The system of remuneration for public sector employees according to the Unified Tariff Schedule, which has been practiced in our country for a long time, has shown its ineffectiveness in the educational industry.
The tariff category established for the qualifications and experience of a teacher does not reflect the effectiveness of his work, and therefore does not stimulate efficiency and improvement of quality.
It was necessary to reform the system of remuneration for educators; a completely new approach was needed. It is this process that continues in the Russian Federation today.
Like any new undertaking that has not yet been sufficiently tested in practice, the new remuneration system (NSTS) contains both advantages and unexpected pitfalls. Let's consider the features of this system, its regulatory framework, analyze how it is being introduced in budgetary educational institutions, and consider its positive and negative nuances.
What is NSOT
NSOT stands for “new wage system.” This is an initiative that replaces the principle of calculating labor remuneration for employees in the educational industry from a salary (based on the Unified Tariff Schedule) to a differentiated approach.
Under the usual system, the salary of a public sector employee was calculated based on the salary (tariff), which corresponded to a certain qualification category in terms of length of service and category of the employee. Labor productivity in each specific time period had virtually no effect on wages.
NSOT declares a different principle for the distribution of salary funds: managers receive the sole right to control their distribution, assigning different amounts depending on the quantity and quality of work of each public sector employee, encouraging the more successful and qualified.
Funds for such payments should appear through savings in funds, as well as by expanding budget allocations at the federal level by about a third.
NOTE! If the temporary volume of work of a public sector employee remained at the same level, as well as the level of his job responsibilities, then the salary based on the NSOT cannot be less than what it was according to the UTS.
New wage system
In accordance with the principles of NSOT, the amount of wages directly depends on the performance of a specialist over a certain period of time. Employees receive financial incentives based on the decision of the manager for achieving certain indicators (volume and quality) in solving assigned work tasks.
What does salary consist of:
- basic salary;
- compensation payments in accordance with the law and the collective agreement;
- incentive payments based on an employment contract (effective contract) or local regulations.
When setting basic salaries, managers need to focus on government decisions taken on this issue at the federal level (by qualification subgroups).
Compensation payments are most often intended to compensate for the lack of normal working conditions. Incentive payments are awarded to motivate improving the quality of work.
NSOT received both positive and negative reviews. Many argue that the new system has not improved the situation of ordinary public sector workers, since the decision on the distribution of the pay fund has become entirely the responsibility of management.
Legislative justification
On August 5, 2008, the Government of the Russian Federation adopted a Resolution according to which, from December 1, 2008, public sector employees belonging to certain industries, and above all, education, will switch from the unified technical system to the NSOT. This document highlights general issues related to the new approach to the labor remuneration system in public sectors.
In Art. 144 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation covers the procedure for documentary regulation of the payment system and other working conditions at each level of distribution of budget funds:
- federal-level institutions must reflect this procedure in collective agreements, additional agreements to employment contracts or other local regulations provided for by federal legislation;
- in regional government agencies - in the same documents, but taking into account the specifics adopted at the legislative level of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation;
- at the municipal level it will be necessary to take into account the intricacies of local government.
This law actually gives priority in establishing a remuneration system directly to the employer, that is, to the management of a budgetary institution.
Principles of NSOT in the educational field
The new wage system for educational institutions financed from the budget is built on the following principles.
- The institution's salary fund is formed in relation to the number of students (finances from the budget are allocated for each student served).
- Taking into account the amount of allocated funds, the educational institution has the right to draw up its own staffing table.
- The entire salary fund consists of two shares: basic (guaranteed for payment in accordance with tariffs and regular compensation) and incentive (it is distributed according to the successes, achievements, workload, and working conditions of employees).
- The accounting for incentive payments also includes those responsibilities of the teacher that previously constituted virtually unregulated employment, for example, conversations with students’ parents and their documentation, checking student work, managing special offices, etc.
- The amount of payment received by management should not exceed the average salary of other employees.
In 2020 with new indicators and without a reduction in wages
Starting from 2020, remuneration for teaching staff will be calculated taking into account the new indicator. From now on, when determining the income of teachers and lecturers, the average monthly earnings of hired employees of private companies and individual entrepreneurs must be taken into account. Starting from this year, this criterion must be taken into account when developing cost plans aimed at increasing the amount of remuneration for teaching staff and employees in other budget sectors. In July 2020, the government of the Russian Federation issued a decree, according to which Rosstat was obliged to prepare the above data by 04/15/2019.
