Article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation: working conditions
According to Article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, every employer with employees is obliged to provide them with proper working conditions. Moreover, several operating objects fall under this requirement:
- Room. The building, workshop, hangar and any other structure where workers are located must be arranged in such a way that each subordinate has enough space, and among the list of rooms there must be a toilet and a utility room where employees can leave their personal belongings or take a break. It is also necessary to monitor the structure of the building itself so that it does not fall into disrepair. Do not forget about fire safety, the requirements for which are also regulated by the labor code;
- Operated equipment. Having conveyors, machines and other mechanical devices at its disposal, the employer is obliged to organize their daily inspection and carry out timely diagnostics. Such control will allow you to avoid serious problems associated with injury or death of a subordinate at work.
Attention! In addition to the listed conditions, Article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation also requires managers to comply with uniform standards of sanitary and epidemiological control established throughout the country for enterprises of any category.
Another comment on Art. 163 Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Article 163 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes the employer’s obligation to ensure normal working conditions to meet production standards. Since production standards are a type of labor standards, the obligation to fulfill which is assigned to all workers, the law’s requirement for the employer to ensure normal working conditions should be extended to all types of labor standards. This means that the employer’s failure to fulfill this obligation, which led to the employee’s failure to comply with any labor standards, gives the employee the right to payment in accordance with Part 1 of Art. 155 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation in an amount not lower than the average salary.
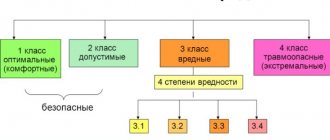
The concept of safe working conditions
Safe working conditions are a separate paragraph of Art. 212 of the Labor Code, which is characterized by the following list of features:
- Contact of personnel with harmful substances of the classes AXOB, SDYAV, BOV and VVZ is completely excluded;
- There is no risk of injury when performing official duties: work at height, with electrical voltage, etc.;
- The equipment is installed in compliance with all safety requirements (the machines have protective covers, and their diagnostics and maintenance are carried out daily).
Harmful working conditions also include work in the Far North and similar areas. However, the organization of such an environment at the enterprise is not mandatory for all managers.
Changing the terms of an employment contract at the initiative of the employer
social and economic - everything that is associated with wages, social status and service to the employee; organizational and technical – directly related to the work process; household and economic – opportunities for food, recreation, sanitary and living conditions; climatic – terrain features (location, geology, weather and nature, etc.)
2 tbsp.
The employer may, on his own initiative, change working conditions. This is provided for in Art. 74 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. But he can do this only if the technological or organizational side of the labor process changes. For example, new equipment is purchased for production, which will allow one to get away from manual labor and completely automate it.
Deterioration of labor safety is the failure by the employer to comply with the minimum requirements of labor protection rules and technical regulations established in the legislation, orders of the Ministry of Labor and the Ministry of Education on the organization of safe work, or the deprivation of workers of the minimum social guarantees for working in hazardous working conditions.
We invite you to read: Notification to an employee about the performance of duties of a temporarily absent employee
The deterioration of operating conditions can also include the unsatisfactory condition of equipment, machines, tools, and violations in the technology of safe work performance.
Example
A gas-electric welder is entitled to receive milk because he was exposed to harmful working conditions. To save money, the employer canceled milk distribution.
Milk must be dispensed subject to the following conditions:
- the workplace must contain harmful production factors specified in the List of hazardous production factors;
- the level of harmful factors must exceed established standards.
This is indicated in paragraph 2 of Appendix 1 to the order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated February 16, 2009 No. 45n.
Therefore, the employee could not cancel the delivery of milk. This is a significant deterioration in his working conditions, which cannot be applied.
According to Article 9 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer must not restrict the employee’s labor rights to provide additional leave of 7 days, payment of 4% of the salary, milk or work clothes.
The level of guarantees cannot be reduced compared to the legally established minimum.
Example
Motivating its actions by a decrease in the number of clients and a worsening financial situation, the employer stopped issuing dermatological cleansers. At the same time, workers continued to carry out work that required the issuance of protective, cleaning or regenerating agents in full.
