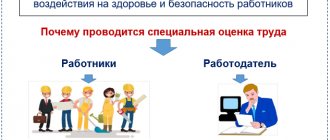
It is mandatory to carry out a special assessment of the working conditions of drivers of cars and special equipment, as well as for all jobs in the organization. The SOUT procedure begins with issuing an order and appointing a commission that will oversee this process and sign all the necessary documents. As a rule, the commission includes a manager, trade union members, a representative of the human resources department and a labor protection engineer. The number of commission members must be odd, including the chairman of this commission. The order to conduct a special assessment must indicate the names and positions of the commission members, as well as the work schedule.
Afterwards, you need to select an organization that will conduct the SOUT. By law, this organization is independent and in its charter can carry out only one type of activity. This laboratory must have all the required areas of accreditation for the factors being measured. This is necessary in order to be able to analyze all the harmful factors in the enterprise. For example, if a driver works at a chemical plant and, according to his job description, is involved in the loading and unloading of chemicals, then in addition to the usual factors harmful to the driver, measurements of the chemicals with which he comes into contact must be taken.
South car driver
Info
For example, if a driver is engaged in driving transport for 80 percent of the time in conditions where the maximum permissible limit is exceeded, harmful working conditions will definitely be established.
And if the hauls are short and there is a break between them for waiting or loading, if the maximum permissible limit is slightly exceeded, it is possible to establish acceptable working conditions. In what cases do you need to evaluate working conditions when changing a car? If a driver switches to another car, this means a change in equipment and a change in working conditions. In this case, it is necessary to conduct an unscheduled special assessment. If the driver drives different cars during the year, the employer must clearly define their list. For example, during the year the driver works on Zil-130, Zil-131 and KAMAZ. These are different cars. If we take the entire operating time as 100 percent, then we can determine the periods of control of each car.
Special assessment of working conditions of car drivers
In the absence of artificial sources of heat and cold in the workplace, intended to create optimal working conditions in the workplace and not provided for by the design of the vehicle, the class (subclass) of working conditions in terms of microclimate parameters is increased by one degree. 9. In the course of assigning working conditions at workplaces to the class (subclass) of working conditions according to the intensity of the labor process, the final class (subclass) of working conditions according to the parameters of the intensity of the labor process increases by one degree in connection with the implementation of professional activities by drivers in conditions of time shortage, with a high degree of responsibility for the result of such activities, due to the significance of a possible error, the possibility of special traffic situations that could create a risk to the life and health of others. 10.
Parameters of tension and severity
During the special assessment, the tension and severity of the work process are taken into account. For such a profession, the main conditions are concentration, extreme attentiveness and caution. Every erroneous movement or incorrect orientation in any unforeseen situations on the road can lead to an emergency with a different outcome. This risk group includes truck drivers. One of the main negative factors leading to accidents in this category of drivers is fatigue. After all, they are given the task of transporting goods over a long distance; the journey can even last several weeks. A person’s normal rhythm of life is disrupted and, accordingly, tension arises. Based on the results of carrying out special assessment and labor conditions at workplaces, a class of working conditions is established, in accordance with which compensation and benefits are assigned, in accordance with the law.
The main purpose of a special assessment is not only to detect harmful production factors in the workplace, but also to further eliminate and improve them. To improve conditions, preventive programs are implemented, which allows employees to feel comfortable.
Car driver hazardous working conditions
- First of all, the harmfulness according to the noise criterion will decrease, since now the maximum limit for this factor is set to the same for everyone - 80 dB.
- The established vibration indicators can also affect the class of working conditions, and in most cases, except for special equipment, they will go into the class of permissible conditions.
- The same applies to the severity of work. The introduced category – sitting working posture, excludes the possibility of interpreting the driver’s posture as uncomfortable, fixed or forced. This is now a common pose.
- Assessing labor intensity using the Special Assessment Methodology will in many cases lead to a reduction in the hazard class. This is due to the fact that out of the previously used 23 indicators, only 6 are now used and all of them have quantitative measurements. The reduction in the hazard class will primarily affect drivers working in areas where there is no heavy traffic and few traffic lights.
Greetings, dear friends! All managers and specialists of passenger motor transport enterprises have taken note of the news about the specifics of conducting a special assessment of working conditions in the workplace of drivers of public urban ground passenger transport, which have finally been registered with the Ministry of Justice of Russia and will come into force in a matter of days. A short overview and the document itself in Word format await you below. The specifics of conducting a special assessment of working conditions at the workplace of drivers of public urban ground passenger transport were approved by Order of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated June 30, 2017 No. 543n and, as I said above, were registered with the Ministry of Justice of Russia on December 13. The specifics of conducting a driver’s SOUT will come into effect on December 25, 2020.
What are the harmful factors for drivers?
By doing simple physical exercises and eating right, you can prevent heart attacks and strokes, as well as maintain the health of your respiratory, digestive and reproductive systems.
Do not put off visiting the doctor if you have health problems. There is no standardized referral form. Stepkin Yu.I., Dr. med. Sciences, Prof., Chief Physician of the Federal State Institution "Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology in the Voronezh Region"
,Mamchik N.P., Dr. med.
Sciences, prof., deputy. chief physician of the Federal State Health Institution
"Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology in the Voronezh Region"
,Kameneva O.V., Ph.D. honey. sciences, head department of hygienic education, training and certification of the Federal State Health Institution
"Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology in the Voronezh Region"
In our country, buses are the most common type of transport, and in rural areas they are the main, sometimes the only vehicle for transporting passengers.
