Scientific approach
Science has its own definition of working conditions. As a rule, this term is understood as a complex of production factors that are of direct importance for the physical and psychological state of a person (work capacity, well-being, attitude to responsibilities), and also affect the effectiveness of his activities. This is how the concept of classification of working conditions by environmental factors is deciphered.
Scientists identify many factors that determine working conditions. Their classification is determined in two directions: the first includes those that are based on the characteristics of production, and the second includes those that do not depend on the nature of production. The latter, as a rule, are of a natural, social, economic or other nature.
https://youtu.be/dv5-YKmfZX4
Legislative support
The standards, namely Guideline R.2.2.755-99, establish hygienic criteria by which working conditions are assessed. The classification of working conditions according to indicators of the harmfulness and danger of factors in the working environment, the severity and intensity of the labor process, developed by the Russian Ministry of Health in 1999, distinguishes three degrees of working conditions according to indicators of the severity and complexity of work. This:
- Optimal, or, as it is also called, easy work.
- Acceptable work with moderate working conditions.
- Harmful, that is, hard work.
Importance of environmental conditions
The classification of working conditions according to environmental factors is based on the characteristics of production, which, in turn, are divided into directly industrial and socio-psychological. The most interesting for legislators and scientists are those that depend on the nature of the work. Such factors, in addition to having a great influence on the formation of working conditions, tend to constantly change. This trend only increases interest in them and requires constant study.
It is necessary to consider in more detail such a concept as the classification of working conditions according to production factors, and the formation of such factors and the strength of their impact on the person who is involved in production.
What is the labor process
The labor process is the actions that an employee performs during the performance of his professional functions to achieve the required result. Its content is influenced by technical and technological equipment, and the method of performing actions.
The work process involves more than just physical labor. It includes the work of all the people involved in the production of the final product. Therefore, in addition to material-energy processes (working with materials, raw materials or energy), information processes are distinguished, implying interaction with information and its transformation.
When performing professional duties, employees use different methods of influencing the subject of work :
- manual – no automated mechanisms are involved in the process, the worker uses only his own physical resources and hand tools;
- machine-manual - the main impact on the object is carried out using special mechanisms, but the movement of parts relative to the working surface is carried out manually;
- machine - the worker puts the initial product into the machine, controls the equipment throughout the entire process, and then removes the finished product at the end of the work; the transformation process is carried out without his direct physical participation;
- automatic - the employee’s participation is limited to setting up the mechanism, monitoring its serviceability, and timely replenishment of the materials used.
The labor process consists of operations :
- limited to one workplace;
- logically completed stages of the labor process, the object of which is a single object of labor.
Operations consist of techniques - a set of continuous actions aimed at achieving one goal. To perform techniques, the employee performs actions - a set of movements necessary to implement part of the work technique. Movement is one specific movement in space of any part of the body necessary to perform work tasks.
Understanding the essence of labor operations and their components, down to movements, allows you to optimize the labor process.
Hygienic classification
The legislator explains the concept of hygienic criteria as compliance of the data of the production environment and labor processes with current standards. The provisions on which it is based are as follows. The classification of working conditions according to the severity of work was developed on the basis of data on the discrepancy between real indicators and accepted standards. This does not take into account professions with extremely harmful working conditions, such as interaction with carriers of infectious diseases, especially toxic substances and medications or narcotic drugs.
Thus, based on the discrepancies between the consequences of harmful conditions and accepted standards, optimal, acceptable, harmful and dangerous working conditions are distinguished.
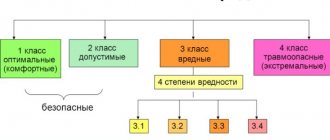
The hygienic classification of working conditions involves their division into four groups:
- Optimal working conditions are those that are designed to most effectively influence a person’s performance and productivity. With them, tension is practically not felt, which cannot but have a positive effect on the results. Standards for optimal conditions apply to microclimate indicators, as well as to the production process. At the same time, safe conditions are considered to be those that have unsafe factors no higher than the accepted acceptable standards. This approach ensures the protection of the health of workers and the creation of conditions for interest in high work results. Such an organization of productivity in an enterprise is considered the best.
