Comments on Article 78 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, judicial practice of application
Agreement of the parties as a basis for termination of an employment contract is used in cases where the desire of only the employee or only the employer is not enough to terminate the employment contract. A mutual expression of will of the parties to terminate the employment relationship is required.
By agreement of the parties, it is possible to terminate any contract - both concluded for an indefinite period and a fixed-term one before its expiration. Agreement of the parties is the only basis for termination of the employment contract, without requiring any other reasons.
The specific date of termination of the employment contract is determined by the parties.
The initiative to terminate an employment contract on this basis can come from any party to the employment contract: both the employee and the employer.
Since labor legislation does not contain a requirement for written termination of an employment contract at the initiative of the parties, an agreement between the employee and the employer on termination of the employment contract can be drawn up in the form of:
- additional agreement on termination of the contract signed by the parties and attached to the employment contract;
- a written application from the employee with the employer’s resolution (by the employer making a corresponding entry on such application);
- in the form of an order (instruction) from the employer to terminate the contract in accordance with Article 78 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, signed by the employee expressing consent to terminate the contract by agreement of the parties.
Clause 20 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated March 17, 2004 N 2 “On the application by the courts of the Russian Federation of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation” contains the following explanations:
Cancellation of an agreement regarding the period and grounds for dismissal
When considering disputes related to the termination of an employment contract by agreement of the parties (clause 1 of part one of Article 77, Article 78 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), the courts should take into account that, in accordance with Article 78 of the Code, when an agreement is reached between the employee and the employer, an employment contract concluded for an indefinite term, or a fixed-term employment contract can be terminated at any time within the period determined by the parties. Cancellation of an agreement regarding the period and grounds for dismissal is possible only with mutual consent of the employer and employee.
Position of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation
Norm Art. 78 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which does not allow an employee to refuse to fulfill an agreement with the employer to terminate an employment contract does not contradict the Constitution
According to the applicant, Article 78 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not allow an employee to refuse to fulfill an agreement reached with an employer, a legal entity, to terminate an employment contract, which violates his right to freely dispose of his abilities to work and is contrary to the Constitution.
The Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation indicated the following. Freedom of labor also implies the possibility of terminating an employment contract by agreement of its parties, i.e. based on the voluntary and agreed expression of will of the employee and employer. Reaching an agreement to terminate an employment contract on the basis of a voluntary agreement of its parties allows for the possibility of annulment of such an agreement solely through the agreed expression of will of the employee and the employer, which excludes the commission by both the employee and the employer of arbitrary unilateral actions aimed at abandoning a previously reached agreement. Such legal regulation is aimed at ensuring a balance of interests of the parties to the employment contract and cannot be considered as violating the constitutional rights of the employee.
The resolution of the issue of granting an employee the right to unilaterally cancel an agreement to terminate an employment contract, as related to a change in the current legal regulation, falls within the competence of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation, as defined by Article 125 of the Constitution of the Russian Federation and Article 3 of the Federal Constitutional Law “On the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation” , does not apply (determination of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation dated October 13, 2009 N 1091-О-О)
Dismissal procedure
An employee has the opportunity to terminate his employment relationship with the company, regardless of what kind of employment contract was concluded (fixed-term or indefinite). It should be noted that dismissal by agreement of the parties requires the voluntary mutual consent of the employer and employee.
The sequence of actions in the process of registering such a dismissal will be as follows:
- An employee who decides to terminate further relations with the company makes an appointment with the employer (authorized person) to agree on the date of dismissal.
- After receiving the consent of the administration, represented by the manager authorized to sign orders, it is necessary to write a letter of resignation, which must indicate the date of termination of the employment agreement. If there is no such date, then by default it is considered the date of submission of the document or this date must be indicated in the resolution of the manager.
- The personnel department, having received an application with the manager’s resolution, is obliged to prepare the appropriate dismissal order, as well as changes to the employment agreement and submit it to an authorized person for signature. The citizen’s signature on the additional agreement to amend the employment contract is affixed at the time he is familiarized with the dismissal order.
- The documents signed by the parties (their certified copies) are transferred to the personnel department for full settlement with the employee. In parallel, the personnel employee fills out the work book of the dismissed citizen.
- The issuance of a work book, as well as the transfer and payment of money due to an employee, is carried out on his last working day (in the second half). Moreover, if an employee does not have the opportunity to personally pick up his work book, in order to send it by mail, it is necessary to obtain written consent from the citizen, and if they express a desire to transfer the document through a representative, the latter must have a properly executed power of attorney.
