In any organization, sooner or later, that “happy” moment occurs when Rostechnadzor employees appear and begin to conduct a scheduled inspection. If you conduct your business activities according to the set rules and regulations, then you have absolutely nothing to worry about. In any case, it would be useful to obtain information about what Rostechnadzor checks during a routine inspection and what is not within the authority of this service. Additional information has never harmed anyone.
Structure of Rostechnadzor
This service carries out its work at the federal level and is nothing more than an executive body. The structure of the service includes several departments that deal with the following issues:
- finance;
- organizational and control activities;
- service and personnel;
- licensing and permitting activities;
- legal nature;
- protection of state secrets;
- cooperation between states;
- safe operation of nuclear installations;
- energy saving;
- safety in the oil and gas, mining and coal industries;
- supervision in construction and in industry in general.
Sometimes the inspectorate deals with issues that were previously within the competence of the Sanitary and Epidemiological Station. The territorial bodies of Rostechnadzor include the following departments dealing with issues:
- activities in the field of transport;
- consumer protection;
- trade;
- epidemiology;
- ecology;
- sanitary condition.
On a note! The competence of territorial bodies includes consideration of requests from legal entities and individuals, as well as monitoring the elimination of identified violations.
History of the creation of Rostekhnadzor
December 23 is the day of the State Institution of Environmental, Technological and Nuclear Supervision. The history of the development and changes of this organization begins from the time of Peter I. The Emperor created the Berg College. After that, additional structures for monitoring work in production were created. When steam engines appeared, a boiler inspection service arose. Next, a factory inspection was created, and then a mining inspection. After that, such institutions as Gosgortekhnadzor, Rospotrebnadzor and Gosenergonadzor “merged” into the Unified Service of Rostechnadzor. Then environmental and nuclear supervision was added. Thus, the Rostekhnadzor service was created.
What are the main functions of Rostechnadzor?
Today, there are various supervised facilities of Rostechnadzor. There are territorial institutions in different regions. For example, the North-Western Directorate of Rostechnadzor is located in the Pskov region. These departments resolve issues that relate to:
- legal nature;
- state protection secrets;
- cooperation between different countries;
- energy saving;
- and others.
Powers of Rostechnadzor
This service has quite broad powers. They include:
- first of all, consumer protection;
- monitoring compliance with the quality provision of services and rules for the sale of goods to the public;
- initiation of all kinds of analyzes and examinations;
- providing evaluation reports on the activities of various organizations;
- monitoring the activities of organizations in terms of sanitary and epidemiological conditions.
Rostekhnadzor inspection: types, how to prepare, what fines check - How to build your own business
In any organization, sooner or later, that “happy” moment occurs when Rostechnadzor employees appear and begin to conduct a scheduled inspection.
If you conduct your business activities according to the set rules and regulations, then you have absolutely nothing to worry about.
In any case, it would be useful to obtain information about what Rostechnadzor checks during a routine inspection and what is not within the authority of this service. Additional information has never harmed anyone.
Structure of Rostechnadzor
This service carries out its work at the federal level and is nothing more than an executive body. The structure of the service includes several departments that deal with the following issues:
- finance;
- organizational and control activities;
- service and personnel;
- licensing and permitting activities;
- legal nature;
- protection of state secrets;
- cooperation between states;
- safe operation of nuclear installations;
- energy saving;
- safety in the oil and gas, mining and coal industries;
- supervision in construction and in industry in general.
Sometimes the inspectorate deals with issues that were previously within the competence of the Sanitary and Epidemiological Station. The territorial bodies of Rostechnadzor include the following departments dealing with issues:
- activities in the field of transport;
- consumer protection;
- trade;
- epidemiology;
- ecology;
- sanitary condition.
On a note! The competence of territorial bodies includes consideration of requests from legal entities and individuals, as well as monitoring the elimination of identified violations.
Powers of Rostechnadzor
This service has quite broad powers. They include:
- first of all, consumer protection;
- monitoring compliance with the quality provision of services and rules for the sale of goods to the public;
- initiation of all kinds of analyzes and examinations;
- providing evaluation reports on the activities of various organizations;
- monitoring the activities of organizations in terms of sanitary and epidemiological conditions.
Types of checks
Throughout Russia and, in particular, in Moscow, Rostechnadzor can conduct scheduled and unscheduled inspections. This is clearly stated in the Law of the Russian Federation under number 294-FZ (dated December 26, 2008). Planned audits are carried out according to a schedule no more than once every three years (Article 9, paragraph 2).
Reasons for conducting an unscheduled inspection:
- Any individual or legal entity can initiate such an inspection if they have received an official request to look into certain violations (for example, in the field of catering, trade, medicine, housing and communal services, and so on).
Important! If the person who applied to the state control body wished to remain anonymous, then such an application will not be accepted for consideration, and it cannot serve as a basis for ordering an unscheduled inspection.
- At the suggestion of the editors of any program in the media.
- Expiration of the period given to a legal entity or individual entrepreneur to eliminate previously established violations.
- If there is a clear threat to the life and health of the population, the possibility of causing harm to the environment and animals, the occurrence of emergency situations, as well as a threat to the security of the country.
Where does the check begin?
The inspection begins with the inspector of Rostechnadzor presenting to the head of the organization his identification (necessarily with a photo) and an order to conduct an inspection, which clearly indicates the goals of the audit.
Important! A document dated the day of the actual audit must be certified with the seal and signature of the head of the control service.
The director of the organization has every right not to allow the inspector to enter the enterprise if the documents presented by him are improperly executed. Important! All persons carrying out the audit must be indicated in the order.
What directly interests Rostechnadzor employees
During a routine inspection, service inspectors must check:
- Availability of a license to carry out certain activities, as well as TIN and Charter of the company or organization.
- Documentation. They check the availability and correctness of employment contracts with employees of the enterprise, diplomas and certificates of their education, as well as medical records of employees. In addition, either a lease agreement for the premises in which the activity is carried out, or a document confirming ownership of the occupied space, must be presented.
- Availability of a company sign and a consumer corner.
- How correct and accurate are the price tags for all goods?
- Availability of information about manufacturers and expiration dates of the products presented, as well as excise stamps, certificates and licenses.
- Price list for all services that a company or organization provides.
- Operation of the cash register.
- How correctly the log of inspections carried out within the company is filled out.
