This section includes:
The physical and/or chemical processing of materials, substances or components with the aim of converting them into new products, although this cannot be used as a single universal criterion for defining production (see "waste recycling" below)
Materials, substances or transformed components are raw materials, i.e. products from agriculture, forestry, fisheries, rocks and minerals and other manufactured products. Significant periodic changes, updates or conversions of products are considered to be related to production.
The products produced may be ready for consumption or may be a semi-finished product for further processing. For example, the product of aluminum purification is used as a raw material for the primary production of aluminum products, such as aluminum wire, which in turn will be used in the necessary structures; production of machinery and equipment for which these spare parts and accessories are intended. The production of non-specialized components and parts of machinery and equipment, such as engines, pistons, electric motors, valves, gears, bearings, is classified in the appropriate grouping of Section C, Manufacturing, regardless of which machinery and equipment these items may include. However, the production of specialized components and accessories by casting/molding or stamping of plastic materials is included in Class 22.2. The assembly of components and parts is also classified as production. This section includes the assembly of complete structures from constituent components, produced independently or purchased. Waste recycling, i.e. processing of waste for the production of secondary raw materials is included in group 38.3 (activities for processing secondary raw materials). Although physical and chemical processing may occur, this is not considered part of manufacturing. The primary purpose of these activities is basic waste treatment or treatment, which is classified in section E (water supply; sewerage, waste management, pollution control activities). However, the production of new finished products (as opposed to products made from recycled materials) applies to all production as a whole, even if waste is used in these processes. For example, producing silver from film waste is considered a manufacturing process. Special maintenance and repair of industrial, commercial and similar machinery and equipment are generally included in group 33 (repair and installation of machinery and equipment). However, repair of computers and household devices is listed in group 95 (repair of computers, personal items and household items), while at the same time, automobile repair is described in group 45 (wholesale and retail trade and repair of motor vehicles and motorcycles). Installation of machinery and equipment as a highly specialized activity is classified in group 33.20
Note - The boundaries of manufacturing with other sections of this classifier may not have a clear, unambiguous specification. Typically, manufacturing involves the processing of materials to produce new products. Usually these are completely new products. However, determining what constitutes a new product can be somewhat subjective
Processing implies the following types of activities involved in production and defined in this classifier:
Processing of fresh fish (removing oysters from shells, filleting fish) not carried out on board a fishing vessel, see 10.20;
Pasteurization of milk and bottling, see 10.51;
Leather dressing, see 15.11;
Sawing and planing of wood; impregnation of wood, see 16.10;
Printing and related activities, see 18.1;
Tire retreading, see 22.11;
Production of ready-to-use concrete mixtures, see 23.63;
Electroplating, metallization and heat treatment of metal, see 25.61;
Mechanical equipment for repair or overhaul (e.g. automobile engines), see 29.10
There are also types of activities included in the processing process, which are reflected in other sections of the classifier, i.e. they are not classified as manufacturing industries.
These include:
Logging classified under Section A (AGRICULTURE, FORESTRY, HUNTING, FISHING AND FISH CULTURE);
Modification of agricultural products classified in section A;
Preparation of food products for immediate consumption on premises, classified in group 56 (activities of catering establishments and bars);
Processing of ores and other minerals, classified in section B (MINERAL MINING);
Construction and assembly work carried out on construction sites, classified in section F (CONSTRUCTION);
Activities of breaking down large quantities of goods into smaller units and secondary marketing of smaller quantities, including packaging, repackaging or bottling products such as alcoholic beverages or chemicals;
Sorting of solid waste;
Mixing paints according to customer's order;
Metal cutting according to customer's order;
Explanations for various goods classified under section G (WHOLESALE AND RETAIL TRADE; REPAIR OF MOTOR VEHICLES AND MOTORCYCLES)
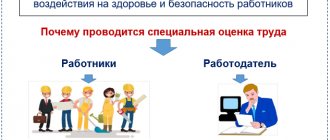
For the purpose of accounting for the work of commercial companies in our country, the OKVED mechanism is used. It reflects the entire range of activities by economic sector. Moreover, if previously in the Russian Federation the previous edition of this document was in force, put into effect in 2001, then since 2014 the accounting authorities switched to OKVED 2. The special assessment of working conditions in OKVED 2 refers to section M. It includes various types of work in the field provision of professional services, including scientific and technical types.
