The length of ladders is more than 5.0 m. The slope should not exceed 60°. Before using the ladder, they are tested with a load of 120 kg applied to one of the steps in the middle of the flight of the ladder, which is in the operating position. Wooden stairs are tested every six months, metal ones - once a year. Extension ladders and stepladders must be equipped with devices that prevent the possibility of them moving and tipping over (for ground - shackles with sharp tips, for smooth surfaces - shoes). When working from an extension ladder at a height of more than 1.3 m, fastening with a safety belt is mandatory. It is not allowed to work on portable ladders and stepladders near or above rotating mechanisms; using manual machines, gas-electric welding; work on tensioning wires and supporting heavy loads.
Training and development of personnel
Exposure to hazardous factors leads to injuries, and harmful factors to occupational illness. By the nature of the action, dangerous and harmful factors are divided into: - physical; - chemical; — biological; -psychophysiological.
Physical factors are divided into: - location of the workplace at a significant height relative to the surface of the ground or floor; — unstable structures, unstable slopes of excavations, trenches, embankments; — moving machines and mechanisms, lifting and transport devices, moving parts of production equipment; - increased voltage in the electrical circuit, the closure of which can pass through the human body; — increased smoke and air pollution in the working area; — increased level of vibration and noise; — increased surface temperature of equipment and materials. Chemical factors: - poisoning; - suffocation; - radiation exposure.
Who needs to be instructed
Joint Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation and the Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation dated January 13, 2003 No. 1/29, which approved the procedure for training in occupational safety, establishes a list of employees whom the employer is obliged to instruct before starting work. These rules are established for:
- all new employees (if a person previously worked at the same enterprise, then quit and was hired again, he still goes through this procedure);
- all citizens who are seconded to the organization from other employers to work in certain areas;
- students from educational institutions sent for internship;
- other persons involved in the production processes of the enterprise.
Persons who have not completed induction training on labor protection are not allowed to work.
Training for employees of a third-party organization - who should conduct it?
General requirements for development, application, evaluation and improvement" (approved by Order of Rostekhregulirovanie dated April 21, 2009 N 138-st) - the following rules are established: When performing work on the territory of the organization, contractors are exposed to the same risks as the organization's employees. Therefore, before starting work, it is necessary to instruct employees of contracting organizations and require them to comply with labor protection at the organization’s site (clause 7.2.2.). The process for selecting contractors working on the organization’s site must contain, among other things, requirements for familiarization with the hazards of the workplace of contractors and (or) their employees, as well as their briefing at the workplace before starting work in order to ensure the labor safety of the contractor’s workers during the execution process their work at the organization’s site (clause 7.2.3.).
Similar requirements are contained in another standard - GOST 12.0.230-2007.
Appendix 2
| Form | |||
| Certificate of admission | |||
| for repair or construction work | |||
| at the existing FPV (workshop, site) | |||
| Gor.________________ | "____" __________ 200__ | ||
| __________________________________________________________________________ | |||
| (name of enterprise (workshop, site) | |||
| We, the undersigned, are the head of the workshop (section) _____________________________ | |||
| (FULL NAME.) | |||
| and a representative of the general contractor responsible for the work ____ | |||
| __________________________________________________________________________ | |||
| (full name, position) | |||
| have drawn up this act as follows. | |||
| The company allocates a site, ______________________________________________ | |||
| for production on it _____________________________________________________ | |||
| (Name of works) | |||
| under the guidance of technical personnel - a representative of the general contractor for the following period: | |||
| beginning “_____” ______________ ending “_____” _______________ | |||
| Before starting work, the following measures must be taken to ensure the safety of work: | |||
| No. | Event name | Deadline | Executor |
| Head of workshop (section) _________________ | |||
| (signature) | |||
| Responsible to introduce the general contractor __________________________ | |||
| (signature) | |||
| Note. If it is necessary to carry out work after the expiration of this permit certificate, it is necessary to draw up a permit certificate for a new period | |||
Introductory training on labor protection in 2 presentations!
Important
It is allowed to perform manual work with cement, lime, etc. at a material temperature of no more than 40°C. Dangerous cargo should be unloaded with the engine turned off.
Info
Rigging work or slinging of loads must be carried out by persons who have a certificate for the right to perform these works. Methods for slinging loads must exclude the possibility of the load falling or sliding.
4.6. Safety requirements when performing electric welding and gas-flame work are regulated by Section 9 of SNiP and the instructions in force at the enterprise. Electric welders must have an electrical safety group of at least II and confirm it annually.
