Art. 22 Labor Code of the Russian Federation: questions and answers
Art. 22 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is devoted to the basic rights and responsibilities of the employer in the process of labor relations with employees. Let's consider the questions that arise when applying this article.
What is the significance of Article 22 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation?
What is the list of rights included in Art. 22 of the Labor Code?
What is the main right of the employer as a party to the employment agreement based on?
How can an employer influence employee behavior?
Why are employers' associations needed?
What are works councils according to Art. 22 Labor Code of the Russian Federation?
What are the rights of an employer in the field of special assessment of working conditions?
What's in Art. 22 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is defined as the obligations of the employer?
What are the responsibilities of the employer in terms of organizing the labor process?
What must an employer observe when paying for work?
How should an employer communicate information with employees?
What should be considered in matters of compensation for harm to an employee?
What are the employer’s responsibilities regarding a special assessment of working conditions?
What other responsibilities are implied for the employer?
Rights and obligations of the employer
The relationship between employer and worker is secured by an employment contract. The document specifies the standards of norms and obligations of both parties based on the legislation of the Russian Federation.
From the moment the contract is signed, they become subjects of the law governing relations in the sphere of labor. They have the ability to fulfill both rights and responsibilities and be responsible for their actions.
The employer must be competent in matters of hiring workers and providing the necessary conditions for the performance of duties. The employer is the bearer of subjective rights and legal obligations arising from the rights of the employed employees.
Rights and obligations of the employer according to Art. 22 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
| Responsibilities | Rights |
| Strictly comply with the country's labor laws. | Conclude an employment contract, make the necessary changes to it and, if necessary, terminate the contractual relationship. |
| Provide a workplace to a hired employee under a contract. | Draw up legal documents regulating labor relations. |
| To ensure high-quality performance of the employee’s job functions, equip him with the necessary technical devices. | Encourage employees for high performance. |
| Comply with labor safety standards at the enterprise. | Hold employees accountable. |
| Comply with the instructions of authorized bodies. | Adopt official regulatory documents of a local nature, etc. |
Questions about legal relations and performance of duty are very significant for both employees and employers. The responsibilities of employers are distributed and grouped according to who they owe to.
What is the significance of Article 22 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation?
Art. 22 is included in the first section of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which provides a basic idea of the concepts with which this code operates. The purpose of creating the Labor Code of the Russian Federation was to regulate the relationship between the two parties to labor relations: the employee and the employer (Articles 1, 15, 20 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). These relationships are of a contractual nature (Article 16 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) and, accordingly, imply the existence of mutual obligations of the parties.
That's why Art. 22 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which establishes the rights and obligations of the employer, largely echoes the content of Art. 21 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which defines the rights and obligations of the employee. What the employee has the right to, the employer is obliged to provide (provide) to him, and vice versa. For example:
- the employee has the obligation to perform the functions assigned to him, and the employer has the right to demand this;
- the employee has the right to compensation for harm caused to him in connection with his work (including moral), and the employer has an obligation to provide such compensation.
At the same time, the lists of the rights of both the employee and the employer, as well as the employee’s responsibilities, are exhaustive, while the list of the employer’s responsibilities is open. This is due to the fact that, by defining the basic principles on which labor relations should be built, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation allows for their individualization (expansion and addition) for each specific employer.
This is done by developing internal regulations. However, Art. 8 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation clearly prohibits the inclusion of norms that worsen the position of the employee in comparison with labor legislation. So, in accordance with internal regulations, the employer may have additional responsibilities, but the employee does not.
Commentary to Art. 21 Labor Code of the Russian Federation
1. This article establishes a total of 14 basic rights and 7 basic responsibilities of workers in the sphere of labor, arising from the basic principles of labor law (see commentary to Article 2 of the Labor Code of Russia). Unlike the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the basic labor rights and obligations of an employee are concentrated in one article of the Labor Code, which allows us to talk about their specific system.
2. When including the basic labor rights of an employee in the Labor Code, not only the relevant provisions of the Constitution of the Russian Federation on the basic labor rights of citizens are taken into account, but also the fundamental international legal standards in the field of labor, enshrined in the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (1948), the ILO Declaration on Fundamental Principles and Rights at Work (1998) and a number of ILO conventions, the European Social Charter (1961), the European Community Charter on Fundamental Social Rights of Workers (1989), the Charter of Social Rights and Guarantees of Citizens of Independent States (1994 g.), etc.