Special assessment of working conditions: OKVED code
To determine the place of a specific type of activity in the OKVED classification, several substantive categories are used. In particular, OKVED for special assessment of working conditions is characterized by the following designations:
- class - 71. This includes work on technical examinations, as well as design;
- subclass - 71.2. This includes work on performing technical surveys, as well as conducting certification activities;
- group - 71.20. The content of this group is similar to the subclass;
- subgroup - 71.20.7. In this subgroup, it is the activities related to carrying out SOUT that are recorded.
At the employer's expense, every five years a comprehensive assessment of each workplace is carried out to determine its compliance with safety requirements. This assessment is carried out by specialists from third-party specialized organizations
, whose activities, according to the Ministry of Economic Development of the Russian Federation, correspond to code 74.30 “Technical tests, research and certification” according to OKVED.
Certification of workplaces is carried out under an agreement with the organization
, which should:
- have accreditation by the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia and be included in the register of accredited organizations located on the official website of the Ministry of Health and Social Development;
- be independent in relation to the legal entity at whose workplaces, according to the agreement, certification is carried out.
What code according to OKPD 2 and OKVED 2 determines SOUT
In the OKPD 2 classifier, services for special assessment of working conditions are coded 71.20.19.130
. This code is the final code in the corresponding hierarchy; it does not require additional clarification; nothing (no number) can come after it.
Activities for carrying out SOUT have a numerical index in the OKVED 2 classifier 71.20.7
. As you can see, the first two numbers are similar to those in the OKPD 2 code.
It is also worth paying attention to the difference. In the section above we were talking about the designation of services according to SOUT (as a product offered), and in this section - about the designation of activities according to SOUT (as a professional occupation).
Main stages
Certification can be divided into three main periods
:
- the stage of planning and preparation of work, including the conclusion of a contract
, the formation of a certification commission and approval of its composition by order of the organization, drawing up a work schedule.
During this period, the commission studies local organizational and administrative documents, establishes harmful and dangerous factors in the workplace and determines where instrumental measurements will be carried out
; - The main stage is the actual carrying out of the necessary instrument measurements with the preparation of appropriate protocols
and the drawing up of certification cards based on them. The certification card must indicate the OKVED code of the organization whose workplaces were certified. If, as a result of the research, it is revealed that the conditions at the workplace do not ensure the preservation of the health of workers, then the employer develops a number of measures to reduce the negative impact of harmful conditions on the health of workers; - preparation of final documents, the main of which are the final protocol of the certification commission
and the certification report with attachments. By order, the employer completes the certification and approves the reporting materials.
How is decryption carried out?
A specific decoding of OKVED 96.04 should be done in stages for a better understanding of the principles of operation of such a resource as OKVED-2:
- Section S of the classifier denotes the provision of other types of services.
- Code 96.0 indicates that the business belongs to other services in the field of personal services.
- 04 is a code that is indicated in this form in registration documents and implies that the activity belongs to other types of physical education and health services.
What can be attributed to this code? This could be the activity of baths, saunas, hammams, solariums or weight loss centers. It is worth noting that rehabilitation services of health centers, massage salons, and fitness centers cannot be provided under this code.
So, OKVED code 96.04 is used for some types of physical education and health services that could not form their own group. Such types of business activities are classified as other services, and for them the new edition of the classifier has a whole separate section. Such activities may include the provision of services in bathhouses, solariums, and weight loss centers. In addition, entrepreneurs working privately in these areas must also register under this code.
Compensations, benefits, fines
Based on the results of certification, employees are determined the compensation and benefits they are entitled to.
: additional vacation time, cash supplement for harmful working conditions, therapeutic and preventive nutrition, etc.
Correctly and timely certification of workplaces minimizes the employer's risks of applying penalties from government supervisory authorities, so it is important to choose the right certifying organization.
The legislation of the Russian Federation provides for penalties for violations of labor protection requirements, ranging from disciplinary to criminal liability. A frequently used penalty is the imposition of an administrative fine; its maximum amount is:
- for persons performing official duties, up to five thousand rubles;
- for organizations carrying out entrepreneurial activities with the formation of a legal entity, up to fifty thousand rubles.
When we talk about the concept of “security agency,” most often we mean a private security company , or private security company. Today it is more correct to call a private security company a private security organization, that is, a private security organization. This is the wording contained in Federal Law No. 272-FZ of December 22, 2008, as amended on January 1, 2010. However, the name “private security company” sounds more familiar, and security organizations continue to use it in advertising and market promotion. Departmental security companies - federal state unitary enterprises, or federal state unitary enterprises, as well as the Federal State Unitary Enterprise "Security" of the Russian Guard, which provides security services to a wide range of consumers, are not considered private.
