Basic and additional wages are a salary or rate and various additional payments and allowances, incentives and compensation payments. The article provides an example of compensation and additional payments, as well as special cases of salary payment.
Although there is no such concept as basic and additional wages in the current labor legislation, in practice it is used quite often. Based on the name itself, you can guess the essence of these terms and the scope of their application. In this article we will briefly talk about what basic and additional wages are, what they consist of, and what factors influence the amount of earnings.
History of the origin of the term
The word “salary” originally meant salt, a product whose production was controlled by the state. It was received by persons in the royal service. In Rome and medieval Europe, people predominantly worked there. During the revolution, a large number of new professions appeared, but remuneration even for such specialists was paid based on the results of their work per day. With the emergence of large corporations in the 19th and 20th centuries, there was a sharp increase in the number of personnel. At the same time, labor began to be paid in the form of a fixed rate. Today, salary is part of the fee along with benefits, allowances and bonuses.
Part-time salary
According to the law, a part-time worker is the same employee of the enterprise as the main employee: he signs the same employment contract, he is subject to internal labor regulations, labor safety standards and job descriptions, he has the same rights and obligations as all other people who work in the same enterprise as him. Therefore, with regard to wages, a part-time worker has the same rights as the main employee, with the exception of one nuance: according to the law, the number of working hours of a part-time worker should not exceed half of his working hours at the main place of employment. Consequently, if the enterprise has established time-based wages, the part-time worker will receive wages for the hours actually worked, that is, less than the main employees of the enterprise in the same positions.
If the enterprise has established a piece-rate form of remuneration, the salary of a part-time worker may ultimately be even higher than the salary of the main employees - the legislation does not directly allow this, but the Labor Code states that the employer has the right to independently establish the form of remuneration at his enterprise . This remuneration option is somewhat risky, because if the main employees compare salaries and find out that it is clearly not in their favor, they can file a complaint with the labor commission, and the employer will have to prove the legal grounds for their decision.
Back to contents
Factors
The level of basic and additional wages is influenced by:
- The price that is paid for means of ensuring the ability to work (satisfying the needs of employees). It depends on the level of wealth, traditions, etc.
- Personnel qualifications.
- Working conditions. A person should receive compensation for working in difficult and harmful conditions.
- Performance. As productivity increases, workers' additional wages increase as the employee produces more products of the required quality. But the salary increase should occur in such a way that all the “winnings” are not used to pay for income.
- Market conditions are the relationship between the demand for personnel and the degree of competition between applicants.
- Results of the organization's activities. Making a profit allows management to pay bonuses, which affects the overall level of income.
- Personnel policy. Advanced training, career advancement, and creative activity should be encouraged and reflected in monetary rewards.
- Degree of socialization. Part of the salary is used to pay taxes and contributions to the state. The larger these mandatory payments, the less funds the employee has left.
About salary
All employed citizens receive income for their work, and it, in turn, is divided into two types: the basic salary and the additional one. The first includes the salary set by the organization. Its amount is fixed and is considered the guaranteed minimum that any working employee can count on. However, the final cash payment may be higher if incentives or compensation are added to it. It also happens that the salary is less than expected, and this may be due to the fact that the employee was on vacation for several days at his own expense.
There is also such a thing as a tariff rate. It is payment for a quota completed within a specific time frame. For example, a person will work a certain number of hours or days. Either he will carry out the agreed number of instructions or serve clients. In any case, the rate will be determined by the employer.
Please note that different regions and enterprises will have their own wages. Therefore, employees in the same positions will receive different amounts. The salary depends on other factors that also need to be taken into account.
Income is affected by:
- Employee qualifications. Naturally, the higher it is, the greater the payments for work will be.
- Working conditions. There are types of work that are life-threatening or harmful to health. If a person works in one of them, then he will receive special allowances that increase his monthly income.
- There is a demand for people with a certain specialty. This factor depends on the city and area. Because, for example, in the village there will be more demand for tractor drivers than for IT technology specialists.
- State of affairs of the company. If the organization fulfills qualitative and quantitative indicators, then employees can count on bonuses.
- Company personnel policy. There are organizations where they organize competitions in production. For example, the shift that completes the most work will be given a monetary reward.
Kinds
The state regulates the minimum wage (minimum wage). This is a social guarantee that is mandatory throughout the country for enterprises of all forms of ownership.
Average salary is an indicator that characterizes the amount of accrued salary per employee. It is calculated by dividing the amount prepared for payment by the average number of personnel.
There is also a division into nominal and real wages. The first represents the amount paid, and the second represents the number of goods that a person can purchase with the money received. In other words, this is a consumer basket.
Salary during maternity leave
According to labor legislation, women are entitled to leave during pregnancy: 70 days before childbirth and 70 days after, while the number of days before or after childbirth may vary, but the total number - 140 - remains unchanged. In case of complicated childbirth or the birth of more than one child, the leave is extended by several more days.
