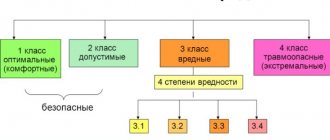
General provisions or what are harmful conditions
Special assessment of working conditions (SOUT) - determination of the degree of danger and harmfulness of the work process.
If, as a result of such an examination, factors are identified that determine the risk for the employee, then he will be assigned some kind of compensation. When determining the danger of labor processes, the following groups of factors are taken into account:
- chemical effects (presence of enzymes, hormonal substances, reagents);
- biological hazard (presence of microorganisms, pathogens in the work process)
- bacterial formations);
- background radiation;
- physical measures, including temperature and noise, humidity and vibration effects, electromagnetic radiation;
- risk of injury;
- other.
Rate of additional insurance contribution to the Pension Fund in 2020
For employees employed in hazardous work, a preferential pension is provided. A preferential pension is awarded only to those who worked in conditions belonging to classes 3 and 4. This list of professions was approved by Government Decree No. 665 of July 16, 2014. If there was a break in the work experience during which the employee was employed in non-hazardous conditions or was unemployed, the benefit is not provided.
So, to recalculate the pension, the following conditions must be met:
- The employee was continuously employed in production, the hazard class of which was confirmed by the SOUTH standards or by certification of workplaces.
- All necessary contributions to the Pension Fund were paid by the employer at an increased rate.
- The employee's profession complies with the requirements of Federal Law No. 400 dated December 28, 2013 (clauses 1-18, clause 1, article 30).
If the employee is a working pensioner, an additional payment to his salary is calculated in the same way as other employees.
►Find out how to correctly apply the results of a special assessment of working conditions>>>
Now the minimum amounts, procedure and conditions for providing guarantees and compensation to employees “for harmfulness” are spelled out directly in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Articles 92, 117, 147, 219 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Previously, they were installed by the Government. 219 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (as amended, valid until 01/01/2014); Government Decree No. 870 dated November 20, 2008.
Let us say right away that the minimum amounts of guarantees and compensation have not changed. However, according to the results of the special assessment, separate guarantees are not provided not only to workers employed in optimal and acceptable working conditions, as was the case before, but also to some of the “harmful workers”.
* For work over 36 hours, the employee is paid a separate monetary compensation in the manner, amount and on the terms established by industry (inter-industry) agreements and collective agreements.
Compensation to workers “for harmfulness” cannot be reduced compared to those established on 01/01/2014 if a special assessment confirms that the employee has retained the same working conditions. 3 tbsp. 15 of Law No. 421-FZ. This is especially important in cases where Labor Code rules change for the worse for the employee.
FROM AUTHENTIC SOURCES
KORZH Valery Anatolievich
Director of the Department of Labor Conditions and Safety of the Russian Ministry of Labor
“According to the new rules of the Labor Code, subclasses of “harmfulness” 3.1 and 3.2 do not give the employee the right to reduced working hours (36 hours) Art. 92 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. For subclass 3.1, no additional leave is granted. 117 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. However, if these compensations were established for the employee based on the results of certification carried out before 01/01/2014, and the special assessment confirms the preservation of the previous working conditions, then compensation should continue to be provided. 3 tbsp. 15 of Law No. 421-FZ.”
Until January 1, 2014, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation prohibited the replacement of additional leave “for harmfulness” with monetary compensation. 126 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (as amended, valid until 01/01/2014). Now replacement is partially possible. An employee can be paid money for part of the “harmful” leave over 7 calendar days. The possibility of such a replacement must be specified in the industry (inter-industry) agreement and collective agreement.
FROM AUTHENTIC SOURCES
“In exchange for days of additional leave, the employee must be paid average earnings.
In addition to this, the employee must also be paid additional compensation in the amount determined by the collective agreement, but not lower than the amount established in the industry (inter-industry) agreement.”
KOVIAZINA Nina Zaurbekovna Ministry of Health of Russia
Now, in hazardous work, an increase in the length of the working week and working day is allowed under Articles 92, 94 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Is it possible to regard an increase in work up to 40 hours in hazardous conditions as overtime work{q}
FROM AUTHENTIC SOURCES
“According to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, work beyond 36 hours in this case is not overtime. Therefore, when recording working hours in total, it should be taken into account according to the standard hours of the accounting period. And in the time sheet it must be reflected as regular work. For such work, in addition to payment for hours worked, additional compensation must be paid in the amount determined by the collective agreement, but not lower than the amount established in the industry agreement.”
