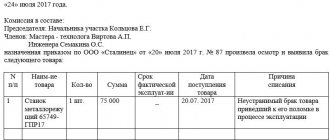
When is it necessary to draw up a form for write-off of food products?
Any company whose activities are related to the sale or processing of food products has at least once encountered the situation:
- when, under the influence of external factors or due to someone else’s fault, the goods have deteriorated
- the product simply did not have time to sell out on time, and it had passed its expiration date
In each of these cases, all damaged goods must be written off. It is important to clarify the reason for the damage to the goods. The amount of taxation and accounting in general will depend on this.
For example, goods that have simply expired are written off as expenses. But if an unforeseen, emergency situation occurred and, as a result, food spoilage, this is already a non-operating category of expenses.
If the goods were damaged by company employees, the organization:
- in the expenses column indicates the full cost of written-off products
- In the income column, the damage caused is recorded, which must be compensated by the employee who caused this damage. This may be voluntary compensation or based on a court decision
In the event that a product becomes unusable for natural reasons (for example, weathered or crumbled), it is included in the loss norms.
If the product is damaged, it must be written off. It is formalized by a specialized act. There is no single form mandatory for all organizations in the legislation. At the same time, there are valid and mandatory templates according to which a document can be drawn up.
Product write-off act template:
- TORG -15, which is compiled in case of product breakdowns
- TORG -16, which indicates the write-off of goods
An organization has the right to draw up an act for writing off food products using one of these forms or using its own template valid within the organization itself.
Certificate of write-off of goods
- Unified form TORG-16
- OKUD 0330216
- Applicable from January 1, 1999
- Approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated December 25, 1998 N 132
1. By what subject is it applied?
It is used by organizations when identifying damage or loss of quality of goods that are not subject to further sale.
2. How many copies are compiled?
Compiled in triplicate.
3. Which employee compiles
The report is drawn up by members of the organization’s commission, which identifies damage and loss of quality of goods that are not subject to further sale.
After the act is signed by the members of the commission and the financially responsible person, it is approved by the head of the organization.
4. What confirms
Confirms the fact of write-off of goods that have lost quality and are not subject to further sale.
5. Application procedure
The report is drawn up by members of the commission when damage or loss of quality of goods that is not subject to further sale is detected.
If necessary, a representative of sanitary or other supervision is present when drawing up the act.
The act indicates the details of the goods (name, price, quantity), signs of deterioration in quality (reasons for write-off).
After the act is signed by the members of the commission and the financially responsible person, the decision to assign the value of the written-off goods is made by the head of the organization and approves the act.
The first copy of the act is transferred to the accounting department and is the basis for writing off losses of inventory items from the financially responsible person.
The second copy of the report remains in the department where the goods were damaged.
The third copy of the act remains with the financially responsible person, from whose account the spoiled goods are written off.
6. Storage location
One copy of the act is kept in the accounting department of the organization.
The second copy of the act is stored in the department of the organization in which the write-off goods were damaged.
The third copy of the act is kept by the financially responsible person, from whose account the spoiled goods are written off.
>Document form
- Download form TORG-16 in the following formats: - MS-Excel;
- Sample of filling out the TORG-16 form.
How to correctly draw up an act for writing off goods
Write-off act template
Of the above forms, the act called TORG-16 has a wider range of potential possibilities. This is because it was created to remove goods from the organization’s balance sheet, and not to consider individual situations, such as battle or scrap, as is the case with TORG-15.
Filling out a document template for writing off food products called TORG-16 is not as difficult as it seems.
In addition to the standard company details, the act must indicate:
- dates of receipt and write-off of food
- complete information about the products being written off
- main reason for write-off
- Below is the cost of all food being written off
All this information is signed by all employees of the organization who made the decision to write off. At the very end, the product-responsible employee must sign.
At the end of the act there should be a decision by the head of the company about what the losses relate to. These may be losses of the company or the employee himself who is guilty of damage.
The procedure for withdrawing inventory items
Actions to write off valuable inventories must be carried out in the presence of a special staff of the organization. This role can be played by the chief accountant, storekeeper, and in some cases, a representative of the sanitary and epidemiological station. The document must be approved by the head of the enterprise and signed by all employees who are members of the commission, as well as by the financially responsible person.