Work sites must be freed from combustible materials within a radius of at least 5.0 m, and from explosive equipment and materials - at least 10.0 m.
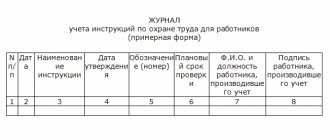
Recording those who have completed induction training
Each employee who has received an “induction” must be recorded in the appropriate journal according to the uniform form assigned to the enterprise. Typically the following information is recorded:
- date of instruction;
- Full name and position of the trainee;
- Full name and details of the instructor;
- signatures of both parties.
You can also enter additional information if the manager deems it necessary, for example, the results of checking the effectiveness of the training.
Requirements for business documentation require the pages of the magazine to be numbered, bound and sealed.
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! A sample of the title and first pages of this magazine must be added to the approved induction program as appendices.
Briefing for contractor's employees
The chief engineer of the General Contracting Organization is personally responsible for the untimely execution of the approval certificate in the form established in the appendix to SNiP. Admission to the site is made after developing, together with the Contractor, a schedule for performing combined work and ensuring joint measures to ensure these works. The Chief Engineer of the General Contractor determines and provides the Contractor with a section of the territory limited by the appropriate coordinates under the guidance of the Contractor, after which the latter is responsible for organizing work in the allocated area. If joint measures are required before the start of work, they are recorded in the approval certificate and implemented within the agreed time frame. 4.9.
Safety requirements during operation
3.1. The person responsible for the safe performance of work by a third party is responsible for:
— for compliance by employees of a third-party organization with labor regulations on the territory and premises of the existing free trade union;
— for the presence of personnel of a third-party organization in places not provided for by the permit.
3.2. The person responsible for carrying out work at the existing free-porting water supply facility is responsible for:
— for the presence of warning posters and inscriptions on the current SPV;
— for conducting targeted training and ensuring labor safety;
— for violations of safety requirements committed by operating personnel and leading to the creation of dangerous conditions and an accident with employees of a third-party organization.
3.3. Employees of third-party organizations are prohibited from:
— clutter the passages inside the premises of operating self-propelled industrial enterprises with materials and waste;
- smoking indoors (except for specially designated areas);
— leave gas welding and electric welding equipment in working condition after work and during lunch breaks.
Conducting induction training for contractor employees
A work permit for work in areas where hazardous or harmful factors are present is issued by the chief engineer of the General Contracting Organization to the foreman or foreman of the General Contracting Organization to perform work in areas where hazardous production factors are present, the occurrence of which is not related to the nature of the work performed. The work permit is issued for the period necessary to complete a given scope of work and is controlled by the chief engineer. Contractors bear full responsibility for the work carried out by their workers in hazardous areas! factors without issuing a work permit. 4.10. Approximate list of places of production and types of work, na1; the implementation of which requires the issuance of a work permit, SNiP. EL. Carrying out work using hydraulic lifting machines and cranes in the security zones of overhead power lines, warehouses of flammable liquids and flammable liquids or liquefied gases. E.2.
Safety requirements before starting work
2.1. Before starting work, the work manager from a third-party organization and a representative of the current self-propelled company are required to issue an approval certificate (Appendix 2).
2.2. The permit certificate is drawn up in two copies, one of which is kept by the person responsible for the safe performance of work at the operating FPV facility, the other – by the person responsible for the safe performance of work by a third party organization.
2.3. Responsibility for compliance with the measures provided for in the approval certificate lies with the heads of the third-party organization and the current self-propelled company.
2.4. The approval certificate must define the area where work will be carried out for a third-party organization and define its boundaries.
2.5. Before starting work, taking into account its specifics, a third-party organization, together with a representative of the current self-propelled company, determines the work for which it is necessary to issue a permit (Appendix 3).
2.6. A work permit is issued before the start of work.
2.7. If the conditions for the work change, or if the safety measures prove to be insufficient, the work permit is canceled by the person responsible for the safe execution of the work of the current self-employed worker.
Resumption of work is permitted only after the issuance of a new permit.
2.8. The work permit is issued in two copies and is kept by the persons specified in clause 2.2 of these Instructions.
2.9. Construction and installation work must be carried out in accordance with the work project or technological maps.
2.10. In cases where repair or construction work is carried out in the auxiliary premises of existing self-propelled fires (shower room, bathrooms, storage rooms, etc.) and does not require turning off equipment or the general power supply, then these works are carried out under the supervision of operating personnel after targeted instruction.