When the tripartite group discussed the new regulations, a clause was added to the document about the inadmissibility of reducing wages for employees of kindergartens, schools and state universities. In accordance with this norm, in 2020 the level of remuneration for teaching staff will not be lower than in 2020. Accordingly, kindergarten teachers will receive a salary no lower than the Russian average (last year - just over 28,000 rubles).
Another important news for teachers was the inclusion of the minimum wage indicator. Last year, this figure was at the level of 6,200 rubles. The new recommendations determine that an employee of an educational institution cannot receive a salary lower than the established indicator, provided that he has fully complied with the established norm and worked a sufficient number of hours. However, no one is immune from situations in which a teacher works less time than he is supposed to. If an employee had to face such a nuisance, wages will be calculated based on the time actually worked, based on the minimum wage.
In order to ensure the full implementation of the recommendations in the institution, the employer, as well as government officials, need to pay attention to certain aspects. In particular, these include:
- The establishment of wages and salaries must be carried out in accordance with the qualification group of the employee.
- If an employee of a budgetary institution works in a position that is not related to professional categories, the rate of his salary is calculated based on the difficulty of the duties assigned to him.
- It is imperative to take into account the need to use incentive payments and all kinds of compensation. This issue should be reflected in regional and municipal regulations.
- Only the head of a kindergarten, school, university, or other budgetary organization has the right to approve the staffing table.
- After the implementation of new recommendations in an educational institution, the teacher’s income should be no less than it was before. This standard applies to all employees, without exception, whose standard of work has remained the same or increased.
- The wage rate should be determined based on the employee’s performance of his own professional duties over a certain period of time (week, month, year).
As for the labor standards for teachers, now its change in one direction or another will directly affect the final earnings. Therefore, the recommendations provide for the reflection of the actual workload of the teacher in the employment agreement. This rule will affect such workers as:
- school teachers;
- university teachers;
- coaches of children's sports sections;
- persons engaged in activities in the field of additional education.
Taking into account these innovations, any changes in the teacher’s working hours should also be reflected in the employment agreement. However, you should remember the conditions under which this may become possible:
- by agreement of the parties to the contract;
- in exceptional cases - unilaterally by the head of the educational institution. This norm can be used if the amount of working time according to the curriculum has decreased, the educational organization has not recruited a sufficient number of students, etc.
Another important innovation is additional attention to teachers with secondary specialized education. The recommendations provide for the impossibility of infringing on the labor rights of employees who do not have a higher education. Accordingly, reduction factors can no longer be used for a specialty that requires an employee with a higher education diploma. Thus, the absence of the necessary document will no longer allow the employer to save on remuneration for an employee of the educational institution. In this regard, he has equal rights with teachers with higher education.
Today, these recommendations have been approved by a considerable number of teaching staff. Indeed, the new document has significantly expanded their opportunities in terms of remuneration and increased their protection from unlawful actions of the head of an educational organization. It is expected that these recommendations will be in effect over the next few years and gradually refined so that the income of teachers grows to a decent level.
Incentive payments for NSOT
Part of the salary, which is precisely the essence of the NSOT, should be paid in addition to the guaranteed amounts as a reward for specific achievements and incentives for further success.
IMPORTANT! Incentive payments, unlike traditional “bonuses”, are paid not for the absence of complaints and the normal performance of one’s official duties, but rather for achievements, special results, and increased efficiency.
Internal regulations need to clearly regulate:
- types of incentive payments;
- criteria for their accrual;
- amounts and/or calculation procedure;
- frequency of payments (weekly, monthly, at the end of half a year or year);
- procedure for assessing the achievement of stated indicators (by the director with the participation of educational councils).
Approximately 30% of the entire wage fund should be used to ensure these payments, that is, this is exactly the share by which subsidies from the state budget are increased as part of the introduction of NSOT.
How to switch to NSOT
In order to introduce a new payment system, each budgetary institution is obliged to make changes or adopt new regulations, which, in essence, regulate changes in essential working conditions, and therefore require the consent of the employees themselves.
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! If we interpret the transition to NSOT as a change in technological conditions or work organization, then it is not necessary to obtain the consent of workers.
To do this, the employer must take a number of steps provided by law.
- Notify employees of the changes in writing within two months.
- If the employee agrees to work under new conditions, he must express this in writing.