In addition to the actions listed above, it is the manager who must determine the source by which the goods will be written off (cost, profit, etc.). In addition, the act must indicate complete information about the product. Then, without fail, check the compliance of the cost, batch and additional characteristics.
In addition, you need to make sure that all specified valuables have already been issued from the warehouse according to the invoice. This information is necessary in order to eliminate discrepancies in tax and accounting data.
The act of writing off inventory items, as a rule, is drawn up in three identical copies. The first remains in the accounting department, the second is stored in the documentation of the structural unit, and the third remains with the authorized person. As mentioned above, if inventory items are obsolete, the seizure act is not issued at all.
Useful information
Sometimes goods lose their appearance and useful qualities during storage. Simply put, they deteriorate and their further sale becomes impossible. It is in this case that an act must be drawn up to write off all spoiled products.
This act is a separate document on the basis of which goods are written off for one reason or another.
- expiration date
- loss of quality
- damage
- any other reason why the product cannot be sold
In most cases, the TORG-16 form, which was approved in 1998, is used for write-off. The law does not provide for any generally accepted forms in which the act must be drawn up. If it is necessary to write off any of the products, the document can be drawn up in free form.
This act must indicate all information about the product being written off. Three copies are also made of the document. The first remains in the company itself. The second is necessary so that the product-responsible employee can write off the goods. The third is given to this employee.
The act must be signed by each member of the commission for writing off goods approved for this by the director of the organization. If the need arises, representatives of sanitary and other supervisory authorities participate in the preparation of the document.
The final approval of the act occurs by decision of the head of the organization. It is he who decides who will pay for the losses.
In most cases, a write-off act for food products is drawn up to remove defective or spoiled goods from the company’s balance sheet, as well as those that have already expired. A similar situation can occur, for example, if the product is stored incorrectly. Or some of the products have too short an expiration date during which they were not sold out.
This is interesting: Sample debt repayment agreement in installments
Noticed a mistake? Select it and press Ctrl+Enter to let us know.
Drawing up an act for writing off goods is not particularly difficult; you can handle it automatically, when it’s commonplace. Another thing is that not everyone wants to write off goods according to the law.
Thank you, we downloaded a sample product write-off act, now we are doing everything as it should be. Recently our boss decided to open a grocery store, I think it will come in handy, but for now I hope that the product will sell well.
Products are also written off at our enterprise. Basically, these are substandard, spoiled and spoiled goods, and goods with an expired shelf life. This product cannot be traded!
In our organization, in the canteen, the act for writing off spoiled or expired food products is drawn up according to a unified form and is usually signed by three members of the commission.
Form TORG-16. Certificate of write-off of goods
The act of writing off goods in the TORG-16 form is useful in cases where goods in the organization’s warehouse have become unusable and need to be written off.
This document confirms the legality of the actions of the storekeeper or other financially responsible person. FILES
The document will be especially useful for food organizations, pharmacies and other companies that deal with perishable goods.
Important point! Write-offs cannot be made without the knowledge of the head of the organization. An order or instruction must be drawn up on his behalf.
If the amounts for which goods are written off are insignificant, and the process of deregistering goods is carried out regularly, then the manager can issue an order of the appropriate content, implying regular write-offs. But still, a reference to the order will be required for the act of writing off goods in the TORG-16 form.
It is worth noting that the procedure for writing off inventory items (inventory) is carried out only in the presence of a commission, the members of which are responsible and sign on the paper that the write-off was carried out according to all the rules. They also check whether the numbers in the document correspond to the actual quantity of goods being written off.
Food write-off act
The act of writing off food products (form No. TORG-16) is the primary document in accounting, which is used in enterprises selling food products (catering and trade). The need for use arises when food spoils.
The situations are typical in a number of cases:
- in case of violation of storage or sales conditions;
- in case of violation of transportation conditions;
- when the quality of the received products does not meet the necessary requirements;
- at the end of the sell-by date (expiration date).
