How are night wages paid?
Night time is considered to be the period from 22:00 to 6:00 (Article 96 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
At the same time, working hours, including night hours, should not exceed 40 hours per week. According to labor legislation, the duration of work at night is 1 hour shorter, without the need for further work. If, for example, the day shift lasts 8 hours, the night shift should be no more than 7 hours. This rule does not apply to those workers who were hired specifically for night work (for example, for part-time work at night with daily pay), or to those who have a shorter working time (workers under 18 years of age, disabled people of groups I and II , persons employed in harmful and dangerous work, etc.). It also does not apply where a shift schedule is adopted with a 6-day work week with one day off.
When working at night, each hour of work must be paid additionally: Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated July 22, 2008 No. 554 established the minimum amount of extra pay for night hours, which is equal to 20% of the hourly tariff rate, or the salary calculated per hour of work. The employer can establish the same or greater percentage of additional payment, fixing it in the collective agreement, employment contract, or other internal regulatory act with the approval of the trade union (Article 154 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
When involving employees in night work, the manager must issue an order indicating the persons working on the night shift, as well as the amount in which they will be paid additionally for night hours.
Example
An employee with a salary of 50,000 rubles. with a 40-hour work week, March 2020 was fully worked, which is 175 working hours according to the standard. Of these, 6 hours, due to production needs, had to be worked at night. The additional payment established by the order for night work is 20%. What will the employee's salary be for March?
Let's determine the hourly rate in March 2020: 50,000 rubles. : 175 hours = 285.71 rub. at one o'clock.
Payment for work at night: 285.71 rubles. x 1.2 x 6 hours = 2057.10 rub.
Salary for March: 285.71 rubles. per hour x (175 hours - 6 hours) + 2057.10 rubles = 50,342.09 rubles.
Article 154 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Wages for night work in 2020
These include:
- medical workers; employees of the penal system; professional, sentry and paramilitary fire protection.
Some workers cannot, under any circumstances, be required to work at night:
- women expecting a child; women raising children under 3 years of age (can work overnight with written consent); employees under the age of 18; mothers and single fathers who are raising children under 5 years of age (can go to work on the night shift after writing a statement of consent).
If a work shift consists of day and night hours simultaneously, the premium will be accrued only for those hours that fall between 10 pm and 6 am. To determine how much to pay an employee for performing his work duties at night, the accountant must: Calculate the salary for 1 day of daytime work.
Payment for night hours during a shift work schedule
In shift mode, work is carried out in 2 or more shifts, when the production process is longer than the permissible working hours; this may also be necessary to increase the volume of output, rational, efficient use of equipment, etc. A shift schedule is established for a certain group of workers, not forgetting about compliance with working time standards.
Employees working on a shift schedule are paid at night, falling for the entire shift, or part of it, in the same way as described above.
Example
The company has introduced a shift work schedule: the day shift lasts from 9-00 to 22-00, the night shift - from 22-00 to 9-00. The additional payment for “night stays” is established by order of the director - 25% of the tariff rate. The hourly wage rate for an employee is 200 rubles. at one o'clock. In March, the employee went on the second shift 4 times. Let's calculate the amount of additional payment for night work in March.
Night time lasts from 22-00 to 6-00, which means that each shift accounted for 8 night hours, and in total 32 night hours were worked in March (8 hours x 4 shifts).
Additional payment to the tariff rate during night work hours is: 200 rubles. x 25% = 50 rub.
The “night” surcharge in March will be: 50 rubles. x 32 hours = 1600 rub.
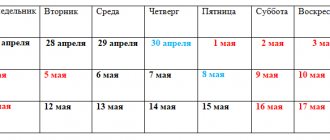
What time is considered night?
Night working hours - from 22.00 to 6.00
The concept of “night time” is defined in accordance with Art. 96 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. According to it, this concept covers the period from 22.00 to 6.00 the next day.
The work shift must be one hour shorter than the day shift, and this hour is not subject to further work. But there are exceptions to this rule:
- the employee was hired specifically to work at night;
- the employee is already working a reduced schedule;
- a person works on a six-day schedule with one day off;
- when production specifics require it.
We pay overtime hours
What is overtime? This is the time worked in excess of the standard working hours during the accounting period. That is, overtime hours are calculated at the end of the accounting period. The total number of overtime hours (Chsv) is determined as the difference between the actual time worked according to the Timesheet (Chf) and the estimated standard hours for the accounting period (Nchr):
Chsv = Chf - Low.
