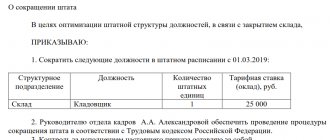
The procedure for dismissal under OSHM
The procedure for dismissing a military personnel under the General Staff Order is as follows:
- To begin with, the military unit receives an official document, which informs about the implementation of organizational and staffing measures.
- Next, the date of dismissal of the military man is determined, and he is also presented with a Conversation Sheet (if he is dismissed according to the General Staff, the conversation sheet is filled out by the commander of the military unit).
- Until the contract termination date arrives, personnel officers are preparing all the necessary documentation, and the military unit commander is preparing a new dismissal order.
- If a serviceman does not insist on dismissal from the ranks of the Military Forces of the Russian Federation, then he may be offered another position (the main condition is that the VUS matches). When there is the same position in another military unit, the military man can be transferred without his consent on the basis of the corresponding order (it is noteworthy that in this case the military man himself is not required to submit a report).
- If a military man is not found an alternative position and is not transferred to another military unit within six months, then he is fired.
» alt=”Dismissal according to general education: sample report, payments, right to a mortgage”>
Payments in case of dismissal under OSHM
To understand what is due and how much is due to a serviceman upon dismissal due to general military service, it is necessary to familiarize yourself with the Federal Law “On the Status of Russian Military Personnel.” In particular, the dismissed person has the right to the following payments:
- One-time allowance. What payments a soldier receives depends on the length of his military service. If the service period exceeds twenty years, then the military man is paid seven salaries. Otherwise, the benefit amount is 2 salaries.
- Housing and subsidies. According to current legislation, a military man who has been in service for more than ten years cannot retire due to organizational and staffing measures, unless the state provides him with housing or provides financial assistance for its purchase.
- Payment of rent. If the state does not provide housing to the serviceman, then after dismissal under the general military service, he is entitled to monthly payments for renting an apartment (in Moscow and St. Petersburg it is 15 thousand rubles, while in other cities of Russia it is 3.6 thousand rubles).
- Additional charges. If the discharged person’s service time in the RF Armed Forces exceeds 20 years, but he has not yet reached retirement age, then he can also count on due payments in the amount of one salary according to rank within 12 months from the date of termination of the contract. How much salary is due again depends on length of service and position.
As for additional benefits, citizens who were discharged from military service in 2020 after 25 years of service, as well as their family members, receive additional employment rights and social benefits.
The procedure for dismissal from the ranks of the RF Armed Forces according to the OshM. What payments are due upon redundancy?
One of the valid reasons why a serviceman may be dismissed is the implementation of organizational and staffing measures.
Expert opinion
Antonov Viktor Sergeevich
Practicing lawyer with 8 years of experience. Specialization: military law. Recognized legal expert.
What is this and who can be fired on this basis? What will the procedure look like? What benefits will the military personnel receive? This article will help you understand all these issues.
Organizational and staffing measures: what is it?
They are implemented through reorganization and liquidation processes. As a result of this procedure, the number of individual ones can be changed:
This phenomenon periodically occurs both in ordinary organizations where civilians work, and in places of military service where military personnel work. In the latter case, the implementation of such measures is regulated by Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of September 16, 1999 No. 1237.
He approved the Regulations on the procedure for military service.
Thus, when carrying out general training in military service, the following changes may occur:
- disbandment, reorganization, renaming, reassignment and other actions carried out in relation to the permanent staff of military personnel;
- changes in the composition and number of staff in the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation;
- renaming positions and specialties of military personnel, as well as other types of organizational and staffing measures.
In addition, a demotion or promotion in a position can only be carried out with the consent of the person in respect of whom such changes are planned.
How to properly resign from military service in this way: procedure
In general, the dismissal procedure as a result of organizational and staffing measures will look like this:
- First of all, the management of a particular institution in which reorganization or liquidation processes are planned to be carried out issues an appropriate order to carry out the OSM.
- Next, all employees are familiarized with this document, and those persons whose positions are subject to reduction, reorganization and other changes may be asked to take a lower or higher position (if it is impossible to transfer them to an equal position).
- If a serviceman does not agree to move to another place, then he must declare his desire to resign. In this case, an individual conversation is first conducted with him. As a rule, it is organized by the commander of a military unit. The results of the conversation are officially recorded in a special form, which is called the “conversation sheet” (Appendix No. 9 to the order of the Minister of Defense of the Russian Federation dated October 30, 2015 No. 660).
