. In fact, there are often cases of termination of employment relationships at the request of the employee, but with certain features.
Agreements may relate to the issue of payment, training conditions for a new employee, and other things. For example, you can agree that the employee leaves for another place without working off. But in return, he undertakes to check the reports of the person who comes to replace him once a week.
https://youtu.be/7MH380F2T6M
Compensation for unused vacation
The biggest difficulty arises with calculating compensation for unused vacation.
In this case, the amount of payments is determined as follows:
- The number of unused rest days for the entire period of work is determined.
- The average monthly salary is calculated.
- Both indicators are multiplied.
It is worth considering that the employer must pay this amount to his former employee. If he did not do this, then you can go to court with a complaint against the director.
What does Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establish?
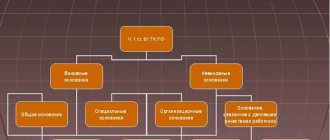
The regulatory act establishes the reasons why an employment relationship may be terminated. Article No. 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is a legal guarantee of labor law that does not contradict the Constitution. Termination of the contract is possible when three conditions are simultaneously met:
- There are reasons established by law.
- The dismissal procedure is followed.
- There is a dismissal order.
Part 1 of Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (clauses 1-4) states that the contract can be terminated at the request of the employee or employer, by agreement of the parties or due to the expiration of the contract. The contract is also subject to termination in the following cases:
- if the employee is transferred to another employer or to an elective position;
- if an employee refuses to perform labor duties due to a change of owner, change of jurisdiction, or reorganization of the enterprise;
- if the employee refuses to continue performing work due to new changes in the contract;
- when an employee is transferred to another position due to health reasons;
- if the enterprise moves to another area;
- if circumstances arose that were beyond the control of either party;
- in case of violation of the rules for concluding employment contracts and the inability to continue working in the future.
Article 77, paragraph 3 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that an employee can be dismissed on his own initiative. This is based on the principles of freedom of labor and choice of place of work. At the request of the employee, the employment relationship can be terminated at any time. In addition, Article 77, paragraph 3 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation contains a reference to Article 80. Labor Code, according to which the employer must be notified of this 14 days before the date of dismissal in writing, moreover, this can be done not only during the performance of work duties, but also on vacation, during illness.
If the reason for dismissal is the impossibility of continuing work for objective reasons (study, pension, violation of labor rights by the employer, the terms of collective agreements, additional agreements), the contract must be terminated within the period specified in the application. An employee can also withdraw his resignation letter if the employer has not found a replacement for him. The contract cannot be terminated in this case.
Article No. 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation in paragraph 2 states that dismissal can also be the initiative of the employer. At the initiative of management, an employee may be dismissed for the following reasons (in accordance with Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- Unsatisfactory completion of the probationary period.
- Changes in working conditions.
- Expiration of the contract validity period.
- Liquidation of the enterprise.
- Real staff reduction.
- Inconsistency with the position held for medical reasons or based on the results of certification at the enterprise.
- Change of owner of the enterprise.
- Single gross or repeated failure to fulfill labor obligations.
- Loss of trust.
- It is an immoral act if the employee performs work related to education.
- Unreasonable decisions that resulted in losses, or gross violations by management.
- If, during employment, the employee provided the manager with false information or forged documents.
- Expiration of the security clearance, if work is related to it.
- Under the circumstances provided for in the employment contract.
- For other reasons established by this legislation.
Paragraph 1 (Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) states that the contract can be terminated by agreement of the parties. This can be done regardless of the validity period of the contract.
In practice, employers themselves offer to terminate the contract on this basis when there are no other legal grounds for dismissal. However, this also requires the desire of the employee. By agreement of the parties, both the employee and the employer can inform about dismissal orally or in writing. The end date of the contract is also agreed upon.
Dismissal by mutual consent (clauses 1 and 2 of Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation)
The first paragraph is about a mutual decision, that is, about reaching an agreement to terminate the paper.
The clause refers to Article 78: it states that the parties can always terminate the contract concluded between them upon reaching agreement. This usually happens when the employee and boss understand that their cooperation is useless and unproductive.
Clause No. 2 refers to fixed-term contracts, that is, concluded for a certain period. Once this period comes to an end, the employee may be fired. Article No. 79 is responsible for this situation.