KOVIAZINA Nina Zaurbekovna Ministry of Health of Russia
Compensation payments related to the performance of labor duties are not subject to personal income tax. 3 tbsp. 217 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Is it possible to exempt from taxation monetary compensation paid to an employee for working in hazardous conditions for more than 36 hours a week{q} The Ministry of Finance believes that it is not.
FROM AUTHENTIC SOURCES
STELMAKH Nikolay Nikolaevich
Advisor to the State Civil Service of the Russian Federation, 1st class
“Despite the fact that payment to an employee for work over 36 hours a week is specified in Art. 92 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation as compensation, it is such in the sense of Art. 164 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is not. In essence, this is a compensation payment for work in hazardous conditions, included in wages. The grounds for exempting such payments from personal income tax in Art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation has not been established.”
If summarized accounting is introduced for “pests,” then the duration of the accounting period cannot exceed 3 months (previously - 1 year) Art. 104 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Increased or additional compensation compared to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, as before, can be independently established by a collective agreement or local regulations. 219 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
First of all, the employer is obliged to explain to each employee when hiring him what harmful and (or) dangerous production factors he will have to interact with - directly or indirectly.
| Name of harmful and (or) dangerous factors of the production environment and labor process |
| Physical factors |
| Microclimate - identified as a harmful and (or) dangerous factor in workplaces located in closed industrial premises where there is technological equipment that is an artificial source of heat and (or) cold (with the exception of climatic equipment not used in the technological process and intended for creating comfortable working conditions) |
| Air temperature |
| Relative humidity |
| Air speed |
| Thermal radiation |
| Aerosols of predominantly fibrogenic action (APFA) are identified as harmful and (or) dangerous factors only at workplaces where the extraction, enrichment, production and use of dust substances related to APFA are carried out in the technological process, and equipment is operated, the work on which is accompanied by release of APDF (dust containing natural and artificial mineral fibers, coal dust). |
| Vibroacoustic factors are identified as harmful and (or) dangerous factors only in workplaces where there is technological equipment that is a source of these vibroacoustic factors. |
| Noise |
| Infrasound |
| Ultrasound air |
| General and local vibration |
| Light environment |
| Illumination of the working surface under artificial lighting |
| Direct glare - identified as harmful and (or) dangerous factors only when performing precision work with the size of objects of discrimination less than 0.5 mm, in the presence of blinding light sources, when working with objects of discrimination and working surfaces with directionally scattered and mixed reflection . |
| Reflected brilliance - with the exception of workplaces in which employees are exclusively employed on personal electronic computers (personal computers) and (or) operate desktop-type copiers, single stationary copiers used periodically for the needs of the organization itself, other office organizational equipment, as well as household appliances not used in the production process. |
| Non-ionizing radiation - with the exception of workplaces in which workers are exclusively employed on personal electronic computers (personal computers) and (or) operate desktop-type copiers, single stationary copiers used periodically for the needs of the organization itself, other office organizational equipment, as well as household appliances not used in the production process. |
| Alternating electromagnetic field (industrial frequency 50 Hz) |
| Alternating electromagnetic field in the radio frequency range |
| Electrostatic field |
| Constant magnetic field |
| Ultraviolet radiation |
| Laser radiation |
| Ionizing radiation - are identified as harmful and (or) dangerous factors only in workplaces where the extraction, enrichment, production and use of radioactive substances and isotopes in the technological process is carried out, as well as during the operation of equipment that creates ionizing radiation. |
| X-ray, gamma and neutron radiation |
| Radioactive contamination of production premises, elements of production equipment, personal protective equipment and employee skin |
| Chemical factor - identified as harmful and (or) dangerous factors only in workplaces during mining, enrichment, chemical synthesis, use in the technological process and/or chemical analysis of chemical substances and mixtures, release of chemicals during the technological process, as well as during production substances of biological nature. |
| Chemical substances and mixtures measured in the air of the working area and on the skin of workers, including some substances of biological nature (antibiotics, vitamins, hormones, enzymes, protein preparations), which are obtained by chemical synthesis and (or) to control the content of which methods are used chemical analysis |