Salary during maternity leave - those same 140 days - must be paid to the employee according to the average earnings (for the last calendar year) or a scholarship if the employee was an apprentice (student).
Moreover, even the unemployed who are registered with the employment service have the right to benefits, since these funds are paid from the Social Insurance Fund. If an unemployed person has not worked anywhere for more than two years before registering, or has never worked anywhere at all, the benefit is paid from the minimum wage.
In addition to the payment of earnings, state benefits are also provided for registration for pregnancy, the birth of a child and for caring for a child up to the age of one and a half years.
Back to contents
Structure
Remuneration for work consists of a basic and additional salary. Let's look at them in more detail.
1. Additional wages - monetary reward for efforts made above established standards (ingenuity, unique working conditions, etc.). It includes allowances, additional payments, and compensation payments provided for by law. Types of additional wages:
- vacation (study, additional, annual);
- severance pay in case of dismissal of an employee;
- preferential hours for teenagers and disabled people;
- a break from nursing mothers;
- downtime is not the fault of the employee;
- amounts paid upon referral to advanced training courses;
- time for performing government duties, etc.
Additional wages also include bonuses based on the results of the organization’s economic activities. They are paid from retained earnings. Their size is set by management individually for each employee, depending on his success, contribution to work results, length of service and other conditions.
2. Basic salary - remuneration that is paid in accordance with the standards (time, service, production) under the employment contract. It is included in the cost of manufactured products, accrued for time worked and includes:
- payment according to tariffs and salaries;
- compensation amounts;
- allowances.
List of additional payments to the salary
Additional payments are both regulated and not regulated by law, since in one case, for example, bonuses, the legislator indicates that the employer has the right to apply or not to apply such incentive measures at the enterprise, and in the other, the employer is obliged to charge various bonuses, for example, for harmful production.
All possible allowances are specified in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, but not all of them are mandatory in the form in which they are indicated.
Supplements are awarded in the following cases:
- Carrying out work in production that is harmful and dangerous to life and health, in accordance with Art. 147 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, such employees are entitled to a bonus of 4% of the basic salary.
- Work in difficult climatic conditions, including in the Far North, Siberia, the Far East, etc. Each region has its own bonus for work, but payments are regulated in accordance with Art. 148 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
- Carrying out work overtime. So in accordance with Art. 152 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the first two hours of work after the expiration of the established time for performing duties are set at one and a half rates per hour of work, and for hours exceeding this norm - at double the rate.
- Carrying out work on weekends and holidays, if the employee does not work in shifts. In accordance with Art. 153 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, such an employee is entitled to double pay for a working day.
- Carrying out work at night. Within the framework of Art. 96 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, work hours from 22 to 6 hours are paid at an increased rate of no less than 20%.
- Combining positions or performing work for a temporarily absent employee of the organization, in accordance with Art. 151 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, payment for such work is negotiated individually between the employee and the employer, on which an agreement is concluded.
Additional salary should always be provided for in an employment or collective agreement, since in the absence of it, the employer has the right not to pay bonuses. But this situation is illegal if the employee works in hazardous industries, in negative climatic conditions, with irregular working hours, etc.
Forms of remuneration
Time-based. An employee receives remuneration for a certain number of hours of work, regardless of the volume of services performed. The amount of money to be paid is determined by multiplying the tariff rate by the labor time spent. If a time-based bonus system is used, then a bonus is added to the salary in a certain ratio. The amount to be paid is calculated based on the data from the time sheet.
Direct system. Additional wages are calculated based on data on the number of units of manufactured products at current prices. If a bonus is provided for exceeding production standards with the achievement of the required quality indicators (no defects, complaints, etc.), then a piece-rate bonus system is used. With a progressive piecework scheme, payment increases for output. If an indirect piecework system is used, the earnings of assemblers, adjusters, and assistant foremen are calculated as a percentage of the salary of the main site workers.
Chord form. It provides for the calculation of salaries for performing certain tasks.
Composition and varieties
Any work, be it hired work or work as an individual entrepreneur (hereinafter referred to as an individual entrepreneur), provides for payment for labor .
If an individual entrepreneur calculates the level of wages based on the financial capabilities of his enterprise, then the employer in a particular company/institution is obliged to pay the employee honestly earned money stipulated by law and the employment contract, regardless of the profitability of the activity.
The main document regulating the need and procedure for calculating wages is the Labor Code of the Russian Federation .
There are two types of remuneration :
- Basic - the calculation is made based on the actual time worked, the quality and quantity of work performed, the established salary or tariff schedule per unit of labor, various incentives, bonuses, additional payments for work under special conditions (non-working hours, night hours, downtime through no fault of the employee, etc.) .d.).