There is a significant deterioration in the workers' standard of living, which is illegal and subject to cancellation in accordance with Article 9 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
It is impossible to create workplaces that do not meet the safety requirements specified in Articles 212 and 215 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Example
The head of the organization ordered the demolition of the sanitary premises and the installation of a plasma cutting machine instead. But modernization of production should not limit the employee’s right to rest during work.
Since work in a metalworking shop is accompanied by increased noise, vibration, interaction with moving mechanisms and other unfavorable production factors, workers have the right to rest in a noise-free area and have the right to eat in normal sanitary conditions, since there are no public catering establishments near the industrial zone , which workers could visit during their lunch break.
Consequently, the employer, having equipped the workplace in such a way that the employee cannot leave for meals, must equip a room at the enterprise for meals, equipped with a microwave oven for heating ready-made food, a kettle, a table and the required number of chairs, while the furniture must meet safety requirements .
However, in some conditions, workers are forced to work in unfavorable environments.
It is impossible to completely ensure the safety of miners in a mine. In addition to technical causes of accidents, there are also natural accidents.
You cannot install an air conditioner near an open-hearth furnace. Smelting metal requires high temperatures.
It is impossible to carry out geological exploration work from a cozy office, without traveling to the tundra or swampy areas. After all, the subsoil is there - peat, coal, gas, and oil.
It is impossible to create natural light for a metro cashier.
The microclimate in such production areas will always be unfavorable. In such industries, chemical products should be considered harmful or dangerous.
To reduce the adverse impact of HFPF on an employee, the employer must take protective measures.
Against industrial noise, you need to use not only headphones or earplugs, but also set regulated breaks in a “noise-free” area.
Workers must be provided with PPE in accordance with the issuance standards for their industry and profession. The established standards cannot be reduced even by one percent.
You cannot reduce the number of regulated breaks or their duration, replace the dispensing of detergents with washing powder, shorten the period of additional leave for work in hazardous workplaces, etc.
Example
In October 2020, at one of the confectionery factories, a worker fell into a vat of boiling caramel. An investigation is now underway. This accident was possible as a result of many factors, one of which was improper placement of production equipment. If safe passage widths had been ensured, the accident might not have occurred.
At the very least, the contributing cause, if not the underlying cause, will be determined during the investigation of this fatal accident. The investigation commission will be headed by the chief state inspector of the Rostrudinspektsiy.
The technical regulations “On the safety of machinery and equipment” establish that the employer must follow the instructions in the manufacturer’s technical documentation and recommendations for maintenance and repair.
The same requirement is contained in Article 215 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Therefore, failure to carry out scheduled maintenance work is a violation of the requirements of both labor legislation and safety requirements for the organization of work.
For violation of labor protection requirements, the employer may be fined under Article 5.27.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
For violation of sanitary norms and rules, liability will arise under Article 6.3 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
In addition, the employer may be punished under other articles of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
Example
If your organization operates vehicles for the transportation of goods or passengers in international road transport without a tachograph, then a fine will be established under Article 11.23 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation for the lack of a device for recording information about the speed and route of transport and about the work and rest hours of drivers.
We suggest you read: How vacation pay is calculated for piecework wages
The absence of a tachograph makes it impossible to track the driver’s compliance with the work and rest schedule established by law, so the employer is obliged to install them. If it doesn’t, it will worsen the employee’s working conditions.
The risk of an accident exists at any technical facility. The main threat associated with the operation of a hazardous production facility occurs in the event of an accident accompanied by such damaging factors as the destruction of metal structures, scattering of parts, fragments, etc.
Hazards of this kind can be eliminated by observing safety requirements when operating the equipment, as well as by equipping it with safety devices - safety and interlocking devices.
Persons responsible for the safe performance of work and the good condition of the equipment must ensure the serviceability of protective, safety and locking devices. Officials of enterprises, within the limits of their official duties, have the right to give orders to eliminate violations of labor protection rules and regulations, to prohibit the operation of equipment and the performance of work if it does not comply with regulatory safety requirements and there is a threat to the health and life of workers.
Thus, a fatal accident occurred in ZAO Anastasievskoye, Krasnodar Territory, with mason P. while carrying out work in a carpentry workshop.
By order of the foreman, a team of workers at the repair site, consisting of two carpenters U. and K., three masons M., P. and Ts., began to manufacture blanks for the containers of the plant growing workshop. The carpenters worked on a circular saw to cut the boards, and the masons carried and laid the cut pieces elsewhere.