Essentially, these are all the stages of severing relations by agreement of the parties.
A mandatory condition for dismissal under Article 78 of the Labor Code is the consent of the parties. Such dismissal can be annulled only when it is proven that psychological or other measures of influence were applied to the citizen during the process of writing the application.
Reinstatement occurs through the court.
We recommend you study! Follow the link:
Step-by-step instructions on how to quit your job voluntarily
Another commentary on Article 79 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
A fixed-term employment contract is terminated upon the expiration of its validity period, of which the employee is warned by the employer at least three calendar days before dismissal, in contrast to the previous wording of the article.
A warning about termination of a fixed-term employment contract must be given in writing. The legislator establishes a general mandatory rule for the employer to warn the employee about the upcoming termination of the employment contract. If there is no written warning from the employer, and the employee continues to work, then the employment contract is considered concluded for an indefinite period (see Article 58 of the Labor Code and commentary thereto). The employment relationship actually continues, but if in the future the parties consider it inappropriate to continue the employment contract, then it can be terminated, but not under Art. 79 TK.
Dismissal of an employee upon expiration of the contract concluded for the duration of the duties of the absent employee does not require such notice.
Parts 2 - 4 of the commented article clarify the moment of expiration of a fixed-term employment contract. An employment contract concluded for the duration of a specific work is terminated upon completion of this work. The legislator links the termination of an employment contract not with its expiration date, but with the deadline for performing specific assigned work (for example, drawing up an accounting report). The fact of dismissal of the employee in this case will be the date on which the work is considered completed (completed).
Part 3 of the commented article provides that an employment contract concluded for the duration of the duties of an absent employee is terminated when this employee returns to work. It must be borne in mind that such an agreement may have a specific period: say, four months or a year and a half, and in the event of an absent employee returning to work early, such an agreement is terminated.
An employment contract concluded for the duration of seasonal work is terminated after a certain period. The grounds for dismissal of an employee will be the end of the season. The list of seasonal work, including individual seasonal work, the implementation of which is possible during a certain period (season) exceeding six months, and the maximum duration of these individual seasonal work are determined by industry (inter-industry) agreements concluded at the federal level of social partnership (see Art. Articles 293 - 296 of the Labor Code and commentary thereto).
Current labor legislation establishes additional guarantees when terminating a fixed-term employment contract, for example for pregnant women. In particular, in the event of expiration of a fixed-term employment contract during the pregnancy of a working woman, the employer is obliged, upon her application and upon provision of a medical certificate, to extend the term of the employment contract until the end of pregnancy. In this case, a pregnant woman is obliged, at the request of the employer (but not more than once every three months), to provide a certificate confirming the state of pregnancy. However, if a woman actually continues to work after the end of pregnancy, then the employer has the right to terminate the employment contract with her due to its expiration within a week from the day the employer learned or should have learned about the end of pregnancy (see Article 261 of the Labor Code and commentary to it).
If it is established during the trial that there have been multiple conclusions of fixed-term employment contracts for a short period of time to perform the same labor function, the court has the right, taking into account the circumstances of each case, to recognize the employment contract as concluded for an indefinite period (see paragraph 14 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation dated 17.03. 2004 N 2).
Cancellation of additional agreement
As noted above, dismissal by agreement of the parties (Article 78 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) can only take place on the basis of an additional agreement, which is drawn up in accordance with all of the specified recommendations. But there are times when the situation has changed and there is no longer a need to fire an employee. What should the parties to the legal relationship do in this case?
An additional agreement by agreement of the parties can be canceled, but for this one condition must be met - the desire of both parties to the legal relationship.
In a situation where the employee himself wants to return to work, he must submit a written application to the head of the company with such a request. If 14 days have not yet passed since the order was issued, then the employer does not have the right to refuse it. In order for a dismissed employee to be able to resume his or her job duties, it is necessary to issue an order to cancel the additional agreement.
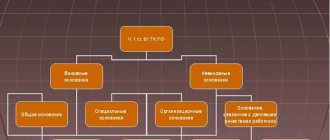
Commentary to Art. 78 Labor Code of the Russian Federation
1. The principle of freedom of contract involves ensuring the possibility not only of concluding a contract, but also of freely terminating it on the mutual initiative of the parties. The commented article establishes the operation of this principle in relation to an employment contract.
2. By agreement of the parties, it is possible to terminate any contract - both concluded for an indefinite period and a fixed-term one before its expiration. Agreement of the parties is the only basis for termination of the employment contract, without requiring any other reasons.
The specific date of termination of the employment contract is determined by the parties.