3. Among the basic labor rights of an employee, individual and collective labor rights are named.
4. A significant part of the labor rights of employees is of an individual nature, for example, the employee’s right to conclude, amend and terminate an employment contract in the manner and under the conditions established by the Labor Code and other federal laws; to provide him with a workplace that meets the requirements and standards of organization and labor safety; for timely and full payment of wages in accordance with their qualifications, complexity of work, quantity and quality of work performed; right to rest, etc.
5. Among the basic rights of workers are rights of a collective nature: for example, the right to participate in the management of an organization can be exercised both directly and through representatives (see commentary to Chapter 8 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
6. Particular attention should be paid to one of the basic rights of an employee - the right to compensation for moral damage caused to him (see commentary to Article 237 of the Labor Code).
7. Reinforcing various rights of an employee in the sphere of labor, the Labor Code provides guarantees for the implementation of these rights (see commentary on the relevant articles of the Labor Code).
8. The legal basis for the implementation of the employee’s right to compulsory social insurance is the Labor Code and the provisions of the Federal Law of July 16, 1999 N 165-FZ “On the fundamentals of compulsory social insurance” (SZ RF. 1999. N 29. Art. 3586).
9. In addition to basic labor rights, Art. 21 of the Labor Code also establishes the basic labor responsibilities of the employee, which are formulated in the most general form.
10. The main labor responsibilities of employees can be set out in more detail, taking into account the specifics of the activities of a given employer, in the internal labor regulations and in the collective agreement, and also clarified and specified in the employment contract concluded individually with each employee (see commentary on the relevant articles of the Labor Code).
What is the list of rights included in Art. 22 of the Labor Code?
In Art. 22 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that the employer has the right:
- to conclude, amend and terminate employment agreements;
- requirement for the performance of specified labor functions, responsible attitude towards property, compliance with labor regulations;
- conducting negotiations with employees and concluding collective agreements;
- adoption of internal regulations (except for individual employers);
- rewarding the employee for a responsible attitude to work and punishment for violations of discipline and causing damage;
- creation of employers' associations;
- formation of works councils (except for individual employers);
- implementation of rights granted by law regarding special assessment of working conditions.
For information on where an employee can check whether his employment contract complies with the requirements of current legislation, read the article “A service for checking employment contracts has been launched.”
Main responsibilities of the employee
If an employee is endowed with rights, then he also has responsibilities. They are:
- compliance with labor laws;
- compliance with labor safety standards;
- conscientious performance of labor duties;
- compliance with labor standards;
- careful handling of property owned by the employer.
In addition, the employee’s responsibility in the field of labor law is to comply with internal labor regulations.
What is the main right of the employer as a party to the employment agreement based on?
The main thing for the employer is always the right, based on the opportunity to attract the employee to work in his own interests and to ask him for fulfilling the agreed requirements. Both of these issues are considered in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation in great detail and are separated into separate sections of the code.
The text of each section contains instructions that the procedures for formalizing (changing) labor relations and punishing employees must strictly comply with the rules established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other laws at the federal level. Despite the presence of such an indication, attention to this issue is additionally drawn to Article 22 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The most important component of the legal basis for the relationship between employee and employer are internal regulations, which can be both industry-specific and individual for each specific employer. It is acceptable for them to take the following forms:
- collective agreement;
- local regulatory act (regulations, order);
- additional conditions included in the employment agreement with a certain employee.
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation gives the employer the right to participate in the development, adoption and amendment of such documents, regardless of their nature. Accordingly, the right to negotiate with the collective of workers (or representatives of the collective) is also provided.
Read about the preparation of one of the mandatory local regulations in the material “Internal Labor Regulations - Sample 2015”.
Employer's rights
The list of employer rights contains the norms of his behavior with employees. They can be divided into three groups according to the type of relationship:
- employer and individual employee;
- employer and workforce;
- between different employers.
In relation to a specific employee, the employer can:
- hire and fire by concluding and terminating employment contracts;
- demand from hired persons compliance with discipline, performance of duties in accordance with the employment contract and careful attitude towards material assets;
- encourage employees by any means (material and moral) for conscientious performance of duties;
- apply penalties to violators in material terms or in a disciplinary manner.