While sawing another board, a piece broke off, which fell on the saw and flew towards the mason P., who was two meters from the circular saw. A piece of board hit mason P. in the stomach, causing him a fatal injury.
During the accident investigation, it was determined that the circular saw did not have a safety guard to prevent the cutting tool from throwing out workpieces and waste.
attention
• safety of workers during the operation of buildings, structures, equipment, and implementation of technological processes;
• working conditions at each workplace that meet labor safety requirements.
attention
GOST 12.2.026.0-93. “Woodworking equipment. Safety requirements for design”, put into effect by Decree of the State Standard of Russia dated March 28, 1995 No. 168
3.1.1. The machine must have protective devices that prevent during operation:
- throwing away processed workpieces and waste with cutting tools.
At CJSC Anastasievskoe, unsatisfactory organization of work during the operation of woodworking equipment was noted, expressed in:
- insufficient control over the safe performance of work;
- lack of protective fences for production equipment.
The General Director did not ensure the safety of workers when operating industrial woodworking equipment. The chief engineer, who is responsible for the good condition of the equipment at the energy repair site, allowed the operation of a circular saw machine that was not equipped with a protective device that prevented the cutting tool from throwing out workpieces and waste during operation.
From the point of view of the structure of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the rules on changing the employment contract are concentrated in Chapter 12 of the Code, which bears the appropriate name, where the employee carries out his activities. All these conditions are prescribed in personal and collective labor contracts.
Concept of labor protection
Occupational safety is a system of rules and regulations aimed at reducing the risk of injury to personnel during the work process. It is based on six main institutions:
- Legal;
- Economic;
- SanPiN;
- Organizational;
- Psychophysiological;
- Treatment and prophylaxis.
The main goal of labor protection is to ensure maximum safety of the health and life of subordinates during their stay at the workplace. It is achieved through the following principles:
- Avoiding contact of personnel with hazardous substances whose concentration exceeds the established norm;
- Reducing the workload on employees;
- Creating safe working conditions, both indoors and behind equipment in particular.
Advice! According to Article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, both special services and committees created within the enterprise by subordinates themselves can monitor the implementation of the listed measures.
The main responsibilities of the employer to ensure working conditions
In addition to the general list of standards aimed at increasing labor safety, Article 212 of the Labor Code also includes personal requirements for employers, failure to comply with which may become a reason for initiating an administrative or even criminal case. This includes:
- Ensuring the safety of the health of personnel and their property during the operation of work premises;
- Purchase and installation of certified equipment, its timely maintenance and repair;
- Providing workplaces with the necessary protective elements (gloves, masks, etc.);
- Distribution of staff working hours in accordance with the requirements of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- Providing subordinates with personal protective equipment;
- Conducting free training to improve the skills of workers, as well as familiarizing them with working conditions;
- Organization of regulatory bodies that inspect personnel workplaces, equipment and condition before each shift;
- Providing an annual free professional examination for subordinates (people without a medical certificate are prohibited from accessing the equipment);
- Providing all necessary information and documentation to staff;
- Organization of measures to prevent accidents, with the involvement of the sanitary and epidemiological group, law enforcement agencies and insurance services;
- Timely payment of labor at the rate specified in the contract.
The listed requirements apply to all employers, without exception. But for enterprises whose personnel work in particularly difficult and dangerous conditions, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation also provides additional rules, such as: provision of increased leave and payment of compensation benefits in excess of wages.
Labor Code: | Useful reading
This article will remind employers that no economic situation cancels the Labor Code. And since employees know their rights even less well than employers, our article is useful for them too.
Below we will list the most egregious violations and mistakes of employers that infringe on the rights of workers, and also give examples of the serious consequences that they are fraught with.
Hiring and firing violations
The biggest mistake employers make is hiring an employee without an employment contract. Many managers think that the absence of a contract relieves them of responsibility for non-compliance with labor laws.
“The general director of one fairly large Moscow trading company thought that if employees worked without a contract, he would be able to arbitrarily reduce or not pay them wages, as well as fire them at any time,” says Alexander Yu, a specialist in labor conflicts at one of the Moscow companies. - However, according to the law, it is enough to find witnesses to labor relations to prove that they existed. In addition, there are documents proving the fact of labor relations: pay slips, orders, instructions.”