- Acceptable working conditions are those under which the indicators of harmful effects are not higher than those established for workers. Under such conditions, workers' endurance can be easily restored after rest. The impact on the body under such loads does not exceed the norms established by law and, according to medical indicators, does not cause significant damage to the health of workers. Acceptable working conditions should not cause irreparable damage to physical condition or affect the ability to reproduce. Such standards cannot harm future offspring. Employees must be fully operational by the next work shift. These two criteria are considered acceptable and safe working conditions.
- Harmful working conditions mean that unsafe factors are involved in production, which have a direct and strong impact on people's health. These indicators exceed acceptable hygiene standards and negatively affect the body. The classification of working conditions according to the degree of harmfulness depends on their influence, which is usually long-lasting and can lead to serious problems in life, and even provoke negative consequences for future offspring. This type of work can no longer be considered acceptable.
- Hazardous working conditions cause increased harm not only to the health, but also to the lives of workers. In addition to causing immediate harm to workers while performing tasks specific to their work, they also have a lasting impact on their well-being. Severe forms of such exposure can cause significant damage to the body of workers. Due to the prolonged influence of such factors, workers experience various types of occupational diseases, many of which lead to infertility or severe disabilities in the offspring. The classification of working conditions by degree of danger is a separate system of criteria, which makes it possible to understand how safe it is for life and health to perform a particular job.
Classification of working conditions | classes
Classification of working conditions according to the degree of harmfulness and danger is carried out based on the results of the special assessment system. We will tell you how many classes are established, and how benefits and compensation to employees are assigned in accordance with them.
Hazard classes of working conditions
Labor legislation of the Russian Federation requires that organizations take measures to improve conditions in the workplace. SOUT allows you to identify what harmful and dangerous factors affect an employee and what class his workplace belongs to.
According to the law, if there is a VOPF, employees are entitled to certain benefits: increased salary, shorter working hours, increased vacation, and so on. Their availability, as well as the amount of contributions to the pension fund, depends on the assigned class.
In total, the law establishes four such classes:
- Optimal
- Acceptable
- Harmful
- Dangerous
If optimal conditions are an ideal, and acceptable conditions are quite rare, then harmful and dangerous conditions are what SOUT experts, supervisory authorities, and employers themselves most often have to deal with. Negative production factors are present in almost any job, even in the office.
Classes of working conditions according to the degree of harmfulness and danger - table
For clarity, we have prepared a convenient table with brief descriptions. More detailed data can be found in Order of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated January 24, 2014 No. 33n.
| Class | Subclass | Description |
| Optimal (1) | There is no exposure to harmful or dangerous production factors, or it does not exceed the standards established as safe for humans. | |
| Acceptable (2) | The impact of VOPF does not exceed the levels established by regulations. The employee’s body condition is restored during the prescribed rest period. | |
| Harmful (3) | Harmful exposure exceeds regulatory levels. | |
| 3.1 | The state of the employee’s body is restored when resting longer than before the start of the next working day (shift), the risk of health damage increases. | |
| 3.2 | Occupational diseases of initial forms or mild severity (without loss of professional ability) may develop after 15 or more years of work. | |
| 3.3 | There is a risk of developing occupational diseases of mild to moderate severity (with loss of professional ability to work) during working life. | |
| 3.4 | It is possible to develop severe forms of occupational diseases (with loss of general ability to work) during the period of work. | |
| Dangerous (4) | There is a threat to the life of the employee; there is a high risk of developing an acute occupational disease. |
How many degrees of harmfulness are harmful working conditions divided into?
As we have already said, optimal and acceptable conditions are rare. On the other hand, 4th grade is also typical for a small number of professions. Practice shows that the most common of the classes is 3rd.
Due to this prevalence, as well as due to the large number of factors, subclasses have been introduced. This is necessary in order to more accurately determine the level of influence of production factors on the worker’s body.
