Required details
9 of Law N 402-FZ and paragraphs. "e" clause 2 art. 9 of Law No. 129-FZ.
Another innovation is that in the primary accounting document the measurement value of a fact of economic life can be reflected only in physical or only in monetary terms.
Another difference is the requirement of Law N 402-FZ to indicate in the primary accounting document, in addition to the signatures of the persons who completed the transaction or operation or formalized the event, their surnames and initials. Previously, such a requirement was contained only in clause 13 of the Regulations on accounting and financial reporting in the Russian Federation.
Let us note that the new Law “On Accounting” does not contain rules establishing the powers and responsibilities of officials of economic entities and the procedure for their transfer. In particular, Law No. 402-FZ does not regulate the procedure for granting the right to sign primary accounting documents, nor does it contain a list of positions of persons signing documents that document transactions with funds. Obviously, these issues can be resolved by economic entities in different ways.
Date of publication: 2015-01-14; Read: 156 | Page copyright infringement
Procedure for approving primary forms
Documents used by an organization to record the facts of its economic life must be approved by the head of the organization. At the same time, the manager must also approve the list of officials who have the right to sign these primary accounting documents.
If the organization decides to use the usual unified forms, they must still be approved as the primary accounting documents used by the organization. Apparently, a large number of organizations will do so, especially since most popular accounting programs are already configured to use the old unified forms.
In this regard, the question is often asked whether the words “unified form” should be removed from the approved sample. I believe that if an organization approves a primary document with such an inscription, this will in no way conflict with the new law.
The main thing is that this document has all the necessary details and is approved by the head of the organization.
People often ask whether a primary accounting document will be legitimate if it does not indicate at all who and when it was approved, that is, there will be no name of the head of the organization and the date of approval. In my opinion, these are clearly unnecessary fears. If you reflect this information on a form, that’s fine; if you don’t, that’s also fine. This information is not required information.
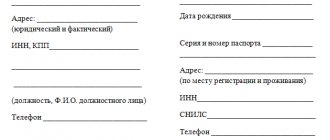
Requirements for mandatory document details
Article 9. Primary accounting documents
1. Each fact of economic life is subject to registration with a primary accounting document. It is not allowed to accept for accounting documents documents that document facts of economic life that have not taken place, including those underlying imaginary and sham transactions.
(as amended by Federal Law dated December 21, 2013 N 357-FZ)
(see text in previous)
2. Mandatory details of the primary accounting document are:
1) name of the document;
2) date of preparation of the document;
3) the name of the economic entity that compiled the document;
4) the content of the fact of economic life;
5) the value of the natural and (or) monetary measurement of a fact of economic life, indicating the units of measurement;
6) the name of the position of the person (persons) who completed the transaction, operation and the person(s) responsible for its execution, or the name of the position of the person(s) responsible for the execution of the accomplished event;
(as amended by Federal Law dated December 21, 2013 N 357-FZ)
(see text in previous)
7) signatures of the persons provided for in paragraph 6 of this part, indicating their surnames and initials or other details necessary to identify these persons.
3. The primary accounting document must be drawn up when a fact of economic life is committed, and if this is not possible, immediately after its completion. The person responsible for registration of the fact of economic life ensures the timely transfer of primary accounting documents for registration of the data contained in them in the accounting registers, as well as the reliability of this data. The person entrusted with maintaining accounting records and the person with whom an agreement has been concluded for the provision of accounting services are not responsible for the compliance of primary accounting documents compiled by other persons with accomplished facts of economic life.
(as amended by Federal Law dated December 21, 2013 N 357-FZ)
(see text in previous)
TORG-12: to be or not to be
The biggest debate is whether the most famous invoice TORG-12 should be preserved in a “unified” form.
It must be stated right away that this primary document has ceased to be mandatory. It can be used, but only on a voluntary basis. The attitude towards this previously popular document is diametrically opposite. From “the most inconvenient document” to “you can’t imagine anything better.”
I think that those sellers who do not like TORG-12 have already come up with and approved the consignment note in the form that will be most convenient for them. Others may have simply removed anything unnecessary from the invoice that was bothering them. And the majority will probably leave everything as it is, approving TORG-12 as their primary accounting document. Until the developers of some accounting program offer them another form.
Is the date of preparation a mandatory requisite of the document?
The forms of primary accounting documents are determined by the head of the economic entity on the recommendation of the official responsible for maintaining accounting records. The forms of primary accounting documents for public sector organizations are established in accordance with the budget legislation of the Russian Federation.