Private security company. What is it, how does it work
A private security company is a commercial, non-state company that provides security services. Only a legal entity can act as a private security company.
According to the requirements of current legislation, private security companies are registered exclusively in the form of LLC, or limited liability company. As such, many private security companies were not puzzled by the renaming of a private security company into LLC ChOO, or a private security organization. A much larger task for them was introducing amendments to the charter of the LLC to bring it into line with the changing requirements of the law, including in terms of the size of the authorized capital, the qualifications of managers and founders (today they must have a higher professional education behind them, appropriate training and have valid private security guard licenses).
Why can a private limited liability company exist only in the form of an LLC, a limited liability company, and, for example, not a PJSC - a public joint stock company, or a JSC - a joint stock company? There is a logical explanation for this requirement for the organizational form of private security companies. First of all, it is due to the fact that the activities of a security organization, its actions, management structure, and composition of owners should not depend on the decisions of shareholders. The activities of security structures are associated with increased responsibility and are strictly regulated in the Russian Federation. The participation of shareholders in the management of the company would inevitably create legal conflicts and threaten public and state security.
According to the definition given in Article 1.1 of the Law of the Russian Federation dated 03/11/1992 N 2487-1 (as amended on 08/02/2019) “On private detective and security activities in the Russian Federation”, “a private security organization is an organization specifically established to provide security services , registered in accordance with the procedure established by law and having a license to carry out private security activities.”
A private security company, therefore, is created solely for the purpose of providing security services, and specializes in providing such services throughout the entire period of its existence, that is, private security companies cannot engage in other types of activities other than those established by law. However, when registering a private security organization in the form of an LLC, a number of “other services” related to ensuring the activities of the enterprise are usually added to the list of “core” OKVED in the field of security, law, consulting, cargo transportation, and electrical installation work.
Please note that the classifier of economic activity codes in the part related to private security activities has undergone changes in 2020 and 2020, so you should be careful when choosing OKVED when registering your LLC or making changes.
Security company services
The services of a security company are subject to legislative regulation. The list of services that private security companies can provide is given in Article 3 of Federal Law N 2487-1.
Considering the current wording “For security purposes, the provision of the following types of services is permitted” outside the legal context, it can be assumed that both private security organizations and licensed private security guards can provide security services. However, so far the practice of providing security services by private security guards without the participation of a security company is not legally supported and is not used. Protect Group experts monitor legislative activities in this area.
Let us note that, according to Article 3 in question, only private security companies and private security guards can provide the services listed below. This is exactly the wording regarding security services contained in the wording of Art. 3 of Federal Law N 272-FZ, in force since December 22, 2008. Persons who do not have the appropriate legal status cannot provide security services. According to the provisions of the article, it is permitted to provide the following security services:
Services to protect the life and health of citizens
In the current version of the law, the essence and meaning of this clause are not disclosed or commented on in any way, and the corresponding clause consists of one phrase. We can assume that this clause allows private security companies to provide personal security services, and also implies that security company employees take care of protecting the life and health of citizens as part of the provision of facility security services and security of public events.
Security services for objects and movable property
A private security company can provide security services for objects (meaning real estate) and movable property, including during its transportation. The article of the law directly states that the protected property must be owned, in possession, in use, economic management, operational management or trust management of the client of the private security company. The exception is the objects and property listed in paragraph 7 of Art. 3 Federal Law N 2487-1.
Services for design, installation and maintenance of security systems and equipment.
Site security services using technical security equipment, including remote control security, including design, installation and maintenance. List of types of technical systems and equipment for installation and maintenance of which a license is required, in accordance with clause 3 of Art. 3 Federal Law N 2487-1, must be established by the Government of the Russian Federation. In practice, this means that such a list is regulated by many departmental regulatory acts, letters and comments, the content of which can be interpreted in different ways, but most of them refer to the considered paragraph 3 of Art. 3 Federal Law N 2487-1, although as such the installation of many types of alarm and video surveillance systems is not licensed. It should be noted that a number of private security services are regulated by the Federal Law “On Licensing of Certain Types of Activities” dated May 4, 2011 N 99-FZ. The law directly and unambiguously establishes that a license from the Ministry of Emergency Situations is required for the installation and maintenance of fire and security alarms.
Consulting services in the field of safety and security
Private security companies are allowed to provide advice and prepare recommendations to clients on issues of lawful protection from unlawful attacks. This means that a licensed private security company, with the help of its specialists, can plan and recommend security measures, routes, the number and placement of posts, the use of technical security equipment, and the implementation of access control for its customers on a reimbursable basis.