- Additional – calculation of payment during non-working hours, fixed at the legislative level. Additional wages include payments for use and non-use of vacation, dismissal benefits, payments during pregnancy and child care, benefits for minor workers, and educational leave.
Forms of remuneration mean the method of calculating remuneration:
- Piecework – the calculation is made on the basis of the actual work performed and depends on the tariff rate for the production of a unit of product (service). As a rule, piecework wages are paid when working on an assembly line, in art, when paying postmen, and advertising agencies.
- Time-based – calculation is made on the basis of tariffs for work per unit of time and actual time worked (time worked fund). Hourly, daily and monthly rates apply to this form. As a rule, all line personnel of enterprises, administration, and engineers rely on this form of labor.
Having decided on the form of remuneration, the employer considers the components of the expected income of employees, which includes three main positions :
- Remuneration is the backbone of the employee’s compensation. It is calculated based on the qualifications of the employee, the quantitative component of labor, the quality and complexity of the work performed.
- Compensation – various allowances for work in conditions other than normal. Normal conditions are regulated by law, and therefore any deviation from the norm is the reason for the formation of compensation payments. The compensation system may include work in special climatic zones with a particular level of environmental pollution.
- Incentive payments are a type of additional employee incentives. As a rule, incentive payments are established when planned quantitative or qualitative indicators are met, for responsible work, for high assessment of the company by outside experts, etc. This type involves the payment of bonuses.
Payment nuances
Downtime through no fault of the employee is documented on a service sheet with the same name. It indicates the reason, culprits, duration, rate. If the downtime was not the fault of the employee, then this time is paid in the amount of 2/3 of the salary. In other cases, compensation is not provided.
If a defect is detected, that is, parts and components do not comply with established standards, then the presence or absence of payment depends on the reasons for its formation. According to Art. 156 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, a product damaged through no fault of the employee is paid at 77% of the rate. Partial defects are compensated depending on the degree of readiness of the product. If the failure occurred due to the fault of the worker, then no payment is made.
Additional wages at night (that is, from 22:00 to 6:00) are calculated based on information from the accounting sheet and paid:
- for time workers – in the amount of 16% increase in the daily hour rate;
- for piece workers - within 16% or 20% of the tariff rate.
The amount of additional wages during overtime is also calculated based on the timesheet data. The first two hours are paid at one and a half times the rate, the subsequent ones at double. Overtime must not exceed 120 hours per calendar year for an individual employee. By agreement with management, such work may be compensated by increasing additional rest time.
The coefficient of additional wages on holidays corresponds to twice the hourly (daily) rate and price. If the employee wishes, the reward can be exchanged for an additional day of rest.
Remuneration for minors is carried out at established rates, and for students and schoolchildren - in proportion to the time worked. The manager can also make payments from his own funds up to the level of the tariff rate.
Additional wages for production workers who work in difficult conditions are not regulated by the state. The calculation is made on the basis of a collective agreement. Specific amounts are determined based on the results of certification of workers' places. It is carried out by comparing measurements of levels of the working environment with certain hazard parameters. The results of the analysis are reflected in a map with information about working conditions.
Monetary remuneration for breaks in work for nursing mothers who have children under the age of 1.5 years is carried out in half the daily rate (for time-based payment) or in the amount of piecework earnings. Additional time spent is credited to the worker's account.
Individuals receive compensation for performing public and state duties in the amount of average earnings at their place of work. This is how additional wages of all types are calculated.
Calculation and payment of additional salary
Payment of additional wages is carried out simultaneously with the transfer of funds at the basic salary or tariff rate, however, its calculation requires taking into account all possible circumstances of assigning additional payments to a specific employee.
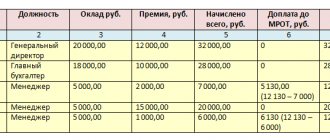
For example, Ivanov A.B. works in a hazardous enterprise for a long time. His salary is 62,000 rubles, the work norm is 120 hours per month. At the same time, for each hour of overtime, a bonus is given in the amount of 0.5% of the employee’s salary. During the month, Ivanov worked 32 night hours from 10 pm to 6 am, as well as 101 hours of day shifts.
Based on the above, you can calculate the size of his salary in the current month:
| Wage | Working conditions | Calculation rules | Notes | Total amount | |
| Basic salary | If the standard is met, the employee is assigned a full salary | – | An employer cannot fine an employee or withhold any funds from his salary. The only source of impact is partial or complete loss of bonuses. | 62,000 rubles before taxes | |
| Additional payment for hazardous production | 4% of salary | In accordance with Art. 147 Labor Code of the Russian Federation | 2,480 rubles | ||
| Payment at night | 20% of the cost of one hour of work | Within the framework of Art. 96 Labor Code of the Russian Federation | 3,306.67 rubles | ||
| Overtime surcharge | 0.5% for each hour of processing | In accordance with local regulations of the enterprise | 4,030 rubles | ||
| TOTAL: | 71,816.67 rubles | ||||
The employee will receive 71,816.67 rubles, however, income tax of 13% will be withheld from this amount, and the employer will provide the employee with 62,480.50 rubles.