Please note that in its letter dated 07/02/2018 No. 1139/0/101-18/28, the Ministry of Social Policy explained that the difference between the calendar standard of working time (more about this in the article “Calendar standard of working time for summarized accounting” of this issue) and the calculated standard of working time (see the calculation in the article “The employee was sick, was on vacation: adjusting the standard of working time”) is that to determine the first, the full use of working time is provided, and the second takes into account the hours not worked by the employee.
It is the calculated standard working time that is used as the value necessary to calculate the overtime hours worked or the unworked hours of the working time standard.
Please note: when recording working hours in aggregate, overtime work in excess of the standard working time on individual days, weeks, and months of the accounting period is not considered overtime, if the general standard of working time for the accounting period is maintained. After all, overtime that occurs on individual days during cumulative accounting can be compensated for by additional days of rest or a corresponding reduction in the duration of work on other days of the accounting period.
Attention!
Overtime work should not exceed 4 hours per two days for each employee and 120 hours per year.
This is expressly enshrined in Art. 65 Labor Code. Failure to comply with this requirement will result in a fine of 1 minimum wage as for non-compliance with other requirements of labor legislation (Article 265 of the Labor Code). But even if an employee has more overtime hours per year than the established maximum (120 hours per year), all overtime hours will be subject to double payment.
Please remember that there are restrictions on having employees work overtime. More details about this can be found in the article “Work Schedules (Shifts)” in this issue.
There are some peculiarities when calculating overtime hours (see letter of the Ministry of Labor dated June 15, 2007 No. 148/13/133-07). Let's look at them in more detail.
This situation may arise when an employee, during the summary accounting, worked on a holiday, which was not planned by his work schedule (shift). As we said above, if an employee was hired to work on a holiday, which, according to his shift schedule, is a day off, then payment for work on such a day is made in the amount of double the hourly wage rate in addition to the salary. At the same time, when calculating overtime hours, work on holidays and non-working days (Article 73 of the Labor Code), carried out in excess of the established working hours, is not taken into account for the accounting period, since it has already been paid in double amount (clause 11 of Method Recommendations No. 138).
We act similarly in a situation where an employee worked on a day off. In this case, if he chooses double pay as compensation, when calculating overtime hours for the accounting period, hours worked on weekends paid at double rate will not be taken into account.
However, be careful! If work on holidays/non-working days was carried out according to the work schedule (shift schedule), then the hours worked on such days are not deducted when calculating overtime hours!
Let me explain. When calculating the normal number of working hours of the accounting period (i.e., the estimated standard of working time used to calculate overtime hours), days are excluded that, according to the work schedule, fall during the time during which the employee, in accordance with the law, was released from performing his work duties due to vacation, performance of state or public duties, temporary disability, completion of advanced training courses, etc.
How to determine the exact number of such “exception” hours, especially in situations of illness or vacation, which are paid in calendar days? Specialists of the Ministry of Social Policy in letter No. 229 note the following: if the employee was on vacation, when calculating the normal number of working hours of the accounting period, days on an 8-hour working day schedule (with a 5-day working week) are excluded, since vacations are granted in calendar days. If the institution has a different work schedule (for example, 6 days with a 7-hour working day), then we exclude the corresponding number of calendar days in hourly terms.
For more information about calculating the standard working time if the employee was sick or was on vacation, read the article “The employee was sick or was on vacation: adjusting the standard working time” in this issue.
Also remember: if the last day of vacation (sick leave) fell on a work shift according to the work schedule, then you need to start work on the next shift, which falls on the work schedule or according to an adjusted work schedule due to his vacation (illness).
Overtime hours have been counted. The next step is paying them.
We pay overtime hours
Art. “commands” in the payment of overtime hours. 106 Labor Code.
With a time-based form of remuneration, work overtime (Ost) is paid at double the hourly rate (Tch) (Part 1, Article 106 of the Labor Code):
Osv = Chsv x Tch x 2.
With a piece-rate form of remuneration for work overtime, an additional payment is made in the amount of 100% of the tariff rate of an employee of appropriate qualifications, whose labor is paid on an hourly basis, for all overtime hours worked (Part 2 of Article 106 of the Labor Code).
Important!
Payment for all hours of overtime work is made at the end of the accounting period or upon dismissal of the employee.
Compensation for overtime work by providing time off is not permitted.
