An external manager is appointed to his position simultaneously with the introduction of external (temporary) management. When a bankruptcy petition begins to be considered, the arbitration court contacts the self-regulatory organization and requests a list of members who have expressed a desire to become. A candidate for external observation must satisfy all the requirements specified in the request of the arbitration court.
The external manager is vested with the right to fully control the enterprise and temporary powers of the head of the organization for the period of supervision.
The candidate is selected from the members of a self-regulatory body that was created by creditors. According to the Bankruptcy Law, an external manager for the position of temporary manager is submitted to the arbitration court for approval, approved by the applicant and the debtor.
An individual with the status of an individual entrepreneur, a person who has the necessary knowledge and is not an interested party in the case under consideration in relation to either the debtor or creditors, can become a temporary manager.
At the stage of controlling the organization, the temporary manager develops a concept that will help restore the debtor’s payment capacity by a certain date. Based on the developed plan, a document is created that is subject to approval by creditors.
Interim manager and his rights
The rights and obligations of the external manager come into force together with the external management approved by the arbitration court.
- Restoring the financial profitability of the debtor through various operations. This may be the sale of non-essential property, rental of equipment or space owned by the debtor. An external manager legally has the right to independently dispose of the property of an enterprise that has obligations to creditors.
- The main responsibility is inventory of property. The interim leadership team, consisting of economists and legal specialists, deals with accounting, financial, statistical accounting and reporting; maintains a register of creditors' claims; takes legal measures to fulfill debt obligations (debt collection); makes counter-objections to creditors presenting their claims.
- Conclude a settlement agreement on behalf of the debtor manager.
- From the date of his appointment, the external manager has the right to refuse to execute various contracts and other transactions of the debtor enterprise that impede the restoration of his payment capacity or cause losses to his enterprise. In this case, special requirements are met. Refusal to conduct a transaction or fulfill contracts is possible only in relation to matters not fulfilled by the parties partially or completely.
The temporary manager has the right to perform work (), which is the foundation for the arbitration court.
Sample charter with a manager instead of a director
You can view an example of such a charter on the Internet. It contains important provisions governing the activities of the company. Main provisions of the document:
- Goals of the Society.
- Rights and obligations of participants.
- Responsibility of the founders.
- Authorized capital of the company.
- Procedure for leaving an LLC.
- Distribution of company profits.
- Structure of the Company's bodies.
- Executive body of LLC.
- The procedure for reorganizing the company.
- Procedure for convening a meeting of participants.
- Company branches.
DOC file
It is in the “Executive body” section that the provision on the possibility of transferring management into the hands of an entrepreneur on the basis of a civil contract is prescribed.
Thus, the answer to the question whether an individual entrepreneur can act as the general director of an LLC is yes, but with the mandatory inclusion of a provision in the company’s charter allowing such an action. Such a solution makes it possible to optimize the Company’s expenses, but does not attract undue attention from the Federal Tax Service.
External manager and his responsibilities
The responsibilities of the external manager are approved in accordance with the Russian Federation Law “On Insolvency” in accordance with Article 66.
- Applying to the court with a request to remove the current head of the debtor company from his position.
- Submitting a claim to the court (on one’s own behalf) to recognize the invalidity of transactions carried out in violation of the Law.
- Applying to the arbitration court with a request to introduce additional protective measures to preserve the debtor’s property asset.
- Objection to the debtor's untenable claims.
- Access to all documents relating to the debtor’s activities.
- Informing the created about the implementation of activities provided for by a specially developed temporary management plan.
- Providing reports on the results of execution of external management plans.
The duty of the temporary manager is to identify creditors not indicated in the documents attached to the application. If such persons are identified, the external manager is obliged to notify them of the bankruptcy of the debtor enterprise.
After the external manager has carried out the relevant operations focused on restoring the debtor’s solvency, a meeting of creditors is held, at which a report on the work done is presented. If the financial profitability of the debtor is restored, then settlements are made with creditors in accordance with the register.
Observation procedure
The purpose of the observation procedure is to preserve the debtor’s property assets, analyze his financial situation and determine the possibility of restoring solvency. The court can make different decisions: declare the debtor bankrupt, approve financial recovery or a settlement agreement, or reject declaring the debtor bankrupt.