In total there are 4 subclasses in the 3rd grade. They differ in the degree of deviation of the labor process factors affecting workers from the norm, as well as the severity of the consequences for the body, including the risk of developing occupational diseases.
How the class of working conditions is established according to indicators of the severity of the labor process
Let's consider how work equipment is classified according to indicators of the severity of the labor process. Here we will be helped by the methodology that is prescribed in the Order of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated January 24, 2014 No. 33n.
In this document, the severity of the labor process is defined as the degree of load on the body as a whole and its functional systems in the process of the employee performing his job duties.
What indicators should you rely on?
These include:
- physical dynamic load;
- mass of lifted and moved cargo;
- stereotypical labor movements;
- static load;
- working posture;
- body tilts;
- movement in space.
The matter is not limited to physical activity alone; other types of stress on the body must also be taken into account:
- intellectual;
- sensory;
- emotional;
- regime.
All these factors are described in detail in Order No. 33n, and together they make it possible to determine working conditions with high accuracy.
Classification of working conditions according to production environment factors
How to determine the class of working conditions according to VOPF? It is important to find out whether their exposure exceeds or does not exceed the standards that are considered acceptable.
An expert from the organization conducting the special assessment, together with members of the commission, during a special assessment, must determine the degree of influence of harmful and dangerous factors on the employee during work.
To do this, he compares the factors of the working environment available in the workplace with factors from the classifier. If the identified factors coincide with those given in the classifier, they are recognized as identified.
Identification includes the following steps:
- identification and description of working environment factors present in the workplace, sources of harmful or dangerous influences;
- comparison and establishment of their coincidence with the factors provided for by the classifier of harmful or dangerous production factors;
- conducting research and measurements of exposure and its consequences;
- registration of identification results by the commission for carrying out the special assessment.
A clear division of workplaces into hazardous classes helps management make effective decisions to improve working conditions and achieve full compliance with labor legislation.
►Find out,
how to prepare a declaration of compliance of working conditions with state requirements>>>
Source: https://www.trudohrana.ru/article/103498-qqq-18-m2-klassy-usloviy-truda
SEE MORE:
Source: https://helpiks.org/5-101124.html
Energy consumption value
In addition to generally accepted standards, there are separate criteria by which one or another activity can be classified as a certain type of severity. The classification of working conditions according to environmental factors takes into account, in addition to the degree of harmfulness of production, the energy costs necessary for a worker to perform a particular task. The level of energy expended can be an indicator of how hard a worker's work is and the level of concentration and willpower it requires. This information has direct implications for further improvement of environmental performance.
The assessment and classification of working conditions of this kind depends on the requirements of the standards, which determine that energy costs directly depend on the position in which the worker performs tasks. Typically this is a standing or sitting position. Standards have established that when working while sitting, the level of energy consumption increases by approximately five to ten percent of the basal metabolism. When standing, this figure increases to 10-12%. With an unnatural posture, the required amount of energy increases by half. In addition, active mental activity requires an additional fifteen to twenty percent of daily energy. Excessively intense or nervous work, which is associated with increased stress, requires separate costs. Thus, reading aloud requires half as much energy as the same action performed silently. Speaking in front of an audience requires twice as much energy, and with the concentration of attention of workers whose work is related to computer technology, these figures can reach one hundred percent. Based on these physiological indicators, standards are formed.
Types of physical activity
The classification of working conditions according to the severity of the labor process depends on the energy expenditure when performing certain tasks and is manifested in the gradual wear and tear of the body, a decrease in working capacity, the onset of fatigue and requires timely rest. Depending on its effect on the body, physical activity can be divided into static and dynamic.
The first is manifested in the need to hold objects in the same state for a long time, which causes rapid fatigue of individual muscle groups. Frequent and prolonged work in a stationary state and the same type of tension provokes overstrain, wear and tear of muscles, as well as deterioration of blood supply in their individual areas. This can cause diseases of the bone or musculoskeletal system and even nervous disorders.