When dismissing a serviceman, an important condition is to carry out a full settlement before he is expelled from the personnel. If this requirement is not met, the dismissed person will be able to appeal the order. This is written in paragraphs. 16th century 34 Regulations, approved. Decree of the President of the Russian Federation No. 1237.
In general, when carrying out activities related to the organizational staff, the grounds for dismissal may be (subparagraph “a”, paragraph 4 of Article 34):
- reduction of the position held, provided that the serviceman cannot be appointed to a similar position and at the same time does not want to move to a lower or higher position;
- the expiration of the maximum period of time during which a person can be at the disposal of the commander;
- recognition by a military medical commission as unfit for service in a specific position, provided that the serviceman does not want to move to other positions;
- reducing the number of positions related to one military specialty, or replacing them with one composition;
- inability to get a previous position, which was held by a specific person before a criminal case was opened against him (if he was found innocent and the case was closed).
REORGANIZATION OF THE ORGANIZATION STRUCTURE
Yulia Khachaturyan,
NIKA, RISK PLAN
"HR service and personnel management of the enterprise", 2006.
Let's imagine the following situation. One day, in the brilliant mind of the head of an organization, or the HR director, or some other top manager, an amazing idea is born: to change the structure of the entire organization. Of course, the bold implementation of a grand vision will lead to a dramatic increase in the efficiency of the entire company. The previous, unproductively working marketing and advertising departments, having become a single promotion department, will be able to achieve unheard of results in the new “role”... At the same time, each of the employees of the reformed departments for some reason does not share the rosy expectations of management and thinks in horror about what negative consequences of such upheavals can directly affect him... And the head of the personnel department is thinking about how to reflect all these grandiose changes in documents, and what articles of laws should be used to guide their implementation? Sounds painfully familiar? Then this article is for you…
“Types” of changes in the structure of enterprises Changes in the structure of an enterprise, as a rule, appear either in the form of: - merger of relevant divisions (see Example 1) or - their separation (see Example 2) However, sometimes reorganization is aimed at reassigning previous departments to other managers ( see Example 3).
Example 1 A single promotion department is formed from the advertising and marketing department, a personnel management department is formed from the recruitment and personnel department, etc.
Example 2 One structural unit involved in promotion is divided into two independent ones.
Example 3. A large holding (one legal entity) was formed from once independent organizations. Before the merger, each of them had its own director and heads of structural divisions who reported directly to him. However, after the creation of a single organization, this state of affairs naturally ceased to suit the owner. It was necessary to create a common control center for previously independent legal entities. On the other hand, it was desirable to leave a significant share of competence to the old directors, so that they could effectively exercise leadership locally. In this regard, the following decision was made. Structural divisions directly involved in production (shops, which together included more than 70% of the employees of the previous legal entity) were left under the subordination of the previous directors. The office personnel of each of the old organizations (accounting, personnel department, programmers) were made part of the corresponding department, controlled from the center. So, for example, previously independent 6 HR departments of 6 enterprises became a single HR department and reported to one person. The last option for changing the structure of an organization is the most complex and its consideration deserves an independent series of articles, so in this one we will focus on the first two, the most common.
Two common methods
So, in practice, there are two most common ways to carry out the merger and division of departments: - we will conventionally call one “simple and convenient”; - the other is “cumbersome and absolutely correct.” Supporters of the first method put forward arguments against the second, and the second, respectively, against the first. At the same time, each of the opponents fights with enviable zeal for their own “brilliant” method of completing this procedure. However, we will name the “pros” and “cons” of each option later, when, in fact, we describe them. In addition, we will talk about the application of each method, both regarding the procedure for merging structural divisions and the procedure for their separation. We combine structural divisions Let's first imagine a situation where two previously independent departments (for example, advertising and marketing) are merged. Ultimately, the enormous changes associated with the global merger of structural divisions must be reflected in the staffing table, from which independent advertising and marketing departments will be excluded and in which an independent promotion department will appear. Innovations related to each specific employee will appear in the form:
- an additional agreement to the employment contract and - an order issued on its basis.