Rest compensation
Officially employed persons are granted annual leave. The right to use them arises after six months of continuous work. In some cases, leave can be granted before this time, subsequent ones - strictly according to the schedule. The basis for the calculation is an order indicating the employee’s data and the duration of the break, which at the legislative level is at least 28 calendar days.
Additional wages are calculated based on average salaries and number of days. For calculation purposes, a period of three calendar months is used that precedes the start of the vacation. The following times and amounts are excluded from the billing period:
- the employee received “sick leave”;
- the employee was on vacation at his own expense;
- the employee did not work due to downtime that was not his fault;
- the employee was unable to perform duties due to a strike;
- for other reasons.
If during the billing period there is a change in tariff rates at the enterprise, then the employee’s salary must be adjusted accordingly. Recalculation is carried out in different ways:
- if the changes affected the billing period, then the rates are adjusted;
- if the salary was increased before the start of the vacation, then the average salary increases;
- conditions changed during vacation - only the part of the salary that falls during the period of change is adjusted.
The exchange of vacation for monetary remuneration is allowed only in part exceeding 28 days (Article 126 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). If an employee resigns, he is compensated for unused vacation time. Additional wages are calculated based on the average daily salary. For valid reasons, an employee may be sent on leave without pay for an individually considered period.
Example
An employee of the organization received leave from October 20 for 28 days. In July and August, his earnings amounted to 5 thousand rubles, monthly bonus - 2 thousand rubles, quarterly remuneration - 4 thousand rubles. The calculations will use the average monthly number of days in the calendar – 29.6.
First you need to determine the amount of bonus payments. They are counted no more than one for each indicator. Therefore, all three things can be included in the calculation. The quarterly bonus is taken into account in full.
Annual remuneration: 4 × 3: 12 = 1 thousand rubles.
Bonus amount: (2 × 3) + 4 + 1= 11 thousand rubles.
The additional salary is: (15 + 11) : 3 : 29.6 × 28 = 8198.12 rubles.
Business trip
The manager was on a business trip for 3 days. His salary for the billing period was 23 thousand rubles, an allowance for combinations - 30%, and a bonus - 15%. The number of days worked is 247. The total amount to be paid will be: (23 + 23 × 30%) × 12 + 23 × 15% = RUB 362,250.
Average salary: 362,250 rubles: 247 days = 1,467 rubles. – this amount is due to the employee per day.
Business travel: 1,467 × 3 = 4,399.80 rubles.
Vacation
Let's take the conditions of the previous example and calculate the amount of payment for 28 days.
The total payment amount remains the same – 362.25 thousand rubles.
Average earnings: 362,250: (29.6: 12) = 1,468.3 thousand rubles.
Vacation pay: 1468.3 × 28 = 41112.40 rubles.
Accounting Features
When calculating vacation pay, as well as compensation for days of unused vacation, the average amount of earnings is determined based on the previous 12 months.
All accrued wages for this period are divided by 12 and then by 29.4.
Calculation and accounting with examples
Example 1:
The employee was granted leave from September 10 for 28 calendar days. Over the previous 12 months, he was credited with 187,333 rubles.
In this case, the average earnings per day will be 531 rubles. (RUB 187,333/12/29.4), the amount of accrued vacation pay is RUB 14,868. (531x28).
There are calculation nuances if not all days in the accounting period were worked.
In this case, an additional calculation is made of the number of calendar days for months with not fully worked out norms.
Example 2:
The employee is on vacation from September 4 for 28 days (calendar). The salary accrued for the period from September to August is 155,000 rubles, while in April he worked only 18 days, in April 30 days according to the calendar.
The average daily payment will be 454.49 rubles. (155,000 rubles/(29.4x11+(29.4/30x18))), and the amount of accrued vacation pay is 12,725.72 rubles. (530.01x28).
Accounting for disability benefits also has its own characteristics.
The employer calculates and pays for the first 3 days of sick leave, and the subsequent days are compensated by the social insurance fund.
To pay for sick leave, the average daily earnings are calculated based on the amount of wage accruals for the previous 2 years and divided by 730 days.
Those payments from which insurance premiums were paid are taken into account.
Then the resulting value is adjusted taking into account the employee’s existing insurance record:
- with more than 8 years of experience, 100% of the average salary is accrued;
- with 5 to 8 years of experience, 80% of the average salary is accrued;
- with less than 5 years of experience, 60% of the average salary is accrued.