Dynamic physical activity is a type of activity in which intense muscle work occurs. Typically, it involves numerous groups, in particular the body and limbs. A striking example of this type of worker is the work of loaders. Incorrectly applied classification of working conditions can pose a huge danger to their health.
Partial or regional muscle work manifests itself in predominantly upper body movement. Limited means that less than a third of all muscles in the body are used. As a rule, this is small muscle work such as packing goods, etc.
Factors determining working conditions
The term “working conditions” is common in everyday life; people often use it, putting their own meaning into the content of this concept in each specific case. For one, working conditions are associated with the amount of earnings, for another - with the length of the working day, for a third - with the physical difficulty of work, etc. And all this is correct, because there are many factors affecting a person, his health and performance.
Working conditions are a complex objective phenomenon that characterizes the environment of the labor process and is formed under the influence of a combination of factors of a different nature and affects a person’s health, performance, his attitude towards work and the degree of satisfaction with work, and as a result - on labor efficiency and other economic results of activity [1].
There are four factors influencing the formation and change of working conditions:
1. Social and economic, the effect of which determines the position of workers in society (labor legislation, standards in the field of labor organization, payment, working conditions and safety, system of benefits, guarantees and compensation for workers).
2. Technical and organizational factors that directly affect the formation of material elements of working conditions (means of labor, objects of labor, technological processes, organizational forms of production, labor and management).
3. Naturally - natural factors (the impact on workers of geographical, climatic, geological and biological features of the area where the labor process takes place).
4. Economic and household factors (organization of food for workers, sanitary and household services).
Working conditions formed under the influence of various factors are a combination of elements that have different effects on humans.
There are four groups of elements of working conditions:
3 pages, 1244 words
Section 1. The “man - environment” system
Topic 1. Human reliability and comfortable living conditions Concepts: habitat, work, health, labor safety system, danger, risk, working conditions (organizational, technical, sanitary and hygienic, legal) classification of habitats (industrial, urban, household, natural ). Types of human activity. Human energy expenditures for various types of...
Sanitary and hygienic.
Psychophysiological.
Aesthetic.
Socio-psychological[2].
Sanitary and hygienic elements are defined by the fact that they are formed and quantitatively assessed by methods of sanitary and hygienic research (microclimate, noise measurements, EMF, air condition, etc.) Elements of this group are standardized through standards, norms and requirements.
Psychological and physiological elements are determined by the content of work activity, various loads on the musculoskeletal system, nervous system and psyche during the work process. These elements represent physical, neuropsychic stress, monotony of work, pace and rhythm of work, forced posture.
Aesthetic elements that form a person’s attitude towards the work environment from the point of view of its artistic perception. They influence the formation of a certain emotional state: architectural, design, artistic design of the exterior, production equipment, workplace equipment and industrial clothing.
Social and psychological elements that characterize the state of workers and the team are formed under the influence of socio-psychological factors and create the corresponding psychological and emotional mood of the employee. The elements of this group are very difficult to quantify; there are no norms, much less standards, but the study of these elements with the help of sociological research creates an objective basis for their measurements.
The compliance of these factors with the required norms and standards is a prerequisite for normal human performance.
Let us dwell in more detail on the sanitary and hygienic elements of working conditions. Most of them are components of the external production environment:
— microclimate (temperature, relative humidity, air speed),
— state of the air (presence of vapors, gases, aerosols),
— illumination,
- noise,
- vibration,
- ultrasound,
- various radiations,
— biological and other influences[3].
They are regulated by establishing standards, sanitary norms and requirements and are quantified using sanitary and hygienic research methods.
27 pages, 13341 words
9 Labor as a type of activity. Psychological signs of labor
... operator performance). Important: a break from work is necessary to restore performance and achieve uniform labor productivity. ... to a certain extent their own activities. The specifics of a person’s management activity will be a constant struggle... control panels should not have any foreign elements that complicate the operator’s work or distract his attention. To...