However, as mentioned above, you can go in two completely different ways to this final result in the form of: - a new staffing table (in which there is a promotion department, but no advertising and marketing departments); — additional agreements to the employment contracts of all employees of previous departments; — orders for transfer to a new, hitherto non-existent structural unit.
Method one: “Simple and convenient” -
Step 1: create a new structural unit, but do not destroy the two old ones. We, that is, representatives of the employer, first come to the advertising department, then to the marketing department (or we call the employees of these structural divisions one by one to the personnel department) and report on the joyful event awaiting the employees. Having made sure that no one is against these wonderful innovations (even the head of the advertising department, who threw something heavy and similar to a hole punch at us), we begin to prepare a new staffing table. At the same time, we are fully aware that the organization will live in accordance with it for one or two days. Thanks to this document, a new structural unit (promotion department) will appear, which will practically duplicate all those positions that exist in the advertising and marketing departments (with the exception of the positions of managers, because there can only be one head of the department). We will also transfer the old advertising and marketing departments with all employees to a new staffing table, which we will approve by order of the head of the organization. (For a sample of the initial staffing table, see Example 9, possible new ones in Examples 10-11). If making a new staffing table is burdensome (for example, the organization employs several thousand people), you can simply issue an order to amend this document. —
Step 2: transfer all employees to a new structural unit. — Ordinary employees: After this, we take an application from each of the ordinary employees with a request to transfer them to the same positions that they, in principle, previously occupied, but in a new department. Then we conclude additional agreements to the employment contract with each of the ordinary workers. The corresponding clause of the additional agreement to the employment contract may sound as follows.
Example 4. 1.1. Add clause 3.1. The employment contract contains the following provisions. From January 11, 2006, the employee is accepted into the following structural unit: promotion department.
Based on these changes, we issue transfer orders (see Example 12).
— Heads of departments: As for the heads of departments, the situation here is more complicated. It is clear that the final staffing table does not include either the position of head of the advertising department or the position of head of the marketing department. In this case, in any case, there will be a position of the head of the promotion department. As a rule, in practice, actions occur according to two algorithms. — First: the staffing table provides for the position of head of the promotion department and deputy of the promotion department. (The situation corresponds to the staffing table presented in Example 10). The position of department head is offered to one of the former department heads, while the other is offered the position of his deputy. —
Second. The positions of a department head and two deputies are being created: for marketing and advertising. (The situation corresponds to the staffing table presented in Example 11). Former department heads take the place of deputies, and the role of department head is offered to a third party. For clarity, let us present these movements in the form of diagrams.
Scheme 1 corresponds to the first algorithm and scheme 2 corresponds to the second.
Diagram 1 Previously held position Position to be held by the employee Head of the Marketing Department Head of the Promotion Department Head of the Advertising Department Deputy Head of the Promotion Department
Scheme 2 Previously held position Position that the employee will occupy Head of the promotion department Head of the marketing department Deputy head of the marketing promotion department Head of the advertising department Deputy head of the advertising promotion department However, in any case, the head of the department must write an application requesting a transfer for his intended position. After which you should make an amendment to the employment contract and issue a transfer order. Please note that if, when drawing up an additional agreement with the main employees, only the clause on the name of the structural unit will need to be “adjusted”, then when the bosses are “moved”, the names of positions, as well as labor functions, will additionally change. If one of the former bosses takes the place of the head of the entire department, then most likely his salary will also increase. (Samples of relevant fragments of an additional agreement with the former head of the marketing department in accordance with the situation according to scheme 1, see Examples 5-6; fragments of agreements in accordance with the situation according to scheme 2, see Examples 7-8).
Example 5. 1.1. Add clause 3.1. the employment contract with the following provision.
From January 11, 2006, the employee is transferred to the following structural unit: promotion department by the head of the promotion department. 1.2.Add clause 3.2. the employment contract with the following provision.
Salary from January 11, 2006 is 21,000 rubles. 1.3.
Add the following provision to clause 3.3 of the employment contract.
Since January 11, 2006, the employee has been performing duties in accordance with the job description of the head of the promotion department, approved on January 11, 2006 by the head of the organization.
Example 6. 1.1. Add clause 3.1. the employment contract with the following provision. From January 11, 2006, the employee is transferred to the following structural unit: promotion department as deputy head of the promotion department. 1.2. Add the following provision to clause 3.3 of the employment contract. Since January 11, 2006, the employee has been performing duties in accordance with the job description of the deputy head of the promotion department, approved on January 11, 2006 by the head of the organization.