Free legal advice by phone:
8 (Moscow and Moscow region)
8 (St. Petersburg and Leningrad Region)
8 (Regions of the Russian Federation)
3. The Labor Code does not determine the form in which the agreement of the parties to terminate an employment contract can be expressed. Such an agreement can be drawn up in the form of a corresponding document (additional agreement) attached to the employment contract, a written statement from the employee with a resolution of the competent official of the organization - the employer, and finally, in the form of an order (instruction) of the employer to terminate the contract in accordance with the commented article, signed by the employee with an expression of consent to terminate the contract by agreement of the parties.
4. In practice, the agreement of the parties as a basis for termination of an employment contract was used if, for some reason, such termination was impossible on a unilateral initiative. Current legislation has removed almost all restrictions on dismissing an employee at his own request, while maintaining the existing restrictions on terminating an employment contract at the initiative of the employer. Therefore, an agreement between the parties as a basis for terminating an employment contract does not make sense for the employee (since he can resign at any time of his own free will) and is potentially dangerous for the employer (in the event of a dispute, he will be forced to prove the absence of pressure on the employee when terminating the employment contract).
5. An agreement to terminate an employment contract by agreement of the parties can only be canceled by mutual consent of the parties (clause 20 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation of March 17, 2004 No. 2 “On the application by the courts of the Russian Federation of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation”). This does not exclude the possibility of dismissing an employee at his own request (Article 80 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) or if there are grounds for this at the initiative of the employer.
6. The agreement on termination of the employment contract may provide for the payment of severance pay to the employee or other compensation payments. However, such a condition is not established upon termination of an employment contract with managers, their deputies, chief accountants and members of collegial executive bodies of state corporations, state-owned companies, as well as business entities, who have concluded employment contracts, as well as business entities, more than 50% of the shares (stakes) in the authorized capital of which are in the state or municipal property (see Article 349.3 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and commentary thereto).
Dismissal by agreement of the parties or by layoff: which is better?
Reduction or dismissal by agreement of the parties? Often, employers offer employees, instead of the required reduction, to resign by agreement of the parties. This is beneficial for the employer because:
- This is the “easiest” of all forms of termination of employment: an employee can be fired at any time, without warning.
- The likelihood of challenging the dismissal in court is minimal.
But what benefits and disadvantages does such dismissal bring to the employee? Agree or not
?
The issue of financial benefits in this case is decisive for the employee. And if the employer wants to simplify his task by dismissing the employee by agreement, he will have to convince the employee with “financial arguments.”
The legislation does not provide for specific rules in this regard, and the employer agrees to this based on considerations of economic feasibility. Therefore, if management offers more favorable conditions compared to the total officially established compensation for reduction (at least three, at most five average monthly earnings), and if the agreement contains additional “beneficial” clauses (for example, if obligations give the employee good recommendations), - dismissal by agreement of the parties will be the best solution.
The main argument that makes dismissal by agreement attractive to an employee is the financial benefits and prospects for further employment. If a laid-off worker wants to receive maximum financial compensation and registers with the employment center, he must not work for at least 60 days in order to receive benefits. Upon dismissal by agreement of the parties, the employee receives all compensation specified in the agreement, regardless of further terms of employment. Therefore, you can find a job immediately after dismissal.
Important:
You should not rely on oral promises; the agreement takes legal force from the moment it is concluded and is not subject to cancellation at the initiative of the dismissed person.
The following actions confirm the fact of staff reduction:
- Appropriate changes are made to the staffing table;
- An order is issued stating that a different staffing table must be adopted. No dismissal may be made until this schedule is accepted;
- Order to reduce staff;
- A notice of dismissal is made for each candidate;
- Those being dismissed put their signatures and date on the issued order regarding the upcoming staff reduction (two months in advance);
- An act on the offer of another job to the employee or another position is provided;
- Act on the dismissal employee’s disagreement with the offer of another job (dates and signature of the dismissed employee) - in case of disagreement or in case of agreement, prepare an Act on the consent of the other proposed job (date and signature);
- Notification letter to the exchange, three months in advance;
- Order of dismissal, where it is necessary to have the signature and date of the dismissed person;
- Payment documents signed by the dismissed person himself, indicating that he received payments in accordance with the law.
Other grounds for dismissal
Grounds for dismissal
- Inconsistency with the position held.
- Such an “unfriendly” entry in the work book does not bode well for the employee in the future; great difficulties may arise with employment and he will have to confirm his qualifications, and the probationary period may, at the initiative of the employer, be increased to the maximum.