What occupational hazards do car drivers have?
Sciences, prof., deputy.
Chief Physician of the Federal State Institution "Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology in the Voronezh Region", Kameneva O.V., Ph.D. honey. sciences, head
department of hygienic education, training and certification of the Federal State Institution "Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology in the Voronezh Region" In our country, buses are the most common type of transport, and in rural areas it is the main, sometimes the only vehicle for transporting passengers.
The work of a driver is characterized by a complex of unfavorable production factors such as high nervous and emotional stress associated with the risk of road accidents, unfavorable microclimate, dust, gas pollution, and static loads. Info Beginner drivers (less than 5 years of experience) visit a doctor three times more often than drivers with more experience.
The most common are acute respiratory diseases, influenza and tonsillitis, which account for 87% of all diseases in this nosological form.
advokat-martov.ru
The act is drawn up in four copies and certified by the seal of the medical organization.
What harmful factors must be indicated? And is it necessary to indicate in the referral the name and address of the medical institution where he will undergo a medical examination? Based on the results of the analysis, we offer you a legal position on the situation: You have the right to indicate the following factors in sending the applicant for a preliminary medical examination:
- general vibration.
- physical overload;
- local vibration;
The above factors are given in accordance with the standards of the Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated April 12, 2011.
Harmful production factors: types and examples by profession
Based on their impact, they can be divided into 4 groups: These may include the following work environment factors: If you want to find out how to solve your particular problem, contact us through the online consultant form or call:
- Saint Petersburg: .
- Moscow: .
- vibration;
- insufficient lighting level;
- radiation;
- humidity;
- exposure to low or high temperatures.
- noise;
They may be present during work or when there is potential contact with hazardous substances that pose a threat to human health or life in the following cases:
- when inhaled;
- upon contact with skin.
For example, these could be products of the oil refining industry, caustic substances, fertilizers, dyes, combustion products, etc.
Truck drivers undergo periodic medical examinations annually. On the basis of Order No. 302N of the Ministry of Health, the labor protection worker, when compiling a list of hazardous professions, puts down the harmfulness point for all, Appendix 2, paragraph 1 (work
1.
clause 3.4.2. 1 time every 2 years Regarding the indication of the point of work at height: In accordance with Order of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated March 28, 2014 No. 155n On approval of the Rules for labor protection when working at height https://budget.1kadry.
ru/#/document/99/499087789/ Work at height includes work in which: 3 a) there are risks associated with a possible fall of an employee from a height of 1.8 m or more, including: 1 when an employee climbs to a height more than 5 m, or descending from a height of more than 5 m along a ladder, the angle of inclination of which to a horizontal surface is more than 75°; when carrying out work on sites at a distance closer than 2 m from unfenced differences in height of more than 1.8 m, and also if the height of the protective fence of these sites is less than 1.1 m; b) there are risks associated with a possible fall of a worker from a height of less than 1.8 m if work is carried out on machines or mechanisms, the surface of a liquid or bulk fine materials, or protruding objects.
Occupational Safety and Health
An unfavorable production factor is the increased content in the air of the working area of chemical substances entering the driver's cabin from the air of the roadside area. Laboratory studies have shown that the level of atmospheric air pollution affects the contamination of the working area of the driver's cabin with nitrogen and carbon oxides and hydrocarbons.
2). Table 1 Results of studies of noise, vibration and microclimate in the driver’s workplace Factor (number of studies conducted) Number of exceedances of MPL Relative indicator, % Absolute excess Noise (315) 110 35.1 1–9 dB Total vibration (105) 51 49.2 6 –11 dB Local vibration (105) 4 4.5 2–8 dB Temperature (210)
Directory of factors of order 302n by profession version 2
worker and social work specialist in a nursing home
Download in Word
Watch 875 social worker in the social center
Download in Word
View machine operator of woodworking machines woodworking production
Download
Certification of workplaces for working conditions of road transport drivers.
Guidelines
In this regard, to assess the working conditions at the driver's workplace, requirements were selected to ensure safe working conditions from the current regulatory documents, which are given in Table 1. Table 1 OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DRIVER'S WORKPLACE NN p/pRequirements for the elements of the workplace driverName of the RD containing labor protection requirements1231.
Cabin 1.1The forced ventilation system must ensure a flow of fresh (outside) air into the cabin per person of at least 30 m
/h. At ambient temperatures above 17 °C, the air supplied to the cabin should not heat up by more than 2 °C relative to the ambient temperature. Air flow velocities at the exit of the ventilation system should not exceed 12 m/s. The ventilation system must ensure: 1. difference
Harmful and dangerous factors for drivers in
A person can fall into such factors due to neuropsychological overload, which is caused by excessive physical exertion and various troubles in everyday life and at work.
It is noteworthy that almost all negative impacts can be avoided if the employer takes care of its own staff and complies with all applicable rules and regulations.
He must take care to provide forklift drivers with personal protective equipment and to properly organize labor protection.
Systematic exposure to local vibration causes vibration disease with loss of ability to work.
This disease occurs gradually, causing joint pain, finger cramps, and vascular spasms.
General vibration has an adverse effect on the nervous and cardiovascular systems, causing disruption of the musculoskeletal system and gastrointestinal tract.
Increased
Harmful working conditions for car drivers
Especially for excavator operators who work with hydraulic hammers.
General vibration is transmitted to the driver's body through a fulcrum on the seat.
And local - through the car’s control elements: levers, steering wheel. The level of vibration also depends on the road surface.
