What conditions are considered essential?
The employer is obliged to offer the employee all vacancies available in the given area that meet the specified requirements. The offer of relevant vacancies can be either simultaneous with warning the employee about changes in the terms of the employment contract determined by the parties, or within the next two months.
If an employee refuses to continue working part-time (shift) and (or) part-time work week, then the employment contract is terminated in accordance with paragraph 2 of part one of Article 81 of this Code. In this case, the employee is provided with appropriate guarantees and compensation.
Changes to the terms of the employment contract determined by the parties, introduced in accordance with Art. 74 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, should not worsen the employee’s position in comparison with the established collective agreement and agreements.
If the employee, for one reason or another, does not agree to continue working in the new conditions, the employer is obliged to immediately offer him (also in writing and against signature) another job available in the area (vacant position) that corresponds to the employee’s health condition, which he can perform taking into account his existing qualifications.
The employer is obliged to notify the employee in writing of the upcoming changes to the conditions of the employment contract determined by the parties, as well as the reasons that necessitated the need for such changes, no later than two months in advance, unless otherwise provided by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
It should be noted that with the adoption of the Labor Code, the legislator made an attempt to fill the legislative gap that previously existed in the Labor Code - in part one of Article 72 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, transfer to another permanent job in the same organization is defined as a change in the labor function (position, specialty, profession) or a change in significant terms of the employment contract.
Subsequently, the employee provided a completed certificate of incapacity for work, which proved a valid reason for failure to appear.
However, the court indicated that making a decision to change the structure, staffing table, and number of employees of an organization falls within the exclusive competence of the employer.
An agreement to change the labor function (transfer) of an employee is drawn up in writing as an amendment to the employment contract; Based on this, the employer must issue the appropriate order (instruction) and familiarize the employee with it against signature. Before we begin to actually answer this question, it is necessary to pay attention to the following circumstances.
Based on Art. 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the surname, name and patronymic of the employee and information about identity documents refer to information about the employee and are not terms of the employment contract. According to Art. 72 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, a separate agreement of the parties is drawn up when the terms of the contract change.
Actions of the employer in specific situations
The boss has more limited rights than the employee. He not only must find work for his employees, load people with responsibilities. Nobody wants to lose good specialists, but there are situations when they do not fit the criteria of a new enterprise. Therefore, the manager must offer an alternative by sending a written notice, for which he needs to receive a refusal or consent.
The employee agrees with the proposed conditions
The employee agrees when he is satisfied with all working conditions. With innovation, new responsibilities arise. If all parties come to a single agreement, all that remains is to change the requirements of the contract. But changes are introduced in the form of additions. The document must indicate which points are changing. This will be an additional agreement or another edition.
The salary under the contract cannot be less than the amount established by the collective agreement, without changing the working conditions. Every person has the right to work in a position that corresponds to the education received.
Attention! If your salary decreases as a result of a change in organizational form or technological equipment, you must contact the trade union.
The employee's consent was not obtained
Company management must notify the employee within two months. If the employee receives an approving response, the boss is obliged to announce the new working conditions:
- Working hours, that is, from what time an employee should come to work and what time to leave it. For workers with a five-day week, this is not so important, since their schedule does not change. This innovation is more typical for replaceable mesh.
- Conditions for new employment. Professional responsibilities must correspond to the level of qualification. In other words, the manager cannot offer the accountant the functions of a cleaner and vice versa.
If the employee nevertheless refuses management’s proposals, then, in accordance with paragraph 2 of Article 81, the parties terminate the contract by mutual agreement.
Dismissal of a dissenter in case of illness
When changing the staffing table or restructuring, the director is obliged to notify the employee first. If he does not agree, offers for other positions follow. The boss does not have the right to change clauses in the contract unilaterally. All actions must be agreed upon with the employee. All notices and explanations are made in writing.
If the employment contract stipulates a change of residence in another locality, this must be stipulated. In this situation, the parties must sign a new agreement with new responsibilities and requirements for the employee. In case of refusal after two months, the employment contract is terminated. Upon termination, all rights of the dismissed person are respected: for example, severance pay and compensation are paid. They are not produced in the same order as wages. That is, the company should not wait until the last minute, but pay the entire amount within three days.
Attention! The Code prohibits firing people who are on maternity leave or sick leave. Therefore, the employer must offer available vacancies at the enterprise or in branches, taking into account the well-being and health status of the person.
In case of refusal, the manager must, without resorting to pressure, achieve termination of the employment contract by agreement of both parties or personal desire. If it is not possible to reach an amicable agreement, then the employer will have to wait until the end of the sick leave and only then act in accordance with the code.
Introduction of a new operating mode
As practice shows, due to changes in the company’s business processes, management may change the work schedule.