| Biological factor - are identified as harmful and (or) dangerous factors only in workplaces where activities are carried out in accordance with sanitary and epidemiological rules SN 1.3.1285-03 “Safety of working with microorganisms of I and II groups of pathogenicity (hazard)” introduced put into effect by the Decree of the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation dated April 15, 2003 No. 42 (registered by the Ministry of Justice of Russia on May 15, 2003 No. 4545), as amended by the Decree of the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation dated May 12, 2010 No. 55 " On approval of SP 1.3.2628-10" (registered by the Ministry of Justice of Russia on July 6, 2010 No. 17704) and SP 1.3.2322-08 "Safety of working with microorganisms of III - IV groups of pathogenicity (danger) and pathogens of parasitic diseases", approved by the resolution of the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation dated January 28, 2008 No. 4 (registered by the Ministry of Justice of Russia on February 21, 2008 No. 11197), as amended by the resolutions of the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation dated June 2, 2009 No. 42 “On approval of sanitary epidemiological rules SP 1.3.2518-09" (registered by the Ministry of Justice of Russia on July 8, 2009 No. 14280) and dated June 29, 2011 No. 86 "On approval of sanitary and epidemiological rules SP 1.3.2885-11 "Additions and changes No. 2 to SP 1.3.2322-08 “Safety of working with microorganisms of III – IV groups of pathogenicity (hazard) and pathogens of parasitic diseases” (registered by the Ministry of Justice of Russia on July 12, 2011 No. 21317). |
| Producing microorganisms, living cells and spores contained in bacterial preparations |
| Pathogenic microorganisms – causative agents of especially dangerous infectious diseases |
| Pathogenic microorganisms – causative agents of other infectious diseases |
| The severity of the labor process - are identified as harmful and (or) dangerous factors only at workplaces in which workers perform work determined by the technological process (labor function) of lifting and carrying loads manually, work in a forced position or a “standing” position, when moving in space. |
| Physical dynamic load |
| Weight of load lifted and moved manually |
| Stereotypical labor movements |
| Static load |
| Working posture |
| Tilts of the worker's body |
| Moving in space |
| The tension of the labor process |
| Duration of concentrated observation - are identified as harmful and (or) dangerous factors when performing work on dispatching production processes, including conveyor type, at the workplace of operators of technological (production) equipment, when driving vehicles. |
| The density of signals (light, sound) and messages per unit of time are identified as harmful and (or) dangerous factors when performing work on dispatching production processes, including conveyor-type ones, at the workplaces of operators of technological (production) equipment, and when driving vehicles. |
| Number of production facilities for simultaneous observation10 |
| Load on the auditory analyzer - are identified as harmful and (or) dangerous factors when performing work on dispatching production processes, including conveyor type, at the workplace of operators of technological (production) equipment, when driving vehicles |
| Active monitoring of the progress of the production process - - are identified as harmful and (or) dangerous factors when performing work on dispatching production processes, including conveyor type, at the workplace of operators of technological (production) equipment, when driving vehicles. |
| Working with optical instruments |
| Load on the vocal apparatus |
We invite you to familiarize yourself with: Apartment rent agreement: subject, types, sides, pros and cons
| Guarantees and compensation for employees engaged in work with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions | Classes of working conditions | ||||
| Harmful | Dangerous | ||||
| 3.1 | 3.2 | 3.3 | 3.4 | 4 | |
| Reduced working hours - no more than 36 hours per week (Article 92 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Annual additional paid leave - at least seven calendar days (Article 117 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Increase in wages - at least 4% (Article 147 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Dispensing milk (Article 222 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated February 16, 2009 No. 45n | Norms and conditions for the free provision of milk or other equivalent food products to employees engaged in work with hazardous working conditions (Appendix No. 1 to Order No. 45n) | ||||
| In jobs with particularly hazardous working conditions, workers are provided with free medical and preventive nutrition (Article 222 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated February 16, 2009 No. 46n) | List of industries, professions and positions in which work gives the right to free therapeutic and preventive nutrition (Appendix No. 1 to Order No. 46n) | ||||
- employed in harmful and dangerous working conditions specified in the Lists of professions and types of work that give the right to early retirement, approved by the Government of the Russian Federation.
- the class of working conditions was established during a special assessment of working conditions or certification of workplaces. There are no other options.
- working in organizations that transfer an increased amount of the additional insurance contribution rate to the Pension Fund of Russia, and performing a certain list of work specified in Article 30 of the Law of the Russian Federation “On Insurance Pensions” dated December 28, 2013 No. 400-FZ.
Work on weekends and holidays
- the employee worked on the day(s) prescribed for him by the VTR Rules. If for an employee, according to the VTR Rules, Saturday and (or) Sunday are not days off, and days off are provided to him on other days of the week, then Saturday and Sunday are regular working days for him and are paid in a single amount.
- the employee worked on one (several) non-working holidays established by Art. 112 TK.