In relation to the team, the employer has the right:
- conclude collective agreements bilaterally;
- adopt collective acts of local significance;
- organize collective bargaining;
- create works councils;
- carry out an assessment of the conditions that exist at work places.
Rights are also defined that relate to relationships between employers, and consist of the provided opportunity to create or represent in associations of employers to protect their interests.
Almost every paragraph of Article 22 defines restrictions on the rights of the employer within the framework of the labor code or other laws at the federal level.
How can an employer influence employee behavior?
By requiring an employee to fulfill all the rules established specifically for him (job functions) and for the entire team (internal labor regulations, labor protection requirements), the employer has the right to:
- encourage him for a responsible attitude towards his duties or for some special achievements in work;
- punish for violations.
Encouragement can be expressed in different forms (Article 191 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). For example, in the form:
- gratitude;
- diplomas;
- awards;
- gift;
- incentive payments.
The use of incentives can have either a systematic form, based on an internal regulatory act, or a one-time form, determined by individual orders of the manager.
Punishments are a consequence of violations:
- disciplinary nature, in which disciplinary liability occurs (Article 192 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- associated with causing damage to the employer and entailing financial liability (Chapter 39 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The possibility of applying punishments is regulated quite strictly by law, requires compliance with certain rules when issuing them and is limited by a time frame.
Read about what disciplinary liability may be in the article “Disciplinary liability of an employee and its types.”
Why are employers' associations needed?
The right of employers to form associations serves the following purposes:
- their representation in any bodies;
- development of unified approaches and documents;
- conducting collective bargaining;
- exchange of information;
- preparing proposals for implementation at the legislative level;
- protection of common interests.
Depending on the scale of these goals, unification can occur at a variety of levels - from territorial to all-Russian. It is also possible to form industry and inter-industry associations.
The process of creating and functioning of associations is based on the rules set out in the Federal Law:
- “On employers' associations” dated November 27, 2002 No. 156-FZ;
- “On the Russian Tripartite Commission for the Regulation of Social and Labor Relations” dated 01.05.1999 No. 92-FZ.
What are works councils according to Art. 22 Labor Code of the Russian Federation?
Since May 2013, after the Federal Law “On Amendments to Article 22 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation” dated May 7, 2013 No. 95-FZ, additions to the text of the article, another right of the employer appeared - to form production councils. This body, which can be created by any employer except an individual employer, is advisory (consultative), formed on a voluntary basis from representatives of the most qualified and active workers.
The goals of its creation are to develop proposals on the following issues:
- optimization of processes of the employer's core activities;
- introduction of new technologies and equipment;
- increasing the level of qualifications of personnel and their productivity.
All necessary aspects related to the formation and process of work of this body are established by the employer by its internal regulations. It should include the following provisions:
- about the powers of the council and the range of tasks it solves;
- the procedure for convening and possible current operating procedures;
- the number of council members and the composition of employee representatives in it.
The right to create a works council, established by Art. 22 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation , is applied with comments regarding its competence: it includes exclusively issues of improving production activities, but not functions related to the process of managing the activities of the employer or representing the interests of employees. The employer is obliged to communicate the result of consideration and implementation of proposals developed by the council to its participants.
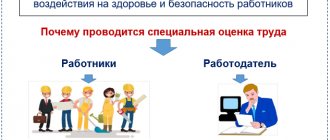
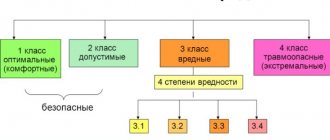
What are the rights of an employer in the field of special assessment of working conditions?
The rights of the employer in the field of special assessment of working conditions are established by Art. 4 Federal Law “On special assessment of working conditions” dated December 28, 2013 No. 426-FZ and include the possibility of:
- requirements to substantiate the results of the special assessment;
- carrying out an unscheduled procedure for assessing working conditions;
- requirements from the organization carrying out the special assessment for documents confirming its competence to conduct such an assessment;
- appealing the results of a special assessment if you disagree with them.
For information on how a special assessment is carried out, read the material “Procedure for assessing working conditions in the workplace (nuances).”
What's in Art. 22 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is defined as the obligations of the employer?