Security services for public events
Private security companies are allowed to ensure order in places where public events are held. To do this, the private security company's license must contain a corresponding clause. Objects of mass traffic, such as large shopping and entertainment centers, supermarkets, also fall under the scope of this clause. The lower limit of the number of people simultaneously present at the facility, after which it can be considered a place of mass stay, is only 50 people. Work to ensure the safety of people and ensure public order in public places implies serious responsibility and requires appropriate qualifications. It is these factors that are associated with additional requirements for private security companies providing security services for public events.
Ensuring intra-facility and access control
Private enterprises can ensure intra-facility and access control at protected real estate sites. This security service is usually included in the range of facilities security services. Stationary security with the implementation of access and security regimes by private security companies is allowed on any real estate, with the exception of those specified in clause 7 of Art. 3 Federal Law N 2487-1.
Exceptions. Changes to the List dated September 20, 2019
A private security company can provide stationary security services for facilities, including provision of access and intra-facility regimes, even if mandatory requirements for anti-terrorism security are established for the protected facilities. The exception is the objects listed in Art. 11 of the law we are considering. In particular, private security companies cannot be involved in the protection of objects subject to state protection, as well as protect objects contained in the list approved by the Government of the Russian Federation (Appendix No. 1 to the Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation of August 14, 1992 No. 587) as amended on 20 September 2020. The last change to the List dated September 20, 2019 concerns the paragraph on facilities in the electric power industry, oil and gas industry, excluding from it the facilities of “strategic enterprises”, “strategic joint-stock companies” and their subsidiaries. In addition, armed security by private security forces of objects located on the territory of closed territorial formations (ZATO) is still prohibited.
How to choose a security company
A security agency must be checked for reliability, and often for the very fact of its existence, before concluding an agreement with it. There are several effective ways to do this.
List of security companies. Security company license - how to check
The activities of private security companies are subject to mandatory licensing. The first thing you should do is check whether the private security company is on the list of licensed private security companies in your city or region.
What is not recommended to do
Customers access lists of existing security companies from various sources. Some Internet sites even offer to download a register of private security company licenses by region or nationwide, with addresses and telephone numbers of security companies. However, Protect Group experts do not recommend using or downloading such information from unverified sources, and here’s why.
Firstly, the provision of information from the register of private security company licenses is carried out by the Russian Guard in accordance with the established regulations. Information is accessible to individuals and legal entities, but is provided in accordance with the procedure established by law. Although the law does not directly prohibit a potential customer of a security service from searching for information in the public domain.
Secondly, you may come across unverified or outdated information about private security companies in the public domain. Moreover, the names, addresses and telephone numbers of security companies may have nothing to do with reality at all. It is much worse if the information about the security company’s license turns out to be outdated or false. At the same time, it is unknown who is responsible for the adequacy, relevance and completeness of the information sought. Being guided by unverified information when making a decision to contact a particular private security company is, to say the least, unreasonable, and in the future it can result in problems with the law for the customer, especially if the latter is obliged to purchase the services of a licensed security company.
Thirdly, data downloaded from unverified sources on the Internet can infect and damage your computer with viruses, malware and applications. Such content can block the operation of the computer, gain access to the data stored on it and steal it. This is deplorable, even if the home computer from which no official correspondence is carried out was damaged. If a machine used by a company executive or security officer is attacked, this can lead not only to significant damage, but also to legal or personnel consequences.
Fourthly, trying to obtain information about the register of private security company licenses on an unverified site, you can accidentally or through thoughtlessness part with your money. Various online sites may directly offer to buy data, or a certain amount may be automatically deducted from your account when you click a button or link. At the same time, the Russian Guard must provide information from the current list of security companies in the prescribed manner, as indicated on the official website of the department, absolutely free of charge.
What does the Russian Guard recommend?
To check whether a private security company is included in the list of security companies, you should send a corresponding request to the Russian Guard. According to information on the official website of the department, this can be done in person by submitting an application in writing, or through the online service “Gosuslugi”. As noted on the official website of the Russian Guard, an extract from the register of licenses for security activities must be sent to the applicant within five working days.
Let's turn to the Unified State Register of Legal Entities
Accurate data on any existing private security company that is operating or has ceased to operate can be found in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities - the Unified State Register of Legal Entities.
