What to rely on when filling out
Standard dishes are contained in a collection of recipes. This can be either a book published in 1994 or 1996.
The list of current collections can be found in Letters of the Ministry of Trade of the Russian Federation dated 06/07/1999 N 21-9/410 and Roskomtorg dated 07/15/1996 N 1-806/32-9.
The list of ingredients from the collection of recipes is simply transferred to the table to be filled out. If a dish is not in the collection of recipes, then this dish must be specially presented as prepared according to the TTK (technological map of the dish). The latter is developed individually in each company.
A program that is necessary for every enterprise.
The very definition of this catering outlet implies simple, unsophisticated food that can evoke nostalgia for the times of the Union. In other words, no sushi. And the abundance of complex items will make calculating dishes, if not more problematic, then certainly more boring.
A list as thick as an encyclopedia is difficult to maintain both professionally and financially, since it is difficult to find general-purpose chefs for a canteen, and maintaining the required composition of products on an ongoing basis is expensive. Technological maps This term refers to a document that contains information about all the features of a dish.
It includes the following data (not necessarily all, some are selective):
- Duration and specifics of storage of the dish.
Components of a document
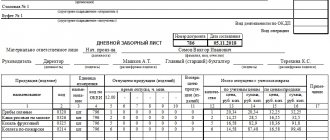
The calculation card is filled out on one side. If one sheet is missing, you can continue the table on the next page. The calculation card indicates:
- On what legal basis is the document based? In particular, this basis is Resolution of the State Statistics Committee No. 132 of December 25, 2012. It is in it that unified forms are prescribed, such as this OP-1.
- Form of paper according to OKUD (0330501) and OKPO.
- The organization, its structural unit (if any), its type of activity according to OKDP, the number of the dish according to the collection of recipes.
- Type of operation performed.
This information is introductory. The essence itself is presented in the form of a table in which the following are listed in separate columns:
- document number and date of its preparation;
- serial number of the prepared calculation;
- deadline for approval of the above calculations;
- names of products and their codes;
- several dates with the same ingredients (in the example and sample - six, but their number may vary) with the rate of use per 100 dishes, price and amount for each.
The last item is intended to reflect in the table changes in the cost of certain products, their weight, etc. For example, if a calculation card is drawn up for buckwheat milk soup, then when the price of buckwheat or milk changes, the total cost of the finished dish naturally changes.
There is a type of document that does not provide for price changes (it has only one approval column). In this case, when the cost jumps, a new document is drawn up, and the old one loses its validity. This fact must be recorded in the costing register.
At the end of the tabular part, the results for the dish are summarized, such as:
- total cost of the raw material set (indicated for each column separately);
- what is the markup;
- final cost, sale price in rubles;
- weight of the finished product in grams;
- signatures of the production manager (chef controlling the process), the compiler of the costing card, as well as the head of the organization (or his authorized representative).
For whom the use of the OP-1 form is mandatory
Form OP-1 was introduced by Decree of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation No. 132, issued on December 25, 1998. Until January 1, 2013, the use of forms provided for by the relevant source of law was mandatory for all legal entities (clause 2 of Resolution No. 132).
However, in connection with the entry into force of the new law on accounting in 2013 (law dated December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ), the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation in information No. PZ-10/2012 expressed the opinion that organizations received the right to use in their activities not only unified primary forms, which include the OP-1 form, but also those that they developed independently.
The Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation has established an exception for organizations in respect of which the use of unified forms is directly prescribed by separate legislative acts. At the moment, no similar sources of law that would oblige organizations to use the OP-1 form have been published in the Russian Federation. At the same time, many Russian catering enterprises continue to use the appropriate form due to the convenience of its structure and established business customs.
Read about the specifics of doing business in the catering industry when using UTII in the article “Peculiarities of using UTII for cafes and restaurants .
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Full and free access to the system for 2 days.
Nuances of filling
The document is intended strictly for one name of dish. It is unacceptable to compile a paper for several culinary delights with different names at once. This, ultimately, turns out to be more convenient for accounting calculations, since both the price of any bleaching product and the markup on dishes (by order of management) can change. Depending on the convenience of a particular organization, the calculation of food storage is set at 100, 50 or 1 dish.