As mentioned above, to pay for overtime hours you need to know the hourly tariff rate (H). If the employee is an hourly worker, then there is no problem. You just need to multiply the hourly rate by 2 and the number of overtime hours.
The situation is a little more complicated with employees who have a fixed salary (monthly tariff rate). The hourly tariff rate must be calculated. There are also nuances here. Here the accounting period comes first (see also the figure below).
Calculation of the hourly tariff rate for payment of overtime hours (if a salary is established)
In this case, the hourly tariff rate is calculated by dividing the salary (Ohm) by the monthly calendar standard of working hours (Nchk) in the corresponding month (see also letters of the Ministry of Social Policy No. 229 and dated 02.17.2012 No. 51/13/116-12) :
Tch = Ohm: Nchk.
If the accounting period is equal to a quarter, half a year, or a year, the hourly tariff rate is calculated by dividing the salary established in the last month of the accounting period by the average monthly number of hours for the accounting period, taking into account the standard working time for this period:
Tch = Ohm: Chs.uch.
In turn, the average monthly number of hours for the accounting period is found by dividing the calendar standard of working time for this period, established in compliance with the requirements of Art. 50 of the Labor Code, for the number of months in the accounting period (Much) (see letters of the Ministry of Labor dated May 18, 2007 No. 380/13/84-07 and the Ministry of Social Policy dated April 24, 2017 No. 1264/0/101-17/282) :
Chsr.uch = Nchk: Much.
Example 1. A summarized recording of working time has been established for an employee. The accounting period is a month. Salary - 3800 UAH.
As of December 2020, the calendar standard working time, calculated according to a 5-day work week with days off on Saturday and Sunday, is 158 hours.
The employee actually worked 168 hours in accordance with the shift schedule, including 10 hours of overtime.
To pay for overtime hours, we calculate the hourly tariff rate:
3800: 158 = 24.05 (UAH/hour).
Overtime pay will be:
24.05 x 2 x 10 = 481 (UAH).
Example 2. Summarized working time recording has been established for the institution’s guards. The accounting period is quarter. The salary of a watchman in December 2018 is 1921 UAH.
The calendar standard for working hours for the 4th quarter of 2020, calculated according to a 5-day work week with two days off on Saturday and Sunday, is 510 hours (176 October + 176 November + 158 December).
In accordance with the work schedule, the watchman worked 517 hours, including 181 in October, 172 in November, and 164 in December.
Let's determine the average monthly number of hours for the 4th quarter by dividing the calendar norm established for this quarter by 3 (the number of calendar months taking into account the period (quarter)):
510: 3 = 170.00 hours.
The hourly tariff rate is:
1921 UAH : 170.00 h = 11.30 (UAH/h),
where 1921 is the monthly salary established in December 2020 (in the last month of the accounting period).
The number of overtime hours is equal to:
517fact - 510norm = 7 (h).
The amount of overtime pay is:
11.30 x 2 x 7 = 158.20 (UAH).
As you can see, in contrast to additional payments for work at night (evening, if provided for in the collective agreement), holidays/non-working days, as well as on weekends (if the employee is specially called to work on a day off), which are accrued based on the results of each month , overtime hours are paid at the end of the accounting period.
Documents and abbreviations used
Labor Code - Code of Labor Laws of Ukraine dated December 10, 1971.
Method recommendations No. 138 - Methodological recommendations for the use of summarized recording of working time, approved by Order of the Ministry of Labor dated April 19, 2006 No. 138.
Letter No. 229 - letter of the Ministry of Social Policy dated 07/05/2012 No. 229/13/116-12.
MW - minimum wage.
The concept of such work
Work is recognized as overtime only if the initiator of its implementation is the employer. Involvement to it is not formalized in writing in all cases. Therefore, the legislator pointed out the fact that if evidence is provided confirming that an employee is at his workplace during non-working hours on the verbal order of the boss, payment should be made as overtime. In cases where a person is at work voluntarily, payment at an increased rate is not charged.
The employment contract may indicate that the working day is irregular. In this case, the employer may initiate work that will not subsequently be paid additionally.
Labor Code of the Russian Federation in Art. 152 indicates that for additional work the amount of remuneration is paid in an increased amount. Also, the employee has the right to replace the cash payment during the rest period. It should be emphasized that the duration of additional rest should not be less than the number of overtime hours worked. An employee can distribute these hours at his discretion, including using them entirely in one day.