It is worth noting: if the employee continues to work, and the boss does not seek to fire him, the contract continues. Termination occurs:
- On the day specified in the paper, and the company must notify the person being dismissed 3 days before.
- If an employee was hired to replace a temporarily absent person, the contract ceases to be valid when the latter returns to work.
- If the worker was hired to perform a specific amount of work, the last day will be the day it is completed. For example, seasonal employees who harvest crops finish on the last day of the season or after the site has been completely “cleaned.”
Agreement of the parties is the mutual consent of the participants in the labor relationship to terminate it on pre-agreed conditions. Specific conditions are fixed on paper by drawing up and signing an agreement in two copies.
This agreement establishes the date of dismissal, upon which the employer must issue documents to the dismissed person and provide him with a payment. In addition, it may determine a special procedure for dismissal, payment of compensation, provision of leave before dismissal under Article 77 and other conditions.
The initiative can come from any of the two parties to the employment contract. The written agreement that the parties draw up upon the agreement on dismissal can be concluded at any time before the resigning person’s last working day.
When dismissing on this basis, it is permissible not to draw up a written agreement, but to agree on the terms orally. However, there is a certain risk associated with a possible violation of oral agreements, so it is still recommended to consolidate the decisions made on paper.
If the parties change their minds about terminating the relationship, then the planned procedure can be canceled if there is a mutual desire of both participants in the labor relationship. It is impossible to revoke an agreement unilaterally.
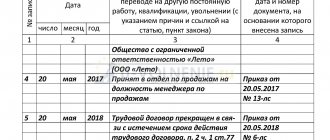
If an agreement is not drawn up, then the employee needs to write a letter of resignation to obtain documentary support for issuing the T-8 order.
The order contains information about the agreement or application, and also indicates the wording of the basis from Article 77 and indicates the paragraph number - 1.
Example agreement:
Paragraph 2 applies when the employment contract has a limited duration and is about to expire. The termination date may be a specific date or the occurrence of an event.
Documentation for this basis includes:
- notice of dismissal - if required;
- dismissal order;
- recording the fact of dismissal in the work book and T-2 card.
A notice is a written warning document, the purpose of which is to inform the employee of the impending termination of work. The conscript must be informed 3 days before the expiration of the contract, if the specific day on which the validity period ends is known. If the exact number is not known, this is possible when replacing an absent employee, then there is no need to warn the conscript 3 days in advance. When the main employee returns to work, the conscript replacing him is dismissed, regardless of whether the warning was fulfilled or not.
If the term ends and the parties remain silent about it, then the contract is extended for an indefinite period.
In the dismissal order, in the line to indicate the grounds, a reference is made to the 2nd paragraph of Article 77 and the wording of this paragraph is given. In the line about the documentary justification, the details of the notification and the clause of the employment contract with the expiration date specified in it are written.
If the validity period expires when the main employee leaves, then an order about this should be drawn up, which will serve as a documentary basis for issuing the order in the T-8 form.
If the reason for the end of the validity period is related to the completion of work or services, then the documentary basis will be a document confirming the fact of completion of work or services (for example, an acceptance certificate).
Example notification:
Dismissal at the initiative of the employee (clause 3 of article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation)
This refers to termination of the contract at the initiative of the employee himself.
The situation is controlled by Article 80:
- A citizen can resign by writing a written application, after working for 2 weeks. The working period can be changed if it is prescribed in the Labor Code or other law.
- If termination of an employment contract at the initiative of an employee is due to the inability to continue working (for example, the start of training or retirement) or violations on the part of the employer, he can himself indicate the period for which he will need to terminate the contract.
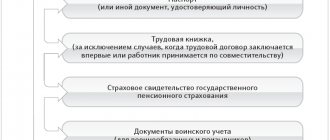
- On the last working day, the employee must receive a work book, full salary and other necessary documents.
- While the work period has not expired, the employee has the right to withdraw the application and continue working, but only if a new person is not invited in writing to take his place.
- If the employment contract has not been terminated and the employee does not intend to leave (would like to continue working), the contract does not terminate.