Employees must comply with the terms of the contract and work the hours assigned to them by the director. Sometimes, to maintain a business, it is necessary to introduce part-time work. By law, this is the time during which a subordinate must perform his duties. This period includes 60 minutes for eating. There are also technical breaks of a quarter of an hour for rest.
A lawyer is ready to answer your question!
When making contributions to funds. The enterprise must keep personalized records, calculate and deduct contributions.
The court found that there were no grounds for introducing a part-time working week in the organization (the defendant), since there were no reasons specified in Part 1 of Art. 74 TK.
But is this so, and if not, then how significantly can the new regulation affect the existing practice of resolving issues related to changes in the employment contract?
The employer did not pursue the goal of preserving jobs, since he had previously issued an order on a massive reduction in staff.
This part of the provisions of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation undoubtedly deserves close attention, since the competent application of the rules provided for by them on changing the employment contract can play an important role both in improving the production activities of any organization and in the rational use of its personnel potential.
The legislator does not regulate in detail what specific changes in working conditions will reasonably entail a change in the terms of the employment contract.
Cancellation of a part-time working day (shift) and (or) part-time working week earlier than the period for which they were established is carried out by the employer, taking into account the opinion of the elected body of the primary trade union organization.
Thus, if the terms of the employment contract determined by the parties are changed, the employer must provide evidence that the terms of the employment contract cannot be maintained for the reasons specified in part 1 of the commented article.
The change in place of work was caused by a decrease in the volume of product sales at the previous place of work (Maikop oil depot), and therefore the employer decided to transfer employees to another place of work (Pavlovsk oil depot), where there was an increase in product sales volumes.
If for some reason the company does not have a provision on periods for performing work duties, the employee has the right to determine the time intervals himself. This must be done taking into account the performance of work during working hours in the interests of the employer. During the labor process, labor time records must be kept. This need lies with the employer.
In the event that, for reasons related to changes in organizational or technological working conditions (changes in equipment and production technology, structural reorganization of production, other reasons), the terms of the employment contract determined by the parties cannot be preserved, they may be changed at the initiative of the employer, with the exception of changes in the employee’s labor function.
Order to change working conditions
A unified form of order to amend the provisions of the employment contract has not been approved. But there are forms N T-5 and N T-5a, when such changes are associated with the transfer of an employee to another job.
The order needs:
- justify the introduction of innovations into work;
- indicate the list of employees affected by the changes;
- give instructions on necessary actions in connection with the changes.
After issuing an order to change working conditions (a sample is attached to the article):
- if the changes are not caused by innovations in organizational or technological working conditions and there is the consent of the employee, the changes are formalized by an additional agreement to the order.;
- If the previous conditions could not be maintained due to changes in organizational processes or technological changes, written notice must be prepared.
The employee must be notified of the contents of the order on changes in organizational working conditions (sample) no later than two months in advance, with the exception of other deadlines specified in the Labor Code.
sample order for changes to the terms of an employment contract
What to do if your health deteriorates during work
The employer, having considered the application, can either agree to amend the employment contract or refuse the employee. The employer can express his opinion in writing (in a resolution on the employee’s application or in a separate letter). If he refuses the employee, the terms of the employment contract remain the same.
This is important to know: Order of the Ministry of Labor 302 of 04/29/19
If the employer does not have the specified work or the employee refuses the work offered to him, the employment contract is terminated in accordance with clause 7 of Part 1 of Art. 77 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. In this case, the employee is subject to dismissal.
If an employer abolishes a subordinate's position, renames it, or revises the functions inherent in it, then no transfer as such occurs.
Labor Code of the Russian Federation: changes to the employment contract
The employer is obliged to offer vacancies in other localities if this is provided for by the collective agreement, agreements, or employment contract. If there is no specified work or the employee refuses the offered work, the employment contract is terminated in accordance with paragraph 7 of part one of Article 77 of this Code.
In this case, the employer is obliged to offer the employee all vacancies available in the given area that meet the specified requirements. The employer is obliged to offer vacancies in other localities if this is provided for by the collective agreement, agreements, or employment contract.
The employment contract does not specify the place where job duties will be performed, and therefore it is impossible to assert that the employee is absent from the workplace. Failure to issue compensation for unused vacation, which is a gross violation of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. [link]You will find a sample notice of dismissal for absenteeism in our article. How to register absenteeism for a civil servant?
It is worth remembering that if, as a result of changes in working conditions, a significant part of the employee’s functions is redistributed to other positions, the scope of job responsibilities is reduced, the number of working hours is reduced, etc., and the changes are significant, then in essence there is a reduction in position (see p. .3 part 1 of section II of this review).