The Unified State Register of Legal Entities contains such information about a legal entity as the individual taxpayer number - INN, legal address, the composition of the founders with the disclosure of their details, last name, first name, patronymic and, in most cases, INN of the head, OKVED, bank details, size of the authorized capital, history of changes, as well as information about the availability of licenses issued to a legal entity and their number without indicating the details of the licenses. So, if a private security company has one license, then this is a license to carry out private security operations. If there is another one, perhaps it is a license from the Ministry of Emergency Situations, which is necessary for the design and installation of a fire and security alarm system.
From the information contained in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, it is therefore possible to draw conclusions not only about whether a private security company exists, but also about its compliance with mandatory requirements.
You can search the Unified State Register of Legal Entities and obtain data from the register online using Internet services that operate legally on a paid or free basis. The interface of some online services of the Unified State Register of Legal Entities allows, using a detailed search in the database, to create and upload a list of private security companies linked to a region or a specific tax office.
Security company website
An important source of information about the private security company is its official website. If a security company has its own website, you should find it and study it carefully.
Sometimes the official website of a small security agency can be difficult to find using search engines. In this case, you can use contact information from the private security company lists or ask a representative of the security agency to provide you with a link.
The private security company's website must contain information about the private security company's license. Many market players post scanned documents on their websites. This is especially important if the customer requires security services that are specially licensed. For example, the protection of public facilities.
On the contrary, the absence of any information about the license should alert a potential client. It is possible that security services advertised on a website where there is no information about the license are provided unofficially. A contractor who provides security services without a license violates the law and bears responsibility for it. For the customer, this means the failure of all security measures. If the law obliges the customer to use security services at his facility, this jeopardizes the operation of the facility and may lead to the closure of the business.
It is possible that, along with the official website of the security company, there are several more pages on which its individual services are advertised. Such sites, however, must contain reliable information and the necessary details.
How to determine if a security company's website is official
The address of the security company on the website must match the actual one
Before concluding a security contract, you must visit the private security company and make sure that it is actually located at the address indicated on the website. For the convenience of their clients, many private security companies offer site visits and conclusion of contracts on site. However, there is always a risk that unidentified persons will come to you under the guise of representatives of a private security company.
It is correct to expect that both the actual and legal addresses are indicated on the official website of the private security company. Legal address is included in the details. The actual address of the office location is included in the contact information. The legal and actual addresses of the private security company must match; this rule applies to any legal entity. In practice, the location or travel address may differ from the legal address, but this is not advisable.
The telephone numbers of the security company must be valid
All telephone numbers listed on the security company’s website must be working, and subscribers must be available for calls during business hours. If the site lists several phone numbers, this is a plus. At the same time, representatives of the relevant structural divisions of the private security company must answer such telephone numbers.
Reviews of the security company
Reviews of security agencies are published on the Internet, as well as various “black” and “white” lists of private security companies.
Reviews about a security company can be either positive or contain criticism of the private security company, its management or individual officials. Often in reviews you can find information about the real leaders and beneficiaries of the private security company, its clients, the work style of its officials, and personnel policies.
Private security agencies receive more negative reviews than positive ones. This is a general rule, and it is due to the fact that commentators more often seek to share negative experiences and complain to others about the troubles that have arisen, while positive experiences of interaction with private security companies do not receive publicity according to the principle “happiness loves silence.”
It should also be taken into account that reviews of private security companies, both positive and negative, can be custom-made; they are left not by real clients, but by copywriters. This phenomenon can be widespread. But most often, a customized review is easy to distinguish from a real one.
“Black” and “white” lists of private security companies are akin to reviews. Any “black list of security organizations” can be formed on flimsy pretexts or without any explanation at all and posted on the Internet by an unscrupulous competitor.
Agreement with a security company
Security services can be provided only on the basis of a valid contract of appropriate form and content, concluded between the private security company and the customer or his legal representative. Providing security services without an appropriate contract is an offense and may result in the revocation of your private security license. What do you need to know about the agreement with private security company?
ORP agreements have a standard form and are largely intended to fix the obligations of the contractor to the customer.
The subject of the contract is security services, often with their more or less detailed description. The contract sets out the rights and obligations of the parties. This part of the contract for the provision of security services usually lists the types of services provided and sets out the methods for providing them. An important point here is the indication of the timing and methods of reporting by the contractor to the customer as part of the provision of services.
A distinctive feature of contracts for the provision of security services are the requirements for the security of the protected property, equipment with technical security equipment, and the procedure for organizing the security system.
The standard clauses of an agreement for the provision of security services are the duration of the agreement, the cost of services and the procedure for settlements between the parties, the liability of the parties, and force majeure circumstances.