Tired of the harassment, the company's warehouse workers, together with those who were unfairly fired, filed a lawsuit against the employer, where, due to the presence of witnesses and documents, his guilt was proven.
https://youtu.be/MlPCKAkmsbE
In this particular case, ignorance of the law cost the employer several million rubles. The employer not only paid compensation to those fired, the difference in the promised and actually paid wages, but also the wages of all plaintiffs for the nine months during which the proceedings lasted.
Violations during dismissal in Russian companies are also, as a rule, the norm.
You can be fired without notice:
- for a single gross violation,
- the employee did not show up for work or was late for more than four hours without warning and good reason,
- came under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
In general, it is impossible to simply fire an employee, even if he violates labor discipline. First you need to collect evidence, issue a warning and follow other procedures.
Often the employer and even the HR department simply do not pay attention to the details.
The employee was absent from work from September 7 to September 12. He is fired for absenteeism from the 9th to the 12th. For two days management had no time for the employee.
However, in court the employee represents sick leave from the 9th to the 12th. The employer leaves the court with nothing.
Discrimination
Discrimination based on gender, age, nationality, and individual discrimination occurs in many companies.
In most cases, employees do not complain to the authorities only because they do not know their rights.
Women often receive reduced wages or are persecuted by management due to pregnancy and illness of children - the threat of dismissal and even dismissal.
Representatives of “non-titular” nations and especially guest workers often work for little money without an employment contract. If you look at the headlines in the media, courts constantly deal with such violations and punish employers.
Here is a typical story: “During an inspection at the hypermarket , six citizens of Uzbekistan were identified and auxiliary workers without the necessary documents and without an employment contract.
As a result, 12 cases were initiated under Part 4 of Art. 18.15 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.”
As for the violation of women's rights, many employers still live in peace only because their employees are not aware of their rights.
According to Rostrud, over the past year, about 30% of all complaints due to violations of labor rights (a total of 120,000 complaints) were filed by women.
Reasons for requests:
— violation of the principles of fair wages (80,000 complaints),
— incorrect execution of employment contracts (40,000 complaints),
— other violations in the field of labor protection (6,000 complaints).
Lack of charter, documents on labor regulations, non-compliance with workers’ rights
Many employers think that violation of labor discipline is a valid reason for dismissal. In this case, employers themselves often violate labor laws. For example, there are no labor rules in society, and this is a violation.
Also, when concluding an employment contract, the employer often indicates job responsibilities and features of the labor regime, which initially contradict the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
For example, an employee is prescribed irregular working hours, while his occupation and position itself do not imply irregular work.
In other cases, it is impossible to “work” workers without good reason, say, in the presence of force majeure, or without overtime pay. In addition, overtime work, in principle, should be paid additionally.
Financial mistakes - fines, salary reductions, etc.
Many employers and employees are not aware that fines, salary reductions and other financial punishments for employees are completely prohibited by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation .
An employer cannot reduce wages, even if such measures are specified in the employment contract.
In Russia there is no primacy of contractual relations over legislation. Whatever the parties sign, if it is against the law, remains illegal .
Moreover, in the case when we are talking only about reducing bonuses (many employers try to get around the Labor Code in this way), everything is not so simple. If the amount of the bonus is specified in the employment contract and its amendments, it cannot be reduced.
A salary reduction is possible only for valid, documented reasons and not on an individual basis..
Favored by employers, delayed wages lead to serious financial penalties. Even without any trial, only by decision of the state inspector, the company will have to pay the employee interest for each day of delay, starting from the next day of the payment deadline until the day of actual payment.
However, the general director himself may be subject to administrative and even criminal liability. Cases of punishment of CEOs are not uncommon.
And here's another . The salary once specified in the contract cannot be lower during the probationary period. Formulation of this kind : “We will pay you 30,000 for two months, and after the probationary period 60,000” is illegal. An employee can always immediately ask the employer: “How does this agree with the Labor Code?”
Interference with an employee's personal life
The head of a network marketing company learned that one of his top employees would soon marry a woman who was once his business partner. However, their relationship was upset, some business claims arose against each other, and they stopped collaborating.
