Safety precautions are a set of provisions and requirements that are aimed at ensuring optimal working conditions. It also includes measures to help eliminate factors that negatively affect the health of employees. The goals of TB are:
- Security.
- Health protection.
- Reducing workplace injuries to a minimum.
- Formation of a system of technical and organizational measures aimed at reducing or eliminating the negative impact of harmful factors during professional activities at the enterprise.
Types of safety training
Before starting to perform their duties, each employee is required to receive several types of instructions on labor protection: introductory, primary, repeated, targeted and unscheduled.
| Type of instruction | Reason for holding |
| Introductory | When hiring |
| Primary | At work |
| Repeated | At work. Frequency: once a year; 2 times per year |
| Target | When carrying out certain types of work |
| Unscheduled | Changes in instructions and operating instructions; change in technological process; after a fire occurs; poor knowledge; violation of PPB. |
Types and organization of instruction
Safety training at the workplace can be:
- introductory, dedicated to the general rules of safe behavior;
- primary, giving the employee the most complete understanding of all aspects of safe work and the procedure for action in case of dangerous situations, without which the employee is not allowed to work;
- repeated, carried out every six months with the aim of periodically repeating the information received during the initial briefing;
- unscheduled, the need for which arises in dangerous situations;
- targeted, when new equipment or technologies appear that require additional rules of conduct when working with them, or new requirements for safe behavior.
Introductory briefing can be carried out separately by a labor protection engineer, or can be combined with the initial one. Primary and all other types of instruction are carried out by the employee’s immediate supervisor, who has undergone special training for this purpose. Instruction can be either individual or group.
All employees are subject to the initial briefing procedure:
- newly hired;
- transferred to a new location;
- hired temporarily: temporary (seasonal) workers, business travelers, trainees;
- part-time workers and homeworkers.
By decision of the employer, employees in certain positions that do not require the use of technical devices may be exempt from initial training.
Initial, repeated and unscheduled briefings for employees occupying the same positions are carried out according to the same program developed by the employer specifically for them. Accordingly, the program may be different for other positions. That is, one employer may have several training programs.
You can find ready-made samples of training programs for various specialties, jobs, positions in ConsultantPlus. Get free trial access and proceed, for example, to a sample loading and unloading training program. Or find a sample that is needed specifically for your specific activity.
At the end of the briefing, the employee is introduced to the safety instructions and his knowledge is tested.
Read more about the procedure for conducting the briefing in the article “How to conduct a safety briefing (nuances)?”
Introductory safety briefing
Instructions are provided to all newly hired persons, regardless of education, age, or length of service. Including students (for example, undergoing internship or industrial training), temporary and seconded employees. The program for which induction training is carried out is developed on the basis of the legislation of the Russian Federation and taking into account the specific aspects of the organization’s activities, and is approved by authorized persons or the employer in the prescribed manner.
Introductory briefing is carried out by a labor protection specialist or an engineer authorized by an enterprise order to conduct briefings and take safety examinations. To carry out such an event, a program and instructions must be developed, approved by the head of the enterprise.
What regulations govern
The main issues of safe operation of the enterprise are regulated by regulations at the federal and municipal levels.
Federal acts include:
- Constitution of the Russian Federation;
- Labor Code of the Russian Federation (section 10, articles 209 – 231);
- Federal Law of December 28, 2013 No. 426-FZ;
- Federal Law of July 24, 1998 No. 125-FZ;
- Federal Law of July 21, 1997 No. 116-FZ;
- GOST R 12.0.006.2002;
- industry and inter-industry agreements containing requirements on labor protection issues.
Acts at the municipal level are documents containing requirements regarding compliance with safety regulations in a separate municipality.
https://youtu.be/P7ByJESuNVs
Key issues covered in the briefing
- General information about the enterprise, organization, characteristic features of production;
- Basic norms of legislation of the Russian Federation in the field of labor protection and local regulations.
- Employment contract, working hours and rest periods, labor protection for women and persons under 18 years of age. Benefits and compensation.
- Internal labor regulations of the enterprise, liability for violation;
- Main harmful factors at work;
- Basic requirements for industrial sanitation and personal hygiene;
- Fire safety rules. Actions of workers in the event of a fire;
- Providing first aid to victims. Actions of employees in the event of an accident at the enterprise, etc.
Completion of the introductory briefing must be confirmed by an appropriate mark in the briefing registration log, the signature of the instructor and the employee himself, as well as a record with the number of the employment order.
Does the procedure for conducting labor safety briefings apply to “remote workers”?
“Distance workers” perform their work functions outside of stationary workplaces, the responsibility for the condition of which lies with employers. They provide services rather than perform specific production tasks. Hiring workers who will work remotely, as required by Art. 312.3 of the Labor Code, the employer must familiarize them with the labor safety requirements that relate to equipment and means of production:
- recommended for use;
- made available to the employee.