The minimum amount of increased wages for work on a weekend or holiday:
- for piecework wages - at double piecework rates;
- when remunerating labor at daily and hourly tariff rates - at double daily or hourly tariff rates;
- employees receiving a salary (official salary) - depending on the standard working hours worked in the month.
Read more List of documents for car re-registration
For employees receiving a salary (official salary), work on holidays and weekends is carried out in the following order:
- if work on a day off was carried out within the limits of the monthly working time norm - in the amount of a single daily or hourly tariff rate (part of the salary (official salary) for a day or hour of work) in excess of the salary (official salary);
- if work on a day off was carried out in excess of the monthly standard working time - in the amount of double the daily or hourly tariff rate (part of the salary (official salary) for a day or hour of work) in excess of the salary (official salary).
Specific amounts of increased wages for work on a weekend or holiday can be established by a collective agreement, a local act (adopted taking into account the opinion of the representative body of workers), or an employment contract.
At the request of the employee, instead of increased pay, working on a day off can be compensated by providing another day of rest. In this case, payment for work on a day off is made in a single amount, and the other day of rest provided is not paid.
Payment for work on weekends and holidays for creative workers indicated in the list of positions, approved. by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated April 28, 2007 No. 252, is determined by a collective agreement, local act, or employment contract.
How are hazardous conditions determined at an enterprise?
Compensation for harmful processes will be provided only if working conditions are recognized as unfavorable for the health of employees. Possibilities for the provision of compensation by the employer must be initially provided for in the cooperation agreement.
We invite you to read: Denial of employment due to a criminal record
The employer is responsible for compliance with labor law standards. He must organize the work process and minimize risks to the health of personnel. And to prevent negative consequences, he is obliged to classify the degree of risk of workplaces. Distribution into classes is made taking into account the danger that accompanies the employee at the stage of performing work duties.
To determine the harmfulness of the entire production and individual workplace, a special commission is involved. At the special request of the employer, SOUT is carried out. Procedure:
- Submitting an application for examination of the SOUT.
- Collection of necessary documentation.
- Submitting a package of papers to a government agency.
- Development of an order in accordance with which a special evaluation commission is created.
- Issue of a special conclusion by the commission. The document takes into account the following points:
- seat class;
- list of measures to reduce harm.
- Implementation of inspection results into the production process.
A specific workplace may be assigned a different hazard class. But regardless of the degree of danger, they all have a certain negative effect on the body. Supplements to wages and non-financial types of compensation are prescribed under the following conditions:
- The level of negative impact received during one work shift does not allow the employee to recover before the next return to work.
- There is a risk in the work process:
- achieving functional changes in the body;
- receiving occupational diseases;
- loss of ability to work.
Therapeutic and preventive nutrition
The provision of milk or other equivalent food products, upon a written application from employees, may be replaced by a compensation payment in an amount equivalent to the cost of milk or other equivalent food products, if this is provided for by the collective agreement and (or) the employment contract. This is stated in Article 222 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Appendix No. 1 to Order No. 45n of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated February 16, 2009 contains the rules and conditions for the free provision of milk or other equivalent food products to employees in place of milk.
Appendix No. 4 to Order No. 45n contains an extensive List of harmful production factors, under the influence of which the consumption of milk or other equivalent food products is recommended for preventive purposes (Appendix No. 3 to Order No. 45n).
Figure 1 Fragment of the list
There are no other guarantees and compensations for an employee with the established subclass of working conditions 3.1.
An employee with an established subclass 3.2 - harmful working conditions of the 2nd degree) is exposed to HAPF, the levels of exposure of which can cause persistent functional changes in the employee’s body, leading to the appearance and development of initial forms of occupational diseases or occupational diseases of mild severity (without loss of professional ability), occurring after prolonged exposure (fifteen years or more). To do this, the employee must establish additional leave.
Article 117 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that annual additional paid leave is provided to employees whose working conditions at their workplaces, based on the results of a special assessment of working conditions, are classified as harmful working conditions of the 2nd, 3rd or 4th degree or hazardous working conditions. Vacation may be longer if the organization has such capabilities. It cannot be less.
Obviously, with subclass 3.2, the employee, in addition, retains an increase in wages in the amount of at least 4% of the salary or tariff rate established in Article 147 of the Labor Code and the provision of milk or other equivalent food products if the employee is affected by the factors specified in Appendix 3 to Order No. 45n.
