What is account 01
Account 01 01 in 2020 refers to assets reflecting fixed assets, their movement and cost. The account is considered non-current.
The concept of fixed assets
Account 01 identifies fixed assets as tangible assets owned by the organization. They are used in economic activities. Their cost is transferred to the cost of manufactured goods or products.
Fixed assets include:
- roads and all transport;
- tools, work equipment;
- breeding stock;
- power machines;
- production equipment;
- structures and buildings owned by the organization;
- all types of transmission networks, these include heating networks and electrical networks.
Included in the account are fixed assets that are capital investments in leased assets and leased land plots. They are non-current assets and take part in production activities not as a means, but as a direct object.
For an object to be recognized as a fixed asset, the following conditions must be met:
- It is used in the production activities of the enterprise.
- There are promising economic benefits.
- The object is not intended for resale.
If the cost of a fixed asset is less than 40,000 rubles, it can be immediately written off as an expense.
https://youtu.be/fzQ-5M_YRLM
Account functions 01
Account zero one in accounting has a number of functions.
Formation of the cost of fixed assets
Initially, the price of the OS is taken into account as the initial price. Expenses for the acquisition of intangible assets include:
- amounts paid to the seller;
- delivery costs;
- expenses for advisory and information services;
- payment for services to intermediaries;
- customs duties when importing OS;
- expenses for contractors' services.
Customs duties as expenses on account 01
A number of costs remain unchanged. For example, amounts for general business expenses. Purchase costs are initially reflected on account 08. After they are fully formed, they are transferred to account 01.
Important! This is done only at the moment when the property is fully equipped and suitable for use. Therefore, if a company purchased a kettle, it should immediately be reflected in the balance of account 01, even if it was in the warehouse all this time.
Depreciation of fixed assets
Depreciation of fixed assets in accounting means the transfer of their value to the cost of manufactured products. This is done gradually.
Depreciation process
There are categories of objects that are not subject to depreciation. These include:
- plots of land;
- livestock;
- environmental management facilities;
- external landscaping;
- road and forestry;
- residential properties that are not classified as non-industrial.
If the repair process took more than a year, and the objects were mothballed for a period of more than three months, then depreciation is no longer calculated.
On the balance sheet of the accounting department, residual funds are reflected at their residual value. This means that the first value minus the accumulated depreciation percentage is reported. Non-depreciated property must be accounted for on the balance sheet at its original cost.
According to the plan, depreciation begins the next day from the date of commissioning. The termination of accrual according to the approved standard occurs after the complete write-off of the cost.
From the moment the book value of a fixed asset becomes zero or receives a negative value, it ceases to be reflected in the balance sheet.
Other possible uses
Account 01 allows you to organize analytical accounting of funds. In this case, each object will be assigned an inventory number. If one object has several parts that have different service lives, in such a situation each part will be counted as separate.
Typical accounting entries for account 01
Here are some accounting entries for the debit and credit of account 01, provided for by the Chart of Accounts and the Instructions for its application (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n):
| Operation | Account debit | Account credit |
| Fixed asset item accepted for accounting | 01 | 08 “Investments in non-current assets” |
| The original (replacement) cost of a retiring asset has been written off | 01/B | 01 |
| An OS object was returned from a branch of the organization | 01 | 79 “Intra-economic settlements” |
| The receipt of a contribution in the form of fixed assets under a simple partnership agreement is reflected | 01 | 80 "Contributions of comrades" |
| Reflects the initial revaluation of an asset | 01 | 83 “Additional capital” |
| Depreciation on a retiring fixed asset item is written off | 02 “Depreciation of fixed assets” | 01/B |
| Animals culled from the main herd are reflected | 11 “Animals in cultivation and fattening” | 01 |
| A claim was filed against the supplier of fixed assets due to an arithmetic error discovered in the supplier’s documents, as a result of which the cost of the fixed assets was overstated | 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors” | 01 |
| The fixed assets object was transferred to a separate division that keeps records on an independent balance sheet | 79 | 01 |
| The fixed assets object was returned upon termination of the simple partnership agreement | 80 | 01 |
| The depreciation of an asset is reflected within the limits of the previously made revaluation credited to the organization’s additional capital | 83 | 01 |
| The residual value of the sold asset has been written off | 91 | 01/B |
| The shortage of fixed assets discovered during inventory is reflected | 94 “Shortages and losses from damage to valuables” | 01/B |
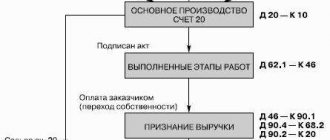
>Reflection of transactions on disposal of fixed assets
What subaccounts are there in account 01
Sub-accounts are opened for account 01:
- 01-1 - this includes all means of primary activity, with the exception of livestock, perennial plantings, plots of land and environmental management facilities. This subaccount takes into account the availability and movement of funds from the main type of activity, which is established by the constituent documents.