There are situations when the declared weight of the product after heat treatment does not meet the standards in the collection of recipes. For example, frozen fish fillets consist of 55% ice. In this case, it is defrosted, weighed and then the proportion is taken into account when it is defrosted.
Blog about sales, marketing and customer service smart capital invest company
Important:
Purchased goods are sold at the purchase price, taking into account the markup. Let's look at the calculation using the example of the preparation of “Berlin cake” by the catering service enterprise.
The calculation is made based on 50 units of the product. To prepare the dish according to the technological maps you need: ground cinnamon - 20 g; butter - 0.1 kg; wheat flour - 0.250 kg; zest - 50 g; sugar - 0.1 kg and egg - 6 pcs. The calculation card is filled out in the following order: the list of food ingredients of the dish and the corresponding units of measurement (kg, g, pcs) are entered in the appropriate columns (Products); in the Price column the selling price per unit of measurement of the product is indicated; in the Gross and Net columns the quantity of products per 50 products is recorded; Accordingly, in the Amount column the cost of individual types of products required to prepare 50 units of a dish is calculated.
What is checked during inventory
The document must be provided during inspections, in particular for regular inventories. When carrying out the latter, a commission headed by the chairman gets acquainted with the register and map, compares the remaining remains of products and documents on their use. Naturally, they must match.
Important point! The final data of the calculation cards regarding the selling price of the dish must exactly match the price of this item in the menu that is provided to customers.
What is needed for calculation
In order to correctly calculate the calculation, you will need:
- Menu indicating the list of dishes.
- Technological map for each dish indicated in the menu.
- The purchase price of all products needed for cooking.
Let's look at each of these points.
When choosing dishes for the dining room, you should not go to extremes. Simple dishes should be presented here. In addition, calculating dishes with complex positions will become even more difficult.
Related documents
The calculation card data is entered into the calculation register. Every document issued and signed must be listed there, even if it only came into force for a short time. Also useful for grocery layouts:
- order-costing;
- menu plan (OP-2);
- requirement for the pantry (OP-3).
In this case, warehouse accounting documents should serve as the basis for OP-1. The actual consumption of products must coincide with that indicated in the papers.
Practical experience shows that it is very rare to comply with standard (ideal) conditions for storing and processing products. If any adjustment is made, information about this is indicated in the document.
Unfortunately, in 1C and other standardized accounting programs there is no possibility of drawing up costing cards. If there is a need for an automated system for filling out these documents, then they resort to purchasing specialized programs or hiring a specialist who is ready to adapt the existing system to generate this paper.
Creation and execution of costing cards
Add original materials and receive prizes from Infourok
Weekly prize fund 100,000 RUR
Laboratory work
No. 11
Creation and execution of costing cards
Goal of the work:
develop skills in working with a spreadsheet to fill out, edit and format table cells
Work progress
1. Study the theoretical part
2. Do the practice task
3. Complete a laboratory report
4. Answer security questions
One of the conditions for guaranteed high quality of finished products is compliance with the technological process of preparation and the norms for adding products to the dish. For this, various documentation is used, including:
Calculation card
(Unified form N OP-1)
Menu plan
(Unified form N OP-2)
Order-invoice (Unified form N OP-20)
Work order for the production of confectionery and other products (Unified form N OP-25)
Calculation cards
– a document that determines the selling price of products sold at retail. The calculation can be made based on the cost of raw materials per 100 dishes or per 1 dish, per 1 kg or per 1 serving.
Technical and technological maps
are being developed for new and signature dishes and culinary products. Each card has its own serial number, scope of application, list of raw materials used to prepare a dish, requirements for the quality of raw materials, standards for laying raw materials in gross and net weight, description of the technological process, requirements for registration and release, quality and safety indicators, nutritional composition indicators and energy value. For ease of work during mass preparation, cooks and pastry chefs should have technological maps at their workplace.