There are separate categories of employees, the amount of their compensation is 100%, regardless of the length of insurance:
- veterans of the Great Patriotic War;
- workers injured at work;
- disabled people;
- women on maternity leave;
- an employee who is the breadwinner (the only one) of three or more children under age.
The calculated daily allowance should not be higher than the amount established by the state.
If the employee did not have accruals for the previous period, the minimum wage established by the state at that time is taken into account. Also, the minimum wage is used if the employee’s earnings are less than his salary.
The average earnings for compensation for other absences are much easier to calculate - the amount of all wages accrued for the previous year is divided by the number of days that were actually worked during this period.
All these payments are made to employees on the basis of supporting documents provided to the accountant.
Features of accruals
The amounts of calculated wages, which are additional, are reflected in account 70 “Settlements with personnel for wages”.
dedadi.ru
Postings
All transactions for accounting for settlements with employees are reflected in account 70 “Settlements with personnel”. It is passive: all accruals are shown on credit, and deductions are shown on debit. The balance reflects the organization's debt to personnel. Sources of payment of additional wages are:
1. Attribution to the cost of production:
- Dt 20, 23, 25, 26 (main, auxiliary production, general production, general business expenses) and accounts of other costs (29, 44). The CT displays a score of 70.
- Accruals for labor associated with the acquisition of inventories, liquidation of property, and capital investments are reflected by posting Dt 08 (10, 91, 15, 11) Kt 70.
- In enterprises with seasonal work, vacations are provided unevenly. In such conditions, the cost of production is calculated in a different way. Amounts for expenses are written off evenly throughout the year, regardless of the month of payment. This creates a reserve for vacation payments. These figures are displayed on accounts DT 20, 26, 25, 23 CT 96 “Reserves for future expenses.” Then they are written off in KT 70.
2. At your own expense
— A percentage of additional wages can be paid from retained earnings (DT 91 KT 70) or income from participation in capital (DT 84 KT 70).
3. At the expense of the Social Insurance Fund (DT 69 CT 70).
In all these cases, account 70 is debited with:
- 50 “Cashier”, 51 “Cash accounts” - salary is paid in cash or sent to cards.
- 44 “Finished products” – if wages are paid in goods.
- 76.4 “Deposited Funds”. If within three days the employee has not received remuneration, then these amounts must be deposited in the accounts and then paid upon demand.
Legislation regarding wages
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that the employer is obliged to pay wages every half month and must familiarize the employee with the procedure for payments and accruals. At the same time, when paying employees the required funds twice a month, the employer must pay half the salary, although in practice many prefer to set a fixed amount or a percentage of the fixed salary and make payments in this way.
The laws of the Russian Federation annually establish the level of the minimum wage. Below this amount, the employer does not have the right to pay the employee, he also does not have the right to limit the maximum wage - all allowances, incentives, etc. must be accrued above the established minimum. Otherwise, the law does not limit employers; they have the right to independently determine:
- wage system;
- type of remuneration;
- salaries and tariff rates;
- order and amount of bonuses.
All decisions of the employer regarding wages must be recorded in the internal documents of the enterprise: internal labor regulations, employment contract, collective agreement, Regulations on bonuses, Regulations on remuneration and the like. Every employee of the enterprise must be familiar with these documents.
Back to contents
Thirteenth salary
This is a bonus that is paid to employees at the end of the year. It can be framed as financial assistance. If the bonus is provided for in the employment contract, then all expenses reduce the income tax base (IPT). But they will have to pay UST, as well as contributions to the pension fund. Bonuses not specified in the employment contract do not reduce the base for calculating the NPP and are not subject to unified social tax. But in this case, it is better to provide the employee with financial assistance. The amount of funds that is not subject to taxes is stipulated by law. It is advisable to issue it if:
- the enterprise calculates the UST at the marginal rate;
- The organization has no taxable net income.
In the first case, the company will need to pay more NPP, saving on UST. In any case, the total amount of deductions will be less than when registering bonuses.
What is salary
Perhaps some people, having read the title of our article, will say that this is an uninteresting topic and accountants, and not ordinary workers, should deal with the calculations.
But we do not agree with this, because every person who receives a salary must control the amount of his payments. Accountants sometimes make mistakes, and in this case, you may not receive your hard-earned money. Sometimes it happens that managers deliberately do not pay the necessary bonuses that are due to employees by law. To prevent this from happening, we recommend that you find out how wages are calculated and what their amount depends on.
Salary is a material reward for work performed. Accrued for hours actually worked.
Sick leave
When paying compensation for temporary disability certificates, the main part of the costs falls on the Social Insurance Fund (SIF). Only the first three days are paid at the expense of the employer. The amount of payment depends on the length of service:
- less than 5 years – 60% of the average salary;
- 5-8 years – 80%;
- from 8 years – 100%.
Full sick leave compensation is due:
- WWII veterans;
- workers with occupational diseases;
- disabled people;
- persons on holiday for the BiR;
- employees with three or more minor children.
