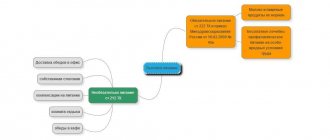
Structural territorially separate division of an organization
Legal status of the separated parts of the company in entrepreneurship and labor relations
Types of separate divisions under the Civil Code and Tax Code of the Russian Federation
What does it mean to recognize a separate division as such for tax accounting purposes?
The procedure for creating a separate division
Sample regulations on a separate division of LLC, JSC
Reporting of separate divisions in 2020
Structural territorially separate division of an organization
As part of the organization's activities, part of its functionality can be transferred to structural units. At the same time, it is important to maintain a line between the separation of a part of the company as a new legal entity and the territorial and organizational relocation of a unit that will remain an integral part of the company.
One of the differences between such actions is the information that is entered into the Unified State Register of Legal Entities (USRLE): a new entry is made about the creation of a company as a result of reorganization, and about a separate division, the tax authorities make notes in the lines reserved for information about the parent organization.
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Full and free access to the system for 2 days.
From this, the subordinate position of the units is obvious. It is also emphasized by law. In Art. 55 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation states that separate divisions are not legal entities, although they have a number of individualizing characteristics.
The list of required features is short:
- administrative isolation, expressed in the presence of the separated part of the company of its own management, acting in accordance with the requirements of Art. 55 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation on the basis of a power of attorney;
- territorial separation, in which the legal address of a dedicated branch of the company differs from the address of the executive body of the legal entity.
By internal decision, a part of the company may be endowed with other isolating characteristics. For example, such signs could be:
- separate balance;
- own personal account;
- personal calculation of payments to employees and other persons.
Examples
So let's see what this number looks like in more detail. For example, we will use the OGRN of St. Petersburg LLC Nevis 1087847036496. We make sure that the number consists of thirteen digits.
- 1 – this figure acts as an indication that the record number is assigned to the OGRN.
- 08 – entry made in 2008.
- 78 is the number of the subject, that is, St. Petersburg.
- 47 – number of the registration authority. This is interdistrict Federal Tax Service No. 15 for St. Petersburg.
- 03649 – record number.
- 6 – control number.
The last number is determined using a formula. Divide the OGRN without the check digit by 11, that is, 108784703649/11=9889518513.5455. We discard the remainder after the decimal point, and multiply the result by 11, that is, 9889518513*11=108784703643. Then from this number you need to subtract 12 OGRN characters: 108784703649-108784703643=6. This is the control number.
Legal status of the separated parts of the company in entrepreneurship and labor relations
The legal status of a separate division follows from its dependent status:
- The rights of the dedicated part of the company are significantly limited compared to the functionality of the parent organization. For example, separate divisions have the right to file claims in court only if they act on behalf of the organization. Separate divisions are not recognized as proper defendants, although Art. 29 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation and allows for filing a claim in court at their location.
- The activities of separate divisions are the same work that the company performs in accordance with the codes of economic activities assigned to it, as well as the activities of employees (secretaries, lawyers, accountants, etc.) to create conditions for the performance of such work, or only part of such activities . Providing separate units with powers to carry out established types of activities is carried out by a legal entity.
- Separate divisions are intermediaries in labor relations, not parties to them. The separated part of the company is not endowed with the legal capacity of a legal entity, and therefore separate divisions cannot act as employers.
If a worker is sent to carry out work activities in a separate unit, then this qualifies as being sent on a business trip (see Regulations on the specifics of sending on business trips, approved by Government Decree No. 749 of October 13, 2008).
Differences between OGRN and GRN
The difference consists of the following three significant points:
- The moment when the number is issued.
- Numerical composition of the number.
- Consistency.
GRN is the name given to the state registration number of the entry with amendments and additions made to the Unified State Register of Legal Entities. This means that every time information about a company is changed from the register, it is assigned a certificate of entry and a state registration number is issued. Whereas the OGRN is appointed once and is valid from the foundation until the liquidation of the organization. Moreover, the differences are also contained in the registration number itself.
Types of separate divisions under the Civil Code and Tax Code of the Russian Federation
The Civil Code (Article 55) and laws on certain types of legal entities recognize the existence of 2 types of separate divisions:
- A branch of a company is a separate division created to carry out the activities of an organization outside its location, the functions of a representative office, or only part of these functions, depending on the scope of powers transferred by the company.
- A representative office of a company is a separate division dedicated to protecting and representing the interests of the company. Representative offices are especially common in organizations operating in several countries.
The Tax Code (Article 11) recognizes any territorially separated parts of legal entities as separate divisions if they have stationary workplaces. Place of work according to Art. 209 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is the place where the employee carries out his work duties or in which he needs to be in order to perform work. The place of work must be controlled by the employer.
A workplace is stationary if it is created for more than a month. The last requirement is related to the deadline for registering a separate division for tax purposes. In accordance with Art. 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, a legal entity notifies the tax authorities about the allocation of branches or representative offices within a month from the moment of their creation. If a workplace is created for a shorter period, then it does not make sense to carry out its tax accounting as a separate division. If it was created for a period of more than a month, then the tax service recognizes it as a separate division.