Wage
If the parties to the Russian Tripartite Commission for the Regulation of Social and Labor Relations have not reached an agreement, these recommendations are approved by the Government of the Russian Federation, and the opinion of the parties to the Russian Tripartite Commission for the Regulation of Social and Labor Relations is communicated to the constituent entities of the Russian Federation by the Government of the Russian Federation.
Local regulations establishing remuneration systems are adopted by the employer, taking into account the opinion of the representative body of employees. The terms of remuneration determined by the employment contract cannot be worsened in comparison with those established by labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, collective agreements, agreements, and local regulations. The terms of remuneration determined by the collective agreement, agreements, local regulations cannot be worsened in comparison with those established by labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms. Information about changes: Federal Law of July 3, 2020 We recommend reading: Where you can refuse an inheritance
How can changes be made to the contract?
Just as an employer is not obligated to comply with an employee's request for a transfer, an employee is not obligated to agree to a transfer offered by the employer.
The general provisions of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provide for changes in the terms of an employment contract only by agreement of the parties (Article 72 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). However, there are exceptions that provide for the notification procedure for the employee about changes in the terms of the employment contract.
The procedure for changing previously determined terms of an employment contract on the basis provided for in Article 74 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation deserves special consideration. As follows from this article, the need to change the terms of the employment contract may be due to changes in organizational or technological working conditions.
Changes in organizational working conditions
There may be other reasons for changing the terms of the employment contract, but, apparently, they should be, firstly, similar to those mentioned and, secondly, equally significant. It should be borne in mind that a decrease in sales and a deterioration in the financial position of an organization are not considered by the courts as reasons allowing the employer, in accordance with Art. 74 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation to change the terms of the employment contract. The courts indicate that such circumstances do not indicate changes in organizational and technological working conditions (see the Determination of the Moscow Regional Court dated September 14, 2010 in case No. 33-17729, Review of the cassation practice of the Supreme Court of the Komi Republic in civil cases for May 2009).
It is important to note that specific organizational and technological changes must be documented.
Date added: 2017-12-14; ; Does the published material violate copyright? | Personal data protection |
Didn't find what you were looking for? Use the search:
How far in advance should an employee be notified of a transfer to another position?
But the employer must be warned about this fact. The employee was absent from work for about 6 hours. He refused to give written explanations.
An analysis of judicial practice over the past year has shown that the most common changes in organizational working conditions are in the form of changes in the structure of the organization, management structure, redistribution of powers between employees, departments, structural units, changes in work and rest regimes.
How to correctly understand Article 74 of the Labor Code - “the duration of a transfer to another job to replace an absent employee cannot exceed 1 month during the calendar year (from January 1 to December 31).
Transfer of an employee deterioration of working conditions labor code article
Thus, new working conditions, entailing a change in the employment contract, can be introduced solely by the employer only if they do not worsen the employee’s position in comparison with the terms of the collective contract (agreement); otherwise, they can be introduced if the content of the collective agreement (agreement) is reviewed accordingly, and if necessary, the opinion of the representative body of workers is taken into account. At the same time, a change in the terms of an employment contract may be a consequence of objective factors, for example, a change in the situation in the commodity markets in which the employer operates entails the need to reform the technologies used or the organization of labor.
Additional terms of the agreement
They are not mandatory and are included by agreement between the employee and the employer, that is, it is unlawful to insist on their inclusion. From Art. 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation it follows that the main requirement for them is not to worsen the employee’s position in comparison with labor legislation, a collective agreement, and internal documents.
Examples of additional conditions:
- establishing a probationary period after transfer to a new workplace;
- requirement of non-disclosure of secrets protected by law;
- the obligation to work in the organization for a certain period of time after completing the training required for the new position, if it was paid for by the employer.
The document may duplicate the rights and obligations of the employee and the employer prescribed in the collective agreement. Their absence in the text is not considered a refusal to exercise rights and fulfill obligations.
Article
Article 73 of the Labor Code provides for the first time that in the event that these circumstances may lead to the mass dismissal of workers, the employer, in order to preserve jobs, has the right, taking into account the opinion of the elected trade union body of the organization, to introduce a part-time working regime for a period of up to six months. A similar situation may arise, for example, when an arbitration court applies to an employer-organization in accordance with the Federal Law “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)” of January 8, 1998.