Private security companies often post a standard form of agreement for the provision of security services with their details on the website. Such a step may indicate that the security company is reluctant to adapt the contract to a specific client. In this case, the customer can record the essential conditions for himself in the appendices, which are an integral part of the contract.
Responsibility of the security company
An agreement with a private security company may stipulate the financial liability of the contractor to the customer in the event of damage to the life and health of people, a protected object or property due to improper fulfillment of its obligations by the security organization. Practice shows that the fact of the latter still needs to be proven. However, in general, such a clause in the contract increases the level of trust in the private security company on the part of clients.
The financial liability of the private security company should be determined by the contract as specifically as possible. This may be a fixed amount, the full cost of the damage caused, or some other wording. It is important to determine how to estimate the value of lost property.
It should be taken into account that compensation for material damage to the customer is carried out not by the security agency from its own funds, but by the insurance company with which the private security company has entered into a liability insurance agreement. This information may not be included in the service agreement.
If a private security company announces its readiness to bear financial liability under an agreement for the provision of security services in advertising, printed products or on an Internet site, it would be useful to check whether the corresponding clause is included in the agreement or its annexes. In themselves, such messages do not oblige the private security company to anything, and in the event of a dispute or litigation will not have legal force.
Sign an agreement with a security company or hire a watchman?
An agreement for the provision of security services with a private security company differs favorably for the customer from an agreement with an individual for the provision of security services.
Firstly, the law cannot assign most of the duties performed by a private security guard to a watchman or watchman. Thus, a watchman cannot carry out checkpoints and intra-facility control, ensure public order at the facility entrusted to him, detain intruders until the police arrive, use special means and technical means of security, and even more so use weapons. The times when the movie “Operation Y” was released are long gone: if today you commit the same actions as the characters in the film, those involved will face criminal liability.
Secondly, there is a risk that such a contract with an individual will be recognized as an employment contract. In this case, the customer’s expenses for maintaining his watchman will increase sharply - one-time in the form of additional personal income tax charges and contributions to extra-budgetary funds for all the time worked and in the future on an ongoing basis.
Additional tariffs in the Pension Fund and special assessment of working conditions.
Starting from January 1, 2014, employers are required to conduct a special assessment of working conditions in accordance with Federal Law dated December 28, 2013 No. 426-FZ. Based on the results of a special assessment of working conditions, classes and subclasses of working conditions are established, on the basis of which an additional tariff for contributions to the Pension Fund is determined (Article 58.3 of Law No. 212-FZ). It should be borne in mind that contributions for additional tariffs are not always calculated.
To determine whether or not to accrue contributions to the Pension Fund at additional tariffs, you must be guided by Lists No. 1 and No. 2 (approved by Resolution of the Cabinet of Ministers of the USSR dated January 26, 1991 No. 10). If an employee’s position is included in one of these lists, then contributions to the Pension Fund using additional tariffs are calculated on his payments. If the position is not included in any of the lists, then the obligation to subject payments to contributions to the Pension Fund at additional tariffs does not arise. The amount of the applied tariff depends on the type of work in which the employee (insured person) is employed, as well as on the results of a special assessment of working conditions.
Tariffs for payments to employees engaged in work contained in the specified lists are as follows (clauses 1, 2, article 33.2 of the Federal Law of December 15, 2001 No. 167-FZ, part 1, 2 of article 58.3 of the Federal Law of July 24, 2009 No. 212-FZ):
Persons employed in underground work, in work with hazardous working conditions and in hot shops (clause 1, clause 1, article 27 of the Federal Law of December 17, 2001 No. 173-FZ)
2014 — 6.0% – joint part of the tariff
2015 — 9.0% – joint part of the tariff
Persons employed in work with difficult working conditions and other hazardous work (clauses 2 – 18, clause 1, article 27 of the Federal Law of December 17, 2001 No. 173-FZ)
2014 — 4.0% – joint part of the tariff
2015 — 6.0% – joint part of the tariff
Depending on the results of a special assessment of working conditions, the following tariffs for additional contributions to the Pension Fund apply; they are applied instead of those listed above (clause 2.1, article 33.2 of the Federal Law of December 15, 2001 No. 167-FZ, part 2.1 of article 58.3 of the Federal Law of July 24. 2009 No. 212-FZ):
Payments subject to additional tariffs are subject to:
– payments in favor of persons entitled to early assignment of a labor pension;
– payments and rewards in favor of the employee from the moment of registration of an employment relationship with him, providing for work under special working conditions. The length of time during which the employee is directly exposed to harmful factors (daily during the billing period or periodically, according to production needs) does not affect the procedure for calculating insurance premiums;
– payments in favor of an employee entitled to early retirement, regardless of working hours (for example, part-time or part-time work week);
– if the employee is already a pensioner (that is, already receiving early retirement), but continues to work under special working conditions, the calculation of pension contributions at additional rates for payments to such a person continues.
