In order to organize the storage of a large volume of documents, organizations create an archive - an independent structural unit that ensures the safety of documents with long storage periods.
In order to organize the storage of a large volume of documents, organizations create an archive - an independent structural unit that ensures the safety of documents with long storage periods.
At the same time, cases that have a storage period of more than 10 years are transferred to the archive no earlier than one year and no later than three years after their completion. Documents with a temporary storage period (up to 10 years) are not transferred to the archive and are stored in the structural units in which they were created.
Before transferring documents to the archive or destroying them, an examination of the value of the documents should be carried out.
Conducting an examination of the value of documents
Examination of the value of documents (EDS)
– study of documents based on criteria of their value to determine the storage period for documents*.
To organize and conduct EDS, a permanent expert commission (EC) is created. In large organizations, in addition to the EC, central expert commissions (CEC) are created. They provide methodological support to the EC in their work.
The main functions of the EC are:
- organizing an annual selection of cases for storage and destruction;
- review and approval of draft nomenclature of the organization’s files, inventories of permanent and temporary (over 10 years) storage, including personnel, acts on the allocation for destruction of files that are not subject to storage;
- preparation of proposals to change the storage periods for documents not provided for in the lists, and to change the storage periods for certain categories of documents established by the lists;
- participation in the preparation and consideration of draft regulatory and methodological documents on issues of working with documents in the organization;
- methodological guidance of work in the field of ensuring the safety of the organization's documentary and archival funds.
These commissions can cooperate with expert verification commissions (EPC) of the archival institution to which the organization’s documents will be transferred. Such cooperation is mandatory if the organization is the source of acquisition of the Archival Fund of the Russian Federation. The EC includes 35 of the most qualified employees of the organization and, without fail, the person responsible for the archive.
The chairman of the EC is one of the deputy heads of the organization.
Every year, when carrying out EDS in structural divisions, the following is carried out:
- selection of cases of permanent and temporary (over 10 years) storage for transfer to the archive;
- selection of cases with temporary storage periods (up to 10 years) to be stored in structural units;
- allocation for destruction of files for previous years whose storage periods have expired.
“1C:Document Flow” implements the function of selecting cases for transfer to the archive and for selecting cases for destruction.
The storage periods for files are determined by lists of documents indicating their storage periods and by the nomenclature of the organization’s files.
When selecting documents, special attention should be paid to cases of permanent and temporary (over 10 years) storage. Such cases must be reviewed page by page. This will allow you to identify errors made during the formation of cases.
Based on the results of the electronic digital documentation in the organization, the following are drawn up:
- inventory of permanent storage files;
- inventory of temporary (over 10 years) storage cases;
- inventory of personnel cases;
- acts on the allocation for destruction of files that are not subject to storage.
Documents in electronic form are included in independent inventories.
Inventories and acts are considered at a meeting of the organization's EC at the same time, approved by the head of the organization after approval of the EPC of the archival institution (if necessary). After this, the organization has the right to destroy the files included in these acts.
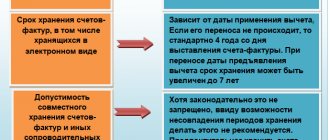
The act includes cases whose storage period has expired by January 1 of the year in which the act is drawn up. For example, completed cases with a three-year storage period in 2020 can be included in an act that will be drawn up no earlier than January 1, 2020. “1C: Document Flow” allows you to fill out an act automatically from files whose storage period has expired. At the same time, unfinished cases and cases whose storage period has not yet expired cannot be included in the act (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1
An act on the allocation of files for destruction is drawn up automatically from the files selected for destruction in the form established by the Storage Rules.
Cases subject to destruction are transferred for processing (disposal). The transfer of cases is formalized by an acceptance note, which indicates the date of transfer, the number of cases to be handed over and the weight of the waste paper.
Electronic files are subject to destruction on a general basis. In this case, the media on which they are recorded are physically destroyed, or destroyed by software and hardware.
Nuances of creating an archive
In large companies, a huge number of documents are generated during the conduct of business, so they are stored in a separate room called an archive. It is represented by a separate structural unit, and during its creation, the management issues a special Regulation, which is a local regulatory act of the company.
It is this Regulation that provides the basic rules for archiving documents in an organization, and also indicates the responsibility of officials involved in this process for various detected violations.