Changing the terms of an employment contract without the employee’s consent
SAPP RF. 1993. N 7. Art. 564). In accordance with it, the main criteria for mass layoffs are the indicators of the number of workers dismissed due to the liquidation of organizations or a reduction in the number or staff of workers for a certain calendar period. These include:
- a) liquidation of an organization of any legal form with 15 or more employees;
- b) reduction in the number or staff of the organization’s employees in the amount of: 50 or more people within 30 calendar days;
- 200 or more people within 60 calendar days;
- 500 or more people within 90 calendar days;
Changing working conditions without the consent of the employee In the current unfavorable economic situation, many unscrupulous employers are unilaterally trying to change the working conditions of their employees, and, as a rule, these changes are not for the better and often make people think about leaving the company. So, recently, very often, employees complain that they are forced to work for lower wages, perform the functions of other specialists (laid off or quit at their own request), and are transferred to other jobs. Are such actions of the employer legal and how to resist them? As we know, when hiring, an employment contract is concluded between an employee and an employer, that is, an agreement that must contain all the essential conditions of the work process, as well as the rights and obligations of the parties.
According to the said resolution, these are: 1) liquidation of an organization with 15 or more employees; 2) reduction in the number or staff of the organization’s employees in the amount of: 50 or more people within 30 calendar days; 200 or more people within 60 calendar days; 500 or more people within 90 calendar days; 3) dismissal of 1% of the total number of employees due to the liquidation of organizations or reduction of numbers or staff within 30 calendar days in regions with a total number of employees of less than 5 thousand people. The above criteria should be followed if other criteria in accordance with Art.
Transfer of an employee deterioration of working conditions labor code article
This is permissible in cases of temporary suspension of work for reasons of an economic, technological, technical or organizational nature, or if it is necessary to prevent destruction or damage to property, or to replace a temporarily absent employee. But even in this case, transfer to a job requiring lower qualifications is allowed only with the written consent of the employee. In cases where, due to changes in technology or reorganization of production that have occurred in the organization, the terms of the employment contract determined by the parties still cannot be preserved, they are allowed to change at the initiative of the employer. The employer is obliged to notify the employee in writing of the upcoming changes, as well as the reasons that necessitated the need for such changes, no later than two months in advance.
The essential terms of an employment contract should be understood as the employee’s working conditions specified in this contract. A change in organizational or technological working conditions means, for example, a change in the structure of the employer's organization, the introduction of new technologies, etc. When organizational or technological working conditions change, it is possible to change the essential terms of the employment contract, but without changing the labor function. The employee must be notified by the employer in writing of the introduction of these changes no later than two months before their introduction, unless otherwise provided by this Code or other federal law (a similar rule was contained in Article 25 of the Labor Code). Consequently, the employer has the right to notify the employee of upcoming changes more than two months in advance. 4. If changes in organizational or technological working conditions may lead to mass layoffs of workers, the employer, in order to preserve jobs, has the right, taking into account the opinion of the elected body of the primary trade union organization, to introduce a part-time working day (shift), but only for a period not exceeding 6 months. The opinion of the elected body of the primary trade union organization is taken into account in the manner established by Art. 372
This is important to know: Order on expanding job responsibilities
Labor Code for the adoption of local regulations (see commentary to it). In these cases, employees must be notified by the employer in writing of the introduction of a part-time working regime, as well as of changes in other conditions provided for by the employment contract, no later than 2 months before its introduction.
Pravoved.RU 196 lawyers are now on the site
The employer wants to transfer the team from 5 shifts to 4 shifts with a reduction in the amount of vacation from 42 to 28 days. At the same time, the volume of work increases, wages remain unchanged.
Collapse Victoria Dymova Support employee Pravoved.ru Similar questions have already been considered, try looking here:
- Can the quality of the canteen be considered as a deterioration in working conditions?
- Dismissal due to deterioration of working conditions and changes in functions
Of course, longer (than two months) notice periods for the employee may be provided for in the collective agreement. See also Art. 306 of this Code. § 3. Article 73 of the Labor Code states that if an employee does not agree to continue working under new conditions, then the employer is obliged to offer him in writing another job available in the organization that corresponds to his qualifications and state of health, and in the absence of such work - a vacant lower position or lower paid work that the employee can perform taking into account his qualifications and health status. In the absence of the specified work, as well as in the event of the employee’s refusal of the offered work, the employment contract is terminated in accordance with clause 7 of Art. 77 Labor Code (an employee’s refusal to continue working due to a change in the essential terms of the employment contract).
CHANGES IN ORGANIZATIONAL OR TECHNOLOGICAL WORKING CONDITIONS: SOME LEGAL ISSUES
Labor legislation provides for two mechanisms for changing the terms of an employment contract: by agreement of the parties by concluding an appropriate agreement in writing (Article 72 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) and unilaterally at the initiative of the employer (Article 74 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
On its own initiative, the employer has the right to change the terms of the employment contract only in accordance with Art. 74 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. For such a change, the following factors must be present simultaneously:
1) a change in the terms of the employment contract determined by the parties must be a consequence of changes in organizational or technological working conditions (changes in equipment or production technology, structural reorganization of production, other reasons);
2) the previous terms of the employment contract determined by the parties cannot be preserved;
3) new working conditions should not worsen the situation of workers in comparison with those established by the collective agreement and agreements;
4) the employee’s labor function must be preserved.