Concept of salary and wages
You should also distinguish between wages and salary. Salary is the amount that is established for the employee according to the staffing table and constitutes, as it were, the main part of the salary, and the salary itself is what is accrued to the employee, taking into account all the required allowances and deductions, for example, such as:
- personal income tax;
- bonus for length of service;
- regional coefficient;
- bonuses based on the results of the billing period;
- additional bonuses due to a professional holiday or other reason;
- withholding funds that the employee did not hand over to the cashier on time or must compensate for material damage caused to the enterprise;
- social payments.
etc.
Back to contents
Standard
During the times of a centralized economy, additional wages were calculated using complex formulas. Now its size is calculated as a percentage of the main one. The basis for calculations is data on payments for previous periods, which must be adjusted with minor changes.
The standard (N) is calculated by dividing all additional payments (DS) by the wages for the previous period:
N = DV: FZP
The result obtained will be the basis for calculating all additional payments in the current period. Of course, an enterprise can calculate the standard using a different algorithm, which takes into account industry characteristics of its activities and other factors.
Calculation and accrual of additional salaries in an organization is an important point in planning the total amount of costs. It is necessary to take into account all situations in which there may be a need to compensate for the efforts made. If insufficient funds are allocated for wages, this can lead to high staff turnover. In the opposite situation, there will be an unintentional increase in production costs, and therefore a loss of profit.
Factors affecting size
For convenience and control, the employer decides on the method of calculating wages even before hiring an employee . The calculation depends on the number of assigned tasks, the number of current personnel, the complexity of the work and the specifics of the enterprise’s activities.
However, when signing a contract, not many employees ask themselves what their real salary is and what the income specified in the contract depends on:
- The nominal level of remuneration is the cost of an employee’s work that the employer is willing to pay for the work performed. It is calculated based on the quantitative and qualitative characteristics of labor, does not depend on the price level and, as a rule, is discussed at the interview.
- Taxation – this factor is very important. An employer will never offer a salary at which it will pay “unaffordable” payments for an employee. From this point of view, taxation is considered from two sides: the level of social contributions on the part of the employer, and the level of tax deductions from the employee’s salary. The higher the taxation in the country, the lower the level of real wages paid out.
- Price level – the level of real wages is directly related to the price level and inflation in the country. The faster inflation rises, the cheaper real wages become. It should be remembered that the employer is not obliged to tie the income of its employees to rising prices.
Thus, the real income of individuals is associated not only with the decisions of the employer, but also with state policy regarding pricing and taxation.
Examples of calculation and payroll are in this video.
Sample additional agreement on wage indexation
Sample additional agreement
Changes in salary must be reflected in additional agreements, which are drawn up for each change separately. The additional agreement is signed by both parties and has the same legal force as the agreement itself. Wage increases occur periodically at every enterprise.
This is justified by the inflationary processes taking place in the state. Rising prices also entail changes in wages. In order to maintain the standard of living of enterprise employees, company management is obliged to respond to all economic situations in a timely manner.
Sample additional agreement on changing salary terms
The employer is obliged to pay remuneration no later than 15 days from the end of the pay period. If the day off coincides with a payday, employees must be paid the day before.
Vacation pay is accrued and paid no later than three days before the start of the vacation. Among other things, the employer is obliged to notify employees of any changes in the terms of payment of remuneration.
Sick pay is also part of the additional salary
Although most of the temporary disability benefits are paid at the expense of the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation, the law obliges the employer to finance the first 3 days of illness from its own funds. The amounts paid during this period are also included in the additional salary.
Sick leave is calculated based on the amount of average earnings per day and the duration of sick leave in days. Average earnings are determined by summing up income subject to contributions to the Social Insurance Fund for the 2 years preceding the year of sick leave and then dividing the result by 730.
We invite you to read: Fine for jaywalking in 2020
Additional salary includes:
- Employee leave. This includes the main annual, additional and academic.
- Compensation for unused employee vacation.
- Renting apartments for your employees. This payment is very common for workers traveling on business to other cities. At the expense of your employer.
- Payment for unexpected downtime that occurred regardless of the employee.
- Payment for breaks for young mothers with infants. According to the regulations, for one child it is one hour, for two or more – two hours.
- Payments to employees for participation in public events.
- Payment for forced time away from production when an employee undergoes the necessary training to acquire or improve his qualifications.
- Payment for the period when a person could not go to work due to labor and employment leave or illness.
- One-time payments to employees for long and conscientious work.
- Payments for herd, class of profession, etc.
- Payment for business trips and the time the employee spent on a business trip.
- Payments to teenagers for reduced working hours.
The main part of the salary includes only the salary (tariff rate). This is a fixed part of the salary. It is reflected in the employment contract and the employer’s staffing table. The introduction of other payments to the salary (based on the law or at the will of the parties to the employment agreement) is additional, but in some cases the salary can only be a fixed salary.