Sanitary and hygienic factors of the production environment have a significant impact on the human body. Some of them have an adverse effect on the employee, which can manifest itself as decreased performance, deterioration of health, and sometimes lead to occupational diseases. Therefore, it is necessary to know not only the cause of these factors, but also to have an idea of ways to reduce their negative impact on the body of workers. It is advisable to pay special attention to the influence of adaptable environmental factors (meteorological conditions, noise, vibration, lighting), the negative impact of which can be significantly reduced through the use of active means of improving the work process.
To create favorable sanitary and hygienic working conditions, all elements of the working environment must be systematically examined and brought into compliance with standards.
The current sanitary and hygienic standards are developed according to individual factors and mainly regulate the maximum permissible concentrations and maximum permissible limits of harmful factors, i.e. concentration levels that, when working daily for 8 hours (40 hours per week), do not cause occupational diseases or general health problems in workers.
It is important to know that doses and levels of harmful factors, even significantly less than the maximum permissible ones, with combined action can become hazardous to health [4].
Tension value
Classification of working conditions by severity and intensity requires analysis of such production factors as the duration and degree of fatigue of the body over a certain period of time. The stress of workers' bodies (physical or mental) may differ depending on the type of their employment and the specifics of the work performed. During intense exercise, fatigue occurs depending on the movement of objects and one’s own body in space and has an energetic character. With active mental activity, the body is exhausted due to emotional stress.
The classification of working conditions according to the intensity of the labor process can be considered using the example of production, which is based on the use of intellectual work. Receiving, perceiving and processing information requires significant effort, which invariably entails energy expenditure. However, depending on the nature of mental activity, they may differ. Thus, the easiest of the existing types is considered to be that intellectual work that does not require independent decision-making. This type is classified as optimal. However, if it is necessary to make decisions according to an existing scheme or algorithm, such work can no longer be classified as the easiest type of activity, so it can only be called an acceptable type of activity of the first degree.
An even more complex category defines activity when solving problems using a previously known algorithm or scheme. Creative thinking requires higher energy costs, and therefore belongs to an acceptable type of activity of the second degree.
What are the factors?
Factors in an organization's work process describe the production conditions that affect workers. The structure includes such elements as characteristics of the external environment, features of the performance of labor operations and the psychophysiological state of a person in the process of work.
Heaviness
The severity of work depends on the physical stress that a person experiences during work. It includes not only physically hard work - lifting and moving a load - but also a person’s posture during work, the number and frequency of similar movements, the dynamics of movement in space, and the distance traveled. Characterizes types of activities that require primarily physical labor.
Tension
Tension characterizes the load on the human nervous system. This includes emotional and intellectual stress, as well as the work of the senses. The work regime falls into the category of tension: the duration of the work shift, the alternation of work and rest both during the working day and between shifts. Used to assess intellectual work.
Selected criteria
In addition to the above criteria, science has developed other working conditions. The classification identifies individual criteria for working conditions. These may include the following factors (conditions):
- physical;
- household;
- social;
- production
According to this division, the classification of working conditions according to environmental factors identifies the following indicators: temperature, pressure, air purity, dryness, quality of lighting, the presence of noise or vibration, vibrations and air movements. Such conditions can affect fatigue and overall performance.
To improve the working environment, it is necessary to create amenities, first of all, domestic ones. These include indicators such as temperature within 18-20 °C, mercury pressure of about 760 mm, and room humidity of about 50%.
Introduction
The relevance of studying the course lies in the fact that a person is exposed to hazards in his work activity, which is carried out in a space called the work environment.
In the production environment, there are objectively harmful and dangerous factors that negatively affect a person in the process of his life.
The goal is to study the factors influencing working conditions.
Tasks:
1. Consider the factors that determine working conditions
2. Define noise and vibration. Consider measures that help reduce and reduce these harmful factors
3. Consider the phases of performance
4. Make a map of working conditions in the workplace.
The object of the study is a person in the workplace. The subject of the study is the factors that determine work.
The theoretical basis of the work was the scientific works of such economists as Akmalov R., Babosov E.M., Babynina L.S., Belyakov, G.I., Kukin, V.L., Sibikin, Yu.D.