- Analysis of the financial profitability of the debtor is the main monitoring procedure, which determines whether the debtor company has enough property to cover legal costs, expenses for and other related payments.
- The external manager must identify possible (intentional) ones.
- The temporary manager also determines whether the debtor’s solvency is subject to restoration.
- Calling creditors to a meeting and providing them with a report on the financial analysis performed.
Carrying out this analysis helps to determine the real possibilities of restoring solvency or recognizing its impossibility. When an external manager prepares a financial analysis, he takes into account:
- market value of the property;
- structure and volume of financial resources;
- statistical reporting;
- production activities;
- competitiveness and other factors affecting the solvency of the enterprise.
The external manager performs his duties during the period when the debtor is given the chance to work without debt obligations. During this time, the interim manager should be presented with true opportunities to restore the financial profitability of the debtor.
External manager and his activities
The position of the temporary manager, approved by the arbitration court, is certified by documents. The document indicates the amount of remuneration, as well as the source of its payment.
If the candidacy of an external manager is not approved for any reason, the arbitration court postpones its consideration and gives additional time (15 days) to select a candidate.
The appointment of an external manager is not an indisputable basis for removing official obligations from the management of the debtor enterprise, which continues its work activities, but with limited powers. For example, any transaction is possible only with the written consent of the external manager.
The external manager is vested with such important powers as establishing the amount of creditors' claims. Such an offer for execution gives rise to many disputes regulated by the arbitration court.
If the external manager finds extra-legal actions in the conduct of the enterprise’s affairs that violate the Law, then he can petition the arbitration court for the complete removal of the management of the debtor enterprise.
An external manager does not replace the management bodies of the debtor enterprise, but only establishes the presence/absence of signs of bankruptcy. It also helps to identify possible prospects for the financial development of the debtor.
At the end of the observation period (18 months), the external manager submits to the arbitration court:
- a report including an analysis of the financial situation and the degree of solvency of the debtor;
- minutes drawn up at the first meeting of creditors;
- application with accompanying documents.
The temporary manager ceases his supervision at the moment the arbitration court makes a decision, which may declare the enterprise bankrupt, order financial rehabilitation, bankruptcy proceedings, or terminate legal proceedings in the case under consideration in some cases stipulated by law.
Procedure for convening a meeting of creditors
The external manager has the right to convene creditors for an initial meeting. 10 days before the arbitration court meeting, the temporary director must hold a meeting of creditors based on the Federal Bankruptcy Law.
Participants in the first meeting are divided into two categories:
- bankruptcy creditors and other authorized bodies with voting rights;
- manager, representatives of the founders, property owner, employees of the debtor enterprise who take part in the meeting without the right to vote.
The external manager informs creditors about the analysis of the debtor’s financial situation and outlines the promising possibility/impossibility of restoring his payment ability. The conclusions and proposals of the interim manager are not mandatory requirements for creditors, but are rather advisory in nature.
At this meeting, the competence of creditors includes:
- adoption of various decisions related to petitions to the arbitration court (financial recovery, recognition of bankruptcy, settlement agreement, election of a committee of creditors);
- definition of self-regulatory organization;
- formulation of requirements for the candidacy of a bankruptcy, administrative or external manager.
Based on the protocol in which the decision of the creditors’ committee is entered, the arbitration court may declare the debtor bankrupt, approve a settlement agreement, allow financial recovery, or reject declaring the debtor bankrupt.
In Russia, the observation procedure is carried out quite rarely. Theoretical advantages do not bring benefits in practice, since the observation procedure has a weak relationship with bankruptcy practice.
The introduction of an observational procedure will give significant results if:
- the need to block the actions of management and other owners of the enterprise that are not under the control of the debtor;
- making a major property transaction;
- prohibitory measures to satisfy claims of creditors.