- Due to staff reduction.
- In case of reorganization (liquidation) of a company, a difficult economic situation (bankruptcy), but if in the first case we are talking about some assistance to the employee to preserve his reputation and draw appropriate conclusions, henceforth avoiding unpleasant excesses - to increase his professional level to the necessary level, then here we are already We will observe a direct evasion of the employer’s requirement to make the necessary payments, including severance pay to an involuntarily dismissed employee.
Labor legislation does not contain and does not describe anywhere the ways to achieve agreement between the parties to an employment contract, the methods and techniques necessary to stimulate it. Obviously, both parties must agree on the terms of termination of the employment relationship, which may be accompanied by monetary compensation or contain other features, depending on the specific situation and the desires of the parties.
As a result, a written agreement on termination of the employment contract is drawn up, which does not require a special and mandatory form. It is worth noting that labor relations are an integral part of market relations, and therefore the legislator has defined the principle of independence of decisions for the employee and management regarding termination of the employment contract. In other words, restrictions on the parties can arise only in one case - when the terms of the agreement contradict the basic laws of the Russian Federation.
Indicating in a standard document the conditions on which the parties reached agreement is not necessary, but, as practice shows, it will not be superfluous. In foreign countries, special attention is paid to this, and detailed obligations of the parties are recorded.
For example:
The former employer must pay a specific amount of money over a certain period. Or, by way of compensation, the former employee is given the named material thing - a car, a private jet, a mobile phone, etc. In addition, payments may be provided to pay off housing and utility costs or study abroad for the children of a former employee, and all promises to carry out such actions are also included in separate clauses in the agreement.
Thus, the parties will be insured against failure to fulfill the stipulated actions, and if one of the parties refuses, they will be able to recover the due compensation in court by filing claims.
From the point of view of the law, “any time” will be recognized, including the moment of being on vacation (regular or educational), when the employee is not at work due to illness.
In accordance with the law, such a basis as dismissal by agreement of the parties is in no way inferior to the usual formulation.
These records are confirmation of the fact that the employee left the organization, with all wage payments provided for this on the day of dismissal and the return of the work book.
Dismissal by mutual agreement of the parties
The law provides for the procedure for terminating relations between an employee and an employer by mutual consent. In this case, the contract can be terminated at any time; the citizen may be on vacation, on sick leave, on maternity leave, etc. In Art. 78, dedicated to this method of dismissal, nothing is written about how this happens.
Once the parties have decided that their work together no longer makes sense, they enter into a termination agreement. After writing the application, a dismissal order is issued, a corresponding entry is made in the work book, the employee receives a paycheck and a book. All this can be done in one day. The fact is that if you are dismissed by mutual decision, you do not need to work for 14 days. An employee will be able to change his mind and stay only if the employer also wishes to do so.
This is not a very common method of dismissal. It is used, for example, if an organization or entrepreneur plans to lay off a person, but he realized this and decided to leave. The problem is that when applying for a new position, potential employers will have many questions. Someone might think that the organization or individual entrepreneur wanted to get rid of the employee for unknown reasons, which increases the risk of refusal when looking for a new job.
Peculiarities
The procedure has its own characteristics during the registration process:
- Based on Article 78 of the Labor Code, termination of the concluded contract can occur at any time at the request of the parties. It is important to note that the law allows the procedure to be carried out even if the employee is on official leave or sick leave. If the employer expresses his own desire, then he cannot do this only if a decision is made to close the enterprise. The trade union does not control the procedure
- Based on Article 208 of the Labor Code, it is possible to terminate not only an employment contract, but also a student contract only if there are certain grounds provided for by law.
What changed
Drawing an analogy between Articles 33 and 81, it is easy to notice the changes that the new code has undergone.
Article 81 significantly increased the powers of the employer when deciding the issue of dismissal.
Some items are completely new and have no analogies with the previous version, such as:
- The presence of immoral misconduct among educators and teachers.
- Disclosure of state, commercial or official secrets.
- Change of ownership of the organization.
- The actions of an employee who has direct contact with material assets, which resulted in a loss of trust in him.
- A decision by management that resulted in serious losses for the enterprise.
- Deliberate forgery of documents when applying for a job.
In addition, in many points that have not changed completely, significant additions have been made.
znatoktruda.ru
Amount and procedure for payment of compensation
On the last day of returning to work, the employee receives full payment for the time actually worked. In addition to salary, the following is due:
- Accrued bonuses and motivational bonuses;
- Compensation for unused rest days;
- Days of incapacity for work, if there was sick leave in the last month;
- Severance pay, if there is such an agreement with the employer, or there is a clause in the employment agreement.