4 pp., 1894 words
Improving labor incentives through improved jobs
... measures to improve labor incentives by improving jobs and working conditions: 1. Provide healthy and safe working conditions...space for fine manual work. Let's consider the optimal placement of labor items and documentation within reach of hands... by the city ecology committee. Harmful production factors include non-optimal air composition and condition: ...
Needs of special groups
Classification of working conditions according to hygienic criteria is also important for certain categories of the population who need to create even more gentle conditions in the workplace. When organizing work in an enterprise where women or minors work, it is necessary to take into account the abilities of their body. Due to the characteristics of the body, women are much less adapted than men to perform exhausting work, for example, lifting weights. Therefore, employing women in such tasks is prohibited by law. The same goes for teenagers. The body of minors has not yet fully formed, therefore, when hiring them, the criteria and classification of working conditions, which are described in detail in the standards, must be taken into account.
Meaning of divisions
Such a system is of great importance for creating optimal conditions for all groups of the population. Classification of working conditions according to working environment factors in the case of minors forces the employer to create amenities that would not interfere with the full development and growth of children. First of all, this concerns physically difficult tasks, which place an excessive burden on the child’s body and its further development. Muscles and bones at this age are not yet fully formed, which threatens sprains, bruises and disproportionate development of the body. A shortened working day is provided for children, and the weight of loads that they can lift during work is clearly limited. Similar provisions regarding carrying capacity are established for women. Such groups of the population can only start working at night in exceptional conditions. Moreover, women are provided with maternity leave and a change of job during pregnancy to an easier one.
The hygienic classification of working conditions is of particular importance for protecting the health of the population, and especially its most vulnerable layers. Thus, the manual on hygienic criteria says that their existence greatly simplifies monitoring the performance of workers and the compliance of conditions with existing requirements. Moreover, the priority of preserving the health of the population helps to improve the quality of life, regularly conducting inspections aimed at identifying inconsistencies in positions held and health problems. In addition, the existence of a unified assessment system makes it possible for each enterprise to keep records and take timely measures to improve them. The classification of working conditions by factors of the working environment makes it easier for the state to inspect workplaces, make decisions regarding their compliance with generally accepted standards, and hold accountable the persons who supervise compliance with these standards. In criminal proceedings, such provisions help to investigate cases of gross violations of the law and choose a preventive measure for individuals guilty of such violations.
How to determine the class of working conditions, taking into account the presence of harmful influences
At each enterprise, regardless of whose ownership it is, the degree of danger and harmfulness of working conditions must be determined (Federal Law No. 426).
If there are negative factors, it is necessary to reduce their influence by using personal protective equipment and other methods (Article 210 of the Labor Code). Indicators of the production environment must be closely monitored and not exceed established limits.
Ensuring safety in the labor process and training workers in the rules of its observance is the responsibility of the labor protection department (Article 212 of the Labor Code).
Assessment of production conditions
To determine the class of hazards present in the workplace, a commission is created, including experts from licensed companies. Based on the results of the inspection and measurements taken, the degree of deviation of existing indicators from the established standards is established.
Thus, a conclusion is made on assigning a certain hazard class to the working conditions. More information about conducting a special assessment of working conditions can be found at https://otdelkadrov.
online/11668-poryadok-provedeniya-spetsialnoi-otsenki-uslovii-truda-sout-na-predpriyatiyah.
Work Environment Assessment Parameters
Working conditions mean the total impact on a person of the environment and the labor process itself. When assessing them, a classification of working conditions is carried out according to factors of the working environment. These include (GOST 12.0.002-80):
- Physical: temperature and humidity in the room (find out about temperature standards in the workplace according to SanPin here);
- dust content in the air;
- air flow speed;
- noise and vibration levels;
- degree of illumination;
- electromagnetic radiation.
- paints and varnishes;
- microorganisms;
- body position during work;
- similar movements performed continuously for a long time;
Excessively exceeding the indicators leads to poor health, loss of strength and loss of concentration, which can lead to injury. Harmful working conditions also contribute to the development of occupational diseases, including reproductive dysfunction. The employee will not be able to effectively perform his duties or will completely lose his ability to work.