Among the responsibilities of the employer in Art. 22 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation indicates the need:
- compliance with all labor legislation standards established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, other laws, internal regulations and labor agreements;
- providing the employee with exactly the work that was agreed upon with him during his employment;
- ensuring the safest possible working conditions and their compliance with state standards regarding labor protection;
- providing the employee with the technical means necessary to perform his job functions;
- eliminating discrimination when paying for work of equal value;
- timely and full payment of wages within the deadlines established by the employer in accordance with the requirements contained in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- compliance with the procedure for representation during collective negotiations with employees, including the conclusion of a collective agreement;
- complete and timely provision of information to employees that they must have when developing a collective agreement;
- familiarizing employees with all internal regulations relevant to their job responsibilities;
- timely compliance with all instructions of supervisory authorities authorized to conduct inspections of compliance with labor legislation;
- adequate response to information from bodies representing the interests of workers regarding violations of labor rights;
- creating conditions for the participation of employees in the management of a legal entity in the forms specified by law;
- providing for the everyday needs of employees arising during the performance of their labor functions;
- performing procedures related to compulsory social insurance;
- compensation for damage (including moral) received by the employee in connection with his work duties;
- performance of duties related to special assessment of working conditions;
- fulfilling other duties provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and internal regulations.
According to the employment contract
The legislation does not limit the employer in selecting qualified, experienced specialists with knowledge of foreign languages and who can drive a vehicle. At the same time, the law does not allow infringement of rights and opportunities based on age, gender, race, social, property status, religious and political beliefs. Only the business abilities of employees are taken into account.
The employer is obliged:
- Comply with the laws of the Russian Federation and acts of local importance.
- Provide the employee with the work specified in the agreement.
- Provide all safety equipment required by hygiene rules and requests from the labor department.
- Set the price of work for all employees in accordance with the functions performed.
- Provide workers with the necessary equipment, technical data and other means to effectively solve tasks.
- Pay wages in full on time established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and the internal regulations of the organization.
What are the responsibilities of the employer in terms of organizing the labor process?
The employer must provide each hired employee with the opportunity to perform exactly those functions that are specified in the employment agreement and job description. The requirement to perform other work is prohibited by law (Article 60 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) and becomes possible only as a temporary measure (Article 72.2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) either with the consent of the employee or without it (in emergency situations).
The ability to perform the work must be technically ensured by the employer (by providing the necessary tools, equipment and other means), if this follows from the essence of the assigned work. If it is impossible to carry out a labor function due to the lack of necessary technical means, the blame for the employee’s downtime lies with the employer, who is obliged to pay for the time of such downtime (Article 157 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Conditions for performing work functions must be as safe as possible for the employee. In this regard, the employer has responsibilities (Article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- to identify harmful and dangerous factors in the workplace;
- informing the employee about these factors and safety measures;
- provision of special protective equipment and training in their use;
- demonstration of safe operation techniques using the provided technical equipment;
- training in emergency behavior and first aid techniques.
To find out whether the cost of workwear issued to an employee should be subject to personal income tax, read the article “When is workwear subject to personal income tax and when not?”
The employer must take care of ensuring the work and rest schedule, as well as the sanitary and domestic needs of people. In particular, it is important to comply with:
- the required length of rest periods (Articles 108–111 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- duration and frequency of regular vacations (Articles 115, 124 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- cleanliness in work areas and regularity of their cleaning (Article 209 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- measures of protection from cold and excessively high temperatures (Article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- conditions for regular comfortable eating and sanitary and hygienic procedures (Article 223 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Another obligation of the employer related to the organization of labor is the need for compulsory social insurance of employees and the payment of related payments aimed at:
- for the formation of a future pension;
- provision of a minimum amount of free medical services;
- payment of sick leave and benefits related to maternity;
- prevention of accidents at work.
Read more about the possibilities of social insurance provided by the Social Insurance Fund in the material “Compulsory social insurance in the Russian Federation - types and contributions.”
Basic concepts and guarantee of employee rights
What are the rights and obligations of the employee and the employer in the field of labor protection? Not all of us will understand this concept correctly. According to the Labor Code of Russia, these are ways to save the life and well-being of participants in the labor process during the performance of duties. This system includes various types of measures aimed at compliance with such types of requirements as, for example, fire and industrial safety during work activities. In turn, labor protection also has its own definitions.
Working conditions are a combination of aspects of the working environment and the work process that affect the productivity and health of employees.