Additionally, according to the requirements of the same article of the Labor Code, an employer who uses the labor of “distance workers” must:
- investigate and take into account incidents and accidents that occurred with its remote workers;
- comply with the instructions of the State Supervision Service, consider the submissions of public control bodies regarding “distance workers”;
- insure remote workers against accidents and damages.
Therefore, in some cases it will still be necessary to conduct all types of labor safety briefings for remote workers. Such briefings are organized in the same way as other communication between the “distance worker” and the employer: in the form of sending .doc, .txt, .pdf and any other files, conferences in Skype, Viber and any other messenger used by the organization. A note about familiarization of the “remote operator” with the safety briefing is made in the same order as with other documents necessary for work. It is advisable to discuss this and write it down in the employment contract, indicate it in the Internal Regulations, the “Regulations on Occupational Health Training” and other documents that address this issue. The employer is allowed to exempt remote workers from instructions in the same way as other employees.
High-quality training is an inexpensive but effective event that allows employees to work with full dedication without risking their own health and safety.
Initial training at the workplace
Initial instruction is carried out with the employee at his work by the head of the unit, before the new employee begins independent work.
Instruction is carried out with the following categories of citizens:
- With every employee who came to the work unit, for seasonal work, part-time work, as well as who works from home.
- With employees of the organization on a temporary or permanent basis, transferred from other structural divisions, coming to a new workplace;
- With employees who are on a business trip from another company. With students who are sent to practice.
The initial training program should include questions contained in the safety and health instructions for a given specialty (position, workplace), as well as in other regulations on safety.
Important!!! No worker should be allowed to work without on-the-job training.
Who conducts the initial briefing?
Although the head of the enterprise is responsible for conducting initial training on labor protection, in practice, more often than not, other officials carry out activities to familiarize themselves with safe work procedures.
Not every person has the right to take steps to familiarize a newcomer with the specifics of safe work in an organization.
The determination of the person who conducts induction at the workplace is influenced by the number of staff and the presence of special staff units capable of conducting introductory activities:
- For large organizations with more than 50 employees, in accordance with Art. 217 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, provides for the introduction of a separate position of a labor protection specialist.
- In small companies with less than 50 employees, responsibilities are assigned to the head of the enterprise, division, department, or individual employee.
- If possible, at the discretion of management, external specialists are invited to conduct training, formalizing it under a civil law agreement (civil law).
In order to train others, the designated employee must first receive proof of completion of the training. The fact of assignment of duties and responsibilities is documented through an internal order with the inclusion of the corresponding clause in the job description.
Sequencing
The passage process does not involve any special difficulties and consists of 5 stages:
- Appointment of a responsible person.
- Development and approval of a training program according to the needs of the company.
- Carrying out actions in accordance with the developed training program.
- Checking the degree of mastery of the submitted material.
- Recording of progress by entries in the log book.
Recording the fact of passing and the presence of approved regulations is a mandatory part of the training at the enterprise and is controlled by supervisory government bodies.
Requirements for conducting
It is impossible to conduct training at the enterprise at one moment. The legislation establishes requirements that must be observed when carrying out:
- The contractor is appointed by a separate order and undergoes occupational safety certification. The issued certificate must be valid.
- When obtaining admission, the order indicates the conduct of internship and initial instruction. One of the current employees with at least 1 year of experience at the enterprise is responsible for the internship.
- The period when initial training is carried out at the workplace should not be later than 1 week before receiving permission to work independently. After completing the internship and immediately before starting work, an order is issued to admit the employee.
- The initial briefing program will help regulate and fine-tune the onboarding process for new employees. The program is drawn up by persons appointed by the head of the organization.
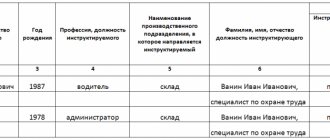
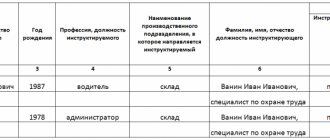
- Information about the initial acquaintance with the job is included in the personal briefing card, the form of which is approved by the manager.
- Details and descriptions related to the briefing are recorded in separate orders and internal regulations signed by the head of the enterprise.
Download an example of an order for organizing training (46.0 KiB, 94 hits)
Sample order: On the appointment of those responsible for conducting workplace briefings (30.1 KiB, 99 hits)
If it is necessary to conduct initial instruction on labor protection in the absence of a manager or other responsible person, responsibilities are transferred to the employee appointed by a separate order, provided that he meets the certification requirements.
When preparing documentation, pay attention to the presence of the date and signatures of all employees and persons involved in the training.
