Sample act of writing off material assets
Debit Credit Description 73 98 Reflection of the cost of damage incurred, intended for compensation 98 91.1 Compensation for the amount of damage incurred is taken into account in other income Norms for writing off damaged dishes and cutlery It is worth noting that there are industry average standards for the operation of utensils, which depend on certain criteria of the utensils themselves:
- Ceramic tableware;
- China;
- Metal utensils, etc.
The applied standards serve for more precise planning, accounting and control of the movement of kitchen and table items. In our country, these norms were established long enough to lose their relevance. But each individual organization can determine its own standards for the use and destruction of utensils.
Sample filling
Let's give a sample act of writing off material assets that have fallen into disrepair, using the example of a children's institution canteen.
Step 1. Fill in the number and date, name of the organization, structural unit, OKPO code, INN and KPP of the institution, financially responsible person, members of the commission for the receipt and disposal of assets, details of the order on the basis of which the commission operates.
Step 2. The commission, in the presence (in our case) of the canteen manager, checks whether the valuables have really become unusable, which they certify with signatures. Decides on the need to exclude from the valuables items that do not meet the requirements for them.
Features of accounting for dishes, keeping an accounting journal
On the issue concerning the procedure for approving lists of positions and work replaced or performed by employees with whom the employer can enter into written agreements on full individual or collective (team) financial responsibility, as well as standard forms of agreements on full financial responsibility, see Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated 11/14/2002 N 823 6.4. Responsibility for the safety of items in circulation may be assigned to employees holding positions or performing work directly related to the use of tableware, cutlery, table linen, sanitary clothing and production equipment <*, in accordance with the Regulations on the material liability of workers and employees for damage caused to an enterprise, institution, organization, approved by the Decree of the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the USSR of July 13, 1976.
How to draw up a TORG-15 act: sample filling and rules
To draw up TORG-15, a special commission is created, composed of members approved by the director of the company. It must include a representative of the enterprise administration, a person financially responsible for the safety of goods, and, if necessary, a representative of the sanitary inspection.
The visa approval of the director of the company must be on the front side of the act. The TORG-15 act is filled out in 3 identical copies, one of which remains in the structural unit, the other is sent to the accountant for display in accounting and withholding the damage from the salary of the guilty employee, and the third is transferred to the person responsible for causing the damage.
When filling out TORG-15, you should pay attention to filling out some points. Thus, the code for the reason for damage/breakage/scrap may not be included in the report if the company does not use an internal coding system. The document must indicate the reason for writing off the damaged goods or marking them down.
For information on how you can organize accounting in trade, read the article
“Trading goods with and without VAT (nuances)” .
Spoiled (damaged) goods should be listed, indicating their name, main characteristics, quantity and accounting value before and after the markdown. The guilty person (if it is possible to identify him) and his position must also be named.
The final part of TORG-15 contains the text of the manager’s order on the further fate of damaged (damaged) inventory items. Thus, the need for their disposal may be indicated. In addition, you should provide the exact amount of damage and the details of the person at whose expense it will be compensated.
Blanker.ru
Register of dishes in public catering organizations As mentioned above, the organization is obliged to keep records of dishes and cutlery to control their safety and movement in production. To do this, many organizations specializing in the provision of catering services use a tableware logbook. Currently, there are many professional software that simplify the task of maintaining such control.
Attention
But even in this case, records are kept within the framework of the approved unified form OP-19. Typically, this form is maintained by a responsible person who has special powers in this part; such an employee is responsible for the safety of dishes, kitchen and cutlery, etc. This magazine is endorsed by a materially interested person who directly conducts his work activity using dishes and other utensils.
The legislative framework
The given form is a unified form OP-8. It was introduced by Decree of the State Statistics Committee No. 132 of December 25, 1998. Until 2013, it was the only possible option for decorating the actual fight of the dishes. But now everything has changed.
Each specific organization determines for itself whether it will use a unified form or create its own form. In the latter case, the company will have to include it in the accounting policy by a separate order. Most organizations prefer to use the familiar, reliable Form OP-8. Indeed, in addition to ease of use, it is easier for regulatory organizations to understand.