2.11. Duties and responsibilities of the parties for the safety of work.
2.11.1. Before starting work, a third-party organization provides the management of the existing self-propelled company with:
— a copy of the order appointing a person responsible for the safe performance of work;
— a list of workers to perform these works, indicating their profession, electrical safety group, and the number of the certificate of knowledge testing on labor protection;
— a log of registration of repeated briefings with a signature of all employees about the completion of repeated briefings.
In addition, the third-party organization is required to provide all its employees with personal protective equipment.
2.11.2. Before starting work, the management of the existing self-propelled company provides the third party with:
— a copy of the order appointing persons responsible for the safe performance of work (position, electrical safety group, certificate number for testing knowledge of labor protection), with the right to issue a work permit, conduct targeted training with all employees of third-party organizations;
— explanatory note (containing characteristics of equipment or structures subject to reconstruction, indicating hazardous production factors).
2.11.3. The person responsible for the safe performance of work by a third party organization is obliged to:
— together with the person responsible for the safe performance of work at the current self-employed labor force, become familiar with safety measures and working conditions directly at the workplace;
— together with all employees, receive targeted training;
— notify the person responsible for the safe performance of work at the existing self-propelled plant about the change in the composition of the team and, until they receive targeted instructions, do not allow them to work.
2.11.4. The person responsible for the safe performance of work at an operating free-port site is obliged to:
— issue a work permit;
— familiarize the person responsible for the safe performance of work by a third-party organization with safety measures;
— conduct targeted training and familiarize employees of third-party organizations with evacuation routes in case of danger.
Who is responsible for the labor safety of contractors? (Gerasimenko N.)
The completion of preparatory work at the construction site must be accepted according to the “Act on the implementation of occupational safety measures”, drawn up in accordance with SNiP. 5. Personal protective equipment is provided to workers according to the list approved by the employer on the basis of the “Rules” approved by the resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated December 12, 1998, paragraph 51 and “
Model norms". 6. Safety signs are installed at the construction site to notify workers about hazardous factors and areas of their action in accordance with the standards of safety standards and on the grounds specified in clauses 4.9 and 4.10 of SNiP. 7. The investigation and recording of industrial accidents is carried out in strict accordance with the Regulations approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 73 of 01/01/01.
Cases involving employees when they perform their job duties and work on behalf of the organization are subject to investigation and recording.
Instruction No. 000 on conducting introductory briefing on labor protection for employees of the organization and other participants in construction involved as a contract and subcontract (Introductory briefing) Introductory briefing on labor protection is carried out with all newly hired workers, regardless of their education or position, with temporary workers and persons seconded from other organizations, with representatives of contractors and subcontractors used at the site as external labor force. The main goal is to become familiar with the basic labor laws and safety regulations in force at a given site.
Compliance with the occupational safety requirements set out in these instructions is mandatory for all persons present at the site and familiarized with signature in the introductory briefing registration log. The victim or eyewitness immediately notifies his work supervisor about every accident that occurs at work; organizes first aid; takes measures to prevent the development of an emergency situation; preserves the situation as it was at the time of the incident until the investigation begins. If it is impossible to record the situation, it is necessary to make a diagram of the incident. All cases with a fatal or serious outcome, group cases are investigated by the labor inspectorate, which, upon completion of the investigation, transfers the investigation materials to the Prosecutor's Office. The remaining cases are investigated by the employer through its own commission. The degree of severity is determined at the request of the employer by clinical expert commissions (CEC) of the medical institution where the victim is treated within 3 days from the date of receipt of the request.
Attention
GOST “Platforms and stairs for construction and installation work” establishes safety requirements for all elements of platforms and stairs; GOST “Scaffolding means” establishes the types and technical requirements, completeness and marking of these means used in construction; GOST “Fencing of inventory sites and areas for construction and installation work” establishes the classification of fencing, technical requirements for them, requirements for resistance to external influences, requirements for reliability GOST 12.4.059-89 “Inventory safety fencing”; establishes requirements for the fencing of workplaces at height and passages to them to protect people from falling into places where there is a difference in height. A complete list of GOST SSBT standards in force at the enterprise is located in the administration and is available for review.
: Is it necessary to conduct introductory safety training with employees of other organizations performing work under civil law contracts with us?