As we can see from the above, the list of what Rostechnadzor checks during a routine inspection is not so small.
What actions are not within the competence of Rostechnadzor
Strange as it may seem, there are certain restrictions in the work of Rostechnadzor. Employees of this service do not have the right to:
- Begin and continue the inspection without the presence of the head of the company or an employee who is acting as a director on a temporary basis.
- Taking samples for further examination without drawing up the appropriate documents.
- Study the provided documents longer than the period allotted by Russian legislation.
- Provide third parties with information obtained during the inspection.
- Make demands that have nothing to do with the operation of this service.
- Subject to examination of products that are not in any way related to testing.
- Stop the work of the organization during control activities (for example, shops or various catering establishments).
- Conduct a test purchase.
Important! There are no clear explanations in the legislation regarding these actions. If a Rostechnadzor inspector makes such a purchase, the fact of its completion must be recorded by representatives of the company or organization being inspected. In the future, based on this document, you can prove the fact of violation of the law.
Now there is a complete understanding of what Rostechnadzor checks during a routine inspection and what is not within its competence. Everything is very simple.
The final stage of verification
Based on the results of the audit, the inspection service employee draws up an act in which he indicates all the identified violations, the procedure for correcting them, deadlines and penalties. Rostechnadzor inspection reports must be drawn up in two copies: one is left with the control service, and the other is handed over to the head of the organization.
On a note! If, at the request of the inspector, all the documents of interest were provided, but he himself was not allowed into the enterprise, then the organization is unlikely to get by without an administrative fine.
Moreover, the amount can be up to 2,000 rubles for the director and up to 1,000 rubles for each employee.
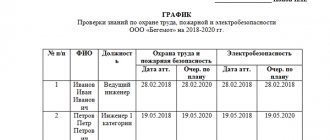
Each company should have a log in which all audits are recorded: the dates of their conduct, who conducted the audit (that is, information about the control service and the specific name of the inspection inspector), its goals and the violations identified.
On a note! Having such a document in hand, the director of any enterprise can easily prove the fact of an audit.
Additional powers of the Rostechnadzor inspector
After completing the inspection and drawing up a report, the Rostechnadzor inspector has every right to:
- Transfer information about the audit and its results to other regulatory services (for example, to the Sanitary and Epidemiological Station).
- Submit inspection materials to the internal affairs bodies.
- Bring to the attention of citizens through the media the fact of such an inspection and its results.
Timing of the inspection
Naturally, the timing of Rostechnadzor’s inspection cannot be extended “indefinitely.” The inspection may last for a maximum of one month.
On a note! In some exceptional cases, when the inspector has very compelling arguments for extending the control event, the deadlines may be extended by another month.
What Rostekhnadzor checks for energy saving
In accordance with Federal Law No. 261-FZ (dated November 23, 2009, as amended on July 13, 2020), Rostechnadzor (namely the Federal Service for Technological, Environmental and Nuclear Supervision) carries out energy saving inspections.
If the organization is not subject to energy inspection (that is, the turnover of energy resources is less than 10 million, the enterprise is not municipal, and the building is leased), then they monitor compliance with the extent to which the owner of the building complies with the requirements for increasing energy efficiency and equipping the energy installations used with metering devices.
Verification of educational institution
It is generally accepted that the Federal Service for Technological, Environmental and Nuclear Supervision (i.e. Rostekhnadzor) mainly controls the work of organizations in the field of construction, industry and energy. But this is a mistaken opinion. Rostechnadzor employees can “show up” at any budgetary institution, for example, a school or institute.
What Rostechnadzor checks in an educational institution:
- Strict compliance with the requirements and regulations for the maintenance and operation of electrical and heating networks and installations, equipment (this also applies to educational equipment), which poses an increased danger.
- Supervises construction work that the institution may carry out (for example, the construction of new buildings or the reconstruction of old ones).
- Assess the technical condition of various lifting equipment (for example, elevators).
Checking gas stations
What does Rostechnadzor check at gas stations? First of all, compliance with licensing rules and regulations.
The fact is that gas stations that started operating 3-4 years ago generally have in their arsenal all the necessary documents and inspection and commissioning reports.
But at stations that began operating much earlier (40-50 years ago), such an examination was not carried out.
Therefore, in accordance with the Regulations on compulsory licensing of production facilities that are characterized by a high explosion hazard, Rostechnadzor conducts inspections of all gas stations throughout Russia and, in particular, in Moscow. In addition to these activities, service employees deal with issues of fuel sales (for example, checking the presence of receipts, a cash register) and its quality.
Finally
We hope that there is now complete clarity on the issue of what Rostechnadzor checks during a routine inspection.
And so that the actions of the inspectors of this service do not come as a shock, the head of the organization needs to be aware of the rights and obligations of his company, the issues within the competence of the inspection services, as well as the availability of the necessary documents, certificates and sanitary books for his employees.
Source:
Rostechnadzor inspections: how to prepare
Rostechnadzor inspections: how to prepare
- What do you need to know about inspectors?
- How does the check end?
- What to look for during inspections?
Victor Kovalev, Leading occupational safety specialist at MEGAPAK LLC (Moscow)
What you need to know about inspectors
Knowledge is power! You can't argue with that. Therefore, the employer’s strength is to have knowledge about the tactics and methods of inspections by Rostechnadzor inspectors.
It is important to understand that inspectors cannot engage in amateur activities. All their work is strictly regulated.
Source: https://kmb-chr.ru/idei/proverka-rostehnadzora-vidy-kak-podgotovitsya-chto-proveryayut-shtrafy.html
Types of checks
Throughout Russia and, in particular, in Moscow, Rostechnadzor can conduct scheduled and unscheduled inspections. This is clearly stated in the Law of the Russian Federation under number 294-FZ (dated December 26, 2008). Planned audits are carried out according to a schedule no more than once every three years (Article 9, paragraph 2).
Reasons for conducting an unscheduled inspection:
- Any individual or legal entity can initiate such an inspection if they have received an official request to look into certain violations (for example, in the field of catering, trade, medicine, housing and communal services, and so on).
Important! If the person who applied to the state control body wished to remain anonymous, then such an application will not be accepted for consideration, and it cannot serve as a basis for ordering an unscheduled inspection.
- At the suggestion of the editors of any program in the media.
- Expiration of the period given to a legal entity or individual entrepreneur to eliminate previously established violations.
