Initial briefing on labor protection. Introductory part
This article contains information that relates to initial instruction on labor protection: a sample list of topics common to many organizations that need to be covered during instruction; lists of persons who undergo this instruction or who may not undergo it; answers to typical questions that arise for decision-makers.
The initial occupational safety training program covers safety provisions that an employee or student will constantly encounter. This instruction is carried out after the introductory briefing, before the immediate start of the activity that the instructee will be engaged in. It is carried out with subordinates one at a time or with a group that will be engaged in the same type of activity.
Who instructs and how
The event aimed at compliance with labor safety standards is carried out by the immediate supervisor of the hired employee. In order to conduct training legally, he himself must first complete occupational safety courses and obtain certificates. The head of a department or workshop, director of a branch or company is usually appointed as a trainer.
The event is held with each employee separately. But in the case of mass recruitment of workers for the same position, when several people will perform the same functions, instruction is carried out by a group.
https://youtu.be/B_Il3LoX230
For whom is initial training on labor protection required?
Primary training on labor protection is necessary for workers:
• large, medium and small companies of all areas of activity, educational, trade institutions, hospitals, offices of companies and firms; • employed by individual entrepreneurs who use hired labor; • working remotely, if the employer provides them with equipment or machinery or recommends its use to perform specific work; • working from home using equipment or materials provided by the employer; as well as pupils and students: • who will begin educational, industrial, and any other practical activities; • before performing each practical task that is new to them during laboratory and practical classes.
Initial briefings on labor protection, samples of which are kept by those responsible for instructing subordinate employees, are mandatory for:
• workers who move to a new place; • employees who have recently been employed and have undergone induction training; • workers who will work in additional professions (for example, a conveyor operator, if necessary, will replace a repairman). At the same time, instruction alone is not enough - appropriate professional training must be carried out; • seconded, temporarily employed, seasonal workers; • employees of contractors and subcontractors who will perform work simultaneously with the main personnel of the customer or work in areas temporarily transferred to their disposal.
This instruction is read to workers by their direct supervisor. Before this, he must undergo full training in all occupational safety issues raised during the briefing and have a valid occupational safety certificate. This obligation is fixed by order.
Initial training program on labor protection
Initial instruction on labor protection, a sample of which must be kept by the management of the company's division, is organized exclusively at the workplace.
An approximate program of initial training on labor safety in the workplace can be found in GOST 12.0.004-2015 “System of labor safety standards. Organization of occupational safety training. General provisions" in Appendix B:
B.2 Program B.2 – Sample program of initial instruction on labor protection in the workplace.
The initial training program at the workplace, as a rule, should include the following questions:
- General information about the employee’s working conditions: the technological process, equipment and production environment at the employee’s workplace, the nature of his work process (tension and severity):
- general information about the technological process and products manufactured by the division;
- general familiarity with the equipment located at the workplace, in the work area and within the territory and premises controlled by the department;
- dangerous and harmful production factors present in the workplace and the risks of their impact on the human body;
- collective protection means installed on the equipment (safety, braking devices and fences, locking systems, alarms, etc.);
- purpose, design and rules for using personal protective equipment (PPE) required in the workplace;
- requirements for the safe organization and maintenance of a clean and tidy workplace;
- safety requirements for operation and maintenance (repair) of equipment located in the workplace;
- safety requirements for the prevention of electrical injuries.
- Procedure for preparing for work:
- requirements for workwear, safety footwear and personal protective equipment;
- checking the serviceability of equipment, starting devices, tools, devices, interlocks, grounding and other protective equipment;
- safe techniques and methods when performing work.
- Scheme of safe movement of an employee within the territory of a unit or organization:
- passages provided for movement;
- emergency exits, restricted areas;
- intra-shop transport and lifting equipment, locations and safety requirements when carrying out lifting operations.