Routing
— a technical document for cooks and confectioners; it may contain the following information: name of the dish, recipe options for the dish (product) per serving (in pcs.), food consumption per number of servings, yield of the dish. On the back of the card: - a detailed description of the technological process is shown.
Calculation of dishes
Costing
- This is the calculation of the cost of production of goods and services. In public catering, calculations mean calculations of the selling price of a unit of production.
When making calculations, the principle of standard calculation is used, i.e. the consumption of raw materials for a specific dish is strictly regulated by the Collection of recipes for dishes and culinary products or technical and technological maps. The calculation is compiled in calculation cards of the established form separately for each type of dish. The calculation is made for one or 100 dishes.
Purchase price
- This is the price at which the product is purchased.
Extra charge
- This is the added value to the purchase price of a product, intended to reimburse expenses and make a profit.
Selling price
– this is the price at which a product is sold with a trade margin.
Calculation of product costs in Excel
It has already been noted that each company will have its own list of costing items. But you can substitute any data into the existing framework, change the formulas if necessary, and get a ready-made calculation.
For an example of costing and selling price calculation, let's take data from the following table:
Costing calculation scheme:
- We calculate returnable waste from the costs of raw materials and materials (we take the specified percentage).
- To determine the additional salary, we take into account the following data: if the basic salary is more than 200 thousand rubles, then the additional salary is equal to 10% of the basic salary; less than 200 – 15%.
- Salary accruals - 30% of the amount of basic and additional wages (the additional 10%, which was introduced in 2020 for an annual income of more than 600 thousand rubles, is not taken into account here).
- Equipment maintenance costs are 5% of the basic salary.
- General expenses – 9% of the average basic salary.
- General production – 18% of (25% OZP + 75% DZP). WZP – basic salary, DZP – additional salary.
- Production cost = the sum of expenses for the maintenance of equipment, raw materials and materials, fuel and energy, components, spare parts and additional parts, accruals for salary, general production and general expenses minus returnable waste.
- Non-production costs (costs) – 3% of production costs.
- Total cost = production cost + production costs.
- We calculate the manufacturer's profit as a percentage of the total cost.
- Wholesale price = full cost + manufacturer's profit.
- VAT is calculated based on the wholesale price.
- Selling wholesale price = manufacturer's wholesale price + indirect taxes (VAT in the example).
Based on the diagram, we will enter the data and formulas for calculation into an Excel spreadsheet.
Explanations for the calculation of some costing items:
- Returnable waste – =B2*12.54% (percentage taken from the first table).
- Additional salary – =IF(B6
- Salary accruals – =(B6+B7)*30%. If we follow the letter of the law and take an additional 10% from an annual salary over 600 thousand rubles, then we use the same “IF” function.
- Equipment content – =B6*5%.
- General production costs – =18%*(B6*25%+B7*75%).
- General expenses – =9%*B6.
- Production cost – =(B2+B3+B5+B6+B7+B8+B9+B10+B11)-B4.
- Production costs – =3%*B12.
- Total cost – =B12+B13.
- Manufacturer's profit – =B14*3.45%.
- Manufacturer's wholesale price – =B14+B15.
- The formula for calculating VAT is =B16*20%.
- To calculate the wholesale selling price – =B16+B17.
The same principle is used to calculate the cost of products B and C.
You can make Excel take the initial data for calculation immediately in the appropriate tables. For example, raw materials and materials - from the production report. Salary - from the payroll. Unless, of course, all this is done in Microsoft Excel.
Military registration form 18
Form 18 is also an integral part of military registration at an enterprise. The form was introduced in 2015 and is still in effect today. There was no information about modifications this year.
- F18 displays data about persons working at the enterprise and included in the reserve. Companies, according to the profile of accounting in the organization, are divided into two types:
- companies with a person appointed responsible for conducting military registration;
- an authorized person who has the competence to reserve jobs for citizens in reserve.
Universities, when compiling Form 18, are required to indicate, at the same time as employees, the data of undergraduate and graduate students.
The frequency of submitting the form to the district military registration and enlistment office is once every two years. According to the rules, it must be submitted by December 31 of the current year. The information recorded in the form must contain data that is current as of January 1 of the following year.