The rights of the external administrator: 1) to dispose of the debtor’s property in accordance with the external administration plan with the restrictions provided by law; 2) enter into a settlement agreement on behalf of the debtor; 3) declare refusal to fulfill the debtor’s contracts in accordance with the requirements of the law; 4) submit to the arbitration court on behalf of the debtor claims and applications for the invalidation of transactions and decisions, as well as for the application of the consequences of the invalidity of void transactions concluded or executed by the debtor in violation of the requirements of this Federal Law, and file claims for recovery of losses caused by actions (inaction ) members of the debtor's collegial management bodies, members of the board of directors (supervisory board), the sole executive body, the owner of the debtor's property, persons acting on behalf of the debtor in accordance with a power of attorney, other persons acting in accordance with the debtor's constituent documents. Responsibilities of the external manager: 1) accept the debtor’s property for management and conduct an inventory of it; 2) develop an external management plan and submit it for approval to the meeting of creditors; 3) maintain accounting, financial, statistical records and reporting; 4) file objections in accordance with the established procedure regarding the creditors’ claims presented to the debtor; 5) take measures to collect debt to the debtor; 6) maintain a register of creditors’ claims; 7) implement the measures provided for by the external management plan in the manner and under the conditions established by law; inform the creditors' committee about the implementation of measures provided for in the external management plan; 9) submit a report to the meeting of creditors on the results of the implementation of the external management plan. An external manager may be released by an arbitration court from performing the duties assigned to him in a bankruptcy case: 1) at the request of the external manager; 2) on the basis of a decision of the collegial management body of a self-regulatory organization of arbitration insolvency practitioners, a petition sent by a self-regulatory organization of arbitration insolvency practitioners, of which he is a member. An external manager may be removed by an arbitration court from performing the duties of an external manager: 1) on the basis of a decision of a meeting of creditors to apply to the arbitration court with a petition in the event of failure or improper performance by the external manager of the duties assigned to him or failure to comply with the measures provided for in the external management plan to restore solvency; or could entail losses for the debtor or his creditors; 3) if circumstances are identified that prevented the person from being approved as an external manager, as well as if such circumstances arose after the person was approved as an external manager. Obligation to transfer documents: an external manager, suspended from performing the duties of an external manager, is obliged to ensure the transfer of the debtor's accounting and other documentation, seals and stamps, material and other valuables to the newly approved external manager within 3 days from the date of his approval.
2) enter into a settlement agreement on behalf of the debtor; 3) declare refusal to fulfill the debtor’s contracts in accordance with the requirements of the law; 4) submit to the arbitration court on behalf of the debtor claims and applications for the invalidation of transactions and decisions, as well as for the application of the consequences of the invalidity of void transactions concluded or executed by the debtor in violation of the requirements of this Federal Law, and file claims for recovery of losses caused by actions (inaction ) members of the debtor's collegial management bodies, members of the board of directors (supervisory board), the sole executive body, the owner of the debtor's property, persons acting on behalf of the debtor in accordance with a power of attorney, other persons acting in accordance with the debtor's constituent documents. Responsibilities of the external manager: 1) accept the debtor’s property for management and conduct an inventory of it; 2) develop an external management plan and submit it for approval to the meeting of creditors; 3) maintain accounting, financial, statistical records and reporting; 4) file objections in accordance with the established procedure regarding the creditors’ claims presented to the debtor; 5) take measures to collect debt to the debtor; 6) maintain a register of creditors’ claims; 7) implement the measures provided for by the external management plan in the manner and under the conditions established by law; inform the creditors' committee about the implementation of measures provided for in the external management plan; 9) submit a report to the meeting of creditors on the results of the implementation of the external management plan. An external manager may be released by an arbitration court from performing the duties assigned to him in a bankruptcy case: 1) at the request of the external manager; 2) on the basis of a decision of the collegial management body of a self-regulatory organization of arbitration insolvency practitioners, a petition sent by a self-regulatory organization of arbitration insolvency practitioners, of which he is a member. An external manager may be removed by an arbitration court from performing the duties of an external manager: 1) on the basis of a decision of a meeting of creditors to apply to the arbitration court with a petition in the event of failure or improper performance by the external manager of the duties assigned to him or failure to comply with the measures provided for in the external management plan to restore solvency; or could entail losses for the debtor or his creditors; 3) if circumstances are identified that prevented the person from being approved as an external manager, as well as if such circumstances arose after the person was approved as an external manager. Obligation to transfer documents: an external manager, suspended from performing the duties of an external manager, is obliged to ensure the transfer of the debtor's accounting and other documentation, seals and stamps, material and other valuables to the newly approved external manager within 3 days from the date of his approval.