Calculation of insurance premiums at an additional rate for insured persons employed in workplaces not specified in the subparagraphs of paragraph.
What is OKVED
This is the All-Russian Classifier of Economic Activities, which contains digital designations for each business sector in Russia. Such codes consist of 2-6 digits, but applications indicate a code of at least four characters. These are the requirements of the tax authorities.
The classifier is regularly edited and updated, even in 2019 they managed to make a couple of changes. But the current option, OKVED-2, will remain in effect in the new year; the prerequisites for cancellation have not yet been encountered.
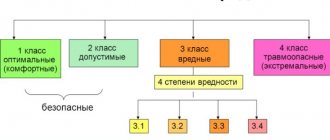
Special assessment of working conditions - activity codes
1–18 tbsp. 1 of Law No. 173-FZ, the legislation of the Russian Federation does not provide for insurance premiums. Insurance premiums at additional tariffs for payments made in favor of employees in whose workplaces the working conditions according to the current results of workplace certification (or from 01/01/2014 according to the results of a special assessment of working conditions) are recognized as harmful and (or) dangerous, but not named in paragraphs. 1–8 p. 1 tbsp. 27 of Federal Law No. 173-FZ, are not accrued.
Reporting to the Pension Fund
From the 1st quarter of 2014, reporting to the Pension Fund has been clarified regarding the reflection of additional contributions:
section 2 has been supplemented with a new subsection 2.4, which reflects information on insurance premiums for an additional tariff depending on the class (subclass) of working conditions, which was established based on the results of a special assessment;
columns 3 and 13 have been added to section 4, which reflect additional accrued additional contributions paid based on the results of the special assessment (part 2.1 of article 58.3 of Law No. 212-FZ);
the column “Special labor assessment code” has been added to section 6 of subsection 6.7. The meaning of these codes can be found in Appendix No. 2 to the Procedure for filling out the calculation according to the RSV-1 Pension Fund form.
Reporting to the Social Insurance Fund
Table 10 “Information on the results of a special assessment of working conditions and mandatory preliminary and periodic medical examinations of workers at the beginning of the year” of Section II of the calculation in Form-4 of the FSS, starting with reporting for the first quarter of 2014, is filled out and submitted without fail (clause 2 Procedure for filling out form 4-FSS). This table has been updated due to the introduction of a special assessment of working conditions.
Table 10 reflects data on a special assessment of working conditions, as well as on mandatory preliminary and periodic medical examinations performed at the beginning of the year (clauses 34–34.4 of the Procedure for filling out form 4-FSS, approved by Order of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated March 19, 2013 No. 107n). Moreover, if the policyholder’s workplace certification for working conditions has not yet expired, then the table must be filled out based on the results of such certification.
You have no rights to post comments
Search Lectures
Stylish OKVED: hairdressing services and beauty salon
The beauty industry has been in high demand on the market for decades. It is customary in society to “meet people by their clothes,” which is why stylists, beauty salons and hairdressing services have become so widespread.
This is an attractive industry for a new entrepreneur. Some provide services personally, which reduces the cost of hiring employees - it is enough to rent 10 square meters. m, and not a two-story beauty salon. You can get by with small investments - this is what attracts businessmen.
To safely and legally make people beautiful: open a beauty salon, provide hairdressing services, do nail extensions, you must follow the law. If you don’t want to fall into the category of violators and run into fines, register an individual entrepreneur or company with the tax office.
The Federal Tax Service will have to collect a whole package of documents. Charters, passports, statements, orders - the list is long, different for each organizational and legal form. But in each case there is an unchanged application for registration according to the tax model. For individual entrepreneurs, the form P21001 is provided, for LLCs - P11001. In both cases, during the filling process, the businessman will be faced with the column “OKVED codes”. Even self-employed people fill out this mysterious section of the application.