- 01-2 - Other production operating systems. This takes into account the movement of funds from other productions and industries that are not related to the main activities of the organization.
- 01-3 - non-production OS. This subaccount records the movement and safety of funds aimed at servicing the social activities of the enterprise, housing and communal services, and consumer services for citizens.
- 01-4 is a subaccount that takes into account working and productive livestock.
- 01-5 - this includes all perennial plantings, including forest strips. Plantings accepted for use are recorded by type and year of planting. The object in this case will be the landing area. Maintenance costs are included in the cost of production obtained from these plantings. Depreciation is not charged for young plantings that have not been put into operation.
- 01-6 - subaccount takes into account the movement of plots of land, water and forest lands, minerals that are transferred to the enterprise for operation. Depreciation is not charged on these items.
- 01-7 - non-inventory objects - this will include movements of capital investments aimed at using land, water and forest resources.
- 01-8 - all household supplies, tools and equipment whose useful life is more than a year.
- 01-9 - these are objects received on lease, rent or credit. Account 001 is also used when a leasing agreement is concluded, but only if the fixed assets will be registered with the organization. Accounting is maintained for each object separately. Adjustments to the value of the leased property will be reflected through account 01k.
- 01-10 - this subaccount takes into account other objects not previously specified.
- 01-11 - the account reflects the disposal of fixed assets.
For analytical accounting, account card 01 is used. It is distributed by location, groups and individual objects.
Leasing concept
Analytical accounting should provide all the necessary data on the availability and movement of funds in Russia and abroad. If fixed assets contain precious metals, then their mass must be indicated on the cards.
What should be understood by this term?
Account 01 in accounting, where fixed assets are reflected, is intended to summarize the available information about their availability and movement. And the question of how to correctly carry out accounting for this position should be and is of interest to almost every accountant.
Before you start talking about accounting records, you should decide what is considered fixed assets. This term migrated to us from the Soviet past. Today, more specific terminology is used, for example, building and equipment, land, etc.
From a legal point of view, this definition should be understood as the property that is recognized by the OS in accordance with regulatory documentation.
Thus, the Order of the main financial department of the country No. 26n dated March 30, 2001 “On approval of the Regulations on accounting of fixed assets” provides a list of property that should be classified as fixed assets.
The property of business entities is registered as fixed assets if the following conditions are met:
- the property will be used in the process of manufacturing products, when performing work or in the process of providing services, for management needs, as well as for transfer for temporary use or ownership;
- will be used for a long time or at least 12 months;
- subsequent resale of the specified object is not provided;
- property registered can bring economic benefits to the enterprise in the future.
Interaction with other accounts in accounting
01 accounting account is allocated according to the plan for accounting for fixed assets. There they must be used at their original cost. The budget account is active. This will mean that all receipts are recorded as a debit, and the decrease, the new value of the value, is taken into account as a credit.