This article clearly indicates that in order to receive rest for overtime worked, the employee’s desire alone is not enough. The head of the enterprise independently decides on the possibility of providing it. If this is not possible, payment is made twice as much.
Regulations under the Labor Code
According to Article 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, entry to the workplace is possible with or without the written consent of a subordinate.
Part 2 of the article indicates that an employee can go out after hours by giving written consent when:
- It is necessary to perform the work that, due to a technical failure, could not be completed during working hours. At the same time, failure to comply will result in damage and, in some cases, loss of property, and will also create a threat to the lives of citizens.
- Failure to complete work on time can lead to the termination of the work functions of a large number of employees of the organization. In this case, we are talking about carrying out temporary work necessary to restore the functionality of a complex.
- It is necessary to replace an employee if the work he performs does not require a break according to the regulations.
Consent is not required:
- When performing work aimed at restoring performance after exposure to elements or disasters.
- When performing work that is considered socially necessary.
Article 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes the length of time that can be worked overtime. Regardless of the position, it should not be more than 4 hours per day and 120 hours annually. This rate is calculated for two periods. Based on their results, a certain value is formed and then compared with the total number of overtime days worked.
What is flexible working time? Read this article.
How to get additional leave for irregular working hours - see.
How do you pay?
Article 152 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation regulates payment for additional hours. The remuneration can be set at least one and a half or double size. It should be noted that employees are entitled to one and a half times more for the first two hours of such work, then the payment increases to double the rate.
As a rule, these payments are stipulated in the employment contract. Related issues are also specified in the local regulations of the enterprise.
If working hours are calculated using the traditional system, overtime is set daily. The first two hours of such work must be paid at the end of each working day at one and a half times the rate.
The legislator has not established how funds for overtime activities should be calculated. In this regard, employers have to resort to Article 153 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which regulates work on holidays and weekends. So, the payment is set depending on the salary, or rather, no less than one and a half times the salary. For piecework wages, the payment amount is calculated depending on the tariff, but also not less than its one and a half equivalent.
Today there is no single algorithm for calculating the hourly rate from the salary, so each employer independently determines this indicator in a way convenient for him. Typically, the calculation procedure is established in a collective agreement or in any other local regulatory act of the enterprise.
Thus, the hourly rate can be set by dividing the salary by the average monthly number of working hours in the corresponding calendar year, depending on the length of the working week. It should be emphasized that incentive bonuses will not be taken into account, since only the hourly rate is taken into account when calculating the surcharge.
Example
The employee's salary is set at 30,000 thousand rubles. Also, depending on the quantity of goods sold, he is entitled to a monthly bonus of 50% of his salary. Plus, his combined position as head of the sales department brings him 10,000 rubles.
The regulation on remuneration of the enterprise establishes the calculation of the hourly rate for payment of months that were partially worked, and also determines the amount of compensation, calculating it by dividing the salary by the average monthly working time. So, in September the employee worked 184 hours, which is the average monthly norm, and he became entitled to receive a bonus. He was also required to work overtime 2 times for 4 hours. Thus, he should be accrued the following payments:
- Salary – 30,000 thousand rubles.
- Prize – 15,000 thousand rubles.
- The additional payment established for combining positions is 10,000 thousand rubles.
- Payment for additional work – 2282 rubles (30,000/184 * 4 * 1.5 + 30,000/184 * 4 * 2).
You can learn more about all the nuances of payment from the following video:
Tariff-free form
In the case of using a non-tariff wage system, one of two calculation options is used:
- In the first case, hours spent at the workplace in excess of the established time are transferred to conditional ones. Due to them, the wage fund increases. It should be emphasized that for the first 2 hours the payment coefficient is set to be no less than one and a half times, and for the subsequent time - no less than double.
- In the second option, for each employee it is necessary to calculate the average earnings per hour of time. The additional payment is calculated in accordance with the employer’s regulations, but must not be less than 50% of the money earned per hour for the first 2 overtime hours. Subsequent hours are subject to payment based on 100% of average hourly earnings.
Payment on weekends at night: what does the Labor Code of the Russian Federation say?
According to the norms of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, for night work, employers are required to pay their subordinates at least 20% of the daily salary or tariff rate. Work on holidays and weekends is paid separately at double the rate, so employees actually receive two additional payments.