The employer is obliged to notify the employee in writing no later than two months in advance about upcoming changes to the employment contract and the reasons that necessitate these changes. If the employee does not agree to work under the new conditions, then the employer is obliged to offer him in writing another job available to the employer (both a vacant position or work corresponding to the employee’s qualifications, and a vacant lower position or lower paid job), which the employee can perform taking into account his health status. In this case, the employer is obliged to offer the employee all vacancies available in the given area that meet the specified requirements. The employer is obliged to offer vacancies in other localities if this is provided for by the collective agreement, agreements, or employment contract. In the absence of the specified work or the employee refuses the proposed work, the employment contract is terminated in accordance with paragraph 7 of part one of Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
If the employees agree to the new terms of the employment contract, the employer signs an additional agreement to the employment contract with them.
The Labor Code does not disclose the concept of “change in organizational or technological working conditions” and does not contain an exhaustive list of such changes, indicating only that they, in particular, are changes in production techniques and technology, structural reorganization of production, and may also be others.
According to paragraph 21 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated March 17, 2004 N 2 (as amended on November 24, 2015) “On the application by the courts of the Russian Federation of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation,” changes in organizational or technological working conditions also include the improvement of workplaces based on their certification ( currently - based on a special assessment of working conditions).
Thus, this list is open. There may be other reasons for changing the terms of an employment contract, which should be a consequence of changes in the organizational or technological working conditions of employees.
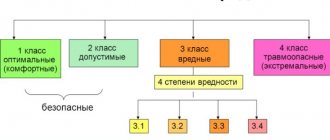
Working conditions at the workplace are in accordance with Art. 74 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is a mandatory condition of an employment contract. Article 209 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation defines working conditions as a set of factors in the working environment and the labor process that influence the performance and health of the employee. Federal Law dated December 28, 2013 N 426-FZ “On special assessment of working conditions” divides working conditions according to the degree of harmfulness and (or) danger into four classes - optimal, acceptable, harmful and dangerous working conditions (Article 14). Classes (subclasses) of working conditions at workplaces are established based on the results of a special assessment of working conditions (Article 3).
The employer is obliged to provide normal conditions for employees to fulfill production standards. Such conditions, in particular, include: good condition of premises, structures, machines, technological equipment and equipment; timely provision of technical and other documentation necessary for work; proper quality of materials, tools, other means and items necessary to perform the work, their timely provision to the employee; working conditions that meet labor protection and production safety requirements (Article 163 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Judicial practice refers to changes in organizational or technological working conditions, in particular:
— structural reorganization, including transfer of division functions to another division, organization of new divisions with redistribution of employee functionality (rulings of the Chelyabinsk Regional Court dated 03/05/2015 in case No. 11-2103/2015, Moscow City Court dated 03/25/2015 No. 4g/8 -571; appeal rulings of the Moscow City Court dated September 22, 2016 in case No. 33-34548/2016, Moscow Regional Court dated September 14, 2015 in case No. 33-20471/2015);
-improvement of production processes (appeal ruling of the St. Petersburg City Court dated December 4, 2014 in case No. 33-18721/2014);
-launch of new proceedings (appeal ruling of the Moscow Regional Court dated October 5, 2016 in case No. 33-27519/2016);
— introduction by the employer of new equipment (decision of the Moscow Regional Court dated September 21, 2010 in case No. 33-18182);
— introduction of new methods, development of new technologies, modernization and replacement of equipment, improvement of the management structure or organization of workplaces (appeal ruling of the Moscow Regional Court dated August 24, 2016 in case No. 33-22966/2016).
At the same time, the following is not recognized as a change in organizational or technological working conditions:
— renaming a structural unit and/or employee position (appeal ruling of the Moscow City Court dated October 6, 2015 in case No. 33-33814/2015, ruling of the Moscow City Court dated June 20, 2016 No. 4g-3680/2016;
-deterioration of the employer’s financial situation, decrease in sales or volume of services provided, crisis phenomena in the economy (rulings of the Moscow Regional Court dated September 14, 2010 in case No. 33-17729, Moscow City Court dated July 20, 2011 in case No. 33-20154) ;
- structural reorganization of a unit with the transfer of the functions of one of them to another as a basis for reducing the employee’s wages in the absence of evidence that, in connection with the reorganization, the employee had a reduced volume of work, a reduced service area, or a reduction in working hours (appeal determination of the Moscow City court dated July 16, 2012 No. 11-11952/2012);
— adoption by the employer of a new local regulatory act regulating wages (appeal ruling of the Tula Regional Court dated April 2, 2015 in case No. 33-969)[1].