Postings
In the debit budget, account 1 interacts with the credit of the following accounts:
- 03 - reflection of the return of fixed assets from income (for example, this may be a return from a creditor);
- 08 - receipt of funds, then increase in their price due to reconstruction, re-equipment;
- 76 - crediting fixed assets from other debtors (cases when no modification is required);
- 79 — on-farm calculations;
- 83 - price increase based on revaluation.
The loan interaction is carried out with the following accounts:
- 02 - reflection of the disposal of funds;
- 11 — transfer of animals to the main herd;
- 99 — write-off as a result of an emergency;
- 83 - price decrease as a result of revaluation, decrease in profit.
Account 01 – Fixed assets in accounting: correspondence of accounts, postings
An important place when a business entity carries out its activities is occupied by movable and immovable assets, which are called fixed assets in accounting. They are used for a long time and are quite expensive. Therefore, there are some features of their reflection and taxation. Account 01 in accounting is used to reflect information about this type of object.
What applies to fixed assets
It is established by law that fixed assets can be called property that is used in business activities for a long time and its value exceeds a given limit.
For accounting purposes, the limit is limited to the cost of 40,000 rubles. That is, an enterprise or individual entrepreneur can consider property a fixed asset if it is used for more than one year and its price is more than 40,000 rubles.
Tax legislation sets a higher limit for the division of objects between fixed assets and materials. It is determined by the amount of 100,000 rubles and above.
This means that fixed assets in accounting and tax accounting may or may not be such. First of all, this applies to intermediate property from fixed assets, the price of which is from 40,000 rubles to 100,000 rubles. After all, in accounting an object from this group will be an asset, but for tax accounting it will not.
bukhproffi
Attention! The main feature of these assets is that they transfer their value to the created product in parts. This process is called depreciation of fixed assets.
Conditions for recognition of OS
In addition to the cost delineation of objects, there are a number of criteria defined in the PBU. These include:
- Objects must be used in the entrepreneurial activity of the subject to manufacture products, perform work, perform services, or manage a company.
- The useful life of an asset must be more than 1 year for it to be called a fixed asset.
- Such objects are not intended for further implementation.
- The use of the object will create income for the enterprise.
bukhproffi
Attention! From the classification it follows that the main assets are buildings, structures, equipment, vehicles, tools, inventory, etc., the cost of which exceeds 40 thousand rubles.
Which accounts does it correspond with?
To account for fixed assets, the Chart of Accounts provides for account 01. On it, funds are recorded at their original cost. The account is active, so an increase (receipt of fixed assets) is recorded as a debit, and a decrease (disposal) is recorded as a credit. Analytical accounting is carried out by types of OS objects.
By debit, account 01 can correspond with the credit of accounts:
- sch. 03 - shows the return of a fixed asset from an income-generating investment (for example, a return from a tenant).
- sch. 08 – reflects the arrival of fixed assets, an increase in their price as a result of re-equipment, completion and reconstruction.
- sch. 76 - receipt of fixed assets from other debtors, when its installation and modification are not required.
- sch. 79 - receipt of fixed assets for intra-business settlements (for example, from the parent company)
- sch. 83 — increase in the cost of fixed assets due to revaluation.
For a loan, account 01 can correspond with the debit of the following accounts:
- sch. 02 - disposal of fixed assets is reflected
- sch. 11 — transfer of fattening animals to the main herd
- sch. 76 - write-off of the cost of fixed assets due to other settlements (for example, due to insurance payments)
- sch. 79 - transfer of fixed assets through the system of intra-business settlements (between branches, parent company, etc.)
- sch. 83 - decrease in the cost of fixed assets as a result of their revaluation
- sch. 91 - disposal of fixed assets
- sch. 94 — the cost of missing OS is shown
- sch. 99 - write-off of fixed assets as a result of emergency circumstances.
Receipt of fixed assets
The receipt of an object can occur in different ways - as a result of a purchase, a contribution to the authorized capital, under a donation agreement, etc.