- Emergencies that may occur in the workplace:
- characteristic causes of accidents, explosions, fires, cases of industrial injuries and acute poisoning;
- employee actions in the event of an emergency, industrial injury, acute poisoning;
- locations of emergency protection and fire extinguishing equipment, rules for their use;
- location of first aid equipment for the victim, first aid kits, rules for their use;
- telephone service locations, telephone numbers;
- the employee’s actions in the event of a dangerous situation that threatens the life and health of others, and in the event of an accident at work;
- the procedure for an employee to report to representatives of the employer about an accident or acute poisoning that has occurred to him.
5 Familiarization with all instructions on the workplace and labor protection by profession (in accordance with the list of professions developed by the employer for each workplace, indicating the numbers of instructions required for instruction).
Instruction programs are developed and approved by the training organizer in the prescribed manner, based on the required measures for organizing work, safety and hygiene when performing specific job functions of the employee, taking into account national regulatory requirements for labor protection.
When conducting initial instruction on labor protection, you cannot simply read the instructions one by one. The briefing program should be worked out in advance, ensuring that the information is understood as best as possible. Diagrams, posters, and training materials will help improve your understanding of the material. At the same time, it is necessary to demonstrate safe working methods.
How to develop a program for conducting initial training in the workplace
The initial training program (hereinafter referred to as PI) is a local regulatory act as part of the training of employees of the organization, drawn up in accordance with Article 8 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Download documents from the article:
Template for the initial training program in occupational safety
Initial training program for storekeeper (sample)
Other required documents
In the upper right corner of the program form there must be an approval stamp and the signature of the head of the organization.
An approval stamp is placed in the upper left corner, but only if your organization has a representative body of employees - a trade union committee, a labor safety committee, an occupational safety representative (an authorized representative of employees), etc.
important
The draft program must be agreed upon with the trade union or other representative body, if any. This is indicated in Article 372 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. If the organization does not have such a body, then approval is not required.
There is no need to coordinate the training program with supervisory authorities. If, for example, employees work on the same type of PC, in standard office conditions with the same furniture and with the same type of electrical appliances, then it is enough to develop for them a general initial training program for office workers.
If the employer decides to exempt office employees from the initial briefing, then they no longer need to undergo repeated briefing. The decision on this must be communicated to each employee in the order. The list of exempt positions must be approved by the employer.
If an uninstructed employee is injured in the workplace, the employer will be held liable. Rostrud will regard unjustified exemption from initial and repeated briefings as admission to work of an untrained employee. Therefore, you need to think carefully about whether it is worth the risk.
At the bottom of the initial briefing program there should be details with information about the program developer and a mandatory indication of the coordination of safety measures with the labor protection service.
As a rule, the PI program is developed by the one who instructs it: a specialist or immediate supervisor who has completed off-the-job training in a 40-hour OT training program. Persons untrained at the training center are not allowed to develop training programs, as they do not have the necessary training.
If the organization is small and there is no occupational safety specialist on staff, then the responsible employee performing occupational safety responsibilities must approve the program before its approval.
Tatyana Chirkina — Editor-in-Chief of the website Trudohrana.ru
Download samples of the necessary documents prepared for you by our experts:
Repeated instruction is also carried out according to the initial instruction program. If the head of a small organization independently develops programs, he can approve them. If the manager has appointed a person responsible for labor protection, he must agree on safety measures when developing programs or IOT.
Initial training program at the workplace for a storekeeper - sample
Find the sample OSH document you need in the most complete library of templates in the Occupational Safety and Health Help System. Our experts have already prepared 2506 templates!
The occupational safety specialist provides methodological assistance to the heads of the organization’s structural divisions in accordance with professional standard No. 524n. Methodological assistance consists of providing departments with up-to-date sets of regulatory legal acts; this is the requirement of the last paragraph of Article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
In addition, the occupational safety specialist must be sure that the initial training program developed by the head of the structural unit fully complies with the requirements of the rules or technical regulations. His signature on approval indicates the division of responsibility for the quality of the program.
There is a requirement for an organization to have a set of current regulatory legal acts on occupational safety in the regulations, but there is no requirement for the mandatory presence of a hologram on them in either Article 212 or 225 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, and Training Procedure No. 1/29 does not contain such requirements.
Do not miss!
In the magazine "Handbook of Occupational Safety and Health Specialists"
Find out whether it is necessary to conduct repeated briefings with office employees>>>
Regulatory grounds
A program for conducting initial training in the workplace by profession is being developed, taking into account all specific features.
In order to prepare a training program, the following documents will be required: a job description or a fragment from a qualification handbook, occupational safety rules, operational documentation for the equipment serviced by the employee. Without these materials, it is impossible to create a valid program of initial training in the workplace.
Typical initial training program at the workplace
Standard initial training programs cannot be published by definition. This contradicts the requirements of Order No. 1/29, since the program must be developed by the employee’s immediate superior.
Many ministries and departments issue standard instructions on labor protection, with the help of which it is possible to develop both IOT and an initial training program, while the standard instructions must be modified to suit the specifics of a particular enterprise, its technological component, and the job responsibilities of employees.
example
Standard instruction on labor protection for a plumber TI-130-2002 (Letter of the FNPR of Russia dated November 12, 2002 No. 109/144, TI-130-2002). In the form in which it is presented, it cannot be applied, because many regulatory legal acts have lost force, and many have received the status of a recommendatory document. Therefore, you need to take the latest labor safety rules, operational documents for the plumber’s tools, his technological maps, and draw up a training program.
Almost all standard IOTs were developed at the beginning of the 21st century, but after that there were significant changes in legislation. Therefore, develop a program according to current labor protection rules, and then you can add advisory nuances from standard instructions to it.
When changes are made to the technology, to the PPE used, to the safety rules, to the technical operation rules, changes must be immediately made to the program. After this, employees should be given training outside the plan. It is carried out regardless of how recently the re-instruction was carried out.
Do not miss!
In the Occupational Safety and Health Help System
You can download samples of PI programs in the workplace for different professions in the electronic Occupational Safety and Health System, in the special section “Templates”.
For example, an approximate program for conducting initial training on labor protection for an electrician on operational switching in distribution networks.
What questions should be included in the program?
The initial training program at the workplace should include questions on the safe organization of the employee’s workspace, and on the correct use of PPE and RPE.
An employee works not only at his workplace, he crosses the work area and other workshops. Therefore, he must know the safe routes to and from the workplace. Therefore, during the initial briefing at the workplace, it is necessary to show the employee safe ways to approach the work area, explain where the first aid kits and the first aid station are located.
In addition, in the initial briefing program, include questions on ensuring employee safety during preparation, conduct and completion of the technological cycle.
Information is also needed about possible accidents in the workplace, about options for developing an emergency situation. Even during the initial briefing, the employee must be trained in actions to eliminate the causes of the accident, for example, to de-energize electrical installations in the event of an electrical injury. The worker must know where the power supply panel is located, the switch, what posters need to be hung, where to get dielectric gloves and boots.
What happens after the end of the initial occupational safety training?
After the instruction is completed, the instructor checks the quality of the knowledge acquired. The legislation does not regulate the procedure and method for performing this check. This could be an oral survey, a requirement to demonstrate how to work under the supervision of experienced colleagues, or testing. If the instructor is satisfied with the demonstrated quality of knowledge, then he:
• allows the worker to work independently; • allows him to begin his internship.
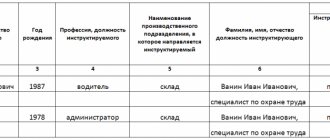
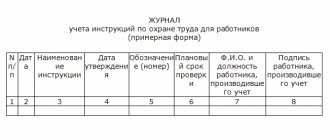
Appropriate entries are made about this in the workplace briefing log.
If the instructing person considers the quality of knowledge acquired by the employee during instructing to be insufficient, he sends him for retraining. Until its completion, this person is not allowed to take an internship or work. The worker is interested in undergoing instructions and testing his knowledge again as quickly as possible, because according to Art. 76 of the Labor Code, the time he is removed from work due to failure to undergo training is not paid.