(as amended by Federal Law dated December 21, 2013 N 357-FZ)
(see text in previous)
5. The primary accounting document is drawn up on paper and (or) in the form of an electronic document signed.
6. If the legislation of the Russian Federation or an agreement provides for the submission of a primary accounting document to another person or to a state body on paper, an economic entity is obliged, at the request of another person or government body, at its own expense, to make copies on paper of the primary accounting document drawn up in in the form of an electronic document.
7. Corrections are allowed in the primary accounting document unless established by federal laws or regulatory legal acts of state accounting regulatory bodies.
The correction in the primary accounting document must contain the date of the correction, as well as the signatures of the persons who compiled the document in which the correction was made, indicating their surnames and initials or other details necessary to identify these persons.
8. If, in accordance with the Russian Federation, primary accounting documents, including in the form of an electronic document, are seized, copies of the seized documents, made in the manner established by the legislation of the Russian Federation, are included in the accounting documents.
The basis for entries in accounting registers are primary documents .
Primary documents are accepted for accounting if they are compiled according to the form contained in the albums of unified forms of primary accounting documentation, in accordance with the Regulations on accounting and financial reporting in the Russian Federation, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 29, 1998 No. 34 n (as amended by 03/26/2007 No. 26n)
If necessary, additional lines and columns may be included in the standard form, but all details provided for in the approved form must be preserved. Changes made must be formalized by an appropriate order (instruction).
Only document forms for recording cash transactions are not subject to change in accordance with the Procedure for using unified forms of primary accounting documentation, approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated March 24, 1999 No. 20.
The forms approved by the State Statistics Committee of Russia provide information coding zones that are filled out in accordance with all-Russian classifiers. Codes that do not have links to all-Russian classifiers (for example, columns with the name “Type of operation”) are intended to summarize and systematize information when processing data using computer technology and are entered according to the coding system adopted in the organization.
In addition, forms independently developed by a small enterprise containing the relevant mandatory details provided for by the Federal Law “On Accounting” are accepted for accounting.
You can independently develop only those documents that are not contained in albums of unified forms.
Mandatory details of primary accounting documents include:
- Title of the document;
- date of its preparation;
- name of the organization on behalf of which the document was drawn up;
- the content of a business transaction in physical and monetary terms;
- the names of the positions of the persons responsible for the execution of the business transaction and the correctness of its execution;
- personal signatures of these persons.
Timely and high-quality execution of primary accounting documents, their transfer to the accounting department within the established time frame for reflection in accounting, as well as the reliability of the data contained in them are ensured by the persons who compiled and signed these documents.
The list of persons authorized to sign primary accounting documents is approved by the head of the organization in agreement with the chief accountant.
Documents used to document business transactions with funds are signed by the head of the organization and the chief accountant.
Instead of the manager and chief accountant, other officials may sign the primary documents, but their list must be approved by the head of the organization and agreed upon with the chief accountant.
The primary document is written evidence of the completion of a business transaction (payment for goods, issuance of cash on account, etc.) and must be drawn up at the time of the transaction, and if this is not possible, immediately after its completion.
All primary documents can be divided into the following groups:
- organizational and administrative;
- exculpatory;
- accounting documents.
Organizational and administrative documents are orders, instructions, instructions, powers of attorney, etc. These documents permit the conduct of certain business transactions.
Supporting documents include invoices, requirements, receipt orders, acceptance certificates, etc. These documents reflect the fact of a business transaction and the information contained in them is entered into accounting registers.
Some documents are both permitting and exculpatory. These include, for example, a cash order, a payroll, etc.
For proper maintenance of primary accounting, a document flow schedule is developed and approved, which determines the order and timing of the movement of primary documents within the enterprise and their receipt by the accounting department.
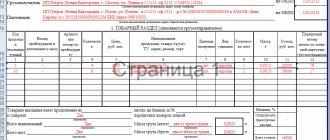
Movement schedule of primary accounting documents
| Name of works | Executor | Submission deadline | To whom is the document sent? | Actually transferred (date) | ||
| FULL NAME. | Job title | |||||
Primary documents received by the accounting department (accountant) must be checked:
- by form (completeness and correctness of the document, filling in the details);
- arithmetically (counting amounts);
- by content (connection of individual indicators, absence of internal contradictions).
After acceptance, information from the primary document is transferred to the accounting registers, and a mark is made on the document itself to exclude the possibility of its double use (for example, the date of entry into the accounting register is indicated).
Accounting registers are specially adapted sheets of paper for recording and grouping accounting data. They are kept in special books (magazines), on separate sheets and cards, in the form of machine diagrams obtained using computer technology, as well as on magnetic tapes, disks, floppy disks and other computer media.