When purchasing an operating system, all costs for its acquisition and preparation for use are collected on account 08, after which the entire amount is transferred to account 01, where accounting is performed. The receipt of fixed assets is accounted for using the following transactions:
| Debit | Credit | |
| 08 | 60 | The purchase of an asset has been completed (the amount is indicated excluding VAT) |
| 19 | 60 | Registered for VAT on the purchased OS |
| 08 | 60, 76 | Work to prepare the object for use, transportation, etc. is taken into account (the amount is indicated excluding VAT) |
| 19 | 60, 76 | VAT on preparation for use is taken into account |
| 01 | 08 | The OS object is registered |
| 68 | 19 | VAT credited |
OS construction
The object can be obtained as a result of capital construction. Moreover, its initial price includes payment for the contractor’s services and the cost of materials for construction.
| Debit | Credit | |
| 08 | 60, 76 | The price of contract work is shown in the accounting |
| 08 | 10 | Raw materials and supplies given for work on the facility are shown in the accounting |
| 08 | 60, 76, 23, 25, 26 | Other costs for building the OS are shown in accounting |
| 19 | 60, 76, 23, 25, 26 | Input VAT on construction work has been taken into account |
| 01 | 08 | The completed OS object has been accepted for operation |
| 68 | 19 | VAT credited |
OS upgrade
The main feature of modernization is that its result changes the original characteristics of the OS object. As a result, its cost, period of use, etc. change. When accounting for expenses, it is advisable to open a sub-account on account 08, in which to collect all costs incurred for modernization.
| Debit | Credit | |
| 08 | 10 | Material costs written off for modernization |
| 08 | 23 | Auxiliary production costs written off |
| 08 | 60, 76 | A third-party contractor was involved in the modernization |
| 08 | 70 | The salaries of employees involved in the work were written off for modernization |
| 08 | 69 | Social contributions of employees were written off for modernization |
| 01 | 08 | Increased OS cost due to modernization costs |
Sale
When selling, proceeds are recorded in the amount established by the contract. In this case, expenses must include sales costs, as well as accrued depreciation. All transactions are shown in account 91.
| Debit | Credit | |
| 62 | 91 | Reflected revenue from the sale of operating systems |
| 91 | 68 | Determined VAT on the sale of fixed assets |
| 01/Disposal | 01 | The original cost of the object is transferred |
| 02 | 01/Disposal | Depreciation calculated over the operating period is transferred |
| 91 | 01/Disposal | The residual value is transferred to other expenses |
| 91 | 60, 76 | Costs for preparation for sale, dismantling, delivery, etc. are indicated. |
| 19 | 60, 76 | The amount of VAT for delivery, dismantling, etc. services has been determined. |
| 68 | 19 | VAT credited |
| 91 | 99 | The financial result of the sale of the OS is reflected |
Liquidation
Liquidation of an asset can be carried out in a situation where it is no longer profitable to use it and it is not possible to sell it. In this case, the decommissioned OS can be disassembled, and the resulting materials can be used for other purposes.
| Debit | Credit | |
| 01/Disposal | 01 | The original cost of the object is transferred |
| 02 | 01/Disposal | Accrued depreciation is transferred |
| 91 | 01/Disposal | Residual value is transferred |
| 19 | 68 | The tax amount was restored based on the residual value |
| 91 | 60, 76 | Expenses include the costs of hiring a third party for the disassembly operation |
| 19 | 60 | VAT charged by the contractor has been taken into account |
| 10 | 91 | Materials received during disassembly of the OS object were capitalized |
Revaluation
This operation is not considered mandatory. However, if its necessity is established by local acts, the revaluation must be performed on the last day of the year. At the same time, the revaluation itself can be of two types - revaluation or markdown
| Debit | Credit | |
| If there is an overestimation | ||
| 01 | 83 | An additional valuation of the fixed asset was made at the expense of additional capital |
| 83 | 02 | The amount of depreciation was adjusted due to additional capital |
| If a markdown occurs | ||
| 91 | 01 | The amount of depreciation of the asset was written off to other expenses |
| 02 | 91 | Depreciation is adjusted against other income |
Unaccounted assets based on inventory results
In order to ensure the reliability of accounting, a business entity must periodically make an inventory of its property, which includes fixed assets. If, as a result of the procedure, unaccounted for objects were discovered, they must be accepted for accounting in the same month. This is done at the current market value of a similar object.