There is an Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation (Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia) dated February 16, 2009 No. 46n, Moscow “On approval of the List of industries, professions and positions in which work entitles the right to free medical and preventive nutrition in connection with especially harmful working conditions, therapeutic and preventive nutrition rations, standards for the free distribution of vitamin preparations and the Rules for the free distribution of therapeutic and preventive nutrition.”
Figure 2 Fragment of the list of industries and professions for order No. 46n.
a) on non-working days;
b) on vacation days, except as provided for in subparagraph e) of paragraph 6 of the Rules;
c) on business trips;
d) on off-duty study days;
e) on days of work in areas where free provision of therapeutic and preventive nutrition is not established;
f) on days of performing work related to the execution of public and state orders;
g) during a period of temporary incapacity for work due to general diseases;
h) during the days of treatment in a medical institution, including a sanatorium type.
Work at night
The minimum amount of increased wages for work at night is established by the Government of the Russian Federation for all remuneration systems and is 20% of the hourly wage rate for each hour of work at night (or 20% of the salary calculated for an hour of work at night). The employer is obliged to pay for night work at least at the specified rates.
The additional payment is calculated only on the hourly tariff rate or salary calculated per hour of work (without taking into account other additional payments and/or allowances received by the employee).
The specific amount of increased pay for night work is established by the employment contract with the employee.
If the organization has a representative body of workers, the specific amount of the increase in wages for night work can be established by a local act adopted taking into account the opinion of the representative body of workers.
Read more Jurisdiction of cases for compensation for moral damage
In addition, the amount of increased wages for night work may be provided for in the collective labor agreement (if there is one).
Production with hazardous working conditions
Harsh and harmful conditions, according to labor legislation, are activities in the presence of factors that increase the likelihood of illness and injury to the worker.
These include:
- high physical activity beyond the permissible norm;
- constant presence in a biologically hazardous environment;
- working with toxic substances;
- increased humidity and pressure.
These factors may occur in organizations that carry out activities in the following areas:
- production of building materials - cement, concrete products, roofing and insulating materials. Workers are constantly in contact with chemicals, the effects of which can impair health;
- mining and metallurgy. Workers are exposed to conditions of great noise and elevated temperatures;
- exploration geology;
- electricity transmission;
- hydrocarbon production;
- production of glass and ceramics;
- construction and installation.
Work in the field of geodesy, geological exploration, and microbiology poses a danger to the human body. Earthenware and glass production, industrial production of thermometers and hydrometers are considered harmful. Jobs in electrical, electronics and electronics manufacturing are also classified as having a negative impact.
Legislation guarantees certain compensation measures for harmful working conditions. One of them is the free provision of milk, guaranteed by Art. 222 TK. It must be provided by the employer to the employee for harm.
We suggest you read: An employee has lost his employment document, what documents need to be provided from his last place of work
Types of compensation measures for hazardous production processes:
- Extending rest time. Additional paid days, at least seven days, are guaranteed to employees and are added to the main leave.
- Reducing the working period by reducing the duration of the shift, work shifts. The maximum weekly workload cannot exceed 36 hours.
- Financial surcharges for harmfulness. In this case, the salary is increased by at least 4%.
- Preferential pension. Employees of dangerous organizations have the right to retire early.
- The right to free health improvement and treatment.
- Free security tools for a safe workflow. This includes special clothing and disinfectants. The employer is responsible for purchasing such tools.
For hazardous working conditions, payment, which is assigned on the basis of a special assessment of the labor safety standard, is provided in kind or in financial equivalent. Workers who are exposed to negative chemical and biological effects during working hours are entitled to enhanced nutrition (milk and other products that neutralize the negative risks of radiation).
In 2019, the employer himself has the right to establish the type and amount of compensation measures, taking into account the provisions of the Labor Code. An increase in the amount can be initiated by him. All financial types of compensation are paid from the employer’s insurance contributions, taking into account the tariffs of insurance organizations.
If negative production factors are eliminated, the employer has the right to cancel additional payments. He can take such a step only after carrying out the next SOUT check. The commission must confirm the absence of hazardous factors in specific workplaces.
Subtleties of purpose
In practice, there are situations where danger is not associated with the entire work cycle, but only with individual work tasks. In general, work in a workshop can be safe, but some part of the work, for example, loading consumables, can have a negative impact on health. Then compensation will be assigned only for the period of performing harmful actions.
In this case, the enterprise administration can choose one of the existing schemes:
- Determining the bonus for each individual employee, taking into account the actual time spent performing dangerous sections of work.
- Establishment of a single additional payment for all employees not lower than the rate prescribed by law.