- If there is a clear threat to the life and health of the population, the possibility of causing harm to the environment and animals, the occurrence of emergency situations, as well as a threat to the security of the country.
How to prepare for an inspection by Rostekhnadzor - Occupational safety blog - Unital-M center
An inspection by Rostechnadzor, like an inspection on labor protection, may come as a surprise to the employer. Therefore, it is important to know what the inspectors will check and how to prepare for the Rostechnadzor inspection.
Whom does Rostechnadzor check?
Rostechnadzor controls hazardous industrial facilities. Therefore, enterprises that:
- develop and use subsoil;
- use nuclear energy (except for the development, manufacture, testing, operation and disposal of nuclear weapons and nuclear power plants for military purposes);
- operate electrical and thermal installations and networks, hydraulic structures;
- work with explosive materials for industrial use;
- receive, use, process, store, transport, dispose of flammable, oxidizing, explosive and toxic substances;
li>use equipment operating under high pressure, stationary lifting mechanisms, etc.
When to expect verification
The reason for the inspection may be a message from the employer about the completion of construction of a capital construction project, information about the commissioning or registration of a hazardous production facility, an accident at a hazardous production facility, citizen complaints about the enterprise’s violation of laws and regulations on industrial safety, etc.
Rostekhnadzor conducts scheduled inspections once every three years. This frequency may increase if compliance with energy conservation and energy efficiency requirements is verified. The annual inspection plan is published on the Rostechnadzor website and is freely available. But there are also unscheduled inspections , the dates of which are not announced. The reason for an unscheduled inspection may be the expiration of a previously issued order or a message that the enterprise poses a threat to the life and health of people and the environment.
The inspection can be on-site - the inspector himself comes to the enterprise, or documentary - it is necessary to collect a package of documents and send it to Rostekhnadzor.
What Rostechnadzor will check
The list of documents that Rostechnadzor will check depends on the field of activity of the enterprise. Before the inspection, you should read the order of Rostechnadzor dated October 30, 2008 No. 280. This is an administrative regulation that describes the inspection procedure. There is also an approximate list of documents that will be needed during an inspection by Rostechnadzor:
- constituent documents, certificate of state registration of a citizen as an individual entrepreneur (for an individual entrepreneur);
- certificate of registration with the tax authority;
- documents confirming the existence of a public benefit facility;
- certificate of registration of a public health organization in the state register of public health organizations;
- permission to commission a hazardous production facility;
- design documentation for the construction, expansion, reconstruction, technical re-equipment, conservation and liquidation of hazardous production facilities and changes to it;
- license to operate hazardous production facilities;
- conclusions of industrial safety examination;
- insurance contracts for the risk of liability for causing harm during the operation of hazardous production facilities;
- documents on the staffing level of employees of the hazardous production facility in accordance with established requirements;
- documents for admission to work at hazardous production facilities for qualified workers without medical contraindications to the specified work;
- documents on certification of workers in the field of industrial safety;
- documents establishing the rules for conducting work at a hazardous production facility;
- documents on the organization and implementation of production control over compliance with industrial safety requirements;
- operational documentation, certificates or declarations of conformity, permits for the use of technical devices at hazardous production facilities, including instruments and systems for monitoring production processes;
- documents on diagnostics, testing, inspection of structures and technical devices used at hazardous production facilities;
- measures to localize and eliminate the consequences of accidents at hazardous production facilities;
- documents on accounting, technical investigation, analysis and prevention of the causes of accidents and incidents, etc.
During an inspection, a Rostekhnadzor inspector has the right to freely visit the inspected enterprise and get acquainted with the necessary documents. Before this, the inspector must show the inspection order, which includes his name. If the order contains the name of another inspector, the employer has the right not to allow the inspector into the enterprise. Remember that the audit cannot go beyond the purposes specified in the order and cannot be carried out in the absence of management.
The inspector can check the accuracy of technical investigations of incidents and accidents at hazardous production facilities, and give instructions on industrial safety within the scope of his powers. If additional examinations and analyzes need to be carried out as part of the inspection, the employer pays for them at his own expense. The check itself is absolutely free.
A Rostechnadzor inspector has the right to give orders to remove people from workplaces if there is a threat to their life and health. It is better for the employer or his representative to accompany the inspector during the inspection and immediately clarify any questions that arise. In addition, the inspector’s mistakes can be used to appeal the issued order or decision on an administrative violation. You can appeal the inspector’s decision within 10 days from the date of issuance of the order or decision on an administrative violation.
If violations are detected, the inspector has the right to issue an order to eliminate them, issue a fine to the employer, or suspend the work of the enterprise. The order specifies the deadline by which the violations must be corrected. Most likely, after this date they will come to you with an unscheduled inspection. In case of a serious violation, a protocol on administrative violation is drawn up and a resolution on administrative punishment (fine or suspension of activities) is issued. Remember that the inspector can suspend the operation of the enterprise for no more than five days, and the court will make a further decision on the case.
by HyperComments
Source: https://www.unitalm.ru/blog/kak-podgotovitsja-k-proverke-rostehnadzora/
Where does the check begin?
The inspection begins with the inspector of Rostechnadzor presenting to the head of the organization his identification (necessarily with a photo) and an order to conduct an inspection, which clearly indicates the goals of the audit. Important! A document dated the day of the actual audit must be certified with the seal and signature of the head of the control service. The director of the organization has every right not to allow the inspector to enter the enterprise if the documents presented by him are improperly executed. Important! All persons carrying out the audit must be indicated in the order.
How is the verification carried out?
Before the start of the inspection, the territorial office of Rostechnadzor issues an order to conduct it. It contains the following information:
- list of members of the commission conducting the inspection;
- reasons, conditions and purposes of the inspection;
- list of objects subject to audit;
- type of inspection and timing of its implementation.
A notice of the upcoming inspection is sent to the inspected enterprise.
Subscribe to our newsletter
Read us on Yandex.Zen Read us on Telegram
On the day specified in the notification, inspectors arrive at the enterprise or, if the inspection is not on-site, but documentary, request the necessary documents. Before the start of the audit, inspectors must present the enterprise representative with official identification confirming that they have the authority to conduct the inspection.
As a rule, inspectors first study the technical condition of production facilities and assess the working conditions of the workers employed there. After this, they begin to study the documentation to be verified.