| Debit | Credit | |
| 08 | 91 | An object that was discovered as a result of an inventory was registered |
| 01 | 08 | The facility is put into operation |
OS shortage based on inventory results
Another result of the inventory may be the identification of the absence of some OS object. In such a situation, the damage from its absence should be written off to the responsible person, or, if there is no such person, to losses. This happens in the amount of the actual residual value.
| Debit | Credit | |
| 01/Disposal | 01 | The cost of the asset is written off |
| 02 | 01/Disposal | Accrued depreciation is written off |
| 94 | 01/Disposal | The residual value of the operating system is written off for shortages. |
| 83 | 94 | The amount of the revaluation carried out is written off |
| If the culprit is identified | ||
| 73/2 | 94 | The total amount of the shortfall is written off to the guilty person |
| 73/2 | 98/4 | The difference between the residual value and the current market value of a similar object is reflected |
| 50, 51, 70 | 73/2 | The deficiency is repaid by the person at fault |
| 98/4 | 91 | The difference between the residual value and the market value is written off to other income. |
| If the culprit is not identified | ||
| 91 | 94 | The amount of the shortage on the fixed asset item is written off as other expenses |
Help us promote the project, it's simple: Rate our article and repost! ( 1 5.00 out of 5)
Source: https://buhproffi.ru/buhuchet/schet-01.html
Postings
The receipt of fixed assets to the account of the enterprise, the arrival of the object on the balance sheet could be carried out in different ways. This can be either a purchase, a gift agreement, or a contribution to the authorized capital.
Carrying out an inventory
As soon as an enterprise purchases a fixed asset, all the costs it incurred for the acquisition and preparation for operation are entered into account 08. Subsequently, the entire amount is transferred to account 01. This is where accounting is carried out. These postings control the receipt of all fixed assets in accounting.
An enterprise may become the owner of an object in connection with capital construction. In this case, the initial price will include payment for the work of contractors and all costs for materials and construction.
Modernization
The main feature of the modernization procedure is that in the process of its implementation, the original characteristics of the objects are adjusted. As a result, the period of use and cost change. In order to properly record expenses, it is recommended to open a sub-account on account 08. All expenses that were necessary for the modernization will be collected here. The procedure is carried out in several types.
Sale
Revenue after the sale must be indicated in the reporting documents in the amount specified in the contract. This also includes all losses that went towards depreciation. All transactions must be reflected in account 91.
Liquidation
The procedure for liquidating an object is carried out if its use for the enterprise has become economically unprofitable. The fixed asset is subject to write-off. In the future, they have the right to disassemble it in order to use the resulting materials for other purposes.
Revaluation
The revaluation operation is not mandatory for the organization. But there are cases when this necessity is determined by local acts. In such a situation, the revaluation procedure will need to be carried out on the last day of the year. There are two types of revaluation possible. This can be a markdown or revaluation.
Unaccounted assets based on inventory results
All business entities are required to regularly conduct an inventory of the property on their balance sheet. This is necessary to ensure authenticity. If the inspection reveals objects that are not registered, they must be included in it in the same month. The cost will be indicated based on the current market price for similar properties.
OS shortage based on inventory results
Based on the results of the inventory, a shortage may occur. In such a situation, the company employee is responsible for the damage. If it is not determined, then it is written off as a loss. The amount is determined based on the actual residual value.
Account 01 in accounting plays an important role for the correct accounting of objects on the balance sheet of an organization, enterprise, and related to the main ones. Interaction between accounts helps to correctly track changes in their value during operation.