An employee is a person who agrees to fulfill certain requirements of the employer.
A harmful production point is a factor that can lead an employee to an occupational illness.
A hazardous work factor is the reason why a participant in the process may suffer damage to various parts of the body.
A workplace is an environment in which a person resides while performing work duties.
Personal and collective protective equipment - materials to prevent or reduce the impact of various harmful influences.
Production activity is a set of actions of people necessary to process raw materials into a finished product.
The environment in which a person works must fully comply with the labor protection conditions discussed in the employment agreement and provide guarantees of the workers’ right to labor protection. The amount of compensation to employees whose professional activities involve hard work, as well as harmful and dangerous production factors, is established in a manner determined by the government, taking into account the commission for resolving social and labor relations.
In addition to payments or their increase, for particularly difficult work or work with hazardous factors, can be discussed in a collective labor agreement. If the workplace certification commission determines that the required safe conditions for performing work duties are met at the employee’s workplace, then no compensation payments are awarded.
What must an employer observe when paying for work?
The employer's responsibilities for remuneration are in fact much broader than those specified in Art. 22 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (non-discrimination in payment for work of equal value, meeting deadlines, complete payment of wages), and require compliance (Articles 135, 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- a remuneration system developed and approved by the employer;
- the procedure for notifying the employee about the formation of the total monthly payment amount;
- forms of issuing money convenient for the employee (cash at the place of work or by bank transfer to the bank specified by the employee);
- frequency of payments at least 2 times a month with an interval of 2 weeks between them;
- dates established for the payment of wages by internal regulations.
Regarding payment terms, the following options are possible:
- wages are paid in advance (on the previous working day), the deadline for which, established by internal regulations, falls on a day off (Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- vacation pay is paid in advance (at least 3 calendar days before the start of the vacation) (Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, letter of the Federal Service for Labor and Employment dated December 21, 2011 No. 3707-6-1);
- Sick leave is paid on the salary payment date closest to the calculation made (10 calendar days are allotted for it) (clause 1 of Article 15 of the Federal Law “On compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity” dated December 29, 2006 No. 255-FZ) ;
- directly on the day of dismissal, all amounts not received by the employee before that day are paid (Article 140 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Failure to comply with the 2-week interval and established deadlines may result in the following for the employer:
- administrative fine for failure to comply with the requirements of labor legislation (Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation);
- payment to the employee of monetary compensation for the delay (Article 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- transfer of vacation at the request of an employee who did not receive vacation pay on time (Article 124 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- the need to pay the employee for the time of suspension of work resulting from a delay in payment of wages (Article 142 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- criminal liability for a manager who caused a delay due to personal interest (Article 145.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation).
How should an employer communicate information with employees?
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation obliges the employer to promptly provide employees (their representatives) with information:
- necessary for the development of a collective agreement;
- reflected in internal regulations;
- which is a response to requests regarding violations of labor laws;
- necessary for employee participation in the management of the organization.
Since a collective agreement is the result of a bilateral agreement, employee representatives participating in its creation on behalf of the collective must be fully aware of all the necessary information associated with this document.
Internal regulations are created for the purpose of employees’ compliance with their provisions, so familiarization with them is a fairly important step in the process of bringing the necessary information to the attention of employees and occurs against signature. Failure to comply with the requirements of these documents, subject to compliance with the familiarization procedure, entails disciplinary liability for employees.
Legislatively, the right to monitor compliance with labor legislation is assigned to trade unions (Article 370 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), which can act for these purposes in various forms - from authorized persons to labor inspectors. A fairly wide range of powers granted to them allows them to quickly identify violations and demand that the employer eliminate them. The employer has a period of 1 week (Article 370 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), during which he must:
- consider the requirement;
- take measures to eliminate the violation;
- inform the body that contacted him about the results of consideration of the appeal and the measures taken regarding it.
The right of employees to participate in the management of the organization is provided for in Art. 52 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. To implement it, a mutual exchange of information is necessary (Article 53 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), in which the parties receive information of the following nature:
- employer - in terms of taking into account the opinions of employees when creating a collective agreement and internal regulations, receiving proposals for improving the work of the organization;
- employee - in relation to changes in the structure of the organization, production technology, prospects for the development of the enterprise.
What should be considered in matters of compensation for harm to an employee?