Act on the fight of dishes
Important
A corresponding entry is made in the journal with a receipt from the person who handed over these items about the quantity of tableware, cutlery, table linen and sanitary clothing handed over. 6.7. When handing over tableware and cutlery, an act for breakage, scrap, damage and loss of tableware and cutlery is drawn up in form N 74 <* (for enterprises without self-service) or N 75 <* (for enterprises with self-service) separately for porcelain and earthenware and high-quality glassware, which is issued by the commission in the prescribed manner. ConsultantPlus: note. Order of the USSR Ministry of Trade dated July 14, 1972 N 134 lost force due to the publication of Order of the USSR Ministry of Trade dated August 20, 1986 N 201, which approved the Album of forms of primary accounting documentation in trade and public catering.
<* See Order of the USSR Ministry of Trade of July 14, 1972 N 134.
Disposal of tableware and cutlery
Sanitary clothing is issued to employees of those professions and positions, the list of which is determined by the relevant current standards. The issuance of tableware and cutlery is carried out against a signature in the register of these items in form N 73 See Order of the USSR Ministry of Trade of July 14, 1972 N 134. Subsequent issuance of these items, as well as the circulation of tableware and cutlery between waiters and washers dishes during the day are made in the order of exchange. At the end of the working day, tableware, cutlery, table linen and sanitary clothing must be returned to the person who issued them. At the same time, the person responsible for the safety of these items must monitor the condition of each returned item.
Act on damage, scrap and loss of dishes and utensils - form op-8
The release of tableware, cutlery, table linen, sanitary clothing and production equipment from the storeroom is carried out by order of the head of the enterprise and is issued with an invoice in form N 19 <*. ConsultantPlus: note. Order of the USSR Ministry of Trade dated July 14, 1972 N 134 lost force due to the publication of Order of the USSR Ministry of Trade dated August 20, 1986 N 201, which approved the Album of forms of primary accounting documentation in trade and public catering. <* See Order of the USSR Ministry of Trade of July 14, 1972 N 134. ConsultantPlus: note. The Decree of the Presidium of the USSR Supreme Council of July 13, 1976 became invalid due to the adoption of Federal Law No. 90-FZ of June 30, 2006.
What does the Ministry of Trade offer?
Today, not all industry departments are in a hurry to develop regulations that regulate specific issues of carrying out activities. Probably, officials believe that the developed documents are quite sufficient, especially for accounting, which is regulated by two dozen standards. One of the industry documents that provides recommendations for recording the movement of tableware, cutlery and equipment is Order of the USSR Ministry of Trade N 276 (hereinafter referred to as Order N 276). He approved the Norms for operational losses of all production equipment of the canteen due to its breakage, scrap, damage and wear. However, before writing off tableware, cutlery, table linen, sanitary clothing and production equipment, they must be capitalized and reflected in accounting. With regard to this issue, the industry Order does not provide recommendations, so we turn to universal regulatory documents on accounting. Their choice depends on how to classify dishes, cutlery and other equipment.
Order of the USSR Ministry of Trade dated December 29, 1982 N 276 “On approval of industry average standards for operational losses of tableware, cutlery, table linen, sanitary clothing, production equipment at public catering establishments and Instructions on the procedure for their use.”
Broken dishes write-off
In this case, the costs of dishes and cutlery belong to the group of material and production costs associated with the main activity, therefore the legislation in this part does not prohibit this operation. Question No. 2. Can the organization adjust the rules for breaking dishes? Since there is no clear regulation of the rules for breaking dishes in tax legislation, the organization has the right to establish such standards itself by internal legal acts. Adjustment of these standards also falls entirely on the leaders of the organization. Having justified reasons for changing the existing system and the size of the applicable loss rates for dishes and cutlery, managers can change internal regulations. Rate the quality of the article. The norms can be based on any specific criteria that correspond to the activity:
- Machine or hand washing of dishes;
- Bar or hall utensils;
- Material for making cutlery, etc.
The basis for the calculation can be both the total volume of sales of public catering services provided, and the volume of sales for individual types of services provided or internal divisions. Write-offs can be made either once a year or gradually for each reporting period (once a quarter or once a month). All this allows you to engage in more accurate planning and maintain appropriate planned budgets for purchases, shortages, expenses, etc.
Exceeding the established standards may serve as a reason for holding the person responsible for this area of work financially liable. Working in the restaurant business and catering industry, many accountants are faced with the task of how to properly keep records of dishes and kitchen utensils. There is not much information on this topic, and most importantly, the regulations adopted in this area and regulating specific operations do not provide a complete understanding of how exactly accounting and reporting should be done. Therefore, accountants have to use general accounting provisions and legal acts that explain them.