The deadline for conducting an audit is 20 working days (Part 1, Article 13 of Law No. 294).
The results of the inspection are recorded in a report drawn up in accordance with the form from Appendix 3 to the order of the Ministry of Economic Development “On the implementation ...” dated April 30, 2009 No. 141.
It contains information:
- about the organization being audited;
- officials who conducted the inspection;
- identified violations, inconsistencies and unfulfilled instructions.
What directly interests Rostechnadzor employees
During a routine inspection, service inspectors must check:
- Availability of a license to carry out certain activities, as well as TIN and Charter of the company or organization.
- Documentation. They check the availability and correctness of employment contracts with employees of the enterprise, diplomas and certificates of their education, as well as medical records of employees. In addition, either a lease agreement for the premises in which the activity is carried out, or a document confirming ownership of the occupied space, must be presented.
- Availability of a company sign and a consumer corner.
- How correct and accurate are the price tags for all goods?
- Availability of information about manufacturers and expiration dates of the products presented, as well as excise stamps, certificates and licenses.
- Price list for all services that a company or organization provides.
- Operation of the cash register.
- How correctly the log of inspections carried out within the company is filled out.
As we can see from the above, the list of what Rostechnadzor checks during a routine inspection is not so small.
In what profile companies and what exactly does Rostechnadzor check?
Rostechnadzor employees have the right to carry out audits of enterprises and organizations defined by the appendix to Federal Law No. 116 (07/21/1997) “On the Industrial Safety of Hazardous Production Facilities”, including companies developing or using:
- subsoil;
- oxidizing or toxic materials;
- explosives;
- nuclear energy;
- hydraulic devices;
- thermal, electrical industrial installations operating at high pressure;
- lifting devices and mechanisms.
The verification criteria are determined taking into account the type of activity of a particular enterprise, but common to all types of activities are:
- Checking documentation related to the use of high-risk facilities, a full list of which is posted in the regulations to Rostechnadzor Order No. 325 (07/25/2013). An approximate set of documents studied includes:
- constituent (title) documents for the company being inspected;
- materials related to industrial safety, including legislative acts of the Russian Federation;
- documentary evidence of a high-risk facility existing at production and its entry in the state register;
- permits, licenses for use, certificates for equipment, instruments, devices;
- design documentation for a dangerous structure or device regarding its reconstruction, conservation, liquidation;
- regulatory provisions on the rules of work;
- magazines on registration of passes, instructions (on safety), recording of emergency situations;
- expert opinions on diagnostics of equipment, safety of buildings and structures;
- schedules for repairs of structures and equipment, including capital ones;
- agreements with professional rescue and emergency structures;
- information about workers engaged in hazardous production, including confirming their compliance (professional, medical) with the type of work performed;
- risk (liability) insurance agreements;
- Rostechnadzor instructions previously issued, as well as confirmation of their implementation.
- Inspection of a hazardous production facility aimed at verifying its integrity and determining non-compliance with safety standards. Based on the results of the inspection, a report is drawn up (in 2 copies), the presence of which must be reflected in the inspection log.
What actions are not within the competence of Rostechnadzor
Strange as it may seem, there are certain restrictions in the work of Rostechnadzor. Employees of this service do not have the right to:
- Begin and continue the inspection without the presence of the head of the company or an employee who is acting as a director on a temporary basis.
- Taking samples for further examination without drawing up the appropriate documents.
- Study the provided documents longer than the period allotted by Russian legislation.
- Provide third parties with information obtained during the inspection.
- Make demands that have nothing to do with the operation of this service.
- Subject to examination of products that are not in any way related to testing.
- Stop the work of the organization during control activities (for example, shops or various catering establishments).
- Conduct a test purchase.
Important! There are no clear explanations in the legislation regarding these actions. If a Rostechnadzor inspector makes such a purchase, the fact of its completion must be recorded by representatives of the company or organization being inspected. In the future, based on this document, you can prove the fact of violation of the law.
Now there is a complete understanding of what Rostechnadzor checks during a routine inspection and what is not within its competence. Everything is very simple.
Why and when is technical supervision needed in construction?
Any construction customer, not being a builder himself and not having the opportunity to constantly be on the construction site, will inevitably face unscrupulous performance of work if he does not take care of technical supervision in a timely manner.
Technical supervision is expert verification activities that ensure:
- the quality of construction work and their compliance with norms and regulations;
- use of building materials specified in the construction project;
- compliance with construction deadlines and scope;
- compliance with the project budget.
Technical supervision specialists can be invited at any stage of construction, but the most effective solution would be to involve them in the work already at the stage of drawing up design estimates. Practice shows that this helps save up to 30% of construction costs. The benefits are obvious for both individuals and organizations.
Functions of technical supervision in construction
The daily tasks of technical supervision are as follows:
- Cost reduction : tracking the volume of work submitted for payment; control over budget compliance. These measures can reduce up to 20% of the estimated cost.
- Improving the quality of work : compliance with technologies, rules and regulations.
- Quality control of materials used : checking certificates, laboratory testing of samples, compliance with storage rules.
- Monitoring the correctness of construction documentation.
The final stage of verification
Based on the results of the audit, the inspection service employee draws up an act in which he indicates all the identified violations, the procedure for correcting them, deadlines and penalties. Rostechnadzor inspection reports must be drawn up in two copies: one is left with the control service, and the other is handed over to the head of the organization.
On a note! If, at the request of the inspector, all the documents of interest were provided, but he himself was not allowed into the enterprise, then the organization is unlikely to get by without an administrative fine. Moreover, the amount can be up to 2,000 rubles for the director and up to 1,000 rubles for each employee. Each company should have a log in which all audits are recorded: the dates of their conduct, who conducted the audit (that is, information about the control service and the specific name of the inspection inspector), its goals and the violations identified.
On a note! Having such a document in hand, the director of any enterprise can easily prove the fact of an audit.
The procedure for obtaining permission from Rostechnadzor
To obtain permission from Rostechnadzor, you must go through a standard procedure. It includes the following steps:
- collection of necessary documentation. Submitting an application to the necessary representative office of Rostechnadzor. A sample application can be found on the website of the regulatory authority. Documents can be sent by mail with a covering letter or in person to a government agency;
- carrying out tests and research. A special commission is being created for this purpose. It must include a government representative. As a result of the inspection, a protocol is drawn up;
- industrial safety research. Conducted on equipment that is produced or used abroad of the Russian Federation;
- a conclusion is drawn up. A decision is made to issue or deny a permit.