An amount calculated at 4% of the salary is a mandatory compensation measure. It is prescribed at all enterprises where working conditions are recognized as harmful as a result of an inspection of the environmental safety standards. Additional incentive measures, including surcharges, may be used.
The same benefits and compensations are provided to employees with subclass 3.4 (harmful working conditions of degree 4). Levels of exposure to HFPF can lead to the emergence and development of severe forms of occupational diseases (with loss of general ability to work) during work, and to workers with hazardous working conditions (class 4).
table 2
| Class working conditions | Subclass working conditions | Additional insurance premium rate |
| If the organization has conducted a special assessment of working conditions | ||
| Dangerous | 4 | 8.0 percent |
| Harmful | 3.4 | 7.0 percent |
| 3.3 | 6.0 percent | |
| 3.2 | 4.0 percent | |
| 3.1 | 2.0 percent | |
| Acceptable | 2 | 0.0 percent |
| Optimal | 1 | 0.0 percent |
Table 3
| Class working conditions | Subclass working conditions | Additional insurance premium rate |
| If the organization uses the results of workplace certification | ||
| Dangerous | 4 | 8.0 percent |
| Harmful | 3.4 | 7.0 percent |
| 3.3 | 6.0 percent | |
| 3.2 | 4.0 percent | |
| 3.1 | 2.0 percent | |
| Acceptable | 2 | 9.0 percent |
| Optimal | 1 | 6.0 percent |
Table 4
| Class working conditions | Subclass working conditions | Additional insurance premium rate |
| If the organization has not carried out a special assessment of working conditions or certification of workplaces | ||
| Dangerous | Not important. The work is specified in paragraph 1 of part 1 of article 30 of Law No. 400-FZ | 9% |
| Harmful | ||
| Acceptable | ||
| Optimal | ||
Table 5
| Class working conditions | Subclass working conditions | Additional insurance premium rate |
| If more than 5 years have passed since the workplace certification | ||
| Dangerous | Not important. The work is specified in paragraphs 2-18 of part 1 of article 30 of Law No. 400-FZ | 6% |
| Harmful | ||
| Acceptable | ||
| Optimal | ||
An analysis of the tables shows that failure to carry out special assessment procedures is fraught with large financial losses.
The insurance period required for calculating an insurance pension is the total duration of periods of work in hazardous working conditions for which insurance contributions were accrued and paid to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation.
So if an employee worked in logging all his life, and received a “gray” salary, was not officially employed, and the employer did not transfer additional tariffs, then he cannot count on a preferential pension.
Experience must be proven
The employer must keep separate time sheets of working time in harmful and dangerous working conditions for full-time employment and for part-time employment. In case of part-time work, the employer will pay less contributions and the employee will receive a less pension. Insurance premiums are calculated at the appropriate additional rates from all payments and remunerations accrued to the employee this month.
Please note the following general principle for calculating guarantees and compensation - all of them are provided only in proportion to the amount of time actually worked in the relevant types of work with hazardous working conditions.
In addition, to assess the negative impact of harmful and dangerous production factors, operational, technological and other documentation for machines, mechanisms, equipment, raw materials and materials used by the employer in carrying out production activities must be taken into account (clause 19 of the order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated April 12, 2011
No. 302n “On approval of lists of harmful and (or) dangerous production factors and work, during which mandatory preliminary and periodic medical examinations (examinations) are carried out, and the Procedure for conducting mandatory preliminary and periodic medical examinations (examinations) of workers engaged in heavy work and at work with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions”).
The state allows the employer to take preventive measures to reduce occupational injuries and occupational diseases of workers and sanatorium and resort treatment for workers engaged in work with harmful and (or) dangerous production factors, approved. by order of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated December 10, 2012 No. 580n at the expense of insurance contributions to the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation.
This means that the cost burden of improving working conditions can be partially offset.
From these funds, the employer can send employees with subclasses 3.1 and hazardous working conditions to sanatorium treatment. Workers with an optimal and acceptable class of working conditions can travel to resorts and sanatoriums, of course, but not at the expense of contributions to the Social Insurance Fund, but, for example, at the expense of the enterprise’s profits. If there is one.
https://www.youtube.com/watch{q}v=-_vuk4h77mk
The employer is obliged to indicate all compensation due to the employee for hard work and work with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions in the employment contract, indicating the characteristics of working conditions in the workplace (Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Overtime
Overtime work is work performed by an employee at the initiative of the employer outside the working hours established for the employee: daily work (shift), and in the case of cumulative accounting of working hours - in excess of the normal number of working hours for the accounting period.