- If the conditions are not suitable for a public sector employee, he must be offered in writing vacancies, if any, including those paid below the current ones, as well as in other regional divisions.
- If there are no vacancies or the employee does not agree to take one of them, he is fired under clause 7, part 1, art. 77 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
- An additional agreement is concluded with the consenting employees with new conditions of remuneration specified in it (they should not be worse than the old ones): amounts of payments for salary, compensation, allowances, incentive part of the salary.
Transition to a new system
For a prompt and legally competent transition, each budgetary institution must develop and approve a procedure for calculating staff salaries, taking into account the changes. This process will go faster if employees do not object to innovations. To confirm consent, you must write an application for amendments. The algorithm of actions will be as follows:
- Carrying out notification of personnel - according to stat. 74 TK for at least 2 months. before the planned changes.
- Obtaining the consent of employees is mandatory in writing in the form of statements from each specialist.
- Drawing up new additional agreements to contracts with personnel - in the conditions it is necessary to describe the new procedure for calculating salaries. At the same time, it is indicated in detail what exactly the earnings will consist of - the amount of salary and compensation amounts, as well as from what moment the changes will take effect.
- Offering other vacancies to those employees who do not agree with the innovations - according to stat. 74 of the Labor Code, the employing company is obliged to offer such work in writing, including lower-level and lower-paid positions in a given area. Offering places of employment in other territories is permitted only if such a clause is specified in the contract, collective agreement or agreement.
- Dismissal of those employees who do not agree with the innovations or with another position offered by the employer - the employee will also have to be fired if the employer does not have any other employment available. Grounds for dismissal – clause 7, part 1, statute. 77 TK.
Note! If, due to the changes, the employer may be at risk of mass dismissal of personnel who do not agree with the new policy, the institution has the right to establish a part-time work schedule before the expiration of the six-month period. If, however, the employee refuses to work, dismissal is carried out on the basis of clause 2, part 1 of the statute. 81 TK.
“The road to hell is paved with good intentions,” says a well-known and very fair aphorism. “It was smooth on paper, but they forgot about the ravines,” a Russian proverb tells us. Very often, some innovations, even if they were introduced with the best intentions, cause harm rather than benefit to society. This was, for example, Gorbachev’s fight “against drunkenness and alcoholism,” the result of which was the growth of moonshine, the cutting down of vineyards and a feeling of humiliation among millions of people who, for various reasons, were going to buy alcoholic beverages.
But there are also “innovations” that are initially aimed at changing the situation for the worse: to lower the level of knowledge (a means to steal not only money, but entire industries).
In 2008, a new remuneration system (NSTS) was introduced in our country for budgetary institutions. The idea was to push managers to save money by allowing these “savings” to be paid in the form of bonuses.
What did this lead to?
PS While I was preparing this material for publication, positive news appeared from our president:
Putin tied the salaries of the heads of the Pension Fund and the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund to the salaries of their employees
Vladimir Putin ordered that the salaries of the heads of the Pension Fund, the Social Insurance Fund and the Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund be tied to the average salary of their subordinates. The corresponding decree was published today on the official Internet portal of legal information.
According to the document, now the salaries of fund managers will be set “taking into account the maximum level of the ratio of their average monthly wages and the average monthly wages of employees of these funds, determined by the government.”
In October 2020, the State Duma Committee on Labor recommended rejecting the bill, according to which it was proposed to limit the salary limit for top managers of state-owned companies to the salary of the President of Russia.
Earlier in January 2020, the Ministry of Labor proposed limiting the salaries of top managers of state-owned companies and heads of government agencies. However, these proposals were not included in the final anti-crisis plan prepared by the Ministry of Economic Development.
The principle of the new system of remuneration of workers
consists in the fact that wages are divided into two parts. Such as: guaranteed - it is paid to the employee for the performance of his official duties, and the second part is called incentive, its size depends on the quality, efficiency and effectiveness of the employee’s work. The exact size of the incentive payment is unknown; as a rule, it depends on the head of the enterprise.
Wages are divided into two groups - piecework wage system and time-based wage system.
There are three components to the standard remuneration system. These are: salary, wages; compensation and incentive payments. In the new system of remuneration of workers
There are also three components, but often these components are slightly different from each other.
New system of remuneration of workers
implies that the salary and wage rate are established on the basis of the qualification and professional level of the employee (professional qualification group), taking into account the volume of work performed, as well as the level of its complexity.