Timing of the inspection
Naturally, the timing of Rostechnadzor’s inspection cannot be extended “indefinitely.” The inspection may last for a maximum of one month.
On a note! In some exceptional cases, when the inspector has very compelling arguments for extending the control event, the deadlines may be extended by another month.
When does Rostechnadzor conduct inspections?
In order to monitor compliance with current legislation in the field of nuclear, technical and energy safety, Rostechnadzor conducts inspections of organizations, entrepreneurs, and individuals. Depending on the type of organization of control, inspections can be carried out scheduled or unscheduled; according to the form of implementation of control activities, inspections can include an inspector’s visit (on-site inspection) or involve checking the company’s documents at the inspector’s workplace (documentary inspection).
Scheduled and unscheduled inspections
Rostechnadzor conducts scheduled inspections of organizations and enterprises according to the approved schedule. The body does not have the right to carry out planned control activities more than once every 3 years. Information on the timing of scheduled inspections of legal entities is publicly available; the schedule of scheduled inspections for 2018 can be found on the official website of the Federal Service (https://www.gosnadzor.ru/activity/control/plans/).
Rostechnadzor has the right to come to enterprises for an unscheduled inspection if one of the following grounds exists:
- Complaint from the public. Any citizen has the right to file a complaint with Rostechnadzor regarding the organization’s violation of labor protection standards, the law on environmental protection, and other provisions and norms, control over compliance with which is entrusted to Rostechnadzor.
- Checking compliance with the order. If, based on the results of a previous inspection (scheduled or unscheduled), Rostechnadzor identified violations and issued an order to eliminate them, then after the expiration of the established period, the inspector has the right to visit the enterprise on an unscheduled basis in order to verify compliance with the order.
- Accident at the enterprise. The basis for an unscheduled visit by an inspector from Rospotrebnadzor may be an accident at an enterprise or another extraordinary event that resulted in harm to the environment, the health of employees, or created a safety threat for citizens living nearby.
In each case, the documentary basis for an unscheduled inspection is the corresponding resolution signed by the head of the territorial body of Rostechnadzor.
During the inspection, the Rostechnadzor inspector can perform the following actions:
- request documents for verification, seize documents for subsequent examination;
- inspect production, office, warehouse and other premises, equipment, and other production facilities;
- conduct interrogations of management and employees of the organization.
In 2020, Rostechnadzor introduced checklists that record a list of questions asked to responsible persons of the enterprise during the inspection. In total, the body approved 50 checklists of the established form, which are used depending on the scope of activity of the company being inspected.
The Rostechnadzor checklist with a general list of questions on industrial safety can be downloaded here ⇒ Rostechnadzor checklist (general industrial safety requirements).
The Rostechnadzor checklist for gas stations can be downloaded here ⇒ Rostechnadzor checklist for gas stations.
Below we will look in detail at what exactly Rostechnadzor checks during scheduled and unscheduled control activities.
Verification of documents
At the initial stage, Rostechnadzor requests the following documents for verification:
- statutory documents of the enterprise;
- local regulations governing the use of electrical equipment, lifting mechanisms, and other production facilities (including hazardous ones);
- regulations on labor protection;
- certificates for the equipment used, electrical appliances, etc.;
- licenses (if the enterprise’s activities are subject to licensing);
- documents about the hazardous production facility (if any): registration in the register, permission to commission, license to use;
- documents on safety measures taken (Safety Briefing Log);
- accident log;
- equipment maintenance log;
- liability risk insurance contract;
- employment contracts with employees who are involved in working in hazardous working conditions or at hazardous production facilities.
During the inspection, Rostechnadzor has the right to request other documents within its powers, and, if necessary, to seize them for subsequent verification or examination for authenticity.
Control of operation of hazardous production facilities
After checking the documents, the inspector carries out a direct inspection of the objects, namely:
- production equipment;
- working conditions;
- premises.
Only the inspector whose name is indicated in the order for the inspection has the right to inspect the equipment. The purpose of the inspection is to certify the facility’s compliance with established safety standards, check the equipment for serviceability, and confirm the correct operation of the facility.
Checking compliance with regulations
If we are talking about an unscheduled inspection after the expiration of the validity period for fulfilling the order, then Rostechnadzor inspects enterprises not for the purpose of eliminating previously identified violations. At the same time, the inspector is assigned the right to conduct additional inspections of other objects, except for those for which violations were previously identified. The inspector also has the right to request any documents in accordance with the powers of Rostechnadzor.
After completing the inspection, the Rostechnadzor inspector draws up a report of the established form and passes it on to the organization’s representative for review. If the enterprise does not agree with the results of the inspection described in the act, or considers the issued order about violations to be unfounded, then the representative of the organization has the right to appeal it by filing a corresponding application with Rostechnadzor.
Rate the quality of the article. We want to be better for you:
What Rostekhnadzor checks for energy saving
In accordance with Federal Law No. 261-FZ (dated November 23, 2009, as amended on July 13, 2020), Rostechnadzor (namely the Federal Service for Technological, Environmental and Nuclear Supervision) carries out energy saving inspections. If the organization is not subject to energy inspection (that is, the turnover of energy resources is less than 10 million, the enterprise is not municipal, and the building is leased), then they monitor compliance with the extent to which the owner of the building complies with the requirements for increasing energy efficiency and equipping the energy installations used with metering devices.
Basic service powers
Technical regulations on fire safety requirements
What Rostechnadzor does is written in Government Decree No. 401 dated July 30, 2004. The powers of Rostechnadzor include:
- monitoring compliance with standards in the field of atomic energy operation, monitoring the validity of permits for the right to carry out activities in the field of atomic energy use;
- monitoring the implementation of safety rules in the nuclear, radiation, technical and fire spheres;
- registration of public benefit organizations;
- control over the protection of nuclear installations, radiation sources, and storage facilities for nuclear materials and substances;
- monitoring the implementation of international safety standards in the field of atomic energy use;
- control of compliance with industrial safety standards during the design, construction, and conservation of hazardous facilities;
- monitoring compliance with electrical safety requirements in the electric power industry;
- monitoring compliance with rules and safety standards of hydraulic structures;
- monitoring compliance with energy studies within established deadlines;
- control of the requirements established by technical documentation in a certain field of activity.