Consequently, salary refers to the minimum amount of money that an employee has the right to claim when performing a certain job function for a specified period of time.
To set the salary level, the most important indicator is the qualifications of the employee. Its concept includes:
- having a certain level of education;
- previous practice of carrying out the relevant work;
- qualification category (if available).
Two other indicators - complexity and volume of work - are no less important, since qualifications are closely related to them. It is this that presupposes the possibility of performing a labor function with a certain level of complexity and volume.
It is important not to confuse this level with personal indicators (for example, resistance to stress, independent decision-making). As a rule, personal indicators have a greater influence on the level of the position held than on the salary.
In what cases is it paid?
Additional leave, like the main one, is subject to payment in accordance with the calculated average wage per day. For some cases related to additional salary, there are specific features when calculating and planning the wages:
Payment of sick leaves. The main part of the costs in this case is borne not by the enterprise, but by the social insurance fund. It is he who allocates funds to pay sick leave to employees. As for the employer, he must pay only the first three days. Therefore, only these three days need to be taken into account when planning the fund.
At the same time, the amount of payments is not the same for all employees - it depends on the insurance length of each of them:
- if the insurance period is less than 5 years, the employee will receive payment in the amount of 60% of the average salary;
- if the length of service is within 5-8 years, then the compensation amount will be 80%;
- with more than eight years of work experience, an employee can count on 100% sick pay.
Also, 100% of payment, regardless of length of service, is due to:
- WWII veterans;
- employees who have suffered a work injury or occupational disease;
- working disabled people;
- employees who are on leave due to employment and labor regulations.
- persons who have three (or more) minor children as their dependents.
pay . Occurs based on the calculated average salary of an employee for one day. In this case, the billing period is the previous year, that is, 12 months. You need to add up the amount of wages received by the employee for a given period and divide it first by the number of months (that is, twelve), and then by the average monthly number of calendar days (29.4). This value is then multiplied by the total number of vacation days.
The total duration of leave for employees is set at 28 calendar days, but in some cases additional leave is also provided.
The remaining additional non-working hours subject to payment (breaks for nursing mothers, time spent on government duties or on business trips) are paid to the employee in accordance with his average salary.
Salary for less than a month
In order to calculate wages for employees who have worked less than a full month, you need to know how the wages of these employees are paid: at an hourly rate, daily rate or monthly rate.
1. When paying at an hourly rate, the established hourly rate is multiplied by the number of hours actually worked. If a bonus is paid, it is multiplied by the established standard of hours and then divided by the number of hours actually worked.
2. When paying at the daily rate, similar payments are made at the hourly rate, only multiplied by the number of days worked. The bonus, if any, is calculated in the same way.
3. When paying at a monthly rate, you first need to calculate the average daily earnings: the established salary must be divided by the number of working days in the month. The resulting average daily indicator is multiplied by the number of days actually worked in the month. The premium is calculated in the same way.
It should be noted that when an incomplete month has been worked, bonuses are usually not awarded, but the employer has the right to establish other standards at his enterprise.
If the enterprise uses a piece-rate form of remuneration, wages are calculated depending on the employee’s production rate for the billing period.
Back to contents
Incentive payments
One of the components of additional wages includes such a thing as compensation payments. They also include payment for time that was not worked by the employee. This includes:
- Payment for all types of vacations, except administrative ones.
- Cash compensation for unused vacation upon dismissal of an employee.
- Payment for temporary sick leave or, more simply, for the time you are on sick leave.
- Payment for the duration of a medical examination at the enterprise.
- Time compensation for working nursing mothers. They are entitled to a break of thirty minutes every three hours.
- Payments for being on business trips.
- Compensation for dismissal of employees who left due to layoffs.
- Payment for downtime caused by the employer.
You can also highlight payments that compensate for working conditions, that is, special additional payments for working in hazardous industries or in the North. This is regulated by the Labor Code, so the employer is obliged to adhere to the established standards.
As already mentioned, additional wages are the sum of two types of payments. Stimulating ones belong to the latter. Their list includes those types that are called additional payments, bonuses or financial assistance.
A number of accruals are regulated by internal documents of the organization, for example a collective agreement. Thus, bonuses can be introduced for professional holidays, such as accountant’s or engine builder’s day, as well as assistance for the birth of a child or for anniversaries.
This list can also include incentives based on work results, for example, the popularly called “thirteenth” salary, which, in essence, is a bonus based on the results of the organization’s annual activities.
All these payments are not directly specified in the Labor Code, that is, they must be enshrined in the internal documents of the organization.
This part of the salary should be distinguished from compensation for costs associated with the performance of labor duties and guaranteed by law (Article 164 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). These include, in particular, payments:
- for business trips;
- for transfer to work in another area;
- in case of downtime due to the fault of the employer;
- for delay in issuing a work book, etc.