It can affect both general and local vibration.
There is less vibration in the city because the road is better. Accordingly, for rural areas its level will be higher. There have also been changes in the vibration assessment methodology for workplace certification.
All this contributed to the creation of working conditions for the car driver during a special assessment. Is the driver provided with additional leave as an employee with hazardous working conditions? The duration of the annual basic paid leave for drivers is 28 calendar days (Article 115 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). In addition, Art. 116 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for annual additional
Changes in the special assessment of working conditions for drivers
Criteria and classification of working conditions" (Approved by Rospotrebnadzor on July 29, 2005).
In it, indicators of labor intensity contain several criteria: intellectual, sensory, emotional stress, monotony, work mode. The first criterion contains an indicator – the content of the work.
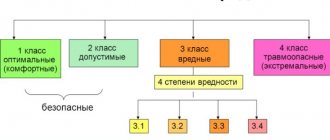
If an employee does not need to make decisions, working conditions are considered optimal, if simple decisions according to instructions are acceptable, complex tasks with a choice according to known algorithms are considered harmful (class 3.
1), creative activity – harmful (class 3.2).
Such indicators were excluded from the methodology for assessing working conditions. Emotional stress, which was assessed during workplace certification, also cannot be objective. For example, a driver tends to feel a sense of risk for his life, since he is a participant in traffic - his workplace was immediately assigned class 3.2.
What are the harmful factors for a car driver?
An assessment was made of the timing of the working day (including Second shift: • from 15.20 to 16.20 171.8 ± 0.3 101.2 ± 0.6 • from 16.20 to 17.20 165.2 ± 0.9 114.2 ± 0.5 • from 18.20 to 19.20 167.8 ± 0.5 115.9 ± 09 • from 20.20 to 21.20 174.2 ± 0.6 122.3 ± 0.6 • from 22.20 to 23.20 185.3 ± 0, 2 140.3 ± 0.2 Third shift (break schedule): • from 6.45 to 7.45 170.0 ± 0.9 102.3 ± 0.5 • from 9.
30 to 10.30 160.3 ± 0.3 110.3 ± 0.5 • from 15.00 to 16.00 170.2 ± 0.9 116.2 ± 0.9 • from 17.00 to 18.00 178.2 ± 0.5 123, 2 ± 0.9 from 19.00 to 20 00 184.9 ± 0.3 142.3 ± 0.6 Analysis of the dynamics of the level of attention of drivers showed that in the second shift the number of errors made is significantly greater, however, the duration of viewing correction tables is lower by the end of the day than in the first shift.
This can be explained by the fact that working at night requires the driver to be more responsible for traffic safety (Table
5). Legal confirmation of the proposed position: In accordance with part four of Art.
Harmful factors for a passenger car driver under order 302n
The legislation does not provide for a unified form of referral for a preliminary medical examination for an applicant or employee (in particular, an applicant-driver).
In practice, it is proposed to fill out the field - the medical organization to which the applicant will be sent. [attention]If the applicant refuses to be examined or the medical commission declares him unfit for this type of work, the conclusion of an employment contract is not allowed. An applicant who is denied an employment contract has the right to demand to know the reason for the refusal. The employer is obliged to communicate it in writing (Part.
Source: https://konsalt74.ru/kakie-vrednye-faktory-u-voditelej-67731/
Changes in the special assessment of working conditions for drivers
Important
Due to changes in legislation and the abolition of workplace certification in the beginning of 2014, the approach to conducting a special assessment of the working conditions of car drivers has also changed. This, first of all, can be associated mainly with the adoption of a new special assessment methodology, which replaced the old procedure for certifying workplaces based on working conditions. Innovations in the legislation and changes made in the methodology will allow the majority of drivers who had harm during the current certification to reduce it to an acceptable level.
This is primarily due to an increase in the permissible noise level for cars and trucks, and its equalization with the permissible level for special equipment. It turns out that the same factor was previously assessed differently depending on the type of vehicle, but now the maximum permissible level of the noise factor has been reduced to one value.
What should a driver do to maintain a harmful class?
Pay special attention to assessing the intensity of the work process. The permissible class is established when the average number of signals is no more than 175/hour. Moreover, according to various estimates, the real value of this indicator can vary from 100 to 400 per hour (depending on the region and time of day). But it is very important to understand that the calculation is on average per shift. Those. Having received the number of signals per hour, it must be multiplied by the share of actual vehicle control per shift. And the lower this share, the lower the final class. Thus, during identification, when experts from the testing laboratory request documents about the driver’s work and rest schedule, it is necessary to take this issue very seriously. Provide internal timing, use tachographs to determine drivers’ working hours. Because the final class will depend not even on the assessment (the numbers from region to region are more or less known), but on the number of driving hours per day.
Make proposals to the list of factors to be assessed during the SOUT. Even if an expert organization says that it is impossible to measure this or that factor, since identification is prohibited, draw their attention to clause 9 of Appendix No. 1 to Order of the Ministry of Labor No. 33n dated January 24, 2014, which states that the final list of harmful The factors to be assessed are determined by the commission, not the expert. One caveat: the list is formed based on state regulatory requirements for labor protection. Therefore, in order to reasonably include, for example, a vibroacoustic factor in the list, it is necessary to: - take into account complaints and suggestions from workers regarding the identification of harmful factors at their workplaces; - analyze cases of identifying prof. diseases among employees (for organizations with a large fleet of vehicles, especially urban passenger transport, this can be very important); - support your conclusions with the requirements of SP 4616-88 (regulatory legal acts containing state regulatory requirements for labor protection include... sanitary standards, sanitary rules and hygienic standards that establish requirements for factors in the working environment and the labor process).