Verification of educational institution
It is generally accepted that the Federal Service for Technological, Environmental and Nuclear Supervision (i.e. Rostekhnadzor) mainly controls the work of organizations in the field of construction, industry and energy. But this is a mistaken opinion. Rostechnadzor employees can “show up” at any budgetary institution, for example, a school or institute.
What Rostechnadzor checks in an educational institution:
- Strict compliance with the requirements and regulations for the maintenance and operation of electrical and heating networks and installations, equipment (this also applies to educational equipment), which poses an increased danger.
- Supervises construction work that the institution may carry out (for example, the construction of new buildings or the reconstruction of old ones).
- Assess the technical condition of various lifting equipment (for example, elevators).
Basic requirements for Rostechnadzor inspections
During any inspection, the main focus is on electrical safety. In order to successfully pass the inspection, you must provide the inspector with the following documentation:
- a valid electricity supply contract,
- order appointing someone responsible for electrical equipment,
- single-line power supply diagram,
- journal for issuing protective equipment,
- logbook for testing knowledge of operating rules in electrical installations,
- report on preventive testing of electrical installations,
- a copy of the minutes of the examination committee meeting,
- set of electrical protective equipment,
- initial permitting documents (act of connection to networks, act of delimitation).
If all of the above documentation is available, you can be sure that the verification will be passed. Of course, the inspector’s attention will be drawn not only to the documents, but also to the technical condition of the electrical equipment. The preliminary technical condition of the installation is assessed during electrical testing. If the identified defects are corrected, then problems with supervision should not arise.
The presence of electrical protective equipment is required by federal regulations. These funds are listed on the balance sheet of the enterprise and are kept in a journal, which is sealed with the seal of the organization.
Checking gas stations
What does Rostechnadzor check at gas stations? First of all, compliance with licensing rules and regulations. The fact is that gas stations that started operating 3-4 years ago generally have in their arsenal all the necessary documents and inspection and commissioning reports. But at stations that began operating much earlier (40-50 years ago), such an examination was not carried out. Therefore, in accordance with the Regulations on compulsory licensing of production facilities that are characterized by a high explosion hazard, Rostechnadzor conducts inspections of all gas stations throughout Russia and, in particular, in Moscow. In addition to these activities, service employees deal with issues of fuel sales (for example, checking the presence of receipts, a cash register) and its quality.
Scheduled and unscheduled inspections of organizations engaged in educational activities
Scheduled inspections are carried out in accordance with the annual Plan for conducting scheduled inspections of legal entities, which is approved by the head of Rosobrnadzor.
The basis for including a scheduled inspection in the annual plan for conducting scheduled inspections is the expiration of three years from the date of:
- state registration of a legal entity;
- completion of the last scheduled inspection of a legal entity, individual entrepreneur;
- the expiration of one year from the date of the decision to grant a license or re-issue a license;
The surveillance activity can be carried out in the form of an on-site or documentary inspection.
Organizations carrying out educational activities are notified of a scheduled inspection no later than three working days before the start of the inspection by sending a copy of the order of the head of Rosobrnadzor on the start of a scheduled inspection by registered mail with return receipt requested or in any other available way.
An unscheduled inspection is carried out in the form of a documentary inspection and (or) an on-site inspection.
Organizations carrying out educational activities are notified by Rosobrnadzor of an unscheduled on-site inspection at least twenty-four hours before the start of the inspection by any available means.
Rostekhnadzor inspections: we meet fully armed
“An auditor is coming to visit us... WHAT SHOULD we DO?” – one of our clients began a telephone conversation with this almost classic phrase. He said that in a week, Rostechnadzor inspectors were scheduled to arrive at his place for a scheduled on-site inspection, and asked him to clarify a number of important points for every owner of a hazardous production facility. When and on what basis can a hazardous production facility be inspected? What documents will Rostechnadzor check? What does an organization face when violations of industrial safety standards and regulations are detected? We will try to give detailed answers to these questions within the framework of this article. So, if your organization does:
- design, construction, operation, conservation and liquidation of hazardous production facilities;
- manufacturing, installation, adjustment, maintenance and repair of technical devices used in hazardous production facilities;
- transportation of hazardous substances to hazardous production facilities;
then, in accordance with the norms of the Federal Law of July 21, 1997 No. 116-FZ “On Industrial Safety...”, Rostechnadzor can periodically conduct scheduled (for HIFs of hazard class 1-3) and unscheduled (for all classes of HIFs) inspections at your enterprise . Supervisory activities are aimed at preventing, identifying and suppressing violations of the requirements established by the legislation of the Russian Federation in the field of industrial safety. The subject of Rostechnadzor inspections is (clause 4 of Article 16 of Federal Law No. 116):
- compliance with mandatory industrial safety requirements;
- compliance with established industrial safety requirements of the buildings, premises, structures, technical devices, equipment and materials used, technological processes being carried out;
- compliance with the requirements of the safety justification (if activities at the hazardous production facility are carried out using a safety justification).
Scheduled inspections of FSETAN are carried out on the basis of annual plans, which are approved by the head of the territorial department of Rostechnadzor and posted on the official website of the department on the Internet (as a rule, this is a file in Excel format that can be downloaded at any convenient time). The basis for carrying out unscheduled inspections may be (clause 7 of article 16 of Federal Law No. 116):
- Expiration of the deadline for the supervised organization to comply with a previously issued order to eliminate violations of mandatory industrial safety requirements.
- Receipt of requests and applications from citizens, legal entities or individual entrepreneurs to Rostechnadzor; information from state authorities, local governments and the media about the occurrence of: 1) threats of harm to the life and health of citizens, harm to animals, plants, the environment, cultural heritage sites, and state security; 2) threats of natural and man-made emergency situations; 3) facts of harm to the life and health of citizens, harm to animals, plants, the environment, cultural heritage sites, and state security.
- Order (instruction) of the head of Rostechnadzor, issued in accordance with the instructions of the President of the Russian Federation, the Government of the Russian Federation and on the basis of the prosecutor's requirements to conduct an unscheduled inspection as part of supervision over the implementation of laws on materials and appeals received by the prosecutor's office.