Example 7. 1.1. Add clause 3.1. the employment contract with the following provision. From January 11, 2006, the employee is transferred to the following structural unit: promotion department as deputy head of the promotion department for marketing. 1.2.Add clause 3.3 of the employment contract with the following provision. Since January 11, 2006, the employee has been performing duties in accordance with the job description of the deputy head of the marketing promotion department, approved on January 11, 2006 by the head of the organization.
Example 8. 1.1. Add clause 3.1. the employment contract with the following provision. From January 11, 2006, the employee is transferred to the following structural unit: promotion department as deputy head of the advertising promotion department. 1.2.Add clause 3.3 of the employment contract with the following provision. Since January 11, 2006, the employee has been performing duties in accordance with the job description of the deputy head of the advertising promotion department, approved on January 11, 2006 by the head of the organization. — Step 3: destroy the old structural unit. So, after we have completed all the steps described above, the following picture emerges. In our new staffing table there are two old structural divisions in which not a single position is filled. Accordingly, the advertising and marketing departments are no longer needed; we can simply liquidate them. We publish a new staffing table (see Example 13-14), approve it by order of the manager, and the procedure for merging departments is completed.
So, in a simple and convenient way, in one or two days we achieved the desired result:
— created a new staffing table that reflects the real structure of the enterprise;
— concluded additional agreements to employment contracts with all employees, which reflected new working conditions;
— issued orders to transfer employees to the promotion department. In a cumbersome and correct way, we will arrive at the same result no earlier than in two months...
Method two: “Bulky and absolutely correct”
Topic: Consulting on personnel issues
What guarantees are provided by current legislation for the heads of two departments when reorganizing the internal structure of an institution, as well as for ordinary specialists if two departments are merged? V.A. Kharitonov, Bryansk
The second method of documenting the procedure for merging two departments is preceded by an analysis of this situation from a legal point of view. So, at one time an employment contract was concluded with each of the department employees, which spelled out the conditions to which he agreed. It is advisable to divide them into two groups:
— about the employee’s labor function;
- other conditions:
- Job title,
- structural unit,
- wages, etc.
Ordinary employees
For all ordinary employees, in the event of a merger of departments, most likely, only one essential working condition will change - the structural unit. Since the labor function of the employees remains unchanged, from a legal point of view there is no talk of any reduction in their positions. We only need to change the clause on the name of the structural unit in the contract with each of the employees. We can do this without their consent, guided by Article 73 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Fragment of the document Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Article 73 “Changing the essential terms of the employment contract.” Parts 1-4, 8. For reasons related to changes in organizational or technological working conditions, it is allowed to change the essential terms of the employment contract determined by the parties at the initiative of the employer when the employee continues to work without changing the job function. The employee must be notified by the employer in writing of the introduction of these changes no later than two months before their introduction, unless otherwise provided by this Code or other federal law. If the employee does not agree to continue working under the new conditions, then the employer is obliged to offer him in writing another job available in the organization that corresponds to his qualifications and state of health, and in the absence of such work, a vacant lower position or lower paid job that the employee can perform with taking into account his qualifications and health status. In the absence of the specified work, as well as in the event of the employee’s refusal of the offered work, the employment contract is terminated in accordance with paragraph 7 of Article 77 of this Code. If the circumstances specified in part one of this article may lead to mass dismissal of workers, the employer, in order to preserve jobs, has the right, taking into account the opinion of the elected trade union body of this organization, to introduce a part-time working regime for a period of up to six months. Changes to the essential terms of the employment contract cannot be introduced that worsen the employee’s position in comparison with the terms of the collective agreement or agreement.