Causing harm to an employee entails financial liability of the employer to him. The Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for several types of such liability:
- for loss of income due to illegal deprivation of the opportunity to work (Article 234 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- damage to employee property (Article 235 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- delay in payment of wages (Article 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- moral damage (Article 237 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Any type of liability will arise if there is (Article 233 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- the employer’s fault for the harm caused to the employee (except for delay in payment of wages, for which the presence of fault does not matter);
- proof of the amount of damage.
Read more about employer liability in the article “Financial liability of the employer to the employee”.
What are the employer’s responsibilities regarding a special assessment of working conditions?
The employer's responsibilities in terms of special assessment of working conditions, as well as rights, are established in Art. 4 of Law No. 426-FZ. They are necessary:
- ensuring that working conditions are assessed for all available jobs;
- providing comprehensive information regarding working conditions at each of the workplaces of the organization performing the special assessment;
- promoting the fullest possible disclosure of all factors influencing working conditions at each specific workplace;
- obligatory familiarization of the employee with the results of the special assessment;
- accompanying the assessment process with the necessary explanations for the employee;
- taking measures to improve working conditions based on the results of a special assessment.
Employee rights
This part of the legal relationship is closely tied to the responsibilities of the employer. The range of rights granted is based on the provisions of legislation, employment contracts, and local regulations.
Rights apply to:
- Possibility of concluding, changing and terminating contracts.
- Ensuring the scope of work specified in the contract.
- Providing a workplace that meets all safety standards.
- Timely payment of labor according to the established salary and available allowances. The salary must correspond to the qualifications of the employee.
- Compliance with the activity regime.
- Informing about upcoming working conditions and possible occupational hazards.
- Maintaining qualifications at the required level (training).
- Membership in workers' trade unions.
- Conclusion of collective agreements with third-party organizations.
- Where appropriate, participate in the management of the enterprise.
- Conducting strikes and protests in an acceptable form.
- Protecting your legitimate interests through forms not prohibited by law.
- Compensation for damage received in the course of professional activities.
What other responsibilities are implied for the employer?
Other responsibilities that an employer must fulfill include, for example:
- the need to issue documents related to work at the request of the employee (Article 62 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- ensuring normal working conditions (Article 163 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- creation of a labor protection system that meets established requirements (Article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
These kinds of obligations of the employer are established in various sections of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which is due to the very system of relations between the employer and the employee, which implies the presence of mutual obligations.
In addition, there may be obligations additionally established for the employer by internal regulations. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Full and free access to the system for 2 days.
Main responsibilities and rights of an employer
According to Art. 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the responsibility for ensuring safe conditions and labor protection falls on the shoulders of the employer. He must:
- protect workers during the operation of the building, production equipment, equipment, and the use of starting materials and raw materials;
- provide workers with means of personal and collective protection;
- create safe, non-life-threatening conditions for each subordinate;
- observe the work and rest schedule in accordance with current legislation;
- provide employees with special clothing, special footwear and other personal protective equipment, neutralizing and washable products purchased at the expense of the enterprise;
- Conduct timely safety briefings, train employees in methods and techniques for safe work performance, and also test their knowledge in this area;
- organize control over the working conditions in the workplace;
- certify employees in terms of safety;
- at its own expense, conduct mandatory preliminary and periodic medical examinations and psychiatric examinations of workers, while maintaining each of them’s position and average salary;
- refuse to hire a person at the beginning of his working career if he has not passed a medical examination;
- report possible risks in the workplace and required protective equipment;
- take the necessary measures to prevent emergency situations, as well as provide the necessary first aid to a person injured at the enterprise;
- conduct an investigation of accidents and occupational diseases that occurred at the enterprise;
- carry out sanitary, household and medical and preventive services to specialists;
- carry out compulsory social insurance of workers against industrial accidents and occupational diseases;
- develop and approve instructions for all subordinates.
Read more about the rights and obligations of an employer under the Labor Code.
According to labor legislation, the employer is vested with a number of powers in this area and can:
- reward employees financially for conscientiously performing their duties and showing initiative;
- require subordinates to comply with established internal rules and fulfill their assigned job responsibilities, including in the field of occupational safety;
- bring to material or disciplinary liability workers who fail to cope with their duties and do not comply with standards;
- unite with other employers, enter into unions with them in order to protect their interests.