Sample act of write-off of food products
The procedure for dealing with food spoilage is determined by the situation that led to negative consequences. In case of spoilage of products before the end of the sales period (reason - non-compliance with temperature conditions or other necessary storage conditions in the warehouse/sales area), it is necessary to conduct an inventory to confirm what happened. As a rule, this will be an unscheduled inventory, the need for which occurs when factors arise that result in a change in the quantitative indicators of inventory items. The inventory is preceded by a corresponding order from the manager.
The inventory is carried out in accordance with the Methodological Instructions (Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 49 of June 13, 1995). Material assets are recalculated, re-measured or re-weighed to determine their actual availability. The data is recorded in the inventory list (form No. INV-3). Then they draw up a matching statement (form No. INV-19): data on discrepancies in the number of goods and materials according to the inventory list and accounting information from accounting registers are entered into it. At the same time, an act of damage (form No. TORG-15) is drawn up for the amount of the cost of damaged products and a second document is an act of write-off of goods (form No. TORG-16). At the end of the product sales period, the algorithm of actions is the same.
Purpose of TORG-16
Buyers and customers have the right to count on proper quality when purchasing a product. Otherwise, there is no point in such a purchase. Who, for example, wants clothes with seams coming apart or bread covered in mold? On the side of buyers there is also legislation obliging the seller to transfer the goods (Article 469 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation):
- corresponding in quality to the purchase and sale agreement;
- suitable for the purposes for which goods of this kind are usually used (if there is no condition on the quality of the goods in the contract between the buyer and seller).
If the product was damaged or lost its quality before the moment of sale, it is no longer possible to sell it to the buyer. The question arises about its write-off from the accounting accounts, which can be formalized by an act on the write-off of goods in the TORG-16 form, approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated December 25, 1998 No. 132.
Receipt of poor quality products
If products of inadequate quality are received (damage during transportation or shipment of initially low-quality products), then a damage report will be used (form No. TORG-2 or form No. TORG-3). The last form of the act is used in the case of imported goods. The function of drawing up the document is assigned to a commission specially created by order of the head. The act includes information about the supplier and records:
- date of dispatch of products;
- date of receipt of products;
- the date of sending the notice of product damage to the supplier (by fax or other means);
- discrepancies in quantitative and qualitative indicators with those indicated in the accompanying documentation.
The condition of the products is also described here. The act is certified by the signatures of the commission members. Subsequently, claims are presented to the carrier or supplier, the basis of which will be the submitted report.
Partial loss of quality
Another option for food spoilage is partial loss of original quality, but sale is still possible. For example, in boxes of tangerines, some citrus fruits (15%) show signs of spoilage. The product is revalued (the loss of quality is taken into account), and it is sold as discounted. The confirmation and basis for the revaluation will be an act in form No. TORG-15 (or in the form in force in the organization), which is drawn up in such a situation. Revaluation is carried out by order of the head of the organization.
First table
After the header in the attached form there is a fairly simple table. It contains columns that should contain information about:
Read more: Mortgage refinancing 2020 the most profitable bank
The reasons for write-off are varied:
- Damage. Intentional or unintentional. The appointment of a financially responsible person is precisely necessary for such cases.
- Marriage. Factory or identified later during inventory.
- Violation of the integrity of the packaging.
- Expiration of the implementation period. This is the most common reason for write-offs.
When closing an organization, unsold goods are also subject to write-off.
Filling out the form for the act of writing off goods in the TORG-16 form can only be done in printed form. On the reverse side of the sheet there must be signatures by a commission convened specifically for such a case, and in most cases not all employees of the institution have electronic signatures. Usually they resort to mixed filling: the columns of the tables are formed electronically, the act is printed, and then all financially responsible persons leave their signatures, and the organization’s seal is affixed (if any).
How to write an act for writing off potato and carrot products
Financial newspaper. Regional issue”, 2005, N 47 WRITTEN OFF GOODS WITHIN THE NORMS OF NATURAL LOSS Organizations involved in the storage and trade of products are faced with the problem of their losses arising from both natural causes and their own fault. Let's consider the procedure for accounting for losses during storage: potatoes - using the example of a wholesale vegetable depot and a retail store; pasta - in retail organizations. There are normalized and non-standardized losses. Normalized goods include the natural loss of goods. The definition of natural loss is given in Orders of the USSR Ministry of Trade dated March 26, 1980 N 75 and the RSFSR Ministry of Trade dated February 22, 1988 N 45. It should be noted that today there is some discrepancy in regulatory documents regarding the norms of natural loss.