Analyze the results of the automated workplace, if any. If an AWP was carried out and the working conditions were found to be harmful, then identification at the driver’s workplace is not carried out. The list of factors to be studied is determined by the expert without taking into account identification restrictions. Those factors for which a hazardous class was established will definitely be added to the list, and to add the rest, use your right to formulate the final document based on state regulatory requirements for labor protection.
The Ministry of Labor is concerned with assessing the working conditions of urban passenger transport drivers and has launched the process of developing features for assessing their work. Although there is no draft document yet, the situation itself has moved forward. And I would like to believe that most of the problems will be reflected in this order to one degree or another. But in any case, if the order is approved, it will not be earlier than in a year. And during this time, transport workers can see their SOUT cards, in which the word “absent” will appear opposite the “benefits and compensation” column. And this will lead to dissatisfaction, complaints, lawsuits, and dismissals.
To avoid this, it is necessary to approach the SOUT process carefully and comprehensively:
- notify employees that special labor safety measures are being carried out at their workplaces;
- scrupulously collect source documentation;
- require the laboratory to perform measurements that comply with approved methods;
- Before familiarizing yourself with the SOUT maps, drivers should check them themselves.
Are there any differences in the methodology for special assessment of drivers’ jobs from the assessment that was carried out during the certification of jobs?
Indeed, there are differences in the new method. They lie in the difference in the assessment of various factors. The most significant changes for drivers are those related to the assessment of noise levels, work intensity and vibration. A new factor has been introduced - sitting posture, which was not there before. And it is important for drivers.
South drivers with
If earlier there were 5 types of vibration and 5 remote controls, now there is one remote control for transport vibration: along the x and y axes - 120 dB, along the z axis - 115 dB. It is possible to establish that the maximum permissible limit is exceeded only during measurements. How is driving time assessed? The duration of driving may influence the assessment of factors such as sitting posture.
Attention
It was introduced for the first time and characterizes the severity of labor. Previously, you had to choose a driving position from three options: forced, fixed or uncomfortable. Disagreements arose as to which of the three should be included in the workplace certification card.
For example, many believed that the driver's posture was fixed because the heel of his right foot was on the floor and the toe was on the accelerator pedal. Some considered the pose forced - the cabin did not allow the use of other poses. Some are uncomfortable. This is actually a normal sitting posture. Evaluation criteria have been developed for it. In this article we will consider the features of conducting a special assessment of the working conditions of car drivers. Unlike other frequently encountered workplaces, the workplace of a car driver differs in that usually the employee is on the move most of the time, which imposes its own characteristics when analyzing working conditions. Analysis of the work process when conducting a special assessment of the working conditions of a car driver First, it is necessary to draw up a so-called “working day photograph”. It records the average statistical time values, as a percentage, during which the driver is in motion, that is, driving the vehicle.
Lesson outline "Driver's workplace"
OUTLINE OF A LESSON ON THE TOPIC: “DRIVER’S WORKSTATION”
1. Lesson objectives:
a) Educational – Teach the student how to sit correctly, how to drive a car and control alarm devices.
b) Developmental – Form professional skills, develop analytical skills.
c) Educational – To develop the professional qualities of the future driver and work culture. 2. Material, technical and didactic teaching aids:
Interactive board, auto simulator.
3. Form of conducting classes:
Story, conversation, demonstration of methods for completing a task, practical implementation of tasks.
4. Must know:
location and purpose of vehicle controls, instrumentation; landing and position of the driver at the workplace.
5. Must be able to:
read instrument readings; quickly and correctly position yourself in the vehicle cabin, observing the correct placement of hands on the steering wheel and feet on the control pedals.
During the classes:
Analyzing the degree of driver reliability, namely his professional suitability, preparedness and performance, deficiencies are almost always discovered, the origins of which lie in the period of formation of initial driving knowledge and skills. Statistics show that from 40 to 70% of road accidents occur due to errors made by drivers as a result of decreased performance. Performance is not constant, it changes throughout the day, day, week. The main reason for decreased performance is fatigue - a natural process that occurs as a result of work activity.
Good performance is facilitated by careful preparation of the workplace and proper care of it. Correct adjustment of the seat, backrest and headrest ensures minimal muscle strain and good visibility. Therefore, at the beginning of this lesson, it is necessary to form in the future driver the correct idea of the driver’s seat. The previously noted requirements for the driver’s workplace, namely: comfort, accessibility of controls, visibility and safety, along with the student’s body size, are the determining factors when setting up the workplace.
The first step in setting up your workstation is to align the driver's seat in relation to the steering wheel. This operation is performed with the clutch pedal fully depressed.
Attention should be focused on the fact that while driving a car, the driver quite often has to use this particular control, and the correct use of it lies precisely in fully depressing the clutch (full pressing of the pedal). When the seat is correctly adjusted and the clutch pedal is pressed, the driver's left leg should always be slightly bent at the knee joint, and when the pedals are released and the feet are on the floor, the steering wheel should not touch the feet so that its rotation is not difficult. An equally important criterion for assessing the correct setting of the driver's seat is visibility. When the driver is positioned remotely relative to the steering wheel, the driver's visibility is deteriorated due to a decrease in the angle of visibility in the straight-line direction along the hood line and a narrowing of the field of view limited by the front inclined pillars of the car body.