The video presents a classification of harmful and dangerous production factors
Working conditions
Depending on the extent to which the parameters of the production environment deviate from the established standards, working conditions are divided into four classes (Article 14 of Federal Law No. 426):
- Optimal.
- Acceptable.
- Harmful.
- Dangerous.
Of these, the first class and acceptable working conditions - class 2 refer to safe working conditions.
Optimal (Class I)
The first class includes a production environment in which microclimate indicators and labor loads comply with standards. At the same time, other harmful factors are absent or do not exceed safe limits.
In such conditions, a person feels light and comfortable and is able to concentrate all his mental and physical strength on work. There is no risk of health damage or work-related injury.
The optimal working conditions are found in offices, banks, and trading companies.
It is worth noting: the first group - optimal working conditions - is extremely rare, since it is very difficult to find a place of work where conditions are created for high performance of employees, and employees do not get tired at the end of the working day. If the inspection determined the working conditions to be safe and harmless, then most likely this will be the second group - acceptable working conditions.
A safe environment is classified as class 2 working conditions, which means there are some harmful factors at work, but their degree does not exceed hygienic standards for working conditions.
To restore the body that has been negatively affected, there is enough time to rest. This impact does not have far-reaching consequences and does not affect the health of the employee and his future offspring.
Read more about the concept of safe working conditions and their provision in production here.
Harmful (III class)
The level of hazardous production conditions of the third class exceeds the indicators established by law. Such conditions lead to occupational diseases and loss of reproductive abilities. The types of hazardous factors are quite numerous.
For example, direct contact with infected material among health workers, negative radiation in X-ray rooms, or bright lighting during gas welding.
Therefore, the third class of harm is further divided into subclasses depending on the severity of the damage caused.
Subclass 3.1 (harmful conditions of the 1st degree)
When a person is exposed to harmful conditions of the first degree, the body requires more time to return to its normal state.
The standard period until the next working day or shift is not enough. In this connection, the physical condition of the body deteriorates and the preconditions for the occurrence of diseases are created.
This allows us to define the class of working conditions as the first degree of the third class of harmfulness.
Subclass 3.2 (harmful conditions of degree II)
The second degree of harm is characterized by the presence of production factors that leave irreversible changes in the employee’s body, provoking frequent sick leave.
These changes concern those organs and systems that are most susceptible to the influence of existing circumstances. They progress to the initial stage of an occupational disease or its mild form without loss of ability to work.
The development of the disease takes quite a long time, exceeding fifteen years.
If a third class of hazard has been identified at production, this does not mean that this indicator will be permanently fixed.
The situation can change for the better or for the worse (for example, the use of other protective equipment or replacement of materials used in production). In some cases, an unscheduled assessment of working conditions should be carried out.
What is the standard frequency for conducting a special assessment of working conditions, read the article https://otdelkadrov.online/11678-periodichnost-otsenki-uslovii-truda.
Subclass 3.3 (harmful conditions of degree III)
The presence of harmful factors of the third degree at work contributes to the development of mild and moderate occupational diseases with loss of the ability to perform this work. The likelihood of diseases becoming chronic increases.
Subclass 3.4 (harmful conditions of IV degree)
Working conditions of the fourth degree of harm lead to the appearance of chronic pathologies and severe occupational diseases, accompanied by complete loss of ability to work and disability.
Dangerous (IV class)
The classification of working conditions ends with the fourth class of harmfulness. It occurs infrequently, since it is typical for enterprises where work involves contact with chemicals and radiation that can create a situation that threatens the life of an employee.
A harmful working environment causes the occurrence of serious diseases that occur in an acute form and are a direct consequence of the performance of job duties.
If conditions of the fourth class of harm have been identified at the workplace, it must be eliminated or re-equipped in accordance with lower hazard indicators.
For information on guarantees and compensation for workers engaged in harmful or dangerous work, see the following video.