If the working conditions of employees deviate from normal, i.e. they have to perform their duties at night, when calculating additional payments, they must be guided by the following standards:
- Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other acts containing labor standards, but not contradicting the Code;
- A collective agreement certified by a representative of the Trade Union organization;
- Labor agreements concluded with personnel;
- Addendums to employment contracts with employees;
- Local documents of the organization.
Payment for work at night and on holidays is regulated by different articles of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation; accordingly, employees are entitled to both types of additional payments. So, according to Art. 96 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, “night time” should be understood as the period from 22:00. 00 min. until 06 o'clock 00 min. For example, if an employee works from 8 p.m. 00 min. until 08 o'clock 00 min. the next day, then the time from 8 to 10 pm is paid at the usual rate, and from 22 o'clock. until 06 o'clock in the morning - double.
What specific norms of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation must be followed when calculating payment for work on holidays and at night:
- Art. 96 Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- Art. 154 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation on payment for night work;
- Art. 153 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation on payment on weekends and official holidays.
The last two articles should be considered in more detail. Yes, Art. 154 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation indicates that each hour of work outside the established schedule must be paid at an increased rate, and it cannot be lower than the monetary base regulated by legal acts. The exact amounts of remuneration for night work are established by collective agreement, taking into account the opinion of representatives of the Trade Union and can only deviate to a greater extent.
It is worth noting that, even if employees are employed on a shift schedule that involves working at night, they are still entitled to compensation for this, as well as additional payments for holidays. The only exception is the situation when, instead of cash payments, the employer provides subordinates with time off for overtime: in this case, additional payments are canceled.
Art. 153 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which regulates the specifics of remuneration on weekends or holidays, obliges additional payments to be made in at least double the amount:
- For employees working at hourly or daily tariff rates - at least one daily rate in accordance with the tariff;
- For employees working on a transaction basis - a minimum of double piecework wages;
- For employees receiving a salary in accordance with their official salary - at least one hourly or daily rate in excess of the salary, provided that the work was performed within the established number of working hours according to the monthly norm. Double payment is made if processing exceeds the monthly norm.
Thus, labor legislation allows increased additional payments for overtime work, but they must be made at double the rate. Also, the law does not prohibit the establishment of increased additional payments for work on holidays and weekends, however, this must be reflected in local acts of enterprises: labor or collective agreements, additional agreements to them, etc.
Changes in labor legislation
From July 1, 2020, it is possible to conclude employment contracts in a new way, pay for overtime work, work on weekends and holidays, and many new nuances are being introduced regarding irregular hours.
According to the new amendments, if an employee works more than normal on a holiday or day off, then now these days must be paid only once at double the rate. The previous procedure, when it was necessary to pay for the same hours again as overtime (at time and a half for the first two hours, at double time for the remaining hours) is no longer applied.
The amendments changed the procedure for paying overtime work. The rule of time and a half pay for the first two hours of overtime work will now apply exclusively on weekdays. According to the new rules, weekend overtime must be paid at double the rate.
If an employee went to work on a day off for half a day, the organization must pay double only for the hours that were actually worked. From July 1, Article 93 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is applied in a new edition. According to the new rules, the employer has the right to establish both part-time options at once. For example, a 4-day week with a 7-hour workday on Mondays and Fridays. Previously, you only had to choose one of these two options. Another change concerns the procedure for establishing irregular working hours. Amendments to Article 101 limit the employer’s right to establish an irregular work regime.
From July 1, the employer does not have the right to establish an irregular day for an incomplete week and part-time working day. For example, when an employee works 4 days a week with a 6-hour working day.
An irregular work schedule for a part-time week can now be introduced only when the employee works full time. Thus, the week may be incomplete, but the day itself must be complete. Otherwise, the employer has no right to introduce an irregular regime.
Payment for work on weekends and holidays, at night - innovations in payment
Before making such entries in a document, the head of the company asks the opinion of the trade union. According to the instructions, payment in this case should be made at least double the amount:
- employees working for piecework - not less than double the piecework rate.
- workers whose work must be paid at hourly and daily tariff rates - in an amount not lower than double the hourly or daily tariff rate;
- employees receiving an (official) salary - in an amount not lower than a single hourly or daily rate (part of the salary) for 1 hour or 1 day of work in excess of the salary in the case when work on a non-working holiday or day off was carried out within the monthly working hours; or in an amount not lower than double the hourly or daily rate (part of the salary) for 1 hour or 1 day of work in excess of the salary, if the work was performed in excess of the monthly working time standard;
We recommend reading: Unpaid traffic police fines in Yaroslavl
Constitutional Court in paragraph.