When deciding on a change in accordance with Art. 74 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation of the terms of the employment contract, the employer must take into account that in the event of a dispute with the employee about the legality of dismissal or a change in the terms of the employment contract determined by the parties, it is the employer who will have to provide evidence confirming not only the fact of a change in organizational or technological working conditions and the existence of a cause-and-effect relationship between organizational or technological changes in working conditions and changes in the terms of the employment contract (clause 21 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated March 17, 2004 No. 2 “On the application by the courts of the Russian Federation of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation”), but also the impossibility of preserving the previously determined conditions of the employment contract . From the explanation set out in the Ruling of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation dated May 11, 2012. No. 694-O it follows that part 1 of Art. 74 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, providing for the possibility of unilateral changes in the terms of an employment contract by the employer, limits this right only to cases where it is impossible to maintain the previous conditions due to changes in organizational or technological working conditions. The need for the employer to provide evidence of the impossibility of maintaining the previous terms of the employment contract is also indicated in judicial practice in specific cases (for example, the appeal ruling of the Moscow City Court dated April 2, 2013 in case No. 11-10169, the Moscow City Court ruling dated April 14, 2011 in the case No. 33-9777, etc.).
11 It is necessary to cancel that in some judicial acts a change in the remuneration system is assessed as an independent change in organizational working conditions (for example, the ruling of the Moscow City Court dated August 26, 2010 in case No. 33-26687), which is very controversial, since such an interpretation of organizational working conditions creates unlimited opportunities for the employer to change the terms of remuneration unilaterally. According to the author, for the purposes of applying Art. 74 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, a change in the remuneration system must be a consequence of a change in working conditions (for example, a structural reorganization of departments with a redistribution of job responsibilities).
List of used regulations
1. Labor Code of the Russian Federation //SPS ConsultantPlus;
2. Federal Law of December 28, 2013 N 426-FZ “On Special Assessment of Working Conditions” // SPS ConsultantPlus;
3. Determination of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation dated May 11, 2012. No. 694-O // SPS ConsultantPlus;
4. Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated March 17, 2004 N 2 (as amended on November 24, 2015) “On the application by the courts of the Russian Federation of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation” // SPS ConsultantPlus.
Deterioration of working conditions
Unilateral deterioration of working conditions is illegal. If an employer wants to reduce an employee’s salary or transfer him to a lower-paid position, this can only be done with the employee’s consent. The employer does not have the right to transfer an employee to another position with a lower salary or worse working conditions without the employee’s consent. The employer may offer the employee other conditions in writing. If the employee agrees, then an additional agreement is concluded to the employment contract, which sets out new working conditions.
If you liked the material, share it!
All materials about labor conditions
For deterioration of working conditions, the employer may be held administratively liable, and if this caused serious harm to the employee’s health or an accident occurred, then criminal liability. Read the article about what deterioration of working conditions is from a legal point of view, as well as about the employer’s responsibility.
The Labor Code in Kazakhstan was pretty much shoveled in times of crisis
For the employer to make such a decision, it must be confirmed by an official decision of the examination committee in the manner prescribed by law. This norm applies only to those workers who, by their position, are responsible for observing and ensuring labor safety and health at enterprises or industrial safety,” Nurymbetov explained the first of five grounds for terminating an employment contract. The second new basis is the absence of an employee from work for more than one month for reasons unknown to the employer.
What constitutes a significant deterioration in working conditions?
Working conditions (hereinafter referred to as WT) are a set of factors in the working environment and the labor process that affect the performance and health of the employee.
A significant deterioration in working conditions is the changes that have occurred in the technological process and affect labor safety.
Such deterioration includes unsatisfactory organization of work. In this case, the impact on workers of harmful and (or) hazardous production factors increases significantly, or the levels of their negative impact are significantly exceeded.
Unsatisfactory organization of work
An example of unsatisfactory organization of work is sending two workers to work in a manhole at the same time and appointing a third worker as insured. If two workers are descending into a well, each descending worker must be insured on the ground by a separate personal belayer. In this case, we are talking about failure to comply with the requirements of the work plan, issuing a work permit with a significant violation of all labor protection requirements. This puts workers at risk of injury.
How does the Labor Code of the Russian Federation interpret the concept of “deterioration of working conditions”?
Deterioration of labor safety is the failure by the employer to comply with the minimum requirements of labor protection rules and technical regulations established in the legislation, orders of the Ministry of Labor and the Ministry of Education on the organization of safe work, or the deprivation of workers of the minimum social guarantees for working in hazardous working conditions.
The deterioration of operating conditions can also include the unsatisfactory condition of equipment, machines, tools, and violations in the technology of safe work performance.
