Disagreements between an employer and his subordinate are not uncommon and are often resolved peacefully in the course of business. But, if a compromise cannot be reached, both parties can turn to the territorial court to resolve the problem.
Most often, disputes arise on financial grounds: withholding fines, non-payment of wages, sick leave, vacation pay, bonuses. But in many cases, outright violations of contractual relations and illegal dismissal are recorded.
This type of disagreement, where the parties are the employer and the employee, is called an individual labor dispute.
What is a statute of limitations?
From the point of view of civil law, this term defines a certain period during which it is possible to file a claim in court to protect and restore violated rights. In paragraph 1 of Art. 196 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the general limitation period is 3 years from the moment of actual detection of a violation of a citizen’s rights.
Meanwhile, in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation there is no concept of a “limitation period”, but there is a “term for filing a lawsuit”. Both concepts have the same essence, but when it comes to labor relations, it is more correct to talk about the time limit for going to court to resolve an individual labor dispute.
Defendant enterprise
The employee applies to the authorized bodies to resolve the conflict with the employer regarding dismissal, cash payments and other ITS.
Dismissal
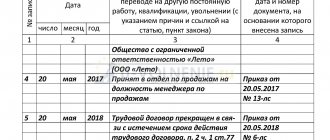
The employee has one month after the termination of the employment relationship to challenge the decision to dismiss. Attempts to negotiate with the employer peacefully can only lead to missed deadlines.
The applicant can protect his rights through the court or by contacting the labor inspectorate. Sometimes the labor commission will be able to help resolve the conflict. Practice shows that even after the inspection’s decision, the case ends up in court. The difficulty is in proving the groundlessness of the reason for interrupting the employment relationship: the presence or absence of absenteeism, disciplinary inconsistency, disclosure of official secrets. Often these facts are proven only through court.
The logical option would be to go to court directly, without making a decision by the labor inspectorate, especially since this is not prohibited by law.
Issues related to reinstatement at work, changing the wording of the reasons for dismissal, transfer to another job, refusal to hire, payment for forced absences are dealt with exclusively by the judicial authorities.
If wrongful dismissal or transfer to another job is proven by the court, it decides to reinstate the plaintiff immediately, even before the decision comes into force. The main thing is not to miss the statute of limitations for filing an application.
Cash compensation
The most common are conflicts over late payment of wages and non-payment of other compensation.
The statute of limitations for labor disputes regarding the recovery of wages is one year. It is calculated starting from the day of delay in payment of wages and other obligations. Until 2020, the period was defined as three months. The extension of validity is good progress in the area of regulating disputed relations, since very often workers missed deadlines for going to court and, as a result, found themselves without payments.
Others
For ITS that are not related to dismissal and monetary payments, the limitation period is set at three months. These include: various types of disciplinary punishments, reprimands, illegal infringements of the rights of an employee.
The period begins from the day when the employee learned of the violation of his rights. This fact can be confirmed not only documented, but also in the presence of factual circumstances. The plaintiff does not pay the state fee and does not bear court costs.
What are the deadlines for applying to a labor court?
According to Art. 391 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, claims filed by:
- workers with violated labor rights;
- employees reporting illegal actions of employers;
- employers who suffered damage due to the fault of a subordinate;
- citizens who have received an unlawful refusal to hire;
- citizens working for individuals who are not individual entrepreneurs;
- persons who have been discriminated against.
The statute of limitations for employees is different from the statute of limitations for employers. All of them are spelled out in Art. 392 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which establishes the right to go to court for both parties, as well as the grounds for appeal.
IMPORTANT! In relation to individual labor disputes, the general provisions of civil law do not apply. In this matter, you need to be guided exclusively by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Time limits for filing a lawsuit for an employee
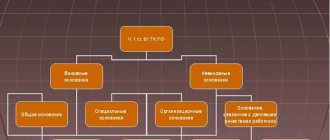
Under Part 1 of Article 92 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, employees are provided with the following deadlines and grounds for going to court:
- 3 months from the date of establishment of the fact of violation of the employee’s rights or from the day when the employee should have learned about this violation;
- 1 month from the date of receipt of the work record book or dismissal order for cases of disputes regarding dismissal;
- 1 year from the date on which full cash payment is due for disputes based on non-payment or incomplete payment of wages.
Due to such short deadlines (except for the third point), as well as legal illiteracy, most workers who have labor disputes go to court late. The court is obliged to accept the statement of claim and begin proceedings in the case even after the deadline has expired. But, if on this occasion the responding party petitions for dismissal of the claim, then, unless the plaintiff has a valid reason for missing the deadline for filing the claim, the court will refuse to consider the case.
Time limits for going to court for an employer
Employers, in turn, have a longer period of time to go to court. In Part 2 of Art. 392 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, this period is stated as 1 year, during which the recovery of damage caused by the employee can be demanded in court. The countdown begins from the moment the damage is discovered. The application can be submitted both for employees currently on staff and for those already dismissed. In case of missing the agreed deadlines for going to court, employers must also provide a valid reason.
Calculation of limitation periods for labor disputes
The general limitation period by civil law is established at three years (Article 196 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). For certain types of claims, the law may establish special limitation periods, shorter or longer than the general period (clause 1 of Article 197 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
In labor legislation in Art. 392 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes special deadlines for going to court to protect one’s labor rights (the statute of limitations).
In accordance with paragraph 2 of Art. 199 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the limitation period is applied by the court only upon the application of a party to the dispute made before the court makes a decision. This provision applies to labor relations by analogy (question 51 of the Review of judicial practice of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated December 3, 2003, December 24, 2003 “Review of legislation and judicial practice of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation for the third quarter of 2003”).