An external manager is not a permanent sole body that manages the organization; its powers are temporary and exercised exclusively on a non-permanent basis. The external manager is vested with his powers in a special manner; he is approved by the arbitration court simultaneously with the introduction of external management. The arbitration court issues a ruling on the approval of the external manager.
The decision to approve the external manager is subject to immediate execution and can be appealed. An external manager is vested with certain rights and responsibilities in accordance with his status. His legal capacity is of an exclusively special nature.
The external manager has the right:
- dispose of the debtor's property in accordance with the external administration plan;
- enter into a settlement agreement on behalf of the debtor;
- declare refusal to fulfill the debtor’s contracts;
- submit to the arbitration court on its own behalf demands for the invalidation of transactions and decisions, as well as for the application of the consequences of invalidity of void transactions;
- carry out other actions provided for by the Bankruptcy Law.
The external manager is obliged:
- take over the debtor's property and conduct an inventory of it;
- develop an external management plan and submit it for approval to the meeting of creditors;
- maintain accounting, financial, statistical records and reporting;
- submit, in accordance with the established procedure, objections regarding the claims of creditors presented to the debtor;
- take measures to collect debt to the debtor;
- maintain a register of creditors' claims;
- implement the activities provided for in the external management plan;
- inform the creditors' committee about the implementation of measures provided for in the external management plan;
- submit a report to the meeting of creditors on the results of the implementation of the external management plan;
- exercise other powers. The competence of the external manager includes the authority to establish the amount of creditors' claims, dispose of the debtor's property, and may also include refusal to execute the debtor's transactions.
One of the most important aspects of the external manager’s activity is establishing the amount of creditors’ claims. Establishing the amount of creditors' claims is not always certain.
The external manager has the right to refuse to execute contracts and other transactions of the debtor within three months from the date of introduction of external management. In this case, special requirements must be observed. Refusal to execute contracts and other transactions of the debtor can be declared only in relation to transactions not executed by the parties in whole or in part, if such transactions impede the restoration of the debtor's solvency or if the debtor's execution of such transactions will entail losses for the debtor in comparison with similar transactions concluded with comparable circumstances.
A temporary manager in the case of bankruptcy of a legal entity is necessary in the case when the observation stage is introduced 3 days after the start of the bankruptcy procedure. It lasts on average 3-5 months. The new manager studies the financial position of the debtor company and makes a conclusion about the likelihood of financial recovery.
Director – sole executive body of a legal entity
The General Director is the sole executive body of the organization and is elected by the general meeting of the company's participants or the board of directors (Article 63, paragraph 3 of Article 69 of the Federal Law of December 26, 1995 No. 208-FZ, Article 37 and paragraph 1 of Article 40 of the Federal Law Law of 02/08/1998 No. 14-FZ).
When electing a general director, minutes of the general meeting of participants are drawn up (for more information, see “Drafting a decision on the appointment of a general director (sample 2017)”).
If the company has a single founder, then the head of the organization is appointed by the sole decision of this founder (clause 2 of Article 7 and clause 1 of Article 40 of the Federal Law of 02/08/1998 No. 14-FZ, clause 2 of Article 2 and Article 69 of the Federal Law Law of December 26, 1995 No. 208-FZ) (for more details, see, “We are drawing up a decision on the appointment of a general director (sample 2017)”).
For your information, the term of office of the General Director is established by the minutes of the general meeting of participants (decision of the sole founder). The maximum duration of an employment contract with a director is 5 years (Articles 58, 59, 275 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Candidate selection
Only an individual can hold this position. Lenders have the right to nominate themselves, or the Arbitration Court appoints a person who meets the requirements:
- he must be a citizen of the Russian Federation;
- he must not have a criminal record or administrative fines;
- for the last three years he has not taken part in the management of the debtor company;
- he is not an interested party (relative, successor, etc.)