What is overtime
Overtime is considered to be work in excess of the established working day (Article 62 of the Labor Code). Overtime work under the hourly wage system is paid at double the hourly rate.
Under the piecework wage system, for overtime work, an additional payment is paid in the amount of 100% of the tariff rate of an employee of appropriate qualifications, whose labor is paid on an hourly basis, for all overtime hours worked.
At enterprises where, due to production (labor) conditions, the daily or weekly working hours established for a given category of workers cannot be observed, it is permitted to introduce summarized recording of working hours so that the duration of working hours during the accounting period does not exceed the normal number of working hours. In the case of cumulative accounting of working hours, all hours worked in excess of the established working hours in the accounting period are paid as overtime. Compensation for overtime work by providing time off is not permitted.
Extra pay for overtime work at night
Each hour of work at night (from 10 p.m. to 6 a.m.) is paid at an increased rate compared to work under normal conditions (Article 154 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). According to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated July 22, 2008 No. 554, the minimum increase in wages for night work is 20 percent of the hourly tariff rate (salary (official salary) calculated per hour of work) for each hour of work at night. At the same time, the authors of the letter draw attention to the fact that if working conditions deviate from normal conditions, then the employee is entitled to increased pay for each type of deviation from normal conditions. For example, if an employee was required to work overtime at night, then such work should be paid both as overtime and as night work. Let us remind you that overtime work (i.e. work performed at the initiative of the employer outside the working hours established for the employee) is paid for the first two hours at least one and a half times the rate, for subsequent hours - at least double the rate (Art. 152 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Create HR documents in the web service using ready-made templates
Payment for night guards on public holidays 2020
Unlike weekends, non-working holidays are the same for all employees, regardless of the regime; the list of such days is established by part one of Art.
112 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Therefore, if according to the schedule an employee must go to work on a holiday, such a day of work is subject to payment in an increased amount according to the rules of Art. 153 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. At the request of an employee who worked on a day off or a non-working holiday, he may be given another day of rest. For example, the salary of a security guard at a school will not differ in terms of accrual from the standard salary of any other employee.
An order or instruction is drawn up by the employer in the form established by the document flow.
It includes:
- information on the formation of additional payments for work at night and on holidays.
- first name, last name and patronymic of the employee;
- the period of the work schedule when it will be valid;
- schedule;
Salary and minimum wage: how to compare these values
The monthly salary of an employee who has fully worked the standard working hours during this period and fulfilled the labor standards cannot be less than the minimum wage (Part 3 of Article 133 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The salary includes the following parts:
- salary (official salary), tariff rate;
- compensation, namely additional payments and allowances for work in special climatic conditions; remuneration for work in conditions deviating from normal (that is, for work in harmful or dangerous working conditions; for work at night; overtime work, etc.);
- incentive payments (for example, additional payment for length of service; bonuses for performing specific work, based on the results of the reporting period, for quitting smoking, for saving consumable materials, etc.). Also see “What does a salary consist of: Rostrud has issued a memo on wages.”
Thus, the salary as a component of the salary may be lower than the minimum wage, provided that the total monthly salary, including incentive and compensation payments, is not less than the “minimum wage”. Are additional payments for overtime work, for work on holidays and weekends or at night included in the salary in order to compare it with the minimum wage? Experts from the Ministry of Labor stated the following. Since overtime work is carried out outside the normal working hours, it is not necessary to include the corresponding payments in the salary in order to correlate it with the minimum wage. A similar approach, according to the authors of the letter, should be followed when taking into account other compensation payments. For example, if work on weekends and non-working holidays or at night was carried out within the normal working hours, then additional payments for it are taken into account when comparing the employee’s monthly salary with the minimum wage. If such work was performed outside the normal working hours, then there is no need to include additional payments in the salary in order to correlate it with the minimum wage.
>Overtime work at night
Payment for work on holidays
In 2020, the minimum wage is 11,280 rubles.
If the accruals are below the established minimum, then the employee is given an additional payment up to the minimum wage. How did the decision of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation affect the rules for calculating wages? Judicial representatives decided that additional payments for work in non-standard conditions cannot be taken into account when comparing earnings with the minimum wage.
That is, when calculating the minimum wage, do not include:
- Overtime work.
- Allowances for night work.
- Additional pay for working on holidays and weekends.