Accounting policy
The functions of the parent organization include the responsibility for organizing accounting, which should be the same for all structural divisions.
Accounting can be handled by both the head office and a division. The first method is acceptable if all primary documents are collected on time, by a certain date and transferred to the head office. This method is usually practiced if the branch does not have a large number of business transactions.
In the second case, if the responsibility for maintaining accounting records is assigned to a department, then the administration of the enterprise will have to organize an appropriate vacancy, an office, and a place for storing and processing documents.
But since the parent organization is a legal entity that is obliged to account to the fiscal authorities not only for its own activities, but also for its representative offices, the final formation of financial and economic indicators should take place in the head office. In this case, reporting is generated by summing up the indicators that formed the separate divisions.
What does it mean to recognize a separate division as such for tax accounting purposes?
Despite the fact that in accordance with Art. 11 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, a territorially delimited part of a company with a workplace created for a month or more is recognized as a separate division, its legal capacity differs from the rights and obligations of a branch or representative office.
Subscribe to our newsletter
Read us on Yandex.Zen Read us on Telegram
The separated part of the company, recognized as such for tax purposes, usually does not have an administrative management apparatus, its own property and funds, and cannot independently exercise the powers of the company or protect its interests. The reason for this is the purpose of recognizing by the Federal Tax Service the territories with existing jobs as a division of the company.
As stated in Art. 11 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, recognition of a separate division as such is carried out for the purpose of implementing the legislation on taxes and fees.
For example, if an organization is developing subsoil in the Far East, and its executive body is located in Central Russia, then paying taxes at the location of the legal entity is inappropriate for tax control, as well as for other reasons. According to Art. 335 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the company is registered at the place of mining. Obviously, their production stretches over more than a month, and the employees’ workplace will be a mine, quarry, etc. Then, for the purposes of paying mineral extraction tax, the tax authorities may recognize the presence of a separate division of the company.
The procedure for creating a separate division
Unlike separate divisions, which acquire this status at the direction of the tax authority, branches and representative offices are created according to a more complex procedure. The following stages are distinguished:
- Making a decision on the separation of a part of the company according to the procedure established by law or internal regulations of the company.
For example, the Law “On Limited Liability Companies” dated 02/08/1998 No. 14-FZ defines the following decision-making procedure:
- submitting the issue for consideration by the General Meeting of Shareholders 30 days before its convening;
- reviewing the question;
- agreement of 2/3 of the meeting participants with the opening of a separate division.
In Art. 65 of the Law “On Joint Stock Companies” dated December 26, 1995 No. 208-FZ states that the creation of branches and representative offices may fall within the competence of the board of directors if this is provided for by the company’s charter.
- Adoption of a local act regulating the work of a separate division of the company. Typically this is a branch/representative office provision.
- Appointment by order of the head of the parent organization of the management of a separate division. Usually, at the same time, a power of attorney is issued in the name of the head of the department, since without it the head will not be able to manage the department of the company (Article 55 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
- Submitting an application to the Federal Tax Service in form P14001, approved. by order of the Federal Tax Service “On approval of forms and requirements...” dated January 25, 2012 No. ММВ-7-6/ [email protected] , on entering information about the division into the Unified State Register of Legal Entities. As indicated in the letter of the Department of Tax Policy of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 16, 2009 No. 03-02-07/1-541, a separate division of a legal entity is considered created from the moment of making additions to the state register.
- Submitting form S-09-3-1 to the Federal Tax Service, approved. by order of the Federal Tax Service dated 06/09/2011 No. ММВ-7-6/ [email protected] within a month after the allocation of part of the organization. This is done to register a separate division with the tax service.
Sample regulations on a separate division of LLC, JSC
| Form of the Regulations on Separateness division of OJSC |
In Art. 5 of Law No. 14-FZ determines that an LLC operates on the basis of a regulation approved by the parent company. Usually the situation is similar with other legal entities (see Article 91 of Law No. 208-FZ, etc.).
The content of the provision is determined solely by the organization itself. Based on established practice, it includes sections:
- general provisions as a set of information about the parent organization and the allocated part, such as: names, addresses, etc.;
- purpose of creation, for example, ensuring compliance with the interests of a legal entity;
- legal status as a combination of rights, duties and responsibilities;
- the procedure for control carried out by the head office;
- data on management procedures, management competence;
- participation in labor relations;
- the procedure for disbanding a unit;
- other provisions as necessary.
Search and verification of enterprises
With the help of OGRN, anyone can obtain information about a specific organization on the Federal Tax Service website. Using this service, it is easy to obtain detailed information about the company. For example, these:
- Information about state registration.
- TIN.
- Legal address.
- Information about management and founders.
- Changes from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities.
OGRN helps to obtain genuine information, as well as avoid cooperation with unreliable companies.
https://youtu.be/ZfVfAIYCvbM
https://youtu.be/TUaY48XskrM