If there is no suitable candidate, the court makes a request to the state. an organization that manages financial recovery matters. She must provide a temporary manager within a week. Note that such a person does not have to register as an individual entrepreneur, unlike those managers chosen by lenders. If the selected candidate is unable to perform the duties assigned to him, another person is appointed in his place.
The temporary manager performs his duties from the moment of appointment and until:
- no bankruptcy or external manager will be appointed;
- the debtor and his lenders will not enter into a settlement agreement;
- the court will not decide to refuse to recognize the fact of bankruptcy.
The post of manager and personnel order
So, according to current legislation, an individual entrepreneur does not have the right to appoint himself to the position of manager and pay himself a salary, but he may well hire a third-party employee and give him the right to perform the main set of executive functions if he has a signed order, job description, employment contract and power of attorney. Since the concept of “general director” does not exist, you can enter into the staffing table one of the following management positions provided for in the qualification directory. The director of an individual entrepreneur can be:
- executive;
- commercial;
- towards;
- sales services;
- by personnel.
It is worth considering that even if there is an executive director on staff, full legal responsibility before the law and government bodies always lies with the individual entrepreneur himself.
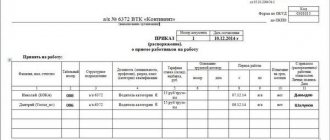
When a manager is appointed to a post, a personnel order is drawn up, which must have a number and be entered in the individual entrepreneur’s order book. The order must have the inscription “Russian Federation”, the name of the individual entrepreneur, all details, date of completion and subject. The essence of the order is stated below: “Appoint I.I. Ivanov to the position of executive director. from April 1, 2020 with a salary according to the staffing table.”
The order must be certified with the seal and signature of the entrepreneur. This document is valid from the moment of signing. From this time the employee is considered accepted for the position. He may obtain a copy of this document upon request. Next, all other necessary documents are signed with the appointed manager, an entry is made in the work book, and the employee begins to perform his job duties.
An individual entrepreneur resorts to hiring such a manager when there is a high workload and there is no desire to visit government agencies on their own, which usually wastes a lot of valuable working time. The hired employee will deal with current affairs, resolve issues with suppliers and authorities, manage staff, the work of a department or an entire store, and the entrepreneur will have more opportunities to develop the business, engage in advertising, promotion and search for new partners and clients. This is a very important area of activity, for which there is often little free time due to the constant resolution of current issues.
vseobip.ru
This article describes in detail whether an individual entrepreneur can have a general director, and everything you need to know about it. The CEO of a particular company is always chosen through a vote of the founders. In a large number of situations, an employee will be nominated for a position whose list of main job responsibilities includes unauthorized management of the economic complex using all power, as described in the charter.
The bosses will always be paid the required amount of salary, the amount of which is shown in the employment agreement. The law of our state, of course, implies a variation in the transfer of the powers presented not to individuals, but to purely independent businessmen, only in such a case, the correct name of the manager would be not a director, but a manager.
Director's service and the concept of individual entrepreneur
The boss will be able to become one of the managers. In a large number of situations, a certain managerial employee of a certain legal entity becomes a director. A businessman cannot be designated as a legal entity. It follows from this that the individual entrepreneur has the right to appoint himself as the head of the company.
Also, the individual entrepreneur will be able to hire a staff of employees, including a director. This is possible in cases where an individual entrepreneur has control over several enterprises or stores, each of which must be managed by a boss from the staff.
When one of the indicated bosses on behalf of the businessman directly takes part in the execution of the agreement, the text of the agreement will be worded slightly differently.
Managing Director or Principal Director
The main director is inherently shown to be a managerial position, which is determined through the approval of the working staffing table. If a businessman is hired, the company will enter into a civil agreement with him. The involvement of businessmen as sole executive employees is initially advisable for the company in terms of easing the tax burden.
A businessman must receive his payment for the work done and personally makes all calculations when dealing with funds outside the budget. The amounts of all payments will not be determined by the amount of compensation purchased and will be shown in fact as established, effectively by these decrees, of the taxation system.
When an individual is shown as the chief director, the company will lose all “salary” taxes in total, when it is possible to say so. To avoid any problems, it is best to register in advance a company with one or another person who fulfills the obligations of the general director. Only after this the LLC will be able to be managed by the businessman and make his own adjustments to the Unified State Register of Legal Entities. Once you become familiar with the above data, no one will have a question about whether it is possible for an individual entrepreneur to designate himself as a boss.