Food write-off act
The standards are given in the journal "Accounting in Agriculture", No. 1, 2010. And when writing off losses from spoilage of vegetables, you need to use the Norms for the natural loss of weight of table root crops, potatoes, fruit and green vegetable crops of different ripening periods during storage, approved by order of the Ministry of Agriculture of Russia from August 28, 2006 No. 268. Please note: companies using the Unified Agricultural Tax are governed by the same rules as income tax payers. This is due to the fact that when calculating the unified agricultural tax, material costs are taken into account, which are determined according to the rules of Article 254 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (subclause 5, clause 2, article 346.5, clause 3, article 346.5 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Is there no need to restore VAT? As for the amount of VAT that was accepted for deduction on expenses that form the cost of written-off unusable products, then, in our opinion, it is not necessary to restore it.
We draw up a write-off act for food products - sample
Simply put, they deteriorate and their further sale becomes impossible. It is in this case that an act must be drawn up to write off all spoiled products. This act is a separate document on the basis of which goods are written off for one reason or another. For example:
- expiration date
- loss of quality
- damage
- any other reason why the product cannot be sold
In most cases, the TORG-16 form, which was approved in 1998, is used for write-off. The law does not provide for any generally accepted forms in which the act must be drawn up. If it is necessary to write off any of the products, the document can be drawn up in free form. This act must indicate all information about the product being written off. Three copies are also made of the document. The first remains in the company itself.
Second page
On the second page there is a table that should provide data on:
- Code and full name of the product.
- OKEI code and the name of the unit of measurement by which the written-off inventory value is measured. This can be a unit, kg, gram, etc.
- Quantity. This column usually contains only one number. If the previous column does not indicate units of measurement, then it is assumed that the number of occupied spaces in the warehouse is indicated here.
- Masse. The total weight of all goods written off in a specific line and one piece (if possible) is indicated.
- Price and value.
- Other data that is fundamentally important when writing off. This column is called “Note”.
After the second table, the total write-off amount is indicated separately in words. Directly below it are signed by the chairman and all members of the commission who were present during the write-off and guarantee that the procedure was carried out correctly. After them, the financially responsible person signs. All “autographs” must have a transcript. The positions of the persons who placed them are written next to them.
The act of writing off goods in the TORG-16 form is completed by the decision of the manager as to what this write-off should be attributed to. This may be a write-off as expenses or the appointment of a financially responsible person responsible for the shortage. If the latter, then the employee will be required to compensate for the damage caused.
Writing off spoiled harvest
The mass of fruits and vegetables is subject to write-off within the actual shortage, but not higher than calculated according to the norms of natural loss. Natural loss norms are established for standard fresh vegetables and fruits when storing products in containers and without containers. The norms for natural loss do not include losses resulting from damage to containers, as well as defects and waste obtained during storage and commodity processing.
https://youtu.be/SdDePX0_Av8
Absolute waste is spoiled products. They are weighed and written off according to the act. Exercise.
What are the rules for writing off spoiled food?
For retail trade, standards are established for standard goods sold by weight as a percentage of their retail turnover to compensate for losses incurred during storage of goods in the utility room and on shelves, as well as during preparation for sale and sale of goods due to shrinkage, cracking, and consumption of substances through respiration. As for vegetable warehouses and vegetable stores, the approved standards for retail enterprises are limiting and are applied only in cases where, when checking the actual availability of goods, there is a shortage against accounting balances. The shortage of goods within the established norms of natural loss is written off from financially responsible persons at the prices at which the goods were capitalized, based on the write-off method established by the accounting policy.
Attribution of commodity losses to distribution costs is made at purchase prices.
How should an act for write-off of food products be drawn up, document form
In June, 34.5 tons of potatoes were sold. The balance of goods according to the inventory carried out at the end of the month amounted to 0.2 tons. The organization uses the method of valuing goods using the FIFO method. VAT is not considered in the example. 1. Let’s determine the rate of natural loss: (5 tons + 30 tons) x 1.2% = 0.42 tons.