The inspection can be carried out only by officials who are specified in the order or order of Rostechnadzor (its territorial body) to conduct the inspection. The document specifies the grounds for the inspection, the duration and purpose, the scope of the inspection activities, as well as instructions for inspectors. After completing the inspection, Rostechnadzor inspectors are required to draw up an Inspection Report in two copies. The report is drawn up in a standard form approved by Order of the Ministry of Economic Development of Russia dated April 30, 2009 No. 141. The powers of the inspection body, the procedure and timing of the inspection, the responsibilities of inspectors and other details are set out in the Federal Law of December 26, 2008 No. 294-FZ “On protection of the rights of legal entities and individual entrepreneurs in the exercise of state control (supervision) and municipal control.” Rostechnadzor's performance of the state function of monitoring and supervising compliance with industrial safety requirements is described in detail in the Administrative Regulations, which were approved by Order No. 280 of the Ministry of Natural Resources of Russia dated October 30, 2008. When to expect an inspection by Rostechnadzor According to clause 5 of Article 16 of Federal Law No. 116, the basis for inclusion organization in the register of annual scheduled inspections is the expiration of 1 year (for hazardous production facilities I-II hazard class) and 3 years (for hazardous production facilities III hazard class) from the date:
- making a decision on the commissioning after construction, technical re-equipment, reconstruction and overhaul of hazardous production facilities, including buildings, premises, structures, technical devices, equipment and materials used in the operation of hazardous production facilities;
- registration of hazardous production facilities in the Rostekhnadzor register;
- completion of the last scheduled inspection.
The enterprise is notified of a scheduled inspection being carried out against it at least 3 days before the start of control activities. A copy of the order or order of the head (deputy head) of Rostechnadzor is sent to the supervised organization by registered mail with return receipt requested or in any other available way. With an unscheduled inspection, everything is different. Rostechnadzor can initiate it at any time, having sufficient grounds (see paragraph 7 of Article 16 of Federal Law No. 116). The supervised organization (legal entity or individual entrepreneur) is notified of such an inspection at least 24 hours before the start of its conduct by any available means. Moreover, if Rostechnadzor received a statement (appeal) about violations of mandatory requirements, about non-compliance with mandatory requirements of the buildings and equipment used, if such violations create a threat of harm to life, health of people, harm to animals, etc., preliminary notification to the supervised organization is not allowed (clause 9 of article 16 of Federal Law No. 116). The period for conducting scheduled and unscheduled inspections is no more than 30 working days. In exceptional cases, the period for conducting supervisory activities may be extended by the management of Rostechnadzor, but not more than by 20 working days (clause 10 of Article 16 of Federal Law No. 116). What documents will Rostechnadzor check?
, which will be checked by Rostechnadzor inspectors during a scheduled/unscheduled inspection (in accordance with the provisions of the Federal Law of July 21, 1997 No. 116-FZ “On Industrial Safety...” and other regulations in the field of industrial safety, including technical regulations, federal standards and rules). Rostechnadzor can also check other specialized documents, orders, journals, schedules, which are determined by the specifics of hazardous production facilities and are indicated in the FNP by type of facility, technical regulations, and other legal acts. During an on-site inspection, department specialists will conduct an inspection and visual analysis of equipment and its parts for serviceability, reliability and operational safety. Based on the results of the inspection, Rostechnadzor inspectors draw a conclusion (draw up a report) on the presence/absence of violations of industrial safety standards and regulations at the supervised organization's hazardous production facilities. Rostechnadzor identified violations: what threatens the organization? If, during an inspection, Rostechnadzor has identified violations of industrial safety requirements at a hazardous production facility, it issues an order to the supervised organization to eliminate these violations, indicating specific deadlines. In addition, the enterprise, its manager and other officials are held administratively liable in accordance with Articles 9.1, 9.19 of Chapter 9 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation (CAO RF) in the form of the following fines and other penalties: 1. Violation of industrial safety requirements or conditions for licensing activities on OPO entails the imposition of an administrative fine:
- for citizens (individuals) – from 2000 to 3000 rubles;
- for officials (for example, general director, chief engineer) - from 20,000 to 30,000 rubles or disqualification for a period of 6 months to 1 year;
- for legal entities - from 200,000 to 300,000 rubles or administrative suspension of activities for up to 90 days.
2. Violation of industrial safety requirements for the receipt, use, processing, storage, transportation, destruction and accounting of explosives at hazardous production facilities shall entail the imposition of an administrative fine:
- for citizens – from 4,000 to 5,000 rubles;
- for officials - from 30,000 to 40,000 rubles or disqualification for a period of 1 to 1.5 years;
- for legal entities - from 300,000 to 400,000 rubles or administrative suspension of activities for up to 90 days.
3. A gross violation of industrial safety requirements (a violation that led to an immediate threat to the life or health of people) or a gross violation of the conditions for licensing activities at a hazardous production facility (for example, the absence or improper execution of a License - the name is incorrect, the types of activities are incorrectly indicated) entails the imposition of an administrative fine:
- for officials (for example, general director, chief engineer) - from 40,000 to 50,000 rubles or disqualification for a period of 1 to 2 years;
- for legal entities - from 500,000 to 1,000,000 rubles or administrative suspension of activities for up to 90 days.
4. Operation of a hazardous facility, with the exception of the commissioning stage, without a contract for compulsory insurance of the hazardous facility shall entail the imposition of an administrative fine:
- for officials - from 15,000 to 20,000 rubles;
- for legal entities – from 300,000 to 500,000 rubles.
Forewarned is forearmed Remember, an inspection by Rostechnadzor is not a heavy burden that falls on the owner of a hazardous production facility. This is an indicator of the safety of a hazardous production facility. Suppose you have been operating the hazardous production facility for 20 years. And not once during this period was there even a hint of a serious accident. But life is changeable, and there is always a human factor. Therefore, in order to avoid sanctions from Rostechnadzor and maintain the reliability of your facility: 1. Receive, develop, and carefully store permits, regulatory and technical documents for hazardous production facilities, instructions and regulations, schedules and journals, orders and acts in a timely manner and in full. And communicate every provision of every document to everyone in your organization. 2. Maintain technical devices (their components), buildings and structures at hazardous production facilities in good condition, promptly carry out their inspection and diagnostics, technical examination and examination. 3. Follow changes in industrial safety legislation, make timely adjustments to documents, reissue permits and licenses. 4. Monitor the quality of staff work, conduct timely training and certification. By operating your hazardous production facility within the law, you contribute not only to industrial safety, but also to our general safety.