Director at IP
It is worth saying that the director himself may not be directly involved in directorship.
Every individual businessman who has the status of an individual can fulfill certain obligations of a legal entity. In particular, the recruitment of employees to the staff is shown. Certain citizens are interested in the question of whether an individual entrepreneur can be hired as a director by someone else?
Of course, an entrepreneur who is registered as an individual entrepreneur is always shown as a personal representative of his interests, but if a certain need arises, another person can take over the business.
For example, there are cases when, for some reason, a businessman needs to place his business under the management of a specially hired employee. It is worth mentioning the following reasons:
- Difficult situation in the family.
- Parallel management of other companies.
- Disease.
No matter what happens, an individual entrepreneur can always become a director. In a certain situation, an employee will be able to sign an order of his appointment, understand effective instructions for the position, take on certain responsibilities as an employee needs, and acquire a salary in accordance with the amount that will be specified in the employment agreement.
In a large number of situations, the director of an individual entrepreneur can become the simplest manager of a certain working specialty.
You must understand that the post of general director cannot be presented to a hired employee. Decisions on certain issues regarding the direction of the company’s work will still be made by the person on whom the company is registered. Some variation for management positions is likely for salaried personnel.
Literally anyone can choose the necessary position for a particular company, having familiarized themselves in advance with the regulations of the unified qualified directory.
In this article, you found out whether an individual entrepreneur can have a general director. If you have any questions or problems that require the participation of lawyers, then you can seek help from the specialists of the Sherlock information and legal portal. Just leave it on our website.
Editor: Igor Reshetov
www.cherlock.ru
Of course, a businessman, having registered as an individual entrepreneur, represents his business independently. But if necessary, another person can conduct business. For example, it happens that for personal reasons: illness, difficult family situation, running another business in parallel, an entrepreneur is forced to leave his business under the supervision of an employee.
An individual entrepreneur may have a director. In this case, the employee signs an order of his appointment, reads the job descriptions, performs specific duties and receives a salary as agreed. As a rule, the director of an individual entrepreneur is simply a manager of a certain area of activity (for example, the director of a store).
General Director is a position that cannot be offered to an employee. The main decisions remain with the person on whom the business is registered, that is, with the individual entrepreneur. But some options for leadership positions for hired personnel are possible: commercial director, executive director, manager, personnel director, director of a certain direction, etc. You can find a suitable position in the Unified Qualification Directory.
According to Article 413 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the law cannot consider any obligations if the creditor and the debtor are the same person. Therefore, an individual entrepreneur cannot appoint himself as a director, since civil obligations in this case do not make sense. Also, an entrepreneur cannot pay his own salary or enter into an employment contract with himself. The status of an individual implies that the individual entrepreneur performs his social functions directly, unlike a legal entity, where personification is simply necessary, that is, in order to express its will, the company needs a manager appointed for this.
To avoid further disagreements, accompany this appointment with two more documents:
- Job description.
- A standard employment contract, which specifies all the duties of the appointee, his areas of responsibility, work schedule and functions.
Don't forget to provide your employee with a power of attorney to perform certain functions, this will make things easier for both of you. And so that there are no problems with payment at the bank (so that your director’s signature on payment documents does not cause disputes), you together draw up a card with sample signatures at the bank.
Here is a sample of each of the necessary documents: an order for hiring, an order for taking on the position of director, a job description for a commercial director.
So, you can perform the duties of a director yourself, but you do not have the right to appoint yourself as one. Or you can hire a director for an individual entrepreneur as a manager or executive director. Think for yourself whether you need a person who will share with you all the power.
zhazhda.biz
Manager's responsibilities
The main task of the temporary manager is to preserve the assets of the debtor company. He is also required to determine:
- Is it possible to repay debts?
- How liquid is the debtor’s property;
- will it be possible to restore solvency if external management is introduced;
- what is the market value of the debtor company.