The leader did not like to remember this episode from his life. And now his employee was reminding him of this again. His first desire was to simply fire his groom. However, the business largely depended on the efforts of a specialist.
Then the manager gave the employee an ultimatum: either he leaves the company, or receives a strong promotion and a much larger salary, but breaks up with his fiancée.
The distressed groom told his bride about the conversation, and she insisted that he sign a new contract in front of witnesses and then go to court.
As a result, according to the court, the groom received large compensation for moral damage, all the bonuses that were specified in the contract, and a new increased salary for the entire duration of the process.
There are three main organizations that an employee can contact :
* Federal Labor Inspectorate
* Prosecutor's office
* Court
Moreover, in labor disputes, the employee is exempt from paying court costs, including state fees. This means that going to court does not require the employee to pay any costs at all.
However, the court must be contacted within three months from the day the employee learned of the violation of his rights, and in disputes about dismissal - within one month from the date he was given a copy of the dismissal order or from the date the work book was issued.
Both employees and employers must always know and take into account Russian realities - both inspectors, the prosecutor’s office, and the court in most cases take the side of the “weak,” that is, the employee.
Fyodor Swarovsky , Illustrations: Konstantin Amelin , Shutterstock.com
Afterword:
Sergey Kozlov, General Director of Megaplan
I have had to be both fired and fired. Either way, it's stressful. And rather negative stress. As they say, once we fire someone, someday we will be fired.
The current Labor Code is a legacy and achievement of the socialist era. And here I am on the side of employers, not TC. It is high time to change the dismissal procedure to the North American style.
He said “you and fayed” and paid a fixed amount, for example three monthly salaries. And no sanctions or courts.
Look, the economy would develop faster, and workers would hold on to their jobs.
Subscribe to our chat on Telegram
Listen to the article on iTunes
For Android: try this option and be sure to write how you like it.
Source: https://Megaplan.ru/letters/trkodex/
Responsibility for failure to fulfill duties
If an employee does not organize proper working conditions for his staff according to the labor code, then 4 different types of liability may be applied to him:
- Disciplinary (The mildest measure, which is provided for cases that do not result in injuries at work or increased health risks for subordinates. This can be an oral or written reprimand);
- Material (The most common punishment for violation of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which is expressed in penalties. In this situation, their amount will be from 50 to 100 non-taxable minimums);
- Administrative (Another common option for punishing employers is by removing them from official duties. For violation of Article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation - for 1-3 years);
- Criminal (An extreme measure that is used in cases where non-compliance with working conditions has resulted in serious injury or even death of a subordinate. Imposed in the form of arrest for a period of up to 3 years).
Advice! But in order to bring their boss to justice, the staff needs to prove his guilt with documentation, confirming his complaint with photographs or video materials of the workplace.
We found out what requirements for managers are prescribed in Article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, and what the director may face for ignoring them. In conclusion, it remains to add that labor safety conditions must be fully and always met. Without them, the likelihood of injury at work increases significantly.
Labor Code: Labor Code and the Role of the State
- Article of the Labor Code: special assessment of working conditions and employer activities
- Application of SOUT results by the employer
- Prohibition of discrimination
In the list of articles on special assessment of working conditions contained in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, it is necessary to pay special attention to Article 210. It describes the key areas of strategy and policy implemented by the state in the field of labor protection for workers. This section also contains reference to the OSA, which is therefore seen as an important element of such a policy. In this article of the Labor Code, SOUT acts as a subject of state regulation. In other words, the legislator assumes the obligation to formulate and control the implementation of rules for its implementation and examine the level of quality of such work.
Carrying out medical examinations
Routine medical examinations, the conduct of which in relation to employees working at the enterprise is enshrined in Articles 212 and 213 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, is another direct responsibility of the manager. He must organize them at the expense of the enterprise. Thus, medical examinations upon entry to work are paid for by the employer.
The following must also undergo a medical examination at the employer’s expense:
- minor workers;
- persons employed in work with harmful and dangerous conditions;
- workers in the food industry, public catering and trade, medical and preventive care and children's institutions, water supply facilities;
- workers carrying out certain types of activities associated with a source of increased danger;
- workers whose activities are related to the movement of vehicles.
Employees who have not passed a mandatory medical examination or a mandatory psychiatric examination are not allowed to work.