2. The total amount of potato shortage at the end of June: 5 t + 30 t - 34.5 t = 0.5 t - the balance of potatoes according to accounting data; 0.5 t - 0.2 t = 0.3 t - shortage.
The norms of natural loss of food products in the field of trade and public catering are approved by Order of the Ministry of Economic Development of Russia dated September 7, 2007 N 304, and the norms of natural loss applied during transportation by all types of transport (except pipelines) are approved jointly with the Ministry of Transport of the Russian Federation. It must be borne in mind that the norms of natural loss of products/goods during storage differ from the norms of loss for the same goods/products, but during their transportation, and also depend on the type of transport by which they are transported. Therefore, for each case it is necessary to look for the appropriate regulatory document.
To determine the amount of product losses due to natural loss, you can use the following formula. The amount of natural loss is determined as the quotient of the product of the mass of goods sold by the rate of natural loss divided by 100.
There's nothing here!
Natural loss rates apply only to goods sold during the reporting period, regardless of shelf life at the retail outlet. When calculating the amount of natural loss within the established norms for a retail trading network, the retail turnover does not include goods: those sold to other stores, store branches (stalls, tents) that have independent records of material assets; sold in small wholesale to social and cultural institutions (kindergartens, sanatoriums, hospitals, etc.) and other enterprises, organizations and institutions; returned to suppliers, as well as submitted for processing; written off according to acts due to spoilage, reduction in quality, curtains and damage to containers. (For the ending, see “Financial newspaper.
If, as a result of the shortage, there were no perpetrators, then for profit tax purposes, excess losses had to be taken into account as part of non-operating expenses, but only in the case of documentary confirmation by government authorities of the absence of perpetrators (clause 5, clause 2, article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
How to write an act for writing off potato and carrot products
Filling out a document template for writing off food products called TORG-16 is not as difficult as it seems. In addition to the standard company details, the act must indicate:
- dates of receipt and write-off of food
- complete information about the products being written off
- main reason for write-off
- Below is the cost of all food being written off
All this information is signed by all employees of the organization who made the decision to write off. At the very end, the product-responsible employee must sign.
At the end of the act there should be a decision by the head of the company about what the losses relate to. These may be losses of the company or the employee himself who is guilty of damage. Useful information Sometimes goods lose their appearance and useful qualities during storage.
The procedure for conducting an inventory is described in the Guidelines for the inventory of property and financial obligations, which are approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 13, 1995 N 49. During the inventory process, the actual availability of property is checked by mandatory recalculation, reweighing or re-measuring inventory items. The data obtained is entered into the inventory list (form no.
Preparation of the act for production
Despite the absence of a regulated form of the act, a number of standards should be observed when drawing up the document. As a rule, these are the norms of record keeping, that is, the preparation of the form itself and the correct indication of data.
For example, the date that will appear in the document must correspond to the day the act was executed. It is imperative to register all the procedures that were carried out before write-off, namely the inventory and the stages of its implementation.
The title is indicated in the form of the genitive or prepositional cases:
- “Act of write-off of materials”;
- “Act on write-off of materials.”
Further, the text states the basis for drawing up the act, namely the order number signed by the director of the organization. This item is written in the upper right corner of the form only on the first page (if there are several pages).
In addition, the document states:
- place of document preparation;
- a list of officials (commission members) who are involved in monitoring the write-off procedure (with full indication of names and positions and highlighting the full name of the chairman of the commission);
- list of inventory items;
- quantity of goods to be written off;
- the final true value of inventories at the time of withdrawal;
- the reason for the loss of the material value of a given product.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with: Claims for the protection of honor and dignity with compensation for moral damage: sample
The above data, in most cases, is presented in the form of a table.
As for the phrases “we, the undersigned,” “drew up this act,” they should be avoided, since these phrases are not used in office work.
Upon completion of the act, all members of the commission affix their signature to the document. Moreover, if you make up a commission of one person, the write-off of material assets can be simplified. To do this, you need to make sure that all functional responsibilities for storage and use are documented to belong to one employee of the company. The advisability of making such a decision rests with the chief accountant.
Regulating the write-off of expired goods
Art. 472 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation prohibits putting up expired goods for sale. Following this article, the selling company must take into account that the buyer must have time to use the product sold.
- grocery products;
- pharmaceutical products;
- chemical products for household purposes;
- perfumery and cosmetic products.
It is prohibited to sell any product from the listed categories if the expiration date is not displayed on it.
But what to do with goods that do not have an expiration date or have expired? In this case, you can do the following:
- Return the products to the manufacturer or supplier (depending on who the batch was purchased from).
- Recycle.
- Carry out destruction.
Please note that if the product is not sent to the supplier/manufacturer, then an expert opinion from the state supervision commission is required with a decision indicating further actions regarding such products. Only two groups of goods are allowed to be destroyed without commission:
- Food products with external signs of spoilage and/or with probable danger when consumed.
- Products without information about the exact origin from the supplier.
How to correctly fill out the Write-off Act TORG-16.
The TORG-16 form consists of two pages. The first page states:
- name of the enterprise and its structural unit (if any);
- enterprise code according to OKPO, OKDP;
- document (order, instruction) on the basis of which the act is drawn up; its number and date;
- act number and date of its execution.
Next, fill out a table indicating:
- date of receipt of the goods (according to the TORG-12 consignment note or 1-T consignment note);
- date of write-off of the goods;
- TN number and date;
- reason for write-off (expiration date, violation of packaging integrity, defects, etc.);
- write-off reason code (if a coding system has been introduced).
The remaining unfilled lines are crossed out.
Try the program for Business.Ru stores, which will allow you to fill out forms in a couple of clicks. Automate accounting and tax reporting, always be aware of all mutual settlements with employees, control cash flows in the company, and a personal calendar will promptly remind you of important events. Check out the full functionality of the Business.Ru program for free>>> On the second page the following is noted:
- name of the product, its code;
- unit of measurement of the product and code of the unit of measurement according to OKEI;
- quantity of goods;
- weight of one item of goods and its net weight;
- price for one item of goods and the total cost of goods;
- reason for writing off the goods.
The total amount to be written off is indicated in numbers at the bottom of the table in the “Total” column, and in words in the line “Write-off amount”.
Documentary support of expired products
In each company, the manager himself sets the algorithm for writing off products. The organization's regulations must contain the following:
- The procedure for finding and removing goods whose expiration date has expired;
- The procedure for sending identified expired products for recycling or destruction;
- A documentation procedure that reflects the entire process.
An act of writing off spoiled food must be issued if overdue food is detected. This is a general rule for any write-off product, not just food.
The form must contain the name of the product in accordance with the documentation from the supplier; the time of registration, quantity, and location of the expired product are recorded when an overdue period is detected. A separate field in the document records further actions regarding the product (return to supplier/recycling/destruction).
When a delay is detected, forms No. Torg-15 and No. Torg-16 are used. The 1st form is used when identifying product damage, and the 2nd form is used when removing damaged goods from circulation; further actions with such goods are immediately indicated.
The concepts of “recycling” and “destruction” should not be confused. The first means the possibility of further use of the product, the second only means the liquidation of the product. However, any action is permitted after receiving a conclusion from the expert commission. For destruction, in addition to the already completed documentation, an additional order is written.
The transfer of recycling products is documented as a sale, i.e. it is necessary to create an invoice, UPD, etc.
By following the links, you will find sample forms for each form: No. Torg-15 and No. Torg-16.
Expired product
It is no secret that the sale of expired products is prohibited. They must be withdrawn from sale and destroyed. How to write off the cost of expired goods and take into account the costs of their disposal?
Product expiration date
Shelf life to the period after which a product is considered unsuitable for its intended use. Expiration dates are indicated for food products, materials and products, the quality of which deteriorates after a certain period from the moment of their manufacture, i.e.
they acquire properties that pose a danger to human health, and therefore lose their suitability for their intended use. Selling goods after the expiration date is prohibited.
An organization selling expired goods and its officials may be subject to administrative and, in some cases, criminal liability.
https://youtu.be/YgHDeksHeqE
The responsibility to establish the expiration date for food products, perfumes and cosmetics, medicines, household chemicals and other similar products rests with the manufacturer. The manufacturer determines the duration of the shelf life independently based on the individual characteristics of the product, which affect the period for which the product retains its properties.
Documenting
Organizations that sell goods with a set expiration date need to conduct constant monitoring to identify expired goods, since goods with an expiring date must be removed from circulation. You can also identify expired products during inventory.
To reflect data on the actual availability of goods in storage areas and at all stages of their movement in the organization, an inventory list of inventory items f. N INV-3 .
The inventory list is drawn up in two copies and signed by the responsible persons of the commission on the basis of recalculation and weighing of inventory items separately for each location and the financially responsible person or group of persons in whose custody the assets are located.
Relevant reports are drawn up for unusable or damaged materials and finished products identified during inventory.
To write off expired goods, use the act on damage, damage, scrap of inventory items N TORG-15 .
The final inventory data is reflected in the statement of results identified by the inventory (N INV-26) . According to this statement and the conclusion of the inventory commission, the head of the organization makes a decision to write off damaged goods from the balance sheet.
Spoiled food for animal feed
Food products prohibited for consumption can be used for animal feed, as raw materials for processing or for technical disposal in accordance with clause 16, part 3 of the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of September 29.
1997 N 1263 “On approval of the Regulations on the examination of low-quality and dangerous food raw materials and food products, their use or destruction.” The sale of expired goods for livestock feed at reduced prices is recorded in the organization's accounting records as a regular sale of goods.
As a rule, there are no problems recognizing expenses for tax purposes in this case, since there is income from the sale of goods.
The reduced price for expired goods can be justified on the basis of the following documents (example 1): - results of an examination of expired goods, confirming the possibility of using expired goods for animal feed (the examination is carried out by Rospotrebnadzor); — decisions of the Rospotrebnadzor unit on the use of spoiled goods for animal feed; — agreements for the sale of expired products;
— invoices and acts for the transfer of expired goods.
Example 1. As a result of the inventory, expired food products worth 10,000 rubles were identified. Goods are accounted for at purchase price. The head of the organization decides to sell expired goods to a pig-breeding complex. Several units of goods worth 200 rubles.
were sent for examination, the cost of which was 2360 rubles, including VAT - 360 rubles. Expired goods were sold to a pig-breeding complex for 5,500 rubles, including VAT - 838.98 rubles. The following entries were made in the accounting: D-t. 41 “Goods”, subaccount. “Products with expired expiration date”, Kt. 41 “Goods”, subaccount.
“Goods in warehouses”, 10,000 rubles. expired goods written off; Dt sch. 44 “Sales expenses” Set of accounts. 41 “Goods”, subaccount. “Expired goods”, 200 rubles. the goods have been submitted for examination; Dt sch. 44 “Sales expenses” Set of accounts. 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” 2000 rub. expenses for examination of goods are reflected; Dt sch.
19 “Value added tax on acquired assets”
K-t sch.
Write-off of expired goods
60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” 360 rub. reflected “input” VAT on expert services; Dt sch. 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” Set of accounts. 51 “Current accounts” 2360 rub. services for conducting the examination have been paid for; Dt sch. 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees”, subaccount. “VAT”, Set of accounts.
19 “Value added tax on acquired assets” 360 rub. submitted for reimbursement of “input” VAT on expert services; Dt sch. 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” Set of accounts. 90 “Sales”, subaccount. 1 “Revenue”, 5500 rub. expired goods were sold to the pig-breeding complex; Dt sch.
90 “Sales”, subaccount. 2 “Cost of sales”, Set of accounts. 41 “Goods”, subaccount. “Expired products”, RUB 9,800. the purchase price of expired goods is written off; Dt sch. 90 “Sales”, subaccount. 3 “Value added tax”, Set of accounts. 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees”, subaccount. “VAT”, 838.98 rub.
VAT is charged on the sale of expired goods; Dt sch. 90 “Sales”, subaccount. 2 “Cost of sales”, Set of accounts. 44 “Sales expenses” 2200 rub. the costs of the examination are written off as expenses; Dt sch. 99 “Profits and losses” Set of accounts. 90 “Sales”, subaccount. 9 “Profit/loss from sales”, 7338.98 rub.
(9800 + 2200 — (5500 — 838,98))
the loss from the sale of expired goods is reflected.