OKVED code 71.20.7 - Activities for assessing working conditions
Form of a special assessment card for workers' working conditions
CARD No.________
special assessment of working conditions
_______________________________________________________________________________
(name of profession (position) of the employee)
Name of structural unit ______________________________
Number and numbers of similar jobs __________________________
Line 010. Issue of ETKS, EKS _____________________________________________
(issue, section, date of approval)
Line 020. Number of employees:
Line 021. SNILS of employees:
Line 022. Equipment used: _________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
Materials and raw materials used: ____________________________
__________________________________________________________________
_
_
Line 030. Assessment of working conditions based on harmful (hazardous) factors:
| Name of factors of the production environment and labor process | Class (subclass) of working conditions | Effectiveness of PPE *, +/-/not assessed | Class (subclass) of working conditions with the effective use of PPE |
| Chemical | |||
| Biological | |||
| Aerosols with predominantly fibrogenic action | |||
| Noise | |||
| Infrasound | |||
| Ultrasound air | |||
| General vibration | |||
| Local vibration | |||
| Non-ionizing radiation | |||
| Ionizing radiation | |||
| Microclimate parameters | |||
| Light environment parameters | |||
| The severity of the labor process | |||
| The tension of the labor process | |||
| Final class (subclass) of working conditions | not filled in |
* Individual protection means
Line 040.
Guarantees and compensations provided to the employee(s) employed at this workplace:
| No. | Types of guarantees and compensation | Actual availability | Based on the results of the assessment of working conditions |
| need to establish (yes, no) | base | ||
| 1. | Increased wages for the employee(s) | ||
| 2. | Annual additional paid leave | ||
| 3. | Reduced working hours | ||
| 4. | Milk or other equivalent food products | ||
| 5. | Therapeutic and preventive nutrition | ||
| 6. | The right to early assignment of a labor pension | ||
| 7. | Conducting medical examinations |
_________________________
________________________________________________________________________
__________________________
Date of preparation: ___________________
Chairman of the commission for conducting a special assessment of working conditions
Members of the commission for conducting a special assessment of working conditions:
Expert(s) of the organization that conducted the special assessment of working conditions:
| __________________ | __________________ | __________________ | __________ |
| (No. in the register of experts) | (signature) | (FULL NAME) | (date of) |
| __________________ | __________________ | __________________ | __________ |
| (No. in the register of experts) | (signature) | (FULL NAME) | (date of) |
I am familiar with the results of the special assessment of working conditions:
©2015-2018 poisk-ru.ru All rights belong to their authors.
Main or additional OKVED
When filling out the application, you must first indicate the main type of activity, the one that brings the greatest profit. Additional services include secondary services that generate a smaller share of income. You can specify up to twenty options.
Entrepreneurs often indicate a dozen encodings at once so that they do not have to update the Federal Tax Service information. Remember that each new type of commercial activity must be entered into the Unified State Register of Legal Entities or the Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs. Tax inspectors must be aware of the changes, otherwise they face a fine.
searching results
Search OKPD special assessment of working conditions
| OKPD | Decoding | Frequency |
| Other technical testing and research services | 449 | |
| Services provided by professional organizations | 102 | |
| Services in the field of technical regulation and standardization | 60 | |
| 45 | ||
| Services related to business activities, other, not included in other groups | 26 | |
| Other services not included in other groups | 18 | |
| Services for the analysis of the chemical and biological properties of various substances (for example, air, water, household and industrial waste, fuel, metals, soil, minerals, chemicals) | 15 | |
| Other security services | 14 | |
| Other engineering and technical services, not included in other groups | 11 | |
| Valuation services on a fee or contract basis | 10 |
What is included in this code
Some types of entrepreneurial activity, especially if it has a narrow specialization, are not able to form a separate group. This may be due to the fact that the scope is not extensive enough or there are no subspecies and varieties in it. It is precisely this kind of activity that is usually called “other” on the pages of the all-Russian classifier, that is, a separate code is not used for it, it is designated by one code, which includes several types of services.
For example, in the new edition of the classifier a whole section has appeared dedicated to other types of business services. One of the types is the physical culture and health type of activity, as well as the organization of some events that have a healing effect on the human body. This can be the activity of private types of rehabilitation therapists and personal trainers, as well as the activity of some health institutions.
Class OKVED 80 contains the following codes with a detailed description of the type of activity and interpretation:
Activities of private security services
Activities of private security services
This grouping includes:
- provision of one or more services: security and escort, collection and transportation of money, making payments or transfer of valuables using personnel and equipment to protect such property
This grouping includes:
— provision of armored vehicles;
— services for the provision of lie detectors;
— fingerprinting;
— security services;
— destruction of documents and information on any media for security purposes
This group does not include:
- activities to protect public order and security, see OKVED code 84.24
Operation of security systems