This reason is the most popular reason for dismissal. The employee is required to submit a written application document outlining a request to terminate the contract. The obligation of management to accept the application and formalize the dismissal at the end of the service period is 1 month for management personnel and 2 weeks for all other persons.
The order is processed and payments are calculated on the last day of the warning period. The order contains a reference to paragraph 3 of Article 77 and the wording of this paragraph; in the line for indicating the document details, data on the employee’s statement of personal desire to resign is provided.
In the application, indicating the reason for terminating relations with the employer is not mandatory; it is enough to note your own desire to quit and promptly notify management of your intentions.
Application example:
Dismissal at the initiative of the employer (clause 4 of article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation)
The employer can also terminate the contract.
This may be due to the following situations:
- Unsatisfactory result of the probationary period. In this case, it is necessary to notify the citizen in writing 3 days in advance. The applicant must do the same.
- Closing of an organization, change of owner, layoff of employees.
- Constant violations by a citizen.
- One-time gross violation: absenteeism, theft of someone else's property, coming to work while intoxicated, etc.
- Loss of confidence of the boss in the employee due to certain violations.
- Providing false documents, discrepancy between the knowledge and skills of a citizen and his position.
- Committing an immoral act - especially applies to educators and teachers.
- Making an unreasonable decision, resulting in serious losses for the organization, applies to leadership positions.
Please note that all these reasons are listed in Articles No. 71 and No. 81.
The clause stipulates that the initiative for dismissal comes from the employer. Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes cases when this is possible. Among the most common reasons are liquidation, layoffs, violations of discipline, and failure to fulfill duties.
When terminating the contract under clause 4, with proper documentation, it is not necessary to obtain the consent of the person being dismissed. The dismissal procedure boils down to collecting the necessary documents, informing the employee about the inevitable event, issuing a T-8 order, recording the fact of dismissal in the necessary documentation, as well as making settlements with the dismissed person.
Dismissal due to transfer to a new position (Clause 5 of Article 77 of the Labor Code)
The clause refers to the transfer of an employee to a new position or place of work.
For example, when promoting, an employee must first be fired from his previous job and only after that he must be given a new job.
This also includes a transfer to another place, more precisely, to another employer.
Please note: in any situation, the consent of the employee himself is required - he cannot be transferred forcibly. Article 72.1 applies here. It talks about certain situations:
- A transfer to another job is a change in the functions of an employee or his entire department while maintaining the previous employer.
- When moving from one place of work to another, the employment contract is concluded anew.
- A citizen’s transfer to another workplace or to another unit, transfer to another structural unit of the same area can take place without re-issuing papers.
- If a new place is not suitable for a citizen due to health reasons, he cannot be transferred.
An employee has the right to change jobs and transfer to another organization with which he has an agreement. If there are no obstacles to the transfer on the part of the current employer, dismissal is carried out without working out the 5th point.
Documentary justification - a statement of termination of the contract in connection with the planned transfer to another company.
Dismissal of management personnel (clause 6 of article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation)
When a new owner comes to the management, dismissal can only affect representatives of the management team; all other workers can continue to work in their places. Any employee himself can terminate the relationship if he does not want to work with the new management, while the order contains the wording from clause 5 of Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Documentary justification includes:
- documentary evidence of a change in the owner of the company or its reorganization;
- warning employees about innovations;
- statement from an employee who does not want to continue working in the organization.
Dismissal due to changes in the terms of the employment contract (Clause 7, Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation)
Dismissal may also be associated with a change in any conditions: for example, with the relocation of the entire organization to another city or with the deterioration of the employee’s health and the inability to conscientiously perform duties.
Paragraph No. 7 talks about refusal to continue work due to changes in the terms of the contract.
More details are provided in Article 74 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation:
- If there have been changes in organizational or technological labor conditions (for example, machines have changed or departments have been merged), the paper can be changed by the employer. This does not apply to the employee’s job responsibilities; the boss cannot change them without the consent of the citizen.
- The employee must be warned in advance (2 months) about the changes and their reasons.
- If an employee does not agree with the changes, the company must offer him in writing another position - similar or lower. If you refuse it, the citizen may be fired.
- If employees are threatened with mass layoffs, in order to save their jobs, the organization has the right to introduce part-time work or a week for up to six months. If the employee refuses to work in this mode, the contract is terminated and the citizen receives compensation.