Accordingly, two months before the start of restructuring, we must prepare notifications about the upcoming change in working conditions for each employee (see Example 15) and familiarize employees with them. They periodically need to be offered vacant positions that appear in the organization. Two months later, we prepare a draft of a new staffing table and approve it with the head of the organization. If, after sixty days, a specific ordinary employee agrees to these innovations, then we sign an additional agreement with him to the employment contract and issue a transfer order. If the employee proudly refuses, then we dismiss him under paragraph 7 of Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, that is, due to refusal to continue work due to a change in the essential terms of the employment contract. Heads of departments As for former heads of departments, the situation here is more complicated. It is assumed that after they occupy the new position “reserved” for each of them, not only such terms of the contract as the name of the department, positions and salaries will change, but also labor functions. We cannot unilaterally transform one employee’s labor function into another, using Article 73 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. In fact, we are reducing the positions of department heads. And, accordingly, we must notify the persons occupying them, in accordance with Article 180 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, two months in advance about this unfortunate event. (For a sample layoff notice, see Example 16). At the same time, we, guided by the requirement of Article 180 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, will have to periodically offer each of the employees other vacant positions existing in the organization within two months. After the new staffing table is approved two months later, we propose that department heads be transferred to the appropriate positions. If the bosses agree, we make additional agreements to the employment contracts and issue appropriate transfer orders. If employees refuse to transfer, they will be dismissed under paragraph 2 of Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (reduction in the number or staff of employees). At the same time, they must be paid appropriate monetary compensation. Fragment of the document Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Article 178 “Severance pay”. Upon termination of an employment contract due to the liquidation of an organization (clause 1 of Article 81) or a reduction in the number or staff of the organization's employees (clause 2 of Article 81), the dismissed employee is paid severance pay in the amount of average monthly earnings, and he is also retained the average monthly earnings for the period of employment , but not more than two months from the date of dismissal (including severance pay). In exceptional cases, the average monthly salary is retained by the dismissed employee for the third month from the date of dismissal by decision of the employment service body, provided that within two weeks after the dismissal the employee applied to this body and was not employed by it.
Algorithm of actions
Let’s systematize what has been said step by step:
Step 1: we notify ordinary employees of changes in the essential terms of the employment contract two months in advance.
Step 2: notify department heads about the reduction of their positions.
Step 3: two months later, we prepare a draft of a new staffing table and approve it with the head of the organization.
Step 4: we transfer ordinary employees to vacant positions in the new staffing table if the employees agree.
If they refuse, we dismiss them in accordance with paragraph 7 of Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Step 5: we transfer the heads of departments to the positions “reserved” for them, if the former heads of departments agree to this, and if they refuse, we terminate the employment contract with them in accordance with paragraph 2 of Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The merger of two departments into one is completed. Separating structural divisions Now let's consider a diametrically opposite situation: one promotion department was divided into two departments.
Method one: “Simple and convenient” Separation of departments in a simple and convenient way is carried out practically according to the same scheme as their merger. That is, we:
Step 1. We create two new structural divisions, but do not destroy the old one. We approve a new staffing table, which includes three structural divisions: the marketing department, the advertising department, and the promotion department.
Step 2. We transfer all employees to the new structural unit. — Ordinary employees: We take applications from ordinary employees for transfer to the marketing and advertising departments. After this, we conclude additional agreements to employment contracts with these employees, and on their basis we issue transfer orders. — Head of the department: It should be taken into account that the former head of the promotion department will have to be demoted in any case. And he will become either the head of the advertising department or the head of the marketing department. For the position of head of the second department, you will have to look for a worthy candidate. Accordingly, the head of the promotion department must write a statement with a request to translate it, for example, by the head of the advertising department. After which you should make an amendment to the employment contract and issue a transfer order. —
Step 3. Destroy the old structural unit. After this, an order should be issued approving the staffing table, from which the promotion department will disappear and only the advertising and marketing departments will remain. Method two: “Bulky and absolutely correct”
Ordinary employees
For all ordinary employees, in the case of division of departments, as well as in the case of their merger, usually only the structural unit changes. Accordingly, guided by Article 73 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, we notify employees of the change after two months of its name. Then, two months later, we prepare a draft of a new staffing table and approve it by the head of the organization. If we obtain the consent of a specific employee to introduce innovations, we sign an additional agreement with him to the employment contract and issue an order for transfer, and if he refuses, we fire him. Heads of departments The head of a department should be notified two months before the division of departments about the reduction of his position. After the new staffing table is approved 60 days later, we offer him to take the place of head of one of the departments. If we agree, we make an additional agreement to the employment contract and issue a transfer order. If the boss refuses, the employment contract will be terminated under paragraph 2 of Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (reduction in the number or staff of employees).