Insurance LawPermalink
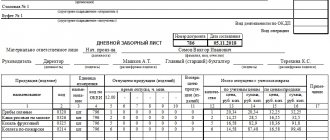
Act on damage, scrap and loss of dishes and utensils (filling sample)
Unified form N OP-8
Approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated December 25, 1998 N 132
———— ¦ Code ¦ +———+ Form according to OKUD¦ 0330508 ¦ LLC “Manyashiny Raznosoly” +———+ ———————————————— according to OKPO¦ 54321889¦ organization +———+ Canteen No. 2 ¦ ¦ ——————————————————-¦ ¦ structural unit +———+ Type of activity according to OKDP¦ 55.30 ¦ ¦ (OKVED) ¦ +———+ Type of operation¦ — ¦ ———— APPROVED Head Director —————— position Alexandrova O.A. _____________ ——————— signature transcript of signature April 30, 2011 “—” ————— —- year ——————————————— ¦ Number ¦ Date ¦ Reporting period ¦ ¦ document+———————+ ¦ ¦ ¦ from ¦ to ¦ +———+————+———-+———-+ ¦ 4 ¦ 04/30/2011¦04/01/2011¦ 04/30/2011¦ ACT ———-+————+———-+———— ABOUT DAMAGE, SCRAP AND LOSS OF COOKWARE AND Utensils Head of the economic department Jediev Said Eldarovich Financially responsible person ————- ——— ————— position last name, first name, patronymic The commission established: ——————————————————————————————————— ——————————— ¦Number by¦ Dishes, cutlery ¦ Price,¦ Battle, scrap, lost, missing ¦ Circumstances of the battle, ¦Note¦ ¦order +————————-+ rub . +—————————————————————+ scrap, loss, loss.¦ ¦ ¦ ¦name¦ code ¦ kopecks. ¦ battle, scrap ¦lost, missing¦ everything ¦ Guilty persons ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +——————+——————+—————————+ (position, surname, ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ amount, ¦ quantity, ¦ amount, ¦ amount, ¦ i., o.) ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ quantity, ¦ rub. kopecks, rubles kop.¦ pcs. ¦ rub. cop. ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦pcs. ¦ ¦pcs. ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +———+————+————+——+——-+———+——-+———+—————+———— +———————-+———-+ ¦ 1 ¦ 2 ¦ 3 ¦ 4 ¦ 5 ¦ 6 ¦ 7 ¦ 8 ¦ 9 ¦ 10 ¦ 11 ¦ 12 ¦ +———+————+ ————+——+——-+———+——-+———+—————+————+———————-+———-+ ¦ 1 ¦Plates ¦26.21.12.112¦ 30-00¦ 5 ¦150-00¦ 1 ¦30-00 ¦ 6 ¦180-00 ¦Guilty of the loss and ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦deep ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦boe ( lome) not ¦ ¦ +———+————+————+——+——-+———+——-+———+—————+————+ identified. Broken dishes and+———-+ ¦ 2 ¦Plates ¦26.21.12.112¦ 32-00¦ 2 ¦ 64-00 ¦ 4 ¦ 128-00 ¦ 6 ¦ 192-00 ¦scrap aluminum spoons ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦flat, ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦occurred in the hall ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦diameter ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦service ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦25 cm ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦visitors. Tea ¦ ¦ +———+————+————+——+——-+———+——-+———+—————+————+no spoons Returned +----- + ¦ 3 ¦ Parties ¦26.21.12.112.112, 25-00 ¦ 125-00 ¦ 4 ¦ 100-00 ¦ 9 ¦ 225-00 ¦ Dining rooms ¦ ¦ ¦ Democratic, ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦diameter ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦20 cm ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +———+————+———— +——+——-+———+——-+———+—————+————+ +———-+ ¦ 4 ¦Spoons ¦28.61.14.141¦ 15-00¦ 6 ¦ 90-00 ¦ — ¦ — ¦ 6 ¦ 90-00 ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ tableware ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ aluminum ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +——— +————+————+——+——-+———+——-+———+—————+————+ +———-+ ¦ 5 ¦ Tea spoons¦ 28.61.14.111¦ 20-00¦ — ¦ — ¦ 8 ¦ 160-00 ¦ 8 ¦ 160-00 ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ (stainless¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦steel) ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +———+————+————+——+——-+———+——-+———+—————+— ———+ +———-+ ¦ 6 ¦Sugar bowl ¦26.21.12.124¦120-00¦ 1 ¦ 120-00 ¦ — ¦ — ¦ 1 ¦ 120-00 ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦faience ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +———+————+————+——+——-+———+——-+———+—————+————+ ———————-+———-+ ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ———+————+————+——+——-+———+——-+———+—————+————+———— ———-+———— Total¦ 19 ¦ 549-00 ¦ 17 ¦ 418-00 ¦ 36 ¦ 967-00 ¦ ———+———+——-+———+————— +————- Reverse side of form N OP-8 ————————————————————————————————————— —————————— ¦Number according to¦ Dishes, cutlery ¦ Price,¦ Battle, scrap, lost, missing ¦ Circumstances of the battle, ¦Note¦ ¦order +————————-+ rub. +—————————————————————+scrap, loss, loss.¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ name- ¦ code ¦ cop. ¦ battle, scrap ¦ lost, missing¦ total ¦ Persons responsible ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ nie ¦ ¦ +——————+——————+—————————+ (position, surname, ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ amount- ¦ amount, ¦ amount- ¦ amount, ¦ quantity, ¦ amount, ¦ i., o.) ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦quantity,¦rub.
Types of utensils in the establishment
Most varieties of tableware are included in material inventories (clause 118 of the Instructions to the Unified Chart of Accounts No. 157n). But there are dishes that are more correctly considered as the main means. These are utensils with a useful life of more than 12 months. Make the final decision yourself and write it down in your accounting policy as to which goods should be included in fixed assets and which ones should be included in inventories.
Order of the Federal Penitentiary Service of the Russian Federation No. 787 dated September 27, 2005 will help you correctly determine the service life of the dishes; the operation of the dishwasher is also described there. Please note that if, after the expiration date, the dishes are still suitable for further use, then there is no need to write them off. If the required item is not found in the document, the institution’s commission has the right to establish a useful life according to the manufacturer’s accompanying document (warranty or standard service life).
There are two types of dishes: kitchen (pots, frying pans, kettles, cans, buckets, tanks, etc.) and dining (plates, cups, saucers, bowls, mugs, etc.). Cutlery (knives, forks, spoons, etc.) belongs to the dining room.
All utensils in an institution can be divided into three types (see Table 1).
Table 1. What types of cookware are there?
| Types of cookware | Purpose |
| Functional | Utensils needed for the statutory activities of the institution. |
| Management | Utensils used for administrative purposes. The accounting policy prescribes the procedure for accounting for dishes by name and number of copies. The reason for write-off will be the impossibility of further operation. |
| Disposable | Dishes that are used once. |
Utensils used in canteens of institutions must meet the requirements of the Sanitary and Epidemiological Rules SP 2.3.6.1079-01, approved by Decree of the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation No. 31 dated November 8, 2001. For some institutions, separate standards have been approved, including certain requirements for utensils used. For example, for preschool institutions, SanPiN 2.4.1.3049-13 applies, approved by Decree of the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation dated May 15, 2013 No. 26.
Accounting for dishes and detergents can be checked by Rospotrebnadzor. How to pass an inspection of an institution's canteen, read the article in the journal Accounting in Education. After reading the article, you can prepare in advance for the arrival of inspectors.