How to register
To document information about the training, proceed as follows:
- The briefing card must contain instructions according to which the activities were carried out and the date indicated.
- Next to each instruction there must be a signature of the employee being instructed and the person responsible for the implementation.
- The personal card must be stored and filed in a personal file for the entire period of the person’s employment.
- If an employee is transferred to another position, appropriate additions are made to the records of the activities carried out.
Additionally, the employee is instructed if he has to perform work that was previously unusual for him, while expanding the responsibilities according to the job description.
Repeated training at the workplace
Such briefing, including coverage of the technological features of work associated with increased danger, is carried out with the corresponding category of workers quarterly, with the rest - once every six months.
Repeated safety training is carried out according to the same programs that are developed for initial instruction, to test the level of knowledge, instructions and safety rules with each employee individually or simultaneously with a group of employees of the same work unit or profession.
Electrical safety briefing
An important component of production safety is compliance with electrical safety measures. This is facilitated by training in the principles of safe handling of electrical equipment.
The Order of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation dated July 24, 2013 No. 328n “On approval of the Rules for labor protection during the operation of electrical installations” indicates which categories of workers are trained in electrical safety issues.
There are 2 groups of employees:
- using a computer, copy machine and other similar devices and devices;
- working with power tools and electrical installations.
Appendix 1 to the Order of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation dated February 19, 2016 No. 74n contains a list of groups for which instruction is required.
An employee whose work will not involve special power tools undergoes training on the first day of work and is assigned group 1.
An employee who uses power tools undergoes training and an exam and will be assigned a Group 2 rating.
Re-instruction is carried out once every 3 or 6 months.
Unscheduled briefings are carried out when working conditions change, an emergency occurs, or the use of new equipment.
Electrical safety briefing for 1 qualification group.
Targeted briefing
This type of instruction differs significantly from all others in that it is carried out only in certain cases:
- The team (employees) receive permission to perform work of a certain complexity.
- It requires performing work that these individuals have not encountered before.
- Conducting various excursions and other unscheduled events.
- Participation in eliminating the consequences of natural disasters, etc.
The instruction is carried out either by an occupational safety engineer or another person authorized by order.
Unscheduled briefing
Conducting unscheduled briefings by the direct supervisor is provided directly at the workplace in the following cases:
- introduction of new or revised regulatory documentation;
- replacement of equipment or changes in technological process;
- violation by the employee of labor safety rules;
- requirements of officials of the state regulatory and supervisory authority;
- a break in work for more than 30 days (work with increased danger) and more than 60 days for other types of work.
Unscheduled briefings are carried out by analogy with periodic briefings. But special attention must be paid to the reason for their implementation. Unscheduled briefings do not at all cancel out periodic (repeated) briefings
Procedure for completing the briefing
At all enterprises, organizations and institutions whose administration has been granted the right to hire, a logbook of induction training must be kept. The log is kept by a safety engineer (or an employee who, in accordance with the order of the head of an enterprise, organization or institution, performs practical work on labor protection and safety), who conducts an introductory briefing and records all entries in the specified log.
In addition to this log, there should also be a log of workplace training. This journal contains all records of on-the-job training, repeated and unscheduled briefings.
The log should be divided into two parts:
- in the first part of the journal, entries are made about the training at the workplace
- in the second part, notes are made on repeated and unscheduled briefings.
The preparation of entries in the journal is the responsibility of the heads of structural units, and in their absence, the responsibility of the head of the enterprise.
All magazines must be numbered, laced, and sealed with the company's seal.
Unscheduled and targeted lectures
In addition to the above methods of teaching labor safety rules, enterprises conduct targeted and unscheduled training events . Targeted occupational health and safety training is carried out in the situations listed below:
- Before performing a one-time task that is not related to the main activity of a particular employee.
- In an emergency situation related to force majeure in the organization.
- Before performing actions that require a special outfit.
The basis for conducting an unscheduled lesson may be the receipt of requirements from regulatory authorities. One of the reasons for such requirements may be a violation of safety regulations by an employee, which caused an injury . Also, the basis for organizing training sessions may be the replacement of production equipment or changes in the production process.
It should be noted that the lectures in question contain information that is based on the reasons that necessitated the classes.
By taking training seriously and following instructions, an employee adapts better to the enterprise and also makes fewer mistakes when honing work techniques
FAQ
Question No. 1 Who should conduct safety training?
Answer: The introductory briefing should be conducted by a safety specialist, and the initial and all subsequent briefings should be conducted by the head of the department.
Question No. 2 How often should safety training be carried out?
Answer: Training is carried out once every three months - for workers who service equipment and are considered sources of increased danger, and once a year - for all other workers.
Rate the quality of the article. Your opinion is important to us: