Home / Dismissal and reduction / All about reducing the number or staff of employees - what is the difference between the procedures?
In times of financial instability, many employers are forced to resort to measures such as reducing the number of their subordinates. This procedure has a number of features, non-compliance with which can lead to problems with supervisory authorities and legal proceedings with subordinates.
This article will help you understand the difference between staff reduction and headcount. Let's consider all the pros and cons of this procedure. All presented materials will be supported by an analysis of judicial practice.
Regulatory definitions, according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Dismissing subordinates when reducing the number of employees is a rather complicated procedure. Employers take this step for several reasons:
- Automation of the production process (the company no longer needs a position);
- Difficult financial situation;
- Ineffectiveness of maintaining a staff unit.
In labor legislation, the issue of dismissal is regulated by Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation . In it, terms such as reduction in numbers and staff are combined into one concept. A clear answer to the question “reducing the number or staff of employees: what is the difference?” is not found either in the Labor Code or in related legislative acts.
Despite the fact that the terms are combined in the law, judges assign different meanings to these 2 concepts (data can be taken from the analysis of judicial practice).
The differences must be carefully studied, since in practice, when employees are dismissed due to a reduction in staff or numbers, not only the algorithm of actions will differ, but also the list of guarantees provided to employees (Article 180, Article 179 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). In case of non-compliance with the dismissal procedure, the manager may fall under Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses, as well as under the sanctions provided for by labor legislation.
Reduction in headcount
The employer, on his personal initiative, has the right to consolidate the already formed staff of subordinates.
Example
The legal department of Company P employs 3 lawyers headed by a chief. The administration came to the conclusion that in order to increase the profitability of the company and improve working conditions for employees, it is necessary to reduce the number of lawyers (the workload is small).
To do this, it is worth firing 1st specialist and getting the opportunity to increase the salaries of the remaining ones. After consulting with the head of the department, the business owner came to the conclusion that the least experienced employee, who, moreover, had disciplinary sanctions, would have to be laid off. Dismissal is carried out under the same clause 2, part 1, art. 81 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
How do these concepts differ in practice?
On the issue of differences between staff reduction and headcount reduction, a stable position has been formed in judicial practice:
- A reduction in headcount is regarded as a partial reduction of work units in a certain position. For example, if the company has 7 positions for electricians, then after reduction, there may be 3 of them left.
- Staff reduction means the complete cancellation of a specific position, without taking into account how many people worked in it. That is, after the reduction, the position of electrician at the above-mentioned enterprise would be completely abolished.
General information about the procedure for dismissal due to staff reduction or headcount reduction is described in this article.
If we talk about benefits and compensation payments upon dismissal under clause 2 of Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, then in both cases they will be the same. But the guarantees provided to employees during layoffs are observed in different ways in practice. And in the event of labor disputes regarding violation of rights to these guarantees, the decisive role will be played by the wording in the dismissal order.
Consequences of mistakes during abbreviation
It is also important to avoid mistakes because labor disputes are most difficult to resolve in court; their resolution often takes a long time. Dismissal due to reduction may be considered illegal for any violation of the law.
If the citizen’s demands are satisfied (and judges often side with individuals), it will be necessary to reinstate the employee at work, pay compensation for the entire period of forced absence, and also, possibly, compensation for moral damage. In addition, employers who violate the Labor Code are punished with large administrative fines.
Let's take into account some nuances
When reducing the number or staff of employees (we have already figured out what the difference between these concepts is), it is necessary to follow a certain algorithm of actions:
- Create a reduction order.
- Notify employees.
- Offer available positions.
- Notify the employment service.
When implementing these points, you need to take into account some nuances, compliance with which will help you subsequently avoid problems with the courts. As for notifying employees, the deadlines are clearly stated here: the manager is obliged to warn subordinates at least 60 days before dismissal . Regarding the offer of vacant vacancies, due to different interpretations of the concepts of reduction of “staff” and “numbers”, with non-compliance with the rights of workers and subsequent litigation, judges make different decisions.
Let's look at the issue in more detail: when the number of employees decreases, some employees remain to work, while the management needs to choose who exactly this will be. Dismissed employees can sue because they were released from their positions illegally, did not exercise their right to the advantage of remaining in their positions (more qualified employees and certain categories of citizens have such a right: participants in hostilities, WWII, etc.), did not offer another vacancy. And in this case, the courts often side with the plaintiffs, reinstating them at work.
If the court finds that a person was fired illegally, the manager will have to pay a penalty, and in some cases, moral damages and lost profits.
When staffing is reduced, the situation looks somewhat different: since it is not the number of units that is canceled, but the entire position, the management does not have a question about which employees to fire and which to keep. In addition, people working in a certain specialty are often simply not suitable for another vacancy. And if the order specifically specifies a reduction in staff, in the event of labor disputes the court generally sides with the employer.
Benefits for employee and employer
If an employer decides to reduce the number of subordinates, he may try to persuade employees to write a statement of their own. This is not advisable; dismissal due to layoffs will be much more profitable for a specialist : in addition to severance pay, he will also receive compensation payments, the amount of which can reach up to 3 average monthly earnings.
As for the benefits of the employer, it would be more appropriate to write in the order “staff reduction” rather than “reduction in headcount.” When worded “staff reduction,” labor disputes regarding compliance with Article 179 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation are most often resolved in favor of the employer; also, the manager does not have to think about who to keep in the position and who to fire.
Dismissal and reduction: what is the fundamental difference
Among all the options for terminating employment, the most controversial and most conflicting is dismissal due to reduction. Quite often, employees file lawsuits with various authorities demanding that they be reinstated in their positions.
In order to avoid endless proceedings in the authorities, the employer must work especially scrupulously on paperwork when laying off workers, focusing on the letter of the law.
When deciding on a reduction, the head of a production or institution must be aware of what kind of reduction is planned: a reduction in staff or numbers. Simultaneous reduction of both types is allowed.
There is a fundamental difference between downsizing and downsizing. It lies in the fact that during staff reduction, some positions are removed from the staffing table itself. When the number is reduced, the number of units assigned to a particular position decreases.
Reductions in staffing periodically occur both in private enterprises and in government agencies. A typical example of staffing reduction is the abolition of the cashier position, when the administration decides to transfer employee salaries to plastic cards. Thus, the position of cashier is leveled. In this case, management makes appropriate changes to the staffing table.
Another convincing example demonstrating the actual essence of the concept of workforce reduction is the situation with 10 teachers in a kindergarten. If 3 groups of pupils are transferred to a preschool lyceum with the study of English, then their number in this kindergarten decreases. Accordingly, it is enough for the administration to retain 7 employees for the educational process. Thus, three specialists are subject to dismissal due to staff reduction.
Analysis of court cases
As for practical experience, judges clearly distinguish between the terms “staff” and “numbers”. To fully clarify the picture of the delimitation of concepts, let's look at some court cases related to this topic.
A special material has been prepared on the topic of who cannot be laid off when reducing staff; we recommend reading it.
One of the firms was undergoing staff reductions, during which the public relations manager was fired. According to the staffing table, the position of manager was not differentiated according to the duties performed, that is, the rates of sales managers and advertising managers remained (for which there were free vacancies). The employee was not offered an alternative; he went to court . The court reinstated him because it considered that the company had not made a reduction in staff, but a reduction in headcount, and the public relations officer should have been offered the position of sales or advertising manager.
If in an enterprise one specialty implies different responsibilities, this must be indicated in the staffing table and different job descriptions must be drawn up for employees. This approach will help the employer win the case in labor disputes.
Another situation. When dismissing the employer, he indicated the reason: “downsizing,” although an entire division with the positions it had was disbanded. The employee sued because he, as a specialist who contracted an occupational disease at the enterprise, was not given the right of priority retention in his position (Article 179 of the Labor Code). The court sided with the employer, finding that there was a reduction in staff, not headcount, and with this procedure, the exercise of this right is not mandatory.
What is staff and headcount reduction?
Staff reduction is the elimination of one or more positions from the staff schedule , i.e. dismissal of all people who work in these jobs.
But staff reductions do not always lead to a reduction in the number of employees. Sometimes new vacancies are created at the same time and people are transferred there.
Each company has a staffing table, which indicates all positions and the number of employees to perform the work.
Downsizing is a reduction in the number of people , in other words, there may be 10 employees at one workplace, but when downsizing, their number is reduced to 6.
What is more beneficial for the parties to legal relations?
It is clear that any reduction is clearly not a joy for workers. However, if, when staffing is reduced, everyone who worked in a certain position will have to look for vacancies, the administration’s decision to reduce the number of employees gives responsible workers a chance to remain in the workplace.
On the other hand, since the law prohibits the dismissal of certain categories of workers, the situation for professionals may not be the best.
The employer, when reducing the number of subordinates, will also have a hard time, because it is necessary to make a difficult choice about dismissing a person with whom, perhaps, a friendly relationship has developed.
Experienced business consultants believe that the decision of the enterprise administration to reduce the number of employees brings tangible benefits to the company itself. Thus, news of the upcoming compaction forces employees to observe discipline more carefully, show their effectiveness, and perform their job duties more responsibly. Experts report cases of deliberate dissolution of such rumors among company employees to optimize work.
Answers to common questions
Question: What should I do if I need to reduce a certain position in the staffing table, but this position is occupied by an employee who cannot be fired?
Answer: This position cannot be made redundant. In this case, the employee can be offered to transfer to another position. But if he refuses, he cannot be forced. The employee will have the right to remain in his position, and the employer will only have to wait for the moment when the employee’s “non-dismissal” status disappears.
Features of staff reduction. Difficulties arising during reduction
Prepared by Albina Bakhteeva
Department lawyer
for working with corporate clients
Law firm NormanDLAssociates
The financial crisis that has broken out all over the world has brought many companies to the brink of ruin, so today one of the main problems is the optimization of company expenses. How to achieve this? Many employers decide to reduce the number or staff of their employees.
This basis for termination of an employment contract at the initiative of the employer is provided for in paragraph 2 of Art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The staff reduction procedure is regulated in some detail by the Labor Code, but in practice controversial issues often arise.
Dismissal on this basis is one of the most controversial and often gives rise to legal disputes between the dismissed employee and the employer. In order to painlessly part with an employee, the employer must be very careful and strictly comply with all the requirements of labor legislation, since it is he who bears the burden of proving the legality of the dismissal. Any violation of the staff reduction procedure may lead to a judicial challenge to the decision and its recognition as illegal. This means that you will have to not only reinstate the employee, but also pay him monetary compensation for forced absence, and in some cases also compensate for moral damage.
First of all, it is necessary to remember that a reduction in numbers or staff must actually take place, and not serve as a cover for the dismissal of an undesirable employee, when immediately after his dismissal another is hired for the same position.
The employer has the right to independently determine the structure and staff of the organization; therefore, he has the right to make changes to the staffing table and reduce positions.
This can happen for various reasons: a change in the market situation, increased competition from other manufacturers, a decrease in the amount of work. Of course, it would be desirable if there was an economic justification for the ongoing reduction in numbers or staff.
It is important to remember: when reducing the number of employees, it is the vacant positions that are subject to reduction first, and only after that the occupied positions are reduced.
Why did the legislator formulate clause 2 of Art. 81 thus: “reduction in the number or staff of employees,” what is the difference between these concepts?
As for staff reduction, this is a reduction in the number of employees in certain positions, while staff reduction is the exclusion of individual staff units from the staffing table.
If there are quite a lot of changes in the staffing table, it makes sense to create a new staffing table; if the changes are isolated, it is more advisable to make changes to the current staffing table.
Before you begin to reduce staff (numbers), you should take into account that you cannot reduce (Articles 256, 261, 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
— women on maternity leave;
— pregnant women;
- women with children under three years of age;
- single mothers raising a child under the age of fourteen (a disabled child under eighteen years of age);
- other persons raising children under the age of fourteen (a disabled child under eighteen) without a mother;
— employees during periods of temporary incapacity for work or while on vacation.
The law allows the dismissal of a pregnant employee if she was hired to fill the duties of an absent employee and there is no possibility of transferring her to a vacant position.
If an employee under the age of 18 is laid off, dismissal can only take place with the consent of the relevant state labor inspectorate.
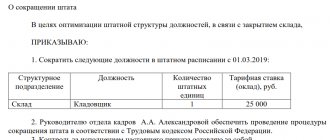
Let's look at the staff reduction procedure step by step.
Stage 1.
An order to reduce the number or staff is issued no less than two months before the expected start of layoffs (Article 180 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The document must indicate the reason for the reduction. In this case, the two-month period is counted from the next day after the workers are notified. It is important to remember that both the changes and the newly created staffing table must be put into effect not from the moment the approval order is issued, but only after 2 months. Therefore, for 2 months after the employee was warned, the previous working conditions must be maintained for him, i.e. his position and his salary.
Stage 2.