Dismissal is an integral part of the labor process, but it is only possible if there are certain reasons. All of them are prescribed in the Labor Code and should not be violated.
The revision of the current working conditions may not suit the worker, in which case the employee may be dismissed under point 7. In this case, we mean the organizational or technological terms of the contract.
Documentary justification:
- notification from management about planned updates to working conditions;
- statement from an employee about unwillingness to accept changes.
If the employee does not write a refusal before the end of the warning period specified in the notification form, then the employee’s agreement with the updated terms of the employment relationship is automatically recognized.
Dismissal on the basis of a medical report (clause 8 of article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation)
The basis from paragraph 8 is used if a medical report requires the worker to be transferred to another job for a long period (at least 4 months). If the employee has no desire to make such a transfer, as well as in the case when the employer has nothing to offer, dismissal is carried out under paragraph 8 of Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Documentary justification:
- offer of suitable work;
- a statement from an employee about unwillingness to accept the employer’s offers.
Dismissal due to relocation of the employer (Clause 9 of Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation)
When the employer moves outside the current locality, the employee may not have the desire to change his usual environment and follow his workplace to another area, while the procedure for terminating the contract is carried out under this paragraph of Article 77.
Documentary justification:
- decision to move;
- a proposal for transfer, which is sent to the worker 2 months before the actual date of relocation;
- written confirmation of unwillingness to transfer, drawn up in response to an offer.
Dismissal for other reasons (clause 10 of article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation)
This clause applies in the following cases:
- call for service;
- reinstatement by decision of the supervisory authority;
- judicial punishment that prevents further work;
- recognition as incompetent;
- death of a participant in labor relations;
- emergencies;
- other points from Article 83 of the Labor Code.
Documentary justification for issuing an order T-8 depends on the reason for termination of the contract and must confirm the fact of its presence.
Dismissal in case of violation of employment requirements (clause 11 of article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation)
The clause applies in case of violation of the requirements for drawing up an employment contract. Specific situations are enshrined in Article 84:
- failure to provide workers with the necessary documents to occupy a specific position;
- employment in a job that is not suitable for medical reasons;
- placement in positions prohibited for this person to occupy by a court decision;
- other situations from Article 84.
As soon as the employer detects the presence of one of the situations listed in Article 84, he must formalize dismissal. However, you must first offer a transfer to another suitable position. If the proposed positions do not suit the employee, then dismissal is issued.
Entry in the work book
According to established standards, a work book is issued on the day the dismissal order comes into force.
It contains the following information:
- The date and number of the entry entered.
- The article under which the contract was terminated.
- The date the order was issued and its number.
In some cases, a former employee cannot come to pick up his work book on the day the document is signed. You can pick it up on another day, in addition, the employer can send the document by registered mail. When issuing a work book, a corresponding entry must be made in the personnel department. This eliminates the possibility of problems arising in the event that a former employee makes a claim about its loss or non-issuance.
https://youtu.be/nHuei-tVIhE
General information about dismissal
It’s better to quit voluntarily than to be fired – that’s a fact. But in any of these cases, the person leaving his place of work has the right to certain monetary payments.
Everyone knows what dismissal is: it is the termination of the employment relationship between the employee and the employer. Simply put, a person ceases to be an employee of a specific organization. You can resign yourself, then the work book will say that the termination of the employment contract occurred on the initiative of the employee, as people say - at his own request. This happens most often.
It is undesirable for the employee’s future working life and career if the dismissal order contains the wording “at the initiative of the employer.” This means that the person was fired. Further, the order must state the basis, that is, the reason why this happened:
- violation of safety rules or regulations established by the system of internal documents of the enterprise;
- inadequacy for the position held;
- systematic absenteeism and similar troubles.
However, it is quite possible that with the abolition of work records, which has been discussed for several years, the wording for dismissal will lose meaning. There are many more reasons for dismissing a person at the initiative of the employer, and not all of them are related to misconduct: this could be the liquidation of an enterprise, a reduction in staff, or a change of owner.
In addition, a person’s employment contract may simply expire or he may be transferred to another place of work. There is also such a formulation for terminating an employment relationship as an agreement of the parties - we will talk about it separately.