A professional qualification group includes a group of certain professions or positions of employees, which is formed taking into account the type of their activity and on the basis of the requirements for their profession. training or skill level.
An increasing factor is applied to the employee’s base rate, which is considered the minimum for a certain position, which reflects the complexity of the work, as well as the employee’s qualification level. As a result, it is not the base rate that is calculated, but the official salary, that is, the wages for performing job duties for one month are fixed.
The wage rate or official salary calculated in this way constitutes the main part of the employee’s salary, which in regulatory documents is referred to as the basic part of the wage fund. This is a guaranteed and main part of the employee’s payment.
In addition to the guaranteed part, there is also a compensation part, which is made in the form of allowances, additional payments, and so on. Compensation payments are not considered constant, which is why they differ from the guaranteed part, which, as a rule, is considered independent of variable parameters.
Payments that are compensatory in nature
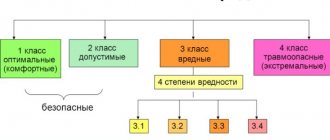
created to compensate an employee for deviation from normal working conditions. These payments occur not because the employee performs a greater volume of work, but because he works in difficult conditions. These include: difficult or unhealthy working conditions, poor climatic conditions, as well as other conditions that deviate from the standards. The amount of compensation payments is equal to the percentage of the salary in a certain qualification and professional group.
Payments of an incentive nature are paid to an employee in order to stimulate his high-quality work. They should not be compared with payments regarding the conscientious performance of work by an employee. For this work he will receive a wage rate or salary. But if he shows good results when performing this type of work, then he should receive an incentive payment for this.
As practice shows, those institutions that have introduced a new system of remuneration for workers
still continue to use the old principle of settlement with employees. This is due to the fact that the manager feels sorry for the employees, since everyone needs money. This is of course not correct, since there is no real transition to the new system.
Premium wage system
implies additional payments associated with expanding or exceeding the employee’s range of responsibilities or achieving a high level of performance.
| Forms and systems of remuneration | ||
| Form of payment | Main characteristics | Documents required for payroll |
| Time-based | Wages are calculated based on established tariffs, rates or salaries for actual time worked |
|
| Simple time-based | Hourly wage rate, which is multiplied by the number of hours worked |
|
| Time-based bonus | The terms of the collective agreement (contract, bonus provisions of the enterprise) establish a percentage increase (monthly or quarterly bonus) to the monthly or quarterly salary |
|
| Piecework | Wages are calculated based on a predetermined amount of payment for each unit of quality work or manufactured products. |
|
| Direct piecework | Earnings are determined at a predetermined price for each unit of production of appropriate quality |
|
| Piece-progressive | An employee’s output within the established initial norm (base) is paid at basic (unchanged) rates, and all output in excess of the initial norm is paid at increased piece rates. |
|
| Piece-bonus | An employee’s salary consists of earnings at basic piece rates, accrued for actual output, and bonuses for meeting and exceeding established labor indicators |
|
| Chord | The amount of payment for work performed is established not for each operation performed separately, but for the entire complex of work |
|
| Indirect piecework | The amount of earnings (usually auxiliary workers) is directly dependent on the results of the work of the main workers they serve |
|
At the end of 2020, the State Duma approved an updated version of recommendations regarding the establishment of an updated system of remuneration for employees of budgetary institutions, including teaching staff. This decision was determined by the tripartite commission for the regulation of social and labor relations. At the same time, the rules that were in force before have lost their force and will not be used in 2020. Today we’ll talk about changes in the remuneration system for teaching staff and how the approach to this issue will change.
Criticism of NSOT
Very effective in theory, in the process of using NSOT it discovered several extremely unpleasant pitfalls.
It was intended that all funds allocated from the budget would be spent within the institution itself, and those that were saved would go to the wage fund, from which they would be distributed by management as an incentive part of the salary.
In practice, it turned out that management, along with the obligation to distribute funds, has an almost uncontrollable opportunity to increase its own salary.
This is easy to do by reducing the volume of services provided by the institution, which naturally has a negative impact on the quality of work. You can also manipulate the base part by setting the “director’s” salary significantly higher than the average for the institution, citing the fact that many employees work at 1.5 times the salary.
NSOT unwittingly placed the management of institutions and its staff in the position of business partners with opposing interests, which cannot but create a certain social tension.