The elected trade union body is notified in writing of the decision to reduce the number or staff of the organization's employees and the possible termination of employment contracts no later than two months before the start of the relevant activities (Part 1 of Article 82 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). If the decision to reduce the number or staff of employees may lead to mass dismissal of workers - no later than three months before the start of the relevant measures.
The form of this document is free. It is mandatory to put down the date, indicate the number of staff units being reduced, and provide a link to the order. It is best if such a document is drawn up in two copies, one of which remains with the employer with a mark on the date of delivery to the trade union body.
If the organization does not have an elected trade union body, then the employer has the right to begin measures to reduce the number or staff of employees (i.e., warn employees about the upcoming dismissal) immediately after making the appropriate decision and identifying the employees to be dismissed.
In this case, the main criterion for the mass layoff of workers is the indicator of the number of dismissed workers for a certain calendar period (clause 1 of the Regulations on the organization of work to promote employment in conditions of mass layoff, approved by Resolution of the Council of Ministers - Government of the Russian Federation of February 5, 1993 N 99), for example ,
— 50 or more people within 30 calendar days;
— 200 or more people within 60 calendar days;
— 500 or more people within 90 calendar days;
— 1 percent of the total number of employees for 30 calendar days in regions with a total number of employees of less than 5 thousand people
Stage 3.
Employees are warned by the employer personally and against receipt at least two months before dismissal (Part 2 of Article 180 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The notice should indicate the date of the planned dismissal, describe the employee’s rights and the guarantees provided in connection with the dismissal.
A situation may arise when employers warned employees in writing about the upcoming dismissal not two months in advance, but, for example, five to six months in advance. In this case, there is no need to re-notify two months before the layoff, since the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes only a minimum period for warning workers, while the maximum period is not limited.
Other notice periods for staff reduction are established for:
— temporary workers who have entered into an employment contract for a period of up to 2 months: they must be notified at least 3 calendar days in advance (Article 292 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
— seasonal workers: they are warned at least 7 calendar days in advance (Article 296 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
If an employer wants to dismiss an employee before the expiration of the two-month period, he must obtain written consent. In this case, the employee is paid additional compensation in the amount of average earnings in proportion to the time remaining before the expiration of the notice of dismissal.
Article 180 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not contain strict instructions on the form of the document on written consent. Therefore, it is enough for the employer to receive a written resignation from the employee before the expiration of the two-month period - it will become an addition to the dismissal order, which the employee must be familiar with against signature.
One copy of the notice signed by the employee remains with the manager, the second copy is given to the employee.
If the employee refuses to sign that he has been warned about the upcoming dismissal, it is necessary to invite the employee to state in writing the reasons for his refusal to sign the relevant notice in the presence of witnesses. If the employee refuses this, then the employer, with the involvement of witnesses, must draw up a special act, which reflects the fact that the employee was warned about the upcoming dismissal and his refusal to sign the document.
A written statement of the reasons for refusing to sign a document notifying the employee of dismissal due to a reduction in the number of employees confirms the fact that the employee has read the contents of the notice.
Stage 4.
The employment service body is notified in writing no later than two months before the start of the relevant activities (if the decision to reduce the number or staff of the organization’s employees may lead to mass layoffs of workers - no later than three months).
The message must provide information about the position (profession, specialty), qualification requirements, and terms of remuneration for each laid-off employee. This responsibility is assigned to the employer, clause 2 of Art. 25 of the Law of the Russian Federation of April 19, 1991 No. 1032-1 “On employment in the Russian Federation.”
Failure to notify the employment service is an administrative offense and may result in the imposition of a fine on the organization in the amount of 30,000 to 50,000 rubles. or administrative suspension of activities for up to ninety days (Article 5.27 of the Code of the Russian Federation on Administrative Offences).
Stage 5.
The employee is offered another available job (vacant position) in the same organization that corresponds to his qualifications, including lower-level positions and lower-paid work (Part 3 of Article 83 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
First of all, the employee is offered a vacant position in the same company, corresponding to the employment contract concluded with him (Part 1 of Article 180 of the Labor Code). In the absence of such, the employer must offer the employee a lower position, which he can perform taking into account his education, qualifications, work experience and health status.
If the employee agrees to be transferred to another job, a written additional agreement to the employment contract is concluded between the employee and the employer, and the employer also issues an order to transfer the employee to another job.