The next element of the driver's workplace to be adjusted is the seat back. Noting the validity of the statement that the position of the backrest primarily affects the driver’s fatigue, it is necessary to pay attention to two important points. Firstly, with the correct position of the hands on the steering wheel, slightly above the middle, the angle at the elbow joint should be about 90 degrees with the shoulders slightly away from the body. Secondly, the driver's back should be straight and fully supported by the back of the seat. To prevent numbness of the cervical spine, it is necessary to adjust the height of the headrest, which should be located at the level of the back of the head, thereby ensuring a stable position of the head with a characteristic rectilinear field of vision.
By adjusting the driver's workplace, we thereby form the correct driver's position, after which it is necessary to fasten the seat belt provided for by the design of this vehicle. The effectiveness of this structural element of the vehicle’s passive safety cannot be underestimated, nor should the requirements of paragraph 2.1.2 of the Road Traffic Rules be neglected, according to which “The driver of a power-driven vehicle is obliged, when driving a vehicle equipped with seat belts, to be fastened and not to carry passengers who are not wearing seat belts.” security."
It is necessary to eradicate the misconception about the functionality of seat belts, according to which “the belt constrains the driver’s actions, interferes with driving, and is not effective in the event of emergency situations.” There are quite compelling counterarguments for these falsely formed stereotypes, namely:
—
with a
correctly configured workplace,
the driver never experiences discomfort from using the seat belt;
— a seat belt is an element of passive structural safety of a car, which serves to reduce the severity of the consequences of an accident and prevent new incidents.
In this context, the belt secures the driver tightly in the seat, preventing injury to the head, thoracic region of the body, and ejection through the front windshield during collisions. If the vehicle rolls over, the belt also holds the driver in place, protecting against many different types of injuries;
— due to the action of the seat belt, the driver’s posture is constantly corrected,
as a result, efficiency increases by an average of 45%.
It is also worth noting that in most foreign-made cars equipped with airbags (Air Bag), this design solution cannot function without fastened seat belts. The significant intensification of the automotive industry around the world, due to the implementation of progressive ideas into design solutions in this industry, has already made it possible to eliminate the mechanism for the driver to fasten a seat belt, since this operation is carried out automatically when the door is closed.
This part of the lesson should be of a deep educational nature, encouraging the formation of competent professional and aesthetic inclinations. The lack of social advertising aimed at improving road safety, the development of a fundamental basis for the formation of a harmoniously developed personality capable of driving a car, encourages to compensate for this deficiency in educational organizations engaged in the provision of such services. This procedure has a problematic status, when it is first necessary to break incorrectly formed stereotypes, and only then instill and develop in future drivers the correct ideas, knowledge, abilities, and skills. A remarkable fact is the reflection in the production of the world film industry of scenes related to the car, where you can always watch episodes in which the driver or passengers getting into the car must fasten their seat belts.
The next stage of getting to know the driver's seat is to form an idea about rear-view mirrors and the rules for using them. Any car is equipped with two or three rear-view mirrors, allowing visual control of the road situation behind a moving car. The position of the mirrors allows the driver to view the entire area around the car. A mirror inside the cabin allows you to view the space behind the car in order to control the movement of traffic flow and perceive warning signals given by vehicle drivers when overtaking and detours. Side mirrors located on the car doors help the driver monitor invisible zones (sections of the road that are outside the driver’s line of sight when directly viewed and viewed through the interior rearview mirror). Such zones always pose a real threat to traffic safety, since they are located to the left and right of the rear side of the car, where vehicles can move, ignoring which can lead to collisions when changing lanes or overtaking. Installation and fastening of rear-view mirrors allow the driver to adjust their position depending on the adjustment of the driver's seat. Therefore, an important point in the preparatory actions before driving is to adjust the rear view mirrors. A mirror located inside the vehicle must allow the driver to fully see the rear viewing window. Exterior side mirrors adjust to the visibility of adjacent lanes and the edge of their vehicle so that the driver not only sees moving vehicles within adjacent lanes, but also controls the distance between vehicles.
Thus, having determined the importance of rear-view mirrors in the process of driving a car, it is necessary to instill in future drivers the need to constantly use mirrors, thereby determining the formation of the correct skills.
Having created all the prerequisites for the driver’s normal work by creating comfortable and safe conditions in the workplace, it is advisable to move on to introducing the vehicle controls and practicing the basic techniques for using them.
Initially, it is necessary to identify the role of the steering wheel in the procedure of driving a car, as well as to form an idea of the correct position on the steering wheel and how to rotate it.
The steering wheel of any vehicle allows the driver to control the movement of the car by changing the trajectory of its movement. Based on the actions performed by the driver when driving a car, the following functional aspects of using the steering wheel can be distinguished:
1. The steering wheel is necessary to perform basic maneuvers such as turning, turning, changing lanes, overtaking and passing. These maneuvers are characterized by significant actions by the steering wheel when changing the trajectory of movement, followed by a stabilizing move of the steering wheel in the opposite direction.
2. No less important are the minimal actions of the steering wheel, which are corrective in nature when the car is moving in a straight line.
Taking into account these features in using the steering wheel, it is necessary to indicate the location of the hands on it. When the car is moving in a straight line, when the driver’s main job is to keep the car on a given trajectory, the hands should always be slightly above the middle of the steering wheel. This allows the driver:
— Provide quick and convenient access to auxiliary controls: the turn signal lever, the headlight switch, the windshield wiper and washer lever, which are located on the left and right sides of the steering column.