Registration of cases
Cases of permanent, temporary (over 10 years) storage and personnel records must be handed over to the archive for their further storage and use. Preparations for the transfer of such cases to the archive are carried out by the preschool educational institution service or secretaries of structural divisions. Preparing cases is about filing them correctly.
For registration of permanent, temporary (over 10 years) storage and personnel files, the following operations are provided:
- file filing or binding;
- numbering of case sheets;
- drawing up a certification sheet;
- drawing up, if necessary, an internal inventory of documents;
- design of the cover of the case (clarification of the name of the organization, registration index of the case, deadlines of the case, title of the case).
Temporary (up to 10 years inclusive) storage cases do not need to be formalized. It is enough to form them correctly for easy search of documents if necessary. Documents can remain in the folder.
First of all, the documents are filed or bound into a file. You must first remove all metal fasteners, pins, paper clips and other unnecessary items from the documents so that during further storage they do not rust, leave marks or damage the paper.
To securely fasten all documents, they are bound in a hard cardboard cover with 4 holes. At the same time, you need to ensure that the text of the document, dates, visas and resolutions on them are freely read.
To ensure the safety of documents and secure the order of their arrangement, all sheets (except for the certification sheet and internal inventory) are numbered in Arabic numerals in order in the upper right corner of the sheet using a simple pencil or numberer. The use of ink and colored pencils is prohibited, as they can smudge and ruin the paper if stored for a long time. Sheets of the internal inventory of case documents are numbered separately. If the case consists of several volumes or parts, then the sheets are numbered for each volume or for each part separately.
If a small number of errors were made in the numbering of sheets, then in this case it is possible to use lettered sheet numbers (with letters - for example, 2a, 2b, 2c). If there are too many errors, then the old numbers are crossed out and a new sheet number is placed next to it. At the end of the case, a new certification sheet is drawn up, while the old certification sheet is crossed out, but remains in the file.
In the sheet - the witness of the case, the number of sheets in the case is indicated in numbers and in words. The sheet - the witness of the case is filed in the case or pasted behind the top of the sheet on the inside of the cover at the end of the case. The form of the document certifying the file is established by the Storage Rules**.
The internal inventory of the case documents is compiled on a separate sheet in the prescribed form, which contains information about the serial numbers of the case documents, their indexes, dates, headings and sheet numbers of the case. A final record is drawn up for the internal inventory, which indicates in numbers and in words the number of documents included in it and the number of sheets of the internal inventory.
If the case is bound or filed without an internal inventory of documents form, then the inventory drawn up in the prescribed form is glued to the inside of the front cover of the case.
Another stage in the design of the case is the design of its cover. The cover of the case for permanent, temporary (over 10 years) storage and for personnel is drawn up and executed in the prescribed form. Here you should indicate:
- name of the organization and its direct subordination;
- name of the structural unit;
- case index;
- volume (part) number;
- title of the case (volume, part);
- deadlines of the case (volumes, parts);
- number of sheets in the file (volume, part);
- retention period for the file;
- archival case code;
If the name of the organization changed during the year, then both names are shown on the cover, with the previous name in brackets and the new name written under it.
In “1C: Document Flow”, a printed form of the case cover, internal inventory and certification sheet is created automatically based on the information entered in the case card (Fig. 2).
Rice. 2
Drawing up and processing of case inventories
Archival inventories are compiled for all completed records of permanent, temporary (more than 10 years) storage and personnel records after EDS.
Inventory are compiled separately:
- for permanent storage matters;
- files of temporary (over 10 years) storage;
- personnel matters;
- cases consisting of documents specific only to a given organization (judicial, investigative cases, scientific reports on topics, etc.).
Preparing electronic files for transfer to the organization’s archive involves drawing up an inventory of electronic files.
Inventories of the affairs of structural divisions are compiled in accordance with the established form in triplicate and submitted to the organization’s archive one year after the completion of the affairs in office work.
Case titles are transferred to the inventory from the approved nomenclature of cases. In the inventory, each case and volume is assigned an independent serial number, while the gross numbering is maintained for several years.