"Pros" and "cons" of each method
"Pros" and "cons" of the first method
"Minuses"
In a conflict situation, a militant employee can prove to the appropriate authority that, from a legal point of view, we did not take entirely correct actions:
— they hid the staff reductions, because in fact the positions of department heads are being eliminated. Accordingly, we did not warn managers about the upcoming reduction two months in advance and did not provide them with other guarantees and compensation required by law. — they tried to camouflage changes in the essential terms of the employment contract of ordinary employees and arbitrarily deprived them of the right to learn in advance about upcoming innovations.
“Pros” The procedure for merging and dividing departments is carried out in the shortest possible time, and registering it in this way is very convenient. “Pros” and “cons” of the second method “Cons” Carrying out the procedure for separating or merging departments in this way takes a lot of time and effort. “Pros” From a legal point of view, we did everything correctly; we are not afraid of inspections or legal proceedings with one or more offended employees.
Example 15. LIMITED LIABILITY COMPANY "KRAKI"
Moscow January 11, 2006
NOTICE of changes in the essential terms of the employment contract
Dear Shabanov Alexander Alexandrovich! In accordance with Article 73 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, we notify you that from March 12, 2006, in connection with a change in the organizational structure of the enterprise, the terms of the employment contract with you dated March 11, 2001 No. 2 on the structural unit in which you work will be changed to condition for performing work in the promotion department. If you refuse to continue working in connection with a change in this condition of the employment contract, you will be dismissed under paragraph 7 of Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
General Director signature I.V. Pashentsev I read the notification on January 11, 2006, signature A.A. Shabanov
Example 16. LIMITED LIABILITY COMPANY "KRAKI"
Moscow January 11, 2006
NOTICE about layoffs Dear Prudnikov Eduard Leonidovich!
In accordance with Part 2 of Article 180 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, we notify you that on March 12, 2006, your position will be reduced.
General Director signature I.V. Pashentsev
The notification was read on January 11, 2006, signature E.L. Prudnikov
Attend a seminar by the author of the publication:
Seminars on taxes, tax planning (for accountants, financial directors, managers and company owners)
How to write a report?
In general, this document is similar to the application that is submitted by civilians when leaving a job of their own free will.
It is compiled in writing on A4 paper. It can be handwritten or typed on a computer. The content should include the following main sections:
- The “heading” of the document - here the full name of the official who is authorized to make such decisions, the name of the institution in which military service takes place and the full name of the serviceman are indicated.
- Title – usually one word is indicated: “Report”.
- Content part - the following information is presented sequentially:
- a request to petition your superiors for voluntary dismissal;
- reason for leaving (in this case it will be organizational and staffing measures);
- message about the availability/lack of housing;
- a note on passing or refusing the medical examination procedure;
- the place where the personal file should be sent for military registration.
- At the end of the document, a list of attachments, the serviceman’s position, military rank and signature are indicated.
- report on dismissal according to general education
- report on dismissal according to general education
Notification of the start of the reorganization procedure
Any form of reorganization begins with a decision to carry it out. Depending on the organizational and legal status of the legal entity, such a decision can be made by:
- General meeting of founders or sole participant (LLC).
- General meeting of shareholders (OJSC, PJSC, CJSC).
- Executive authorities of the Russian Federation and constituent entities of the Russian Federation (government institutions).
- Local authorities (municipal institutions).
The decision must indicate the type of reorganization, the procedure for its implementation, the timing of individual activities, as well as the list of responsible persons.
To transform legal entities from LLC to OJSC and vice versa, it is also necessary to regulate in detail the procedure for the exchange of shares in the authorized capital and securities of the joint-stock company.
Making a decision on reorganization involves notifying the registration authority - the Federal Tax Service inspection at the location of the organization - about the start of this procedure.
Such notification is carried out by sending an application to the Federal Tax Service in the form P12003. This form is approved by law and is subject to mandatory notarization.
Notification of the start of the procedure is submitted to the tax office no later than three days from the moment the decision on reorganization is made. Violation of the established deadline entails the application of financial sanctions in the form of a fine.
Sending a notification will be the basis for entering information into the Unified State Register of Legal Entities about the start of the company reorganization procedure.
What payments are due when leaving the army?
As in labor legislation, when laying off due to organizational and staffing measures, a military serviceman is entitled to a whole list of guarantees and compensations. The main ones include:
- One-time benefit (clause 3, article 3 of the Federal Law of the Russian Federation “On monetary allowances ...”) - its size depends on length of service. If a serviceman has worked under a contract for less than 20 years, then he will be paid 2 salaries, but if he has served for 20 years or more, then the amount will increase to 7 salaries.