The number of “salary” compensations includes, for example:
- payments for special working conditions;
- compensation for work in certain areas with an unfavorable climate;
- when combining positions;
- for overtime work, etc.
Let's look at some of them in more detail.
For example, according to Art. 146 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, employees who work in conditions recognized as dangerous or harmful to health are entitled to a higher level of remuneration compared to other employees.
Read about some of the nuances of harmful working conditions here.
We invite you to read: Vacation schedule for 2020: 10 tips for drawing up (Crib sheet for Employers)
Certain areas for which work in which a compensation bonus is awarded include:
- regions of the Far North;
- areas equated to the northern regions;
- other areas with special climatic conditions.
When determining the coefficient of the corresponding additional payment to wages, it is necessary to take into account the legislation:
- federal (norms of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Law of the Russian Federation dated February 19, 1993 No. 4520-1);
- regional (increased rates of coefficients may be established);
- THE USSR.
IMPORTANT! Many Soviet norms and regulations continue to apply in this area.
For more information about bonuses for work in certain areas, read the article “What benefits are available to workers in the Far North?”
All accruals made in favor of an employee can be conditionally divided into those made for the performance of work duties and those due to him on other grounds. As a result, the earnings of any employee are divided into:
- Basic: Salary for actual time worked;
- Tariff rate for hours actually worked;
- Piece price for the volume of products produced or work performed.
If the basic earnings are calculated by multiplying tariffs per unit of volume or by the number of hours produced, then additional charges are made according to various schemes. Some of them are prescribed at the legislative level, and some are regulated by the needs of the company and are developed by them independently. As a result, the basic and additional wages form the total income of the employee.
Basic salary and additional salary - differences according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Salary is a monetary reward for work performed. But besides this, employees can receive financial assistance for various purposes - medical services, recreation, treatment, etc.
The main part of the salary is basic and permanent payments to employees:
- salary - a fixed amount paid monthly to the employees of the enterprise;
- payment at a tariff rate is a salary for a standard amount of work completed within a certain period of time. This may be a standard of time, number, number of objects served, etc. The rate is determined by the employer.
Additional wages are considered to be monetary payments of a compensatory, incentive or one-time nature. The legislation contains a list of all these payments, and the conditions for accrual have been worked out.
Download the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
What payments qualify as additional wages?
Additional salary includes the following accruals:
- stimulating - raises, additional payments, bonuses, incentive amounts, bonuses for overtime work, inventions, successes and achievements, one-time employer incentives;
- compensation (allowances, additional payments) - according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, these include payment for work in harmful, dangerous conditions, for work related to state secrets, encryption, work in difficult climatic conditions, in areas contaminated with radioactive substances.
The compensation fee includes all types of vacation pay, compensation for unused vacations, length of service, preservation of average earnings during study while away from work, etc. Additional funds also include funds accrued for the entire time when people are absent from work for valid reasons mentioned in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation:
- breaks at work for nursing mothers, if there is one child, an hour break is allowed, if there are two or more children, two hours are allocated per working day;
- fulfillment of government duties;
- sick leave;
- child benefits;
- travel allowances;
- provided payment of housing to employees at the expense of the enterprise;
- forced downtime;
- paid time to undergo medical examinations, various trainings, etc.
For example, teachers are paid extra for leading clubs, extracurricular activities, and professional categories.
The procedure for calculating and paying additional salaries
The calculation of this part of the payments is made for each employee individually. Compensation allowances are calculated in accordance with the regulations of the Russian Federation or regulations of the enterprise, if they provide for better conditions. Overtime hours are taken into account based on worksheet data. You can work no more than 120 hours per year. Additional payments for difficult working conditions are stipulated in the collective agreement, and the amounts are calculated after certification of workplaces. Both parts of the salary are accrued and paid inseparably, at least twice a month.
Not paid: time during which people are absent from work without valid excuses (absenteeism), days taken at their own expense. During this time, no salary will be accrued.
View types of salary supplements in the form of a diagram
Projects of salary forms
Since today's legislation provides for the payment of wages strictly twice a month, no more and no less, which may not be entirely convenient for both employees and employers, drafts of other forms of remuneration are periodically submitted to the State Duma.
For example, in many countries around the world there is an hourly wage. It is believed that such a norm is more conducive to developing the potential of the country’s economy, and workers perform their job duties better when they know how to evaluate a unit of their working time. It is difficult to introduce such a norm on the territory of the Russian Federation, although projects have been discussed since 2000.
Also, a bill requiring weekly wages was also discussed several times. Experts believe that in this way the turnover of funds will be significantly increased, which will have a beneficial effect on the economic situation as a whole.
Was the information interesting or useful?
Yes120
No30
Share online