— Turn the steering wheel to a larger angle.
- Prevent tension in the hands.
— Balance the steering wheel under your own hand weight.
When performing significant actions with the steering wheel, the driver’s hands should not interfere with each other, which is why two main methods of controlling the steering wheel are used when turning or turning the car.
Capture method
. This method is characterized by grabbing the opposite part of the steering wheel with your hand and turning it towards the hand, while the other hand helps turn the steering wheel, located below the grasped hand. The advantage of this method is the speed of its implementation and low physical costs.
Interception method.
A characteristic feature of this method is the alternate rotation of the steering wheel with both hands. One hand rotates the wheel in its own direction, the other hand, sliding, moves in the opposite direction, after which, grabbing the steering wheel, it continues to rotate in the given direction. This method is distinguished by a smoother steering wheel control style and versatility, since the first method is difficult to use on trucks and buses with a large steering wheel. These prerequisites make the interception method a priority.
A sound signal is placed in the center of the steering wheel, which is used to prevent road accidents, as well as to warn the driver of an overtaken vehicle when driving outside a populated area. This location of the sound signal allows the driver to use it without taking his hands off the steering wheel.
In a number of modern, including foreign cars, the sound signal can be located on the steering column, also in close proximity to the steering wheel, where auxiliary controls are located: the turn indicator lever, the headlight switch (low/high beam), the windshield wiper and washer lever . It is worth immediately instilling in future drivers the correct use of these controls, which consists in the fact that access to these levers is only from the outside of the steering wheel. Particular attention should be paid to the procedure for turning on the direction indicators. Firstly, this lever is always on the left side and is located closer to the steering wheel, has arrow symbols pointing left and right, so this lever is difficult to confuse with others. Secondly, the lever has three positions: middle - the indicators are off, lower - left turn indicator, upper - right turn indicator. Considering the fact that many driver candidates at first confuse the positions of the corresponding turns, it is worth paying attention to the fact that the positions of the direction indicators correspond to the movement of the left hand when rotating the steering wheel. Turning on the turn indicators should be done with the fingers of your left hand, without lifting your hand from the steering wheel. The action of these warning signals is accompanied by the inclusion of control light signals
located in a single block of control devices. The turn signal lights turn off automatically when the steering wheel is turned back. Although you should pay attention to the fact that automatic shutdown is possible when the steering wheel is rotated at least 90 degrees. This action is observed when making turns and turns. In other cases, the driver must turn off these indicators himself.
Light direction indicators also have another functional purpose, when the simultaneous activation of the left and right direction indicators symbolizes an “emergency stop”. This hazard warning light
activated by a button with an equilateral triangle symbol (warning triangle). The location of this switch is individual for each car brand.
The next stage of familiarization with the controls will be the presentation of the pedal assembly, which includes pedals: the clutch, the service brake system and the carburetor throttle pedal. Knowing how to use all pedals correctly is a key skill in driving. First of all, the role of the clutch pedal
(far left) in driving, which is used in interaction with
the gear lever
located to the right of the driver. This pedal is used more often than others, and therefore requires clear, correct and coordinated actions. When you press the clutch pedal, the engine and gearbox are briefly disconnected, that is, the supply of torque to the drive wheels is stopped. This action is necessary to engage, shift and disengage gears and is only possible with the pedal fully depressed (clutch disengaged).
Releasing the pedal (engaging the clutch) should be done smoothly but quickly to prevent sudden starting and jerking of the car.
The lever by which the gears are engaged, switched or disengaged has several positions: “N” – neutral, the vehicle is at rest; 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 – gear corresponding to a certain speed of the car; “R” – reverse vehicle. Each forward gear has a specific speed range. The first gear is characterized by the lowest driving speed (0 - 20 km/h) with the greatest traction force, therefore this gear is used for starting from a standstill, making turns when resuming movement, U-turns, overcoming obstacles, as well as off-road driving. The second gear allows you to move at a speed of 20 - 40 km/h, which corresponds to driving conditions in courtyards, residential areas and other adjacent areas, on dirt roads, on long climbs, in dense traffic flows, and also makes it possible to make turns without preliminary stopping movement.
On roads with low traffic intensity, third gear is used when there is a need to increase the speed limit to 60 km/h, while driving on gentle climbs and on well-rolled dirt roads with a dry surface is possible. When road conditions that meet safety requirements allow driving at speeds above 60 km/h, fourth gear is used. It should also be noted that with the right gear selected, adequate for certain driving conditions, there are also economic and environmental aspects, according to which lower gears are less economical, which means that due to the combustion of more fuel, more pollutants are emitted into the atmosphere . Taking these considerations into account, many cars are equipped with five-speed transmissions with five forward gears, which can improve engine efficiency and service life when using the highest fifth gear at speeds above 80 km/h.
Having examined the characteristics of each gear and applied it to the procedure for accelerating a car, which is characterized by the sequential use of gears in increasing order, the fact of the convenience of switching gears becomes clear. It lies in the fact that the lever always moves in the opposite direction, in the forward direction or with a slight deviation, which allows future drivers to quickly remember the gear shift pattern. Also noteworthy is the fact that the reverse gear is isolated from the forward gears, which eliminates the possibility of its accidental use.