Now there will be no disputes on the issue of whether payment for holidays is included in the minimum wage. The decision of the Constitutional Court of Russia dated April 11, 2020 clearly established that payments for work on holidays and weekends, as well as night work and overtime, cannot be taken into account in the minimum wage. Consequently, such allowances must be calculated above the minimum wage.
Let's determine on which days double pay in 2020 is due to all workers.
When can workers work overtime at night?
The administration has the right to detain workers at the end of their main working hours only with their consent, stated in writing, in such cases:
- Due to technical problems, the work was not completed on time. It is impossible to leave it in an unfinished or unfinished state, as this will cause harm to people or property.
- It is necessary to repair equipment and mechanisms in a short time, since their downtime leads to an interruption in the activities of many workers.
- An employee stays behind after his shift because his replacement did not show up.
There are special critical circumstances in which the administration has the right to force employees to work beyond the norm even without their written permission:
- Activities are carried out to improve the defense of the state or to avoid accidents at work.
- Repairs damage after industrial accidents or natural disasters.
- Work is underway to supply people with water, gas, heat, electricity, for the functioning of sewerage, public transport and communications.
It is illegal for teenagers under 18 years of age and pregnant women to work beyond normal limits. Disabled people and women with children under 3 years of age have the right to work extra time if this does not pose a threat to their health. They can refuse such assignments and must confirm by signature that the administration has notified them of this.
If night work is not the norm for a given employee’s work schedule, then it is paid both as night work and as overtime.
It is important to remember that the Labor Code of the Russian Federation allows working beyond the norm for no more than 120 hours per year and no more than 4 hours for two days in a row.
Special contingent of personnel
Certain categories of employees do not have the right to work night shifts, without taking into account their opinion on this matter. Another list defines the circle of workers who can be involved in night work if they express their consent.
It is prohibited to work at night:
- women expecting a baby;
- minor workers, except for special categories provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and certain federal laws, for example, those involved in performances or other events.
You can work at night with written consent:
- mothers of young children (under 3 years old);
- disabled people of any group;
- employees who care for disabled people;
- workers caring for unhealthy family members (according to medical opinions);
- single parents with children under 5 years of age;
- guardians of children under 5 years of age.
FOR YOUR INFORMATION!
An employee belonging to this category must be warned in writing that he has the right to refuse to work at night, and in turn, have his consent endorsed.
Remuneration for night overtime work
Employees work more than normal at the request of the administration. Therefore, increased tariffs are introduced when calculating. The first two hours of overtime work are paid at time and a half, and all remaining hours at double.
If an employee wishes to take time off for hours worked in excess of the norm, then they are paid at the usual single rate. Time off is given for the same number of hours that the employee worked in excess of the norm.
For work at night (from 10 pm to 6 am) at least 20% is added to the regular daily tariff rate. If night work is not the norm for a given employee’s work schedule, then it is paid both as night work and as overtime. That is, 20% is added to one and a half and double tariffs.
Let's look at an example of how overtime work at night is paid. The employee worked 4 hours overtime in a month, 2 of which were night hours. His hourly rate is 100 rubles. The first two overtime hours are calculated at time and a half: 100 x 1.5 x 2 = 300 rubles. The next two hours at a double rate of 100 x 2 x 2 = 400 rubles. Supplement for night hours 20%: 100 x 2 x 20% = 40 rubles. It turns out that the total amount for overtime is: 300 + 400 + 40 = 740 rubles.
In a collective agreement or internal local acts of an organization, an additional payment for night work may be set at more than 20% of the rate.
Who may be required to work at odd hours
Legal acts define categories of persons who are prohibited from engaging in labor activities at night. The following are not allowed for such work:
- Employees are pregnant.
- Minor employees, except for citizens under 18 years of age participating in the creation or performance of works of an artistic nature, as well as persons indicated in the List approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 252 of April 28, 2007.
Article 96 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation also identifies categories of employees who can be involved in work at night, but only taking into account their voluntary consent. These include:
- working women with children under 3 years of age;
- women and men raising children under 5 years of age alone (without a spouse);
- employees with disabilities;
- employees with children with disabilities;
- workers caring for a sick family member (subject to an official medical report).
Citizens belonging to the listed categories of employees may be required to work at night if there are no medical contraindications, and there is also the voluntary consent of the employees themselves in writing. This means that these persons’ refusal to work at night cannot be charged as absenteeism.