If the employee refuses the work provided, then it is necessary to issue a written refusal (this will allow the employer to have further evidence of offering the employee another job and evidence of his refusal).
A situation is possible when an employee is offered a vacancy, but he refuses to familiarize himself with such an offer in writing, then a report about this is drawn up.
Important: it is necessary to offer the employee a list of all available vacant positions that he can fill, taking into account his profession, qualifications and previously held position, both at the time of warning him about the layoff, and within two months before the day of dismissal, if new vacancies have appeared. On the day of dismissal, the employee must also be sent a list of all new vacancies that have appeared.
Failure to comply with this requirement is a violation of labor legislation and entails a fine under Art. 5.27. Code of Administrative Offenses in the amount of 5 to 50 minimum wages.
If the reduction concerns the number of staff for a certain position, then the employer will need to decide which employees to fire. In accordance with Article 179 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, when the number or staff of employees is reduced, the preferential right to remain at work is given to employees with higher labor productivity and qualifications.
If labor productivity and qualifications are equal, preference in remaining at work is given to:
· family - in the presence of two or more dependents (disabled family members who are fully supported by the employee or receive assistance from him, which is their permanent and main source of livelihood);
· persons in whose family there are no other workers with independent earnings;
· employees who received a work injury or occupational disease while working for this employer;
· disabled people of the Great Patriotic War and disabled people fighting in defense of the Fatherland;
· employees who improve their qualifications at the direction of the employer without interruption from work.
Stage 6.
Termination of labor relations is formalized under clause 2 of Art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation - dismissal order.
Termination of an employment contract is formalized by order of the employer in form N T-8 or T-8a, approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated January 5, 2004 N 1. The order must be familiarized to the employee against signature. The employee has the right to receive a certified copy of this order.
If it is not possible to familiarize the employee with the order or he does not want to sign for familiarization, then a note about this must be made on the order. For example, “it is impossible to familiarize with signature” or “I refused to familiarize with signature.”
It is important to remember: Part 3 of Art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation prohibits terminating an employment contract at the initiative of the employer while the employee is on vacation, as well as during his temporary disability.
On the last day of work, the employee must be issued a work book, upon written application, other documents related to the work, and the final payment must be made. In addition to the salary for the last month of work, the final payment must also include the amounts provided for in Parts 1 and 2 of Art. 178 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
It happens that it is impossible to issue a work book on the day of dismissal: the employee is absent or refuses to receive it. In this case, the employer is obliged to send a notice to the employee with an invitation to come for a work book or allow him to send it by mail (clause 36 of the Rules approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 16, 2003 N 225). From the day this document is sent, it is considered that the employer has fulfilled his obligation to issue a work book and is not responsible for the delay in its issuance (Article 234 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Compensation payments upon dismissal due to staff reduction.
When an enterprise's workforce is reduced, the state guarantees the redundant employees payment of monetary compensation and the provision of certain social benefits. Only a mandatory minimum of funds paid is established by law. Organizations have the right to increase their size using their own funds, provided, for example, by a collective agreement, employment contract, etc.
Based on Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, upon termination of an employment contract due to a reduction in the number or staff of the organization’s employees, the dismissed employee is paid severance pay in the amount of average monthly earnings. If the dismissal of an employee on the specified grounds occurs with his written consent without two months’ notice of dismissal, then simultaneously with the payment of severance pay in the amount of average monthly earnings, he must additionally be paid compensation in the amount of two months’ average earnings.
By decision of the employment service body, on the basis of a certificate, the average monthly salary is retained by the dismissed employee in exceptional cases and for the third month from the date of dismissal, provided that within two weeks after the dismissal the employee applied to this body and was not employed by it (Part 2 Article 178 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
In conclusion, I would like to note that in practice, dismissed employees are very often reinstated at their previous place of work due to errors in the downsizing procedure.
However, if the employer strictly follows the procedure described above, then termination of the employment contract with employees at the employer’s initiative due to staff reduction will be legal and justified. Therefore, in our opinion, it is very important for companies to have competent, qualified lawyers who, by complying with all legislative requirements, will be able to prevent possible labor conflicts.
employee reduction order of staff reduction notice of job reduction notice of staff reduction procedure of staff reduction payments in case of job reduction payment in case of staff reduction payment of staff reduction order of staff reduction order of staff reduction order of staff reduction order of staff reduction sample staff reduction payment in case of reduction of position order of staff reduction sample of staff reduction order