Who can be an instructor
This is an important issue that the employer needs to decide before issuing an order for induction training. People who can conduct such training are identified in clause 7.1.2 of GOST 12.0.004-90. These may include:
- trained specialist – labor protection engineer;
- an experienced worker selected for this purpose by management;
- the boss himself or his representative;
- a representative of an accredited organization involved in labor protection;
- foreman, teacher, foreman, head of a structural unit, etc.
NOTE! The responsibility of the instructor selected to conduct the introductory briefing is fixed in the management order.
Legal basis:
In accordance with Article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer is obliged to provide, including:
- safety of workers during the operation of buildings, structures, equipment, implementation of technological processes, as well as tools, raw materials and materials used in production;
- prohibition from work of persons who have not undergone training and instructions on labor protection, internship and testing of knowledge of labor protection requirements in accordance with the established procedure.
Federal Law No. 206-FZ of July 24, 2009 “On Amendments to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation,” which entered into force on January 1, 2010, amended Art. Art. 209 and 211 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The concept of “Occupational Safety and Health Requirements” was set out in a new edition - state regulatory requirements for labor protection, including labor safety standards, as well as labor protection requirements established by the rules and instructions for labor protection.
In accordance with these amendments, the Government of the Russian Federation approved the Regulations on the development, approval and amendment of regulatory legal acts containing state regulatory requirements for labor protection. The document delimited the areas of application of labor protection legislation and legislation on technical regulation, which led to a reduction in the number of types of regulatory legal acts containing state requirements. This list included:
- occupational safety standards
- rules and standard instructions for labor protection
- state sanitary and epidemiological rules and regulations (sanitary rules and regulations, sanitary standards, sanitary rules and hygienic standards that establish requirements for factors in the working environment and the labor process).
Thus, a new type of regulatory legal acts was introduced - labor safety standards. They have become part of a new system of by-laws and establish mandatory rules, norms, procedures and criteria aimed at preserving the health and lives of workers.
One of these mandatory labor safety standards is “GOST R 12.0.007-2009. System of occupational safety standards. Occupational safety management system in the organization. General requirements for development, application, evaluation and improvement" (approved by Order of Rostekhregulirovanie dated April 21, 2009 N 138-st) - the following rules are established:
When performing work on the organization's premises, contractors are exposed to the same risks as the organization's employees. Therefore, before starting work, it is necessary to instruct employees of contracting organizations and require them to comply with labor protection at the organization’s site (clause 7.2.2.).
The process for selecting contractors working on the organization’s site must contain, among other things, requirements for familiarization with the hazards of the workplace of contractors and (or) their employees, as well as their briefing at the workplace before starting work in order to ensure the labor safety of the contractor’s workers during the execution process their work at the organization’s site (clause 7.2.3.).
Similar requirements are contained in another standard - GOST 12.0.230-2007. System of occupational safety standards. Occupational safety management systems. General requirements" (put into effect by Order of Rostekhregulirovaniya dated July 10, 2007 N 169-st) - measures for contractors working on the organization’s site must, in particular, ensure familiarization with the dangers of the workplace of contractors and/or their employees, as well as their instruction at workplaces before starting work in order to ensure the safety and health of the contractor’s employees during the performance of work at the organization’s site (paragraph d. clause 4.10.5.2.).
How to properly organize work with a contractor?
Briefly the main thing:
- Your enterprise must develop a Standard (Regulation) on working with contractors. A template for this provision can be ordered at:
- Fix labor protection requirements in the contract with the contractor
: add a separate section to the contract “Labor safety during work performance” - Make sure that the contractor’s personnel
have certificates for labor protection and the right to work (gas-electric welder, slinger, etc.), and that workers are provided with the necessary protective equipment - Your Customer is not responsible for an accident involving your contractor's personnel. The general contractor (i.e., your organization) is responsible for the subcontractor to the customer.
If an organization engages contractors in its work, it must take a number of measures to ensure that contractors and their employees comply with labor safety requirements
. For this:
- require contractors to report all employee incidents (injuries, illnesses and contractor incidents);
- familiarize the contractor's employees with the hazards in the workplace, give them introductory training, check the availability of certificates of completion of training in labor safety and to perform specific work;
- Monitor compliance with labor safety requirements by the contractor at the organization’s site.
These requirements are specified in clause 4.10.5.2 of GOST 12.0.230–2007 “SSBT. Occupational safety management systems. General requirements".
If all these measures are completed in full, the general contractor is not responsible
for a possible accident with the contractor's employees.
How to establish labor protection requirements in an agreement with a contractor
To ensure labor safety on the territory of the organization, as well as to delimit responsibility for work safety, add a separate section to the contract agreement. It can be called “Labor safety when performing work.”