A gas-electric welder is entitled to receive milk because he was exposed to harmful working conditions. To save money, the employer canceled milk distribution.
Milk must be dispensed subject to the following conditions:
- the workplace must contain harmful production factors specified in the List of hazardous production factors;
- the level of harmful factors must exceed established standards.
This is indicated in paragraph 2 of Appendix 1 to the order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated February 16, 2009 No. 45n.
Therefore, the employee could not cancel the delivery of milk. This is a significant deterioration in his working conditions, which cannot be applied.
According to Article 9 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer must not restrict the employee’s labor rights to provide additional leave of 7 days, payment of 4% of the salary, milk or work clothes.
The level of guarantees cannot be reduced compared to the legally established minimum.
Motivating its actions by a decrease in the number of clients and a worsening financial situation, the employer stopped issuing dermatological cleansers. At the same time, workers continued to carry out work that required the issuance of protective, cleaning or regenerating agents in full.
There is a significant deterioration in the workers' standard of living, which is illegal and subject to cancellation in accordance with Article 9 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
It is impossible to create workplaces that do not meet the safety requirements specified in Articles 212 and 215 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The head of the organization ordered the demolition of the sanitary premises and the installation of a plasma cutting machine instead. But modernization of production should not limit the employee’s right to rest during work.
Since work in a metalworking shop is accompanied by increased noise, vibration, interaction with moving mechanisms and other unfavorable production factors, workers have the right to rest in a noise-free area and have the right to eat in normal sanitary conditions, since there are no public catering establishments near the industrial zone , which workers could visit during their lunch break.
Consequently, the employer, having equipped the workplace in such a way that the employee cannot leave for meals, must equip a room at the enterprise for meals, equipped with a microwave oven for heating ready-made food, a kettle, a table and the required number of chairs, while the furniture must meet safety requirements .
However, in some conditions, workers are forced to work in unfavorable environments.
It is impossible to completely ensure the safety of miners in a mine. In addition to technical causes of accidents, there are also natural accidents.
You cannot install an air conditioner near an open-hearth furnace. Smelting metal requires high temperatures.
It is impossible to carry out geological exploration work from a cozy office, without traveling to the tundra or swampy areas. After all, the subsoil is there - peat, coal, gas, and oil.
It is impossible to create natural light for a metro cashier.
The microclimate in such production areas will always be unfavorable. In such industries, chemical products should be considered harmful or dangerous.
To reduce the adverse impact of HFPF on an employee, the employer must take protective measures.
Against industrial noise, you need to use not only headphones or earplugs, but also set regulated breaks in a “noise-free” area.
This is important to know: Adj. 1 and 2 p. 1 of order 302
Workers must be provided with PPE in accordance with the issuance standards for their industry and profession. The established standards cannot be reduced even by one percent.
You cannot reduce the number of regulated breaks or their duration, replace the dispensing of detergents with washing powder, shorten the period of additional leave for work in hazardous workplaces, etc.
In October 2020, at one of the confectionery factories, a worker fell into a vat of boiling caramel. An investigation is now underway. This accident was possible as a result of many factors, one of which was improper placement of production equipment. If safe passage widths had been ensured, the accident might not have occurred.
At the very least, the contributing cause, if not the underlying cause, will be determined during the investigation of this fatal accident. The investigation commission will be headed by the chief state inspector of the Rostrudinspektsiy.
The technical regulations “On the safety of machinery and equipment” establish that the employer must follow the instructions in the manufacturer’s technical documentation and recommendations for maintenance and repair.
The same requirement is contained in Article 215 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Therefore, failure to carry out scheduled maintenance work is a violation of the requirements of both labor legislation and safety requirements for the organization of work.
Employer's liability for deterioration of working conditions
For violation of labor protection requirements, the employer may be fined under Article 5.27.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
For violation of sanitary norms and rules, liability will arise under Article 6.3 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
In addition, the employer may be punished under other articles of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
If your organization operates vehicles for the transportation of goods or passengers in international road transport without a tachograph, then a fine will be established under Article 11.23 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation for the lack of a device for recording information about the speed and route of transport and about the work and rest hours of drivers.
The absence of a tachograph makes it impossible to track the driver’s compliance with the work and rest schedule established by law, so the employer is obliged to install them. If it doesn’t, it will worsen the employee’s working conditions.
The risk of an accident exists at any technical facility. The main threat associated with the operation of a hazardous production facility occurs in the event of an accident accompanied by such damaging factors as the destruction of metal structures, scattering of parts, fragments, etc.
Hazards of this kind can be eliminated by observing safety requirements when operating the equipment, as well as by equipping it with safety devices - safety and interlocking devices.