Form OP-8. Act on damage, scrap and loss of dishes and cutlery
kopecks, rubles kop.¦ pcs. ¦ rub. cop. ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦pcs. ¦ ¦pcs. ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +———+————+————+——+——-+———+——-+———+—————+———— +———————-+———-+ ¦ 1 ¦ 2 ¦ 3 ¦ 4 ¦ 5 ¦ 6 ¦ 7 ¦ 8 ¦ 9 ¦ 10 ¦ 11 ¦ 12 ¦ +———+————+ ————+——+——-+———+——-+———+—————+————+———————-+———-+ ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ +———+————+————+——+——-+———+ ——-+———+—————+————+ +———-+ ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ ¦ — ¦ + ———+————+————+——+——-+———+——-+———+—————+————+ +———-+ ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ ¦ — ¦ +———+————+————+——+——-+———+ ——-+———+—————+————+ +———-+ ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ ¦ — ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ———+————+————+——+——-+———+——-+———+————— +————+———————-+———— Total¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ — ¦ +——-+———+——-+———+ —————+————+ Total ¦ 19 ¦ 549-00 ¦ 17 ¦ 418-00 ¦ 36 ¦ 967-00 ¦ ———+———+——-+———+——— ——+————- Tableware and cutlery listed in the column “Fight, scrap” in Nineteen quantities ————— pcs. destroyed in our presence in words Director Alexandrova O.A. Members of the commission: ———- _____________ ——————— position signature transcript of signature Chief Accountant M.M. Malinina ———- _____________ ——————— position signature transcript of signature Accountant Mukhina S.M. ———- _____________ ——————— position signature transcript of signature Amount of shortage (nine hundred sixty-seven Administration decision ——————————————— rub. 00 kopecks) arising as a result of the battle (scrap) and loss of —————————————————————— valuables, write off the financially responsible person ——————————————— ——————— (Dzhedaeva S.E.) and include in the organization’s costs ——————————————————————
Comments:
Accounting for dishes and wiring
The utensils that you include in inventory should be reflected in account 105 06 “Other inventory” (clause 118 of the Instructions to the Unified Chart of Accounts No. 157n). The costs of their acquisition must be paid according to KVR 244 “Other procurement of goods, works and services.” And in accounting, carry them out according to article KOSGU 340 “Increase in the cost of inventories.”
If the dishes are a fixed asset, then keep records on the same account 101 00 as part of movable property. Pay expenses for the purchase of stationery according to KVR 244 “Other purchase of goods, works and services.” In accounting, enter them under article KOSGU 310 “Increase in the value of fixed assets.”
The main entries for accounting for utensils as part of inventories are shown in Table 3.
Table 3. Typical entries for accounting for tableware as part of inventory.
| Operation | Establishment | |
| Budget or stand-alone | State-owned | |
| Functional cookware | ||
| Dishes purchased | Dt 0 105 XX 340 CT 0 302 34 730 | Dt 1 105 3X 340 CT 1 302 34 730 |
| Reflects the internal movement of dishes between MOLs (from the warehouse for use) | Dt 0 105 XX 340 CT 0 105 XX 340 | Dt 1 105 3X 340 CT 1 105 3X 340 |
| Broken dishes written off through a write-off act | DT 0 109 60 272 CT 0 105 XX 440 | Dt 1 401 20 272 CT 1 105 3Х 440 |
| Management utensils | ||
| Dishes for administrative needs were purchased | Dt 0 105 XX 340 CT 0 302 34 730 | Dt 1 105 3X 340 CT 1 302 34 730 |
| Transferred for use (the cost is debited from the balance sheet) | Dt 0 109 60 272 KT 0 105 ХХ 440 | Dt 1 401 20 272 Kt 1 105 3Х 440 |
| Disposable tableware | ||
| Disposable tableware was capitalized according to the invoice | Dt 0 105 XX 340 KT 0 302 34 730 or Dt 0 105 XX 340 KT 0 208 34 660 | Dt 1 105 3X 340 KT 1 302 34 730 or Dt 1 105 3X 340 KT 1 208 34 660 |
| Transfer to the production process according to the statement for the release of material assets (f. 0504210) | Dt 0 109 60 272 KT 0 105 ХХ 440 | Dt 1 401 20 272 kt 1 105 3Х 440 |
How to issue detergents to employees of an institution and keep records of them, read the article in the journal Accounting in an Institution.
Did not find an answer to your question? Ask it to the experts of the State Finance System
Registration of tableware accounting
You can get acquainted with their specifics in the article “Maintaining document flow for warehouse accounting of materials.” In addition, there are unified forms that are adapted to documenting business transactions with specific types of inventories. For example:
- waybill form No. 0340002, approved by Decree of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated November 28, 1997 No. 78 - for writing off gasoline;
Download the waybill for the construction vehicle
- form No. 0504143, approved by order No. 52n - for writing off household equipment;
Download the act on write-off of soft and household equipment
- Form No. 0504203, approved by Order No. 52n - for registration of feed and fodder consumption.
Download the form for issuing feed and fodder. As an alternative to standardized forms, an enterprise can use its own.