Who is responsible for labor protection under a subcontract agreement?
The contractor has the right to involve other persons - subcontractors - in the fulfillment of his obligations, unless this is expressly prohibited by law or contract (Article 706 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). If a contractor enters into civil contracts with hired workers, then these are also subcontracts.
The general contractor is responsible for non-fulfillment or improper fulfillment of obligations by the customer under the contract to the subcontractor.
The customer is responsible for compliance with labor safety requirements only to the general contractor. And the contractor and subcontractors interact with each other in terms of labor protection in the same way as the customer and the general contractor.
How to organize labor protection when working under a personnel supply agreement
The lists of works where outsourced labor cannot be used were approved by order of the Ministry of Labor of Russia and Rostekhnadzor dated November 11, 2015 No. 858n/455.
An organization may enter into a civil contract with a contractor for certain works or services of a one-time or periodic nature (Chapter 39 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). One way to find such performers is outsourcing. In this case, the staff is selected by a recruitment agency. It enters into employment contracts with employees, and subsequently provides workers to the customer under a service agreement. There are lists of types of work for which workers cannot be recruited in this way. This applies to work at sites of hazard classes I and II.
The responsibility to ensure the safety of workers and train them in labor safety requirements lies with the employer, in this case, with the recruitment agency (Article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). If an accident occurs with such workers, it is investigated by a commission formed by the receiving party. The commission includes a representative of the employer who sent this employee (Article 341.4 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Hi all! Today our colleague Yana shared two presentations on labor protection on the topics: Introductory briefing on labor protection for employees of the organization and introductory briefing on labor protection for visitors and contractors.
Newbies in labor safety often have questions: what is included in the water safety briefing, how to conduct introductory training in labor safety, etc.
This element in labor protection is purely individual, but it is done according to the same principle or program. The essence of the introductory briefing is to familiarize the newcomer with the specifics of the organization, the features of production, etc.
For a clear understanding of what the introductory briefing consists of, I am making these presentations freely available.
— Introductory training on labor protection for employees of the organization
— Introductory training on labor protection for visitors and contractors
Goals and objectives of induction training
The obligation of all employers to familiarize their employees with labor protection (OHS) requirements is defined in Article 225 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The purpose of the introductory briefing on labor protection is to familiarize the new employee with the existing ones in the organization:
- structure;
- labor regulations;
- equipment and production technology;
- features of the warehouse, territory and transport;
- fire safety measures,
- occupational health and safety instructions.
Obviously, in each organization all these points have their own characteristics and are not similar to similar ones operating in other companies. Therefore, this familiarization is mandatory for all newly hired persons. That is why the briefing is called introductory.
The management of the organization should not confuse the concepts of “instruction” and “training” of employees. The legislation establishes clear rules regarding briefings. During the course, the instructor’s task is to convey to the employee the current rules and regulations, while training is a longer process that takes more than a few hours. Additionally, employers may provide training at their discretion.
What influences the way a company organizes labor protection
The method of organizing OT depends on:
- level of mechanization and automation of the technical process;
- ergonomic indicators (work and rest schedule, emotional and physical stress of workers);
- aesthetic requirements for the working environment;
Occupational Safety and Health
- sanitary factors (air quality, water quality, gas pollution, noise, lighting);
- organizational abilities of management (work regime, form of its organization, discipline);
- the severity of work, emotional and physical stress of employees;
- social factors;
- natural and climatic factors;
- economic factors.
The operating conditions of an enterprise directly affect how labor protection is organized.
Organization of labor protection in production
What is the responsibility for violations in labor protection organizations?
If the head of an enterprise has not taken measures to train employees in occupational safety standards, he is responsible for this before the law.
Criminal liability
This type of liability occurs if an accident occurs at the enterprise due to non-compliance with safety regulations, and the person responsible is caught in it. They are held accountable under Art. 143 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. The culprit of the incident is punished depending on the degree of guilt and the harm caused. The court has the right to fine the guilty person in the amount of up to 400 thousand rubles*, send him to forced, compulsory or correctional labor, and restrict freedom for up to 1 year (possible loss of license for the same period).
If people died, the term of imprisonment is increased to 4 years, and the period of disqualification to 3 years.
Administrative responsibility
They are brought to administrative responsibility under Art. 2.4 and art. 5.27 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. Responsible persons are fined or forced to cease activities until all labor safety problems discovered by the inspector are eliminated.
The legislative framework