After a comprehensive examination of the clutch pedal and gear lever in the context of the speed characteristics of the car, you should become familiar with another pedal (far right) - the carburetor throttle pedal
. In everyday life it is often called “gas” or accelerator. The action of the device (carburetor), which we control through this pedal, is reduced to batch preparation of a combustible mixture (fuel + oxygen) and supplying it to the combustion chamber. Thus, when we press the accelerator pedal, we enrich the combustible mixture with fuel, as a result of the combustion of which the amount of energy increases, the engine develops greater power, which is transformed into a high speed of the vehicle. By releasing this pedal, the speed decreases in proportion to the previously increased speed. Obviously, with the accelerator pedal we primarily vary the speed. It is necessary to pay attention to the fact that future drivers must skillfully handle this pedal, namely, smoothly act on it and constantly move the car without unnecessary acceleration and deceleration. This can be achieved by developing the correct placement of your foot on the gas pedal. Firstly, the foot must rest on the heel, which is located on the line that conventionally separates the brake pedal (middle pedal) and the gas pedal. This is done so that the toe of the right foot, if necessary, quickly moves to the brake pedal, since the right foot controls these two pedals, which is logical, because in the process of controlling the speed of the car, there is no need to simultaneously press both of these pedals. Secondly, resting on the heel, the toe of the foot is tilted to the right and at the same time should rest on the wall of the body tunnel. Thanks to this, the leg will not get tired, since there is double support (heel and toe), and it is also convenient to hold the pedal in a certain position pressed due to the friction that occurs between the toe of the foot and the wall of the tunnel. The degree of response of the car to the accelerator pedal is reflected immediately on two instruments located on the instrument panel.
The first one is the speedometer
(from the word speed - speed), shows the speed limit of the vehicle. This value has two units of measurement: kilometers per hour (km/h) and miles per hour (miles/h). The first unit of measurement is the most common in the European Community among automakers, the second is a characteristic feature of American cars, which have a large presence in the global automotive market. Based on the foregoing, drivers should pay attention to the characteristic differences in the units of measurement reflected on this measuring device, and be guided by them in accordance with the rules established in a particular state. In addition, the speedometer readings can act as a guideline, guided by which the driver can change gears according to their characteristics described above.
The second is the tachometer
, displays the engine speed, characterized by the unit of measurement - revolutions per minute (rpm). The readings of this device are more technical than operational in nature, and are taken into account when adjusting and tuning engine instruments and mechanisms, and also indirectly reflect the degree of wear of engine elements.
In the context of the statement “the faster you go, the longer it takes to brake,” it is important to examine another element of the pedal assembly - the service brake pedal
(brake). As already noted, the impact on this organ is carried out with the right foot, and it is necessary to avoid sudden pressure to prevent wheel locking and subsequent skidding braking when the wheels move from a rolling state to a sliding state. In this case, the traction force on the wheels exceeds the coefficient of adhesion to the road, which results in a loss of traction on the locked wheels and, as a consequence, a skidding of the given axle, which results in the car turning around with possible subsequent collisions or overturning of the car. Therefore, from the very initial stage of getting to know the car, you should learn how to competently influence this control of the car, namely by smoothly repeatedly pressing this pedal. Due to the fact that when you press this pedal, the brake lights on the rear side of the car automatically light up, this method of braking allows other drivers driving behind to perceive such information, analyze it and make an appropriate decision.
In addition to the service brake system, the vehicle is equipped with a parking brake system, the effect of which is to keep the vehicle stationary when stopping and parking, especially on inclined areas. Parking brake lever
located to the right of the driver, next to the gear shift lever. To activate the parking brake, you must pull the lever up until the rear wheels are completely locked, which corresponds to 3–5 clicks of the ratcheting mechanism of this lever. At the same time, the parking brake warning light on the instrument panel lights up. At the moment the movement begins, the lever is lowered down by first pressing the locking button located at the end of the lever. It is important for future drivers to develop the habit of checking the condition of the parking brake lever before driving.
Thus, having become familiar with the vehicle controls, you can sequentially proceed to the engine starting procedure, which is carried out by turning the key in the ignition switch
clockwise. You should pay attention to the location of the ignition switch relative to the steering wheel, on the left or right, since turning the key must be done with the appropriate hand.
Each time the driver starts the engine, the driver should check the condition of the gear shift lever and make sure that it is in neutral. It is advisable to start the engine with the clutch pedal depressed in order to facilitate engine starting by disconnecting it from the gearbox.
Next, it is necessary to consider the operation of instrumentation. First of all, you should study the coolant temperature gauge
, which has the characteristic symbol of a thermometer lowered into liquid. At the initial moment of engine operation, the instrument needle is at the same zero mark. As the engine runs for longer, it warms up and the gauge changes its readings to increase the temperature. The second feature of this device, corresponding to 50 °C, allows you to start moving, causing the end of engine warm-up. When the engine is running, you must not allow it to overheat when the needle approaches the red sector. With proper maintenance and operation of the vehicle, this will not happen, since the cooling system devices automatically maintain the optimal engine temperature (90 - 95 ° C).
It is important to constantly monitor the amount of fuel in the tank during vehicle operation, guided by the fuel level indicator.
. This device has fairly clear symbols and scale gradation, expressed in the residual volume of fuel relative to a full tank. Near the zero mark there is a fuel reserve indicator lamp, the inclusion of which symbolizes the need to refuel the vehicle.
an ammeter , play a major role in ensuring the performance of a car engine.
or
voltmeter
provided by the design of the vehicle. The first of these control instruments shows the degree of charge of the battery, the second displays the voltage generated by the DC generator, which should correspond to 12 - 14 Volts. In addition to the above-mentioned devices, each car has a warning lamp with a picture of a battery, the inclusion of which symbolizes the discharge of this source of electrical energy, which is unacceptable when the engine is running.
a significant decrease in pressure when lit.
oil in the engine lubrication system, which really threatens the occurrence of failures and malfunctions in the engine.