Business transactions must be reflected in accounting registers in chronological order and grouped according to the appropriate accounting accounts.
In appearance, the accounting registers are:
- books (cash register, main);
- cards (fixed asset accounting, materials accounting);
- magazines (loose or lined sheets).
According to the types of records made, registers are divided into:
- chronological (registration log);
- systematic (general ledger of accounts);
- combined (journal orders).
According to the level of detail of the information contained in the accounting registers, they are:
- synthetic (general ledger of accounts);
- analytical (cards);
- combined (order journals).
Entries in primary documents must be made by means that ensure the safety of these entries for the period of time established for their storage in the archive.
Primary and consolidated accounting documents can be compiled on paper and computer media. In the latter case, the organization is obliged to produce, at its own expense, copies of such documents on paper for other participants in business transactions, as well as at the request of the authorities exercising control in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, the court and the prosecutor's office.
For submission to the archive, documents are selected in chronological order, completed, bound and filed in folders. Submission of documents to the archive is accompanied by a certificate.
When storing accounting registers, they must be protected from unauthorized corrections. Correction of an error in the accounting register must be justified and confirmed by the signature of the person who made the correction, indicating the date of the correction.
The contents of accounting registers and internal accounting reports are a trade secret.
Persons who have access to information contained in accounting registers and internal accounting reports are required to maintain trade secrets. For its disclosure they bear responsibility established by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
Correction of errors in primary documents and accounting registers. In accordance with Art. 9 of the Federal Law “On Accounting” it is not allowed to make corrections to cash and banking documents.
Corrections can be made to other primary accounting documents only by agreement with the participants in business transactions, which must be confirmed by the signatures of the same persons who signed the documents, indicating the date of the corrections.
The detail of the primary document that is subject to correction is crossed out with a clear but thin line, so that the original meaning (content) of the corrected detail is visible. An o is made by hand next to it, and the correction is certified by the signature of the person who made the correction, indicating the surname and initials.
Storage periods for primary accounting documents. In accordance with Art.
Document details: we fill it out correctly
17 of the Federal Law “On Accounting”, organizations are required to store primary accounting documents, accounting registers and financial statements for periods established in accordance with the rules for organizing state archival affairs, but not less than five years.
Restoration of primary documents. The accounting legislation does not contain clearly established rules that regulate the procedure for restoring primary documents in the event of their loss.
A number of regulations define only the storage periods for primary accounting documents. The legislation does not establish what an organization should do in the event of loss of documents for reasons beyond its control. In the Letter of the Department of Tax Administration of Russia for Moscow dated September 13, 2002 No. 26-12/43411, the head of the organization is recommended in the event of loss or destruction of primary documents:
- by order, appoint a commission to investigate the causes of the loss or destruction of primary documents, to participate in which, as necessary, representatives of investigative authorities, security and state fire supervision are invited;
- take measures to restore those primary documents that are subject to restoration and storage for the period established by law. For example, copies of statements of cash flows on bank accounts can be obtained from the banks where the organization’s accounts are opened; contracts, acts, invoices can be requested from counterparties, etc.
But it is not always possible to obtain duplicates of all lost documents, for example, if there are a large number of counterparties, due to the absence of suppliers (buyers) at previously known addresses, or due to the lack of such contacts. Thus, for objective reasons, the organization will not be able to restore all lost primary documents.
Practical question: what to do in this case? Should the tax authority be notified?
According to a number of experts, it is not necessary to notify the tax inspectorate, especially since this will not help avoid possible liability, and the absence of primary documents may result in a fine in accordance with Art. 120 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
In this case, the taxpayer can choose three options:
1. If possible, restore lost documents (at least partially). 2. Make corrective entries for undocumented expenses and reflect the corrections in the updated income tax return for the reporting year, because undocumented expenses are not recognized as expenses in tax accounting. 3. To enable representatives of the tax authority, in the event of a tax audit, to determine the amounts payable to the budget by calculation based on the data available to the taxpayer, as well as on the basis of data on other similar taxpayers (clause 7, clause 1, article 31 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) .
Seizure of primary documents. They can be confiscated only by the bodies of inquiry, preliminary investigation and prosecutor's office, courts, tax authorities and internal affairs bodies on the basis of their decisions in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the RSFSR dated July 26, 1991 No. 16/176 approved the Instruction on the procedure for the seizure by an official of the state tax inspectorate of documents indicating the concealment (understatement) of profit (income) or the concealment of other objects from taxation from enterprises, institutions, organizations and citizens.
The chief accountant or other official of the organization has the right, with the permission and in the presence of representatives of the authorities conducting the seizure of documents, to make copies of them indicating the reason and date of seizure.