Based on the inventories of the affairs of structural divisions, an annual section of the consolidated inventory of the organization’s affairs is compiled, the preparation of which is entrusted to the archives of the organization. The annual section of the summary inventory of permanent storage cases is drawn up in four copies in the prescribed form. The annual section of the summary inventory of temporary (over 10 years) storage cases is printed in two copies. Inventories are first approved by the organization's EC, and then approved by its head.
At the end of the inventory, a final record is made in which the number of cases, the first and last numbers of cases in the inventory of cases are indicated in numbers and words, and the presence of lettered and missing numbers in the numbering of cases in the inventory is also specified.
The consolidated inventory is considered complete if the number of file headings in several or one annual section has reached 1000. In organizations with a small volume of permanent storage files generated annually (up to 200 files), the inventory is considered complete if it includes annual sections of the consolidated inventories of permanent storage files for 5 years .
Each completed inventory is assigned a number. Typically, the inventory for files of permanent storage has No. 1, for files with a storage period of 10 years or more - No. 2, for files on personnel - No. 3 with the addition of the letter index “l/s”.
Case inventories are compiled automatically from cases selected for transfer to the archive, according to the form established by the Storage Rules (Fig. 3).
Rice. 3
The storage periods for electronic and paper documents are identical.
Systematization into files of executed documents that have the original on paper is carried out in accordance with the nomenclature of the organization’s affairs by putting appropriate marks on the document’s registration card.
Systematization of executed electronic documents (that do not have an original on paper) is not carried out.
Internal documents are stored in a structured folder system of the “Internal Documents” directory in “1C: Document Flow 8”, which serves to organize documents and limit access to them. The folder structure is built according to document types (“Orders”, “Instructions”, etc.).
Features of domestic legislation in the field of archival storage of documents
The basis of the legal framework regulating the rules for storing various documents is made up of several legislative and regulatory documents. These include:
Tax and Labor Codes;
Federal Laws No. 402-FZ “On Accounting” and No. 125-FZ “On Archiving in the Russian Federation”, which were approved, respectively, on December 6, 2011 and October 22, 2004;
Order No. 558, signed by the head of the Ministry of Culture on August 25, 2010 and approving the list of archival documentation, the storage of which for a certain period is mandatory;
Order No. 526, issued by the Ministry of Culture and dated March 31, 2015. It approves the currently current edition of the Rules for the storage of archival documents.
A characteristic feature of domestic legislation in the field of archival affairs is the inconsistency of existing regulations. As a result, situations often arise when the head of an organization simply cannot determine how long to store a particular business paper.
The procedure for transferring documents to the organization’s archive
Cases of permanent and temporary storage for more than 10 years and documents on personnel are transferred to the organization’s archive no earlier than one year and no later than three years after their completion in office work.
Electronic documents can be stored in 1C: Document Flow permanently. The need to remove electronic documents from 1C: Document Flow is determined during the annual examination of the value of documents.
See also related articles
: Nomenclature of cases: rules for compiling and Current storage of documents: procedure for creating cases.
* GOST R 7.0.8-2013. National standard of the Russian Federation. System of standards on information, librarianship and publishing. Record keeping and archiving. Terms and definitions (approved by Order of Rosstandart dated October 17, 2013 No. 1185-st).
** The forms of all documents given in this section are established in the “Rules for organizing storage, acquisition, accounting and use of documents of the Archival Fund of the Russian Federation and other archival documents in government bodies, local governments and organizations”, approved by order of the Ministry of Culture of Russia dated 03/31/2015 No. 526 (Registered with the Ministry of Justice of Russia on 09/07/2015 No. 38830).
Archive requirements
Each company must take into account the basic requirements for proper archiving of documents in the organization. Record keeping must be subject to the basic provisions of the law. In large companies, the archive is presented in a separate room, which must be protected from company employees or unauthorized persons. Therefore, during the creation of this unit, the following requirements are taken into account:
- the premises must be isolated from other departments and offices;
- it is equipped with fire and security alarms;
- the size of this room depends on how many documents are annually transferred for storage to the archive;
- special long shelving is installed in the room, and it is advisable to choose metal structures;
- a distance is left between the racks, which cannot be less than 75 cm;
- the length of the racks can be different and depends on the height of the ceilings;
- In addition, special safes are installed in the premises, in which the most valuable and important documents are located.
In each company, the area of the selected premises can be completely different, since various factors are taken into account.