A characteristic feature of the design solution of a particular car is emphasized by other indicator lamps that light up on the instrument panel when using a certain device or device: side lights, interior heater, heated windows, mirrors, seats, etc.
The instrument panel with its inherent elements is equipped with backlighting, making it possible to perceive information from this structural unit in the dark.
This stage, in the context of a unified designed pedagogical technology, which provides for the consistent implementation of goals adequate to the process of developing driving skills, is characterized by a high concentration of elements to be mastered. By intensifying the focus of activities on achieving results, it is necessary to identify the degree of students’ assimilation of the material provided for at this stage through a set of control questions.
Control questions
1. What is the role of the driver’s workplace settings and the impact on the likelihood of accidents?
2. Name the sequence of actions when adjusting the driver’s workplace.
3. List the main and auxiliary controls of the car. Explain their purpose.
4. Demonstrate the correct position of your hands on the steering wheel.
5. What is the correct way to influence the elements of the pedal assembly?
6. Explain the order of shifting gears in ascending and reverse order.
7. What are the main control and measuring instruments?
8. Under what readings of instrumentation and warning lamps is it unacceptable to operate the vehicle? Why?
Thus, the formation of an idea of the driver’s workplace with the inherent familiarization with the functionality of the vehicle controls determines the transition to the stage of developing basic skills in using the vehicle controls and mastering the rules of their interaction.
EXERCISES FOR INDEPENDENT SKILL CONTROL
1. Set up the driver’s workplace with an explanation of each operational action performed.
2. Demonstrate proper hand position on the steering wheel and steering wheel actions using interception and grasping techniques.
3. Use the auxiliary controls located on the steering column. Indicate the positions corresponding to each lever switch.
4. Perform actions with all pedals one by one depending on their functional purpose.
5. Change gears in ascending order.
6. Start the engine, check the readings of the instrumentation. Specify parameters that allow and prohibit vehicle movement. Turn off the engine.
7. Apply the parking brake system. Release the parking brake.
Special assessment of working conditions of car drivers
Snip 03/12/2001. labor safety in construction. part 1. general requirements So, in accordance with Art. The driver was deprived of his license: the employer's actions For drivers driving passenger cars, an irregular working day may be established. In this case, the shift schedule is drawn up taking into account the normal length of the working week. Attention The Labor Code stipulates that driving time cannot be more than 9 hours, and with a cumulative accounting of working time no more than 10 hours, when working a shift 2 times a week, but not more than 90 hours a week. Moreover, according to . 1 tbsp. B. And the workplace fell into the category of hazardous. Such differences in assessment caused controversy. According to the Code of the Russian Federation on Administrative Offenses, violation of labor and labor protection legislation entails:
- imposition of an administrative fine on officials in the amount of 1 to 5 thousand rubles; for persons carrying out entrepreneurial activities without forming a legal entity - from 1 to 5 thousand rubles or administrative suspension of activities for up to 90 days; for legal entities - from 30 to 50 thousand rubles or administrative suspension of activities for up to 90 days;
- violation of labor and labor protection legislation by an official previously subjected to administrative punishment for a similar administrative offense entails disqualification for a period of 1 to 3 years.
Also according to Art.
Special assessment of working conditions for car drivers
If the driver works on several cars, the distribution of working time for each car is studied. Next, the organization conducting the SOUT makes all the necessary measurements in the driver’s work area, based on the provided chronology of the work process, that is, measurements are taken where the employee is located during the working day. If one employee works on several vehicles, then measurements are taken in each vehicle. Factors of general and local vibration, noise from the engine and vehicle components, the chemical composition of the air in the vehicle cabin are measured, and gravity and tension parameters are also analyzed. All measured and studied parameters are recorded in primary measurement protocols.
Responsibilities of the certification commission
The Certification Commission has the following rights and responsibilities:
- create the entire list of jobs subject to special assessment;
- take into account employee complaints regarding working conditions;
- prepare proposals to eliminate identified deficiencies;
- study the results of a special assessment in the Republic of Moldova;
- Subtleties of performing a special assessment
When conducting a special assessment, pay attention to factors typical for the driver’s performance:
- noise;
- the content of chemicals in the air inside the cabin;
- general or local vibration.
The noise inside the vehicle cabin is determined by the engine power and the soundproofing of the cabin. The maximum permitted standards within the framework of the special assessment are 80 dB. Excessive noise causes headaches, fatigue and, as a result, decreased attention,
Vibration affects decreased attention, poor coordination and contributes to headaches.
The most unfavorable, from the point of view of working conditions, are the workplaces of tractor drivers and excavator operators, which is due to the nature of the work and the structure of the vehicle body.
Special assessment of working conditions for truck drivers
When conducting research (tests) and measurements of stress factors in the labor process in terms of calculating the density of signals and messages per unit of time, the following minimum values for the number of signals and messages specified in paragraph 6 of these Features and obtained as a result of observation by the driver in the side and interior rear mirrors are accepted type of vehicle: • a) when starting to move – 6;• b) when stopping to pick up (disembark) passengers – 12;• c) when arriving at a stopping point – 6;• d) when slowing down – 6;• e) when maneuvering (changing lanes, turning, turning, reversing) - 12. 8.