Persons responsible for the safe performance of work and the good condition of the equipment must ensure the serviceability of protective, safety and locking devices. Officials of enterprises, within the limits of their official duties, have the right to give orders to eliminate violations of labor protection rules and regulations, to prohibit the operation of equipment and the performance of work if it does not comply with regulatory safety requirements and there is a threat to the health and life of workers.
Thus, a fatal accident occurred in ZAO Anastasievskoye, Krasnodar Territory, with mason P. while carrying out work in a carpentry workshop.
By order of the foreman, a team of workers at the repair site, consisting of two carpenters U. and K., three masons M., P. and Ts., began to manufacture blanks for the containers of the plant growing workshop. The carpenters worked on a circular saw to cut the boards, and the masons carried and laid the cut pieces elsewhere.
While sawing another board, a piece broke off, which fell on the saw and flew towards the mason P., who was two meters from the circular saw. A piece of board hit mason P. in the stomach, causing him a fatal injury.
During the accident investigation, it was determined that the circular saw did not have a safety guard to prevent the cutting tool from throwing out workpieces and waste.
Article 212. The employer is obliged to provide:
• safety of workers during the operation of buildings, structures, equipment, and implementation of technological processes;
• working conditions at each workplace that meet labor safety requirements.
GOST 12.2.026.0-93. “Woodworking equipment. Safety requirements for design”, put into effect by Decree of the State Standard of Russia dated March 28, 1995 No. 168
3.1.1. The machine must have protective devices that prevent during operation:
- throwing away processed workpieces and waste with cutting tools.
At CJSC Anastasievskoe, unsatisfactory organization of work during the operation of woodworking equipment was noted, expressed in:
- insufficient control over the safe performance of work;
- lack of protective fences for production equipment.
The General Director did not ensure the safety of workers when operating industrial woodworking equipment. The chief engineer, who is responsible for the good condition of the equipment at the energy repair site, allowed the operation of a circular saw machine that was not equipped with a protective device that prevented the cutting tool from throwing out workpieces and waste during operation.
The foreman responsible for the safe performance of work violated labor protection requirements by allowing workers to carry out work on woodworking equipment without protective guards, and by not taking measures to eliminate violations of safety requirements during its operation.
Employee rights when working conditions deteriorate
According to Article 219 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, an employee has the right to work in conditions that meet labor protection requirements.
In accordance with Article 22 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer is obliged to ensure labor safety and conditions that comply with labor protection rules, provide workers with serviceable, certified equipment, tested and verified tools.
An employee has the right to refuse to perform work in conditions that threaten life and health. He is obliged to notify his management about this.
During the period while violations in the operation of equipment are being corrected, in which work is impossible for reasons of labor safety, the employee must retain his position, length of service and be paid two-thirds of the salary in accordance with Article 220 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The duration of downtime and an indication that during this period the employee may not be at the workplace must be indicated in the order.
If, for objective reasons, during the hot season, the employer cannot provide air cooling for workers due to production needs, then it is necessary to record an increase in temperature above that allowed in sanitary rules, issue an order that the employee is not allowed to be at work during the downtime, but in this case, wages will be paid in the amount of 2/3.
Dismissal due to deterioration of job requirements
If an employee does not agree to work under new conditions, then the organization is obliged to offer him another job in the same locality. If the employee refuses to work, or there is no vacancy in the organization, then the employer will have no choice but to terminate the employment contract.
What working conditions are considered essential?
In accordance with Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, an agreement with an employee must contain a number of mandatory information:
- labor function according to the position in the staffing table;
- place of work, including the address of a separate unit;
- work start date;
- payment system;
- working hours and rest breaks;
- type of work (for example, the need for business travel);
- specific conditions in the workplace.
Transformations in the company
To make changes to the contract, the employee's consent is required. However, the employer, on his own initiative, has the right to revise previously agreed provisions if new methods of organizing work do not allow them to be maintained in their previous form.
Important! One of the essential conditions that cannot be changed without the consent of the employee is the labor function.
Organizational working conditions
These are forms and methods of organizing activities and management in a company. Russian legislation does not establish a list of changes to conditions, but Art. 74 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation makes an attempt to explain what they can be. Structural reorganization is given as an example.
In 2004, there was a need to clarify these provisions of the Code, and the Supreme Court of Russia recommended that changes in the organizational environment include the following:
- updating the company structure;
- optimization of work and rest schedules;
- rationing labor in a new way;
- change in workload for a particular position.
This list is not exhaustive and may be expanded.
Technical working conditions
They are characterized by:
- composition of the equipment used;
- technological equipment;
- level of automation and modernization;
- the size of the production area.
Technical changes include, but are not limited to:
- improvement of technological processes;
- introduction of additional types of services;
- workshop refurbishment;
- updating work regulations.
Important! Organizational and technical conditions are closely related and often interdependent.
New conditions require new competencies