Most of the objects controlled by Rostechnadzor relate to industry, construction, and energy. However, there are many reasons why inspectors may come to an educational institution. And you need to be prepared for this.
When inspectors can come to an educational institution Currently, Rostekhnadzor (Federal Service for Environmental, Technological and Nuclear Supervision) operates on the basis of the Regulations, which were approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of July 30, 2004 No. 401. In addition to these Regulations, inspectors use other regulations in their work regulatory documents, among which a special place is occupied by the Federal Law of July 21, 1997 No. 116-FZ “On Industrial Safety of Hazardous Production Facilities”. So, based on these documents, an educational institution can be checked to see how it complies with the requirements for operation and maintenance of: - electrical installations and electrical networks (with the exception of household ones); – heating installations and networks (for example, school boiler houses); – certain types of equipment, including educational equipment, which pose an increased danger (this applies primarily to institutions of secondary and higher vocational education). In addition, the inspectors are responsible for construction supervision (Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation of February 1, 2006 No. 54). So if an educational institution is constructing or reconstructing, for example, educational buildings, then the appearance of inspectors from Rostechnadzor is quite possible. Inspectors are also allowed to assess the technical condition of various types of lifting devices (primarily elevator equipment). In addition, Rostechnadzor carries out a number of special functions, in particular, organizing and conducting state environmental assessment at the federal level.
What types of inspections exist? Features of Rostechnadzor inspections, depending on the type of supervision, are determined by various legal acts. For example, construction supervision, in addition to the Town Planning Code of the Russian Federation, is carried out on the basis of a special Regulation, which was approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of February 1, 2006 No. 54. Rostechnadzor, like all other regulatory agencies, during inspections must be guided by the Federal Law of December 26, 2008 No. 294-FZ “On the protection of the rights of legal entities and individual entrepreneurs...” (hereinafter referred to as Law No. 294-FZ). The inspections themselves can be scheduled or unscheduled. Scheduled inspections are carried out no more than once every three years. Rostechnadzor must coordinate the upcoming inspection with the prosecutor's office. At the same time, the case is especially stipulated when the subject of inspection is the institution’s compliance with the requirements of energy saving and increasing energy efficiency. In this case, a scheduled inspection may be carried out more often than once every three years (Article 9 of Law No. 294-FZ). The grounds for an unscheduled inspection are listed in Article 10 of Law No. 294-FZ. Thus, the reason for it may be information about a threat or harm to the life and health of citizens, harm to animals, plants and the environment, etc. Rostechnadzor can also unscheduled check how the institution corrected violations identified during a scheduled inspection. An unscheduled inspection can only be carried out with the permission of the prosecutor's office. True, in some cases (for example, if harm is caused to the life or health of citizens), inspectors can independently begin an inspection, only by notifying the prosecutor’s office about it. Progress of the inspection The head of the territorial body of Rostechnadzor or his deputy can order an inspection. The inspection order specifies the grounds, timing, goals of the upcoming inspection, types and scope of control activities, and a list of experts to be involved. Before starting the inspection, inspectors are required to familiarize the head or other official of the institution with this order. Inspectors must also present their official identification. If the inspectors do not have at least one of these documents, then they can not be allowed into the territory of the institution. It is also worth considering that Rostechnadzor employees do not have the right to conduct an inspection if the head of the educational institution or other officials are not present. The head of the institution does not have to be present during the inspection. This can be entrusted to any official or authorized representative of the institution. In turn, the management of the educational institution is obliged to provide the inspectors with all the necessary documents related to the purposes of the inspection, to provide access to its territory and to the equipment used. An on-site inspection is carried out at the location of the educational institution and (or) at the place of actual implementation of activities. For example, many universities have several academic buildings, often located at different addresses. In such a case, the inspection is carried out both at the location of the university itself, indicated in its charter, and at the location of its separate departments.
First of all, inspectors will check the requested documents. So, for example, if we are talking about power plants, then controllers can check how technical documentation is maintained (for example, special logs in which the operating parameters of a particular installation are recorded), as well as whether the operating personnel have the appropriate permits, etc. Next, they evaluate condition of buildings, structures, structures, premises, vehicle equipment, etc. The inspection period cannot exceed 20 working days. In exceptional cases, it may be extended, but not more than by 20 working days. Inspectors have the right to extend the inspection if, for example, a complex lengthy study or examination is required. Let us note that Rostechnadzor authorities have the right to involve experts who do not have civil and labor relations with the educational institution in conducting on-site inspections. Various expert organizations may also be involved in the inspection. Results of the inspection The Code of the Russian Federation on Administrative Offenses contains many articles, the proceedings under which are within the competence of Rostechnadzor. So, for example, Article 9.11 provides for liability for violation of the rules for the use of fuel and energy and improper use of relevant equipment and installations. Therefore, if a violation is identified that falls under administrative liability, the controllers have the right to draw up a protocol about this, which in the future may become the basis for bringing the educational institution and its management to justice. Rostechnadzor also has the right to suspend the activities of an educational institution if, for example, a real threat to the health and life of citizens is identified. Based on the results of the inspection, an act is drawn up in two copies, one of which, with copies of attachments, is handed over to the head of the educational institution or other official against signature (Article 16 of Law No. 294-FZ). If for some reason the official does not sign the act, then it is sent by mail with acknowledgment of delivery. Information about the inspection must be entered by Rostechnadzor officials into a special audit log, which is the responsibility of the educational institution. An educational institution brought to administrative liability has the right to appeal the relevant decision in an arbitration court. Important to remember So, inspectors must hand over the inspection order to the head of the educational institution or other official and present their identification. Without this, they may not be allowed into the territory. The verification period should not exceed 20 working days. In exceptional cases, the verification period may be extended by another 20 working days. Rostechnadzor must coordinate a scheduled inspection with the prosecutor's office and does not have the right to conduct it more often than once every three years. An unscheduled inspection must also take place with the permission of the prosecutor's office, but in exceptional cases this is not required. Based on the results of the inspection, an act is drawn up in two copies, one of which, with copies of attachments, is handed over to the head of the educational institution or other official against signature. If for some reason the official does not sign the act, then it is sent by mail with acknowledgment of receipt.
What does Rostechnadzor check?