Attention! The amount varies for each person, depending on the established salary and the results of work for the last month. At the personal discretion of the company, other bonuses may be paid if the person has achievements or has worked in one place for many years.
Article 78 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation regulates the termination of a contract with an employer by agreement of the parties. This is a universal base that is used in most cases, as the procedure is simple. This reason is beneficial for both parties, and at the same time allows all issues regarding the processing and transfer of cases to be resolved peacefully, without violating the requirements of the law.
Legal order of procedure
Labor laws establish strict procedures for terminating a contract. However, when it is necessary to dismiss an employee by mutual agreement, the procedure is simplified as much as possible. This is due to the absence of unresolved situations, since one person takes the initiative, while the other fully approves of it.
The manager and subordinate can put their requirements in writing and record them as an annex to the previously executed contract. You can enter any conditions here:
- contract expiration period;
- types and amounts of cash payments to the employee;
- all available types of compensation due to his status;
- other conditions.
Taking into account the text of the drawn up document, the manager issues a dismissal order, and the use of any wording is allowed.
The procedure for terminating the contract, if the parties have reached a consensus, is regulated by Art. 84.1 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. It assumes a certain order and consists of several stages.
- The prepared order is signed by the head of the organization, chairman or general director.
- After this, the document is handed over to the employee for review. If necessary, he is provided with a certified copy. If he is absent or does not want to sign, a special mark is made on the form.
- The employment contract terminates on the last working day. The exception is situations when the position is retained by the employee, even if he is absent from production.
- On the day of final departure, the employee receives certificates of insurance contributions to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation and earnings for the last two years. He is given a work book, which already contains a record of dismissal by agreement of the parties, as well as cash payments.
Advice! If a person cannot pick up the work and money in person or refuses to do so, he is notified in writing of the need to obtain the book or allow it to be sent by mail within the standard period (3 days). In this way, the employer relieves itself of responsibility for the delay in transmitting the document.
The main differences between forms of dismissal
Forms of dismissal
When an employee leaves the company with the wording of his own free will, then, according to labor law, he is obliged to work for another two weeks before leaving for good. In practice, this is what happens, there are exceptions - during a probationary period or serious illness. This is not convenient, for example, when an employee urgently needs to go to a new place of work, and there is already a certain agreement with his superiors.
The situation is completely different when dismissal occurs by agreement of the parties; here he has the opportunity to leave right on the day of signing such an agreement, without working for two weeks. It is necessary to clarify that in the first case, the employer can reduce the required period of service, or do without it altogether.
If an employee decides to leave production, for example, to move to a new place of work, in connection with graduating from a higher educational institution, because he cannot move to the desired position within the company, due to the absence of one in principle. Then the option - dismissal by agreement of the parties, an entry in the employment record for him will be an excellent solution to the problem.
Namely: the employee and the employer sign a document stipulating the period of dismissal, for example, three months from the date of signing. The conditions stipulate the possibility for those who decide to leave the company to attend interviews with potential employers during certain working hours. And for the remaining three-month period, he transfers responsibilities to a new applicant for his position and completes the remaining working moments, which is also beneficial to the employer. And everyone is happy.
Now we will learn about the other side of the required work on the basis of leaving at the employee’s own will.
Namely: during the period of specified service, the employee has the right to change his mind about quitting and withdraw his application, continuing to perform labor functions as usual. Which can create a hidden conflict that no one needs.
The basic principle when choosing a form of dismissal, unless we are talking about forced leaving the organization, is the independence of decision-making by both parties. It is unacceptable for third parties to influence such a decision, much less take part in it.
Advantages and disadvantages
Dismissal by agreement of the parties: pros and cons
The ability to choose the date of dismissal is certainly a positive side, since it greatly simplifies the agreement. In addition, there are no obstacles to consensus regarding the employee’s regular vacation or sick leave.
The fact that drawing up an alternative to redundancy can significantly increase the amount of compensation is also rightfully an advantage.
For the employer, an absolute advantage will be the inability of an employee who has decided to leave the company to suddenly change the planned dismissal and for some reason remain at the same job. The judicial authorities, in such cases, take the side of the employer.
Lack of control by the trade union body can be considered a disadvantage. However, if you carefully read this article, then this minus will not affect you in any way, since now, having information and knowing the practice of application, you will without much effort find what to say to the other party when terminating the employment contract - at any time.
https://youtu.be/nHuei-tVIhE
Top
Write your question in the form below