Upon dismissal, a serviceman must receive monetary allowance accrued for the entire period up to the day of exclusion from the personnel.
In addition to the above, military personnel discharged due to incidental injuries are also entitled to other types of guarantees and compensation. This includes:
- provision of housing;
- permission to wear military uniform;
- receiving additional leave;
- the duration of which is 30 days, etc.
Thus, the main reasons for the dismissal of military personnel due to organizational and staffing measures are:
- reduction;
- reformation;
- replacement of staff and other actions as a result of which the organizational structure of the institution changes.
Expert opinion
Antonov Viktor Sergeevich
Practicing lawyer with 8 years of experience. Specialization: military law. Recognized legal expert.
Moreover, if there are vacancies, the person must be transferred to a similar position or placed at a lower/higher position (in the latter two cases, the consent of the military personnel is required).
Dismissal of employees during enterprise reorganization
- the fact of the reorganization, its form;
- formation of a new company (name), merger, creation of new companies, etc.;
- change of owner.
- maintaining the employee’s labor rights in the new company;
- the employee’s right to resign on the basis of Art. 77 Labor Code (part 1, clause 6).
- salary for actual days worked;
- compensation for unused vacation;
- other payments provided for by internal regulations.
- salary for June 2020 – 25,720 rubles;
- vacation compensation for 10 days – 8,778 rubles. (25.720 / 29.3 * 10 days);
- average monthly earnings – 27,212 rubles. (25.720 / 29.3 * 31 days).
Let's look at the most common mistakes made when registering dismissal during the reorganization process.
Due to violations of the Labor Code, employees of the planning department have every reason to go to court and demand reinstatement at work.
In what cases can one be fired due to organizational and staffing measures?
Organizational and staffing measures (hereinafter - OSM) is a collective concept that is not deciphered in any way in legislative acts.
Referring to the OSHM, they can be fired under the following circumstances:
- reduction of staff, and in the absence of the opportunity to provide another job with an equal position and the refusal of the serviceman to take a lower position;
- reorganization, optimization, change in the structure of a military unit, involving a change in staff;
- renaming of positions due to changes in nomenclature in the lists;
- retirement;
- recognition by a medical commission of a military man as unfit, in whole or in part, to perform his previous duties, but who has not agreed to another position;
- expiration of the contract, etc.
It turns out that in a number of cases a contract employee can be fired without taking into account his opinion and desire, and the contract will have to be terminated. A serviceman planning to serve a full term, allowing him to apply for a pension, is forced to radically change his life plans.
Dismissal due to OSH is regulated by the following legislative acts:
- Law of March 28, 1998 No. 53-FZ (as amended on March 18, 2019) “On military duty and military service”;
- Law No. 306-FZ dated August 3, 2018, which introduced amendments to the laws on pension and social insurance;
- Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- Resolution of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation dated May 29, 2014 No. 8 (as amended on June 28, 2016) “On the practice of application by courts of legislation on conscription, military service and the status of military personnel”;
- Law of May 27, 1998 No. 76-FZ “On the status of military personnel”;
- By Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of September 16, 1999 No. 1237.
If, nevertheless, dismissal cannot be avoided, then it is important that all the legal rights of the serviceman are respected.
NON-WORKING DAYS AND TAX DEADLINES
Taking into account the fact that the Decree of the President of the Russian Federation dated March 25, 2020 from March 30 to April 3, 2020 established “non-working days” that are not “non-working holidays” or “weekends” referred to in Article 6.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, The question arose about whether these days are recognized as working days within the meaning of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Unfortunately, with some delay, this problem was resolved for tax purposes - paragraphs 6 and 7 of Article 6.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation were supplemented with a reference to the fact that “non-working” days introduced by the Presidential Decree are not recognized as working days, like regular weekends. Consequently, deadlines expiring on the specified days should be postponed to the first next working day - on the date of this alert, April 6 should be recognized as such. Fulfillment of tax obligations before this date is possible, but not mandatory. It should be noted that previously the Ministry of Finance of Russia, by official interpretation, allowed the deadline for submitting annual financial statements to be postponed to April 6, 2020.