At the observation stage, the new manager draws up an action plan to return the debtor to solvency and at the same time tries to identify the “traces” of a fictitious bankruptcy. For example:
- accounting records are lost;
- accounts receivable are not controlled;
- debt obligations are not fulfilled despite the fact that the company has the necessary finances;
- the company's management entered into obviously unprofitable contracts;
- there is no information about counterparties who use the debtor’s property.
At the same time, the head of the debtor company must not create obstacles for the temporary manager and must present the original documents upon request. If these originals are lost, the manager has the right to request copies of them from counterparties.
Another duty of the temporary manager is to compile a list of lenders and record their demands (in this case, the debtor has the right to challenge the creditors’ claims; he is given 1 week to do this). 10 days before the first meeting in the bankruptcy case, the manager is obliged to notify creditors of the start of the bankruptcy procedure and hold the first meeting for them.
All financial activities of the debtor company must be under the strict control of the temporary manager. And the head of the debtor company is obliged not only to notify him of the decision to enter into a particular transaction, but also to ask permission. If the observer seems that this step will only worsen the financial situation of the debtor, he has the right to prohibit signing the agreement.
If a deal is concluded behind his back, he has the right to petition the court to declare the deal invalid. In addition, he is given the authority to exclude from managing the company those people who, in his opinion, are not performing their official duties well.
Completing the procedure
Upon completion of the observation stage, the temporary manager draws up a report on the work done, in which he draws conclusions about the financial insolvency of the debtor company. In this document, he can also indicate his recommendations for its financial recovery and return to solvency. The following documents are attached to the report:
- materials on the basis of which the financial condition of the debtor was analyzed;
- minutes of creditors' meetings;
- conclusion on whether bankruptcy is intentional, etc.
All of them are sent to the Arbitration Court, which decides to refuse to declare the debtor bankrupt or transfer the case to another stage of bankruptcy.
The temporary manager receives monetary compensation for his services in the form of a salary (fixed amount) and interest. The debtor pays it, and this payment is included in the priority list. The salary is regulated by the Bankruptcy Law and currently amounts to 30,000 rubles per month. The arbitration court may increase this amount at the request of the lenders and the debtor.
The temporary manager may lose his position. This happens when it becomes clear that he is improperly fulfilling his duties (at the request of the SRO of arbitration managers) or if he himself wants to do so. In this case, payment for his services stops.
So, a temporary manager is an individual who is appointed by the Arbitration Court to the position of head of the debtor company. His task is to find out the true financial position of the company and determine how financial recovery is possible. He receives a monetary reward for his services. Payments are made from the debtor's funds.
Recognition of insolvency, or bankruptcy of a legal entity, is a complex and time-consuming process. An equally complex bankruptcy procedure is external administration. The external manager is the responsible person during its implementation. What is the meaning of this stage of bankruptcy, for what period can it be introduced?
General Director of LLC, founder and individual entrepreneur rolled into one
When an individual entrepreneur runs a profitable business, situations often arise that he needs to expand the boundaries of the enterprise. Can he open an LLC? Yes maybe. But he can register a limited liability company only as an individual. In the same way, the founder of an LLC can register with the Federal Tax Service as an individual entrepreneur. Moreover, the legislation does not limit the number of organizations established by one person. The status of an individual entrepreneur does not increase; it either exists or it doesn’t.
“Double-sided printing of an application for registration of a company or individual entrepreneur is unacceptable” will help you correctly prepare registration documents .
IMPORTANT! An entrepreneur must maintain accounting and tax reporting separately for each business. It will not be possible to combine the reporting of an LLC and an individual entrepreneur or two LLCs. If an entrepreneur is not ready for such a volume of reporting, you can close an individual entrepreneur or an extra LLC by going through the necessary procedures.
As the founder of a newly formed enterprise, an individual can appoint himself to the position of general director. Then the situation arises that a person is an individual entrepreneur, founder and manager of an LLC rolled into one.
Briefly about bankruptcy
Insolvency, or, in other words, bankruptcy is the status of a debtor recognized by an arbitration court, which exempts him from paying monetary obligations to creditors due to his inability to satisfy them in full. According to federal law, bankruptcy can be recognized if obligations to creditors have not been fulfilled within a 90-day period from the moment they were due. Bankruptcy of a legal entity includes 5 procedures:
- Monitoring (financial capabilities are analyzed, property is retained by the debtor).