Destruction of expired goods
Destruction of expired goods
Source: https://printscanner.ru/tovar-s-istekshim-srokom-godnosti/
Writing off expired medications
LLC "Zdorovye" carried out an inventory.
During the inventory, the following was revealed: Name of medicine Number of medicines in the warehouse (packages) Number of expired medicines (packages) Number of usable medicines (packages) Cost of packaging (rub.
)Iodomarin 108 - 108 70 Dexamethasone 56 35 21 26.5 Festal 67 67 - 112 In the inventory lists of goods and materials according to form N INV-3, LLC "Zdorovye" reflected the medications as follows. Valid:
- 108 packages of iodomarin and 21 packages of dexamethasone (inventory No. 2).
Expired:
- 35 packages of dexamethasone and 67 packages of festal (inventory No. 3).
In addition, on the basis of inventory list No. 3, a statement of accounting of the results identified by the inventory was compiled (according to form No. INV-26), - statement No. 6. The tabular section of these forms looks like this:——T——T——————T ————-T——T———T————T————¬¦But- ¦Account,¦ Commodity - ¦ Unit ¦Price,¦ Number ¦Actual¦According to ¦¦measures ¦sub- ¦ material ¦ measurements ¦ rub.
Expired products must be written off
Organizations engaged in the sale of food, as well as other goods whose expiration dates expire quickly, must carefully monitor the expiration dates of existing goods.
For these purposes, you can use operational accounting data, and you can document the procedure for checking expiration dates and identifying expired or close to expiration goods using internal documents developed independently.
Their forms should be approved in the accounting policies.
If expired goods are discovered, the same act, form No. TORG-15, is drawn up. Subsequent documentation depends on whether the goods are disposed of or destroyed.
If goods are disposed of In the event that the organization plans to resell expired goods at reduced prices for use other than their intended purpose (for example, for processing, for use as animal feed, etc.)
d.)
Filling out the document
Form No. Torg-16 is filled out on both sides. The following information must be indicated on the front of the document:
- The number by which the goods are accepted for accounting, i.e. the number specified in the supplier's technical specification or specification form.
- Number and date of the TN or TTN according to which the goods were transferred from the supplier to the seller.
- Number of product write-offs, i.e. day of registration of the act.
- Reason for write-off (expired date, damaged packaging, etc.). If there is a write-off coding system, the code is also reflected in the column allocated for this.
On the reverse side there is a table that describes in detail the products being written off. All products subject to write-off are consistently reflected here, indicating the quantity and cost. The “Total” column indicates the amount of all goods being written off.
In the line “Write-off amount” the total amount is duplicated in words.
You can find a sample of filling out form No. Torg-16 here.
Usually, 3 copies of No. Torg-16 are created: for the accounting department, the department in which the write-off was made, for the financially responsible person.
Form No. Torg-15 is filled out according to the same principle as No. Torg-16. If a product is subject to a markdown, then additionally columns 10-14 must be filled in and the defect in the product is indicated.
This form is also filled out in 3 copies for the same services.
You will find a sample of filling out form No. Torg-15 here.
Signing, approval and further application
The final form TORG-16 is signed by:
- chairman of the inventory commission;
- members of the inventory commission;
- person materially responsible for commodity values.
The head of the organization, after familiarizing himself with the circumstances of the act, makes a decision on the account of which resources to write off inventory items that are no longer subject to sale; information about this decision is also entered into the act.
After which the document is officially approved by the manager, indicating the full name, signature and date, which is the basis for the physical withdrawal of substandard goods from consumer circulation.
Form TORG-16 is reproduced in at least three copies, addressed to:
- financial services (accounting) to write off inventory items from the financially responsible person;
- the service on whose balance sheet the goods and materials were located;
- materially responsible person (for example, a warehouse worker).
After approval of the TORG-16 form, written-off inventory items are no longer subject to sale.
The act in form TORG-16 is the basis for:
- deductions from the salaries of those responsible (if there is evidence) of the cost of substandard goods;
- writing off losses in accounting and tax accounting as expenses.
The form of the unified form TORG-16 in Word format can be downloaded for free at the bottom of the article.
the second side of the form for the write-off of goods
Post Views: 13,785