- Financial recovery (debt repayment schedule is drawn up).
- External control (we’ll talk about this stage in more detail below).
- Bankruptcy proceedings (sale of the debtor's property, applied to bankrupts in order to proportionally satisfy the requirements of credit institutions).
- Settlement agreement (can be concluded at any stage of the process).
Pros and cons of this solution
Appointing an individual entrepreneur as manager of an LLC has its positive and negative sides. The advantages include the following:
- Savings on taxes and other fees. A company headed by an individual entrepreneur does not need to pay high taxes as for an employee, and also transfer insurance contributions to funds. You will also not have to pay for sick leave or compensation provided for by labor legislation.
- Increased liability for damage. If the employee is to blame for the losses, then you can recover from him no more than his wages. If the fault lies with the entrepreneur, then the damage is compensated in full plus lost profits.
- The ability to set your own payment procedure. This will not work with hired workers. They are supposed to pay strictly twice a month. The LLC owner can agree with the entrepreneur on any frequency of payments, for example, once a quarter.
Among the negative aspects of appointing an individual entrepreneur as a manager, the only risks associated with too close attention of the tax authorities are highlighted. There is always a possibility that Federal Tax Service employees will try to reclassify a civil contract into an employment contract.
Another disadvantage is the high wages. A simple hired director receives a salary much less than a managing entrepreneur. At the same time, he is independent, reports only to the constituent assembly, and enters into transactions with counterparties himself.
External control: definition of the concept
External management is a bankruptcy procedure applied to the debtor, which is introduced in parallel with the financial rehabilitation of the organization. This procedure is of a rehabilitation nature and helps prevent the launch of bankruptcy proceedings, which, in turn, is aimed at liquidating the enterprise, and not at returning the company to an economically stable state.
External management as a bankruptcy procedure is introduced if there is a decision of the arbitration court, adopted in agreement with creditors and based on the results of the previous stage of bankruptcy - supervision. The implementation period for measures at this stage is no more than 18 months. In exceptional cases, the period may be extended for another six months. Thus, the duration of external management activities can be no more than two years.
One of the most important differences of this procedure is the removal of the current management of the enterprise from management. The authority to manage the organization is transferred to an external manager. In fact, the manager is a key figure here and plays the role of the general director; he can also dispose of the assets of the enterprise at his discretion. However, the current leadership is only partially stripped of its powers. Some technical functions are retained.
External management as a bankruptcy procedure: briefly about the tasks
The stage of the bankruptcy procedure called “external management” begins to be implemented after the rights of the head of the organization are transferred. The choice of a manager and the decision on the need for the procedure are made at a general meeting of creditors and then approved in court. For it to be accepted, the court must be convinced that it is quite possible to restore the solvency of the bankrupt enterprise. To do this, you must provide appropriate evidence.
The purpose of external management during bankruptcy proceedings is to restore the solvency and normal operation of the organization, as well as the subsequent recognition of solvency. Another important task is to satisfy the requirements of all creditors.
External management as a bankruptcy procedure and the consequences of its introduction
Like any process the execution of which is controlled by the court, external management has the following consequences:
- The head of the organization is almost completely deprived of control over it, with the exception of powers of a technical nature.
- The management bodies of the enterprise cease to carry out their activities, since power is transferred to an external manager.
- Measures aimed at satisfying the requests of all creditors and taken before the launch of this procedure are canceled and declared invalid.
- The organization's property cannot be seized and restrictions cannot be imposed on it, since these measures take place after the enterprise has been declared insolvent in court.
- A moratorium is established on the claims of all creditors regarding financial obligations.
A moratorium cannot be established on those claims of creditors that arose after the consideration of the claim by the arbitration court and the recognition of bankruptcy of the company. Moreover, there are exceptions such as payment of wages and employee benefits, and alimony.
Risks when transferring control
Appointing an individual entrepreneur as a management company of an LLC has certain risks. They need to be taken into account. And they primarily concern the tax authorities. Federal Tax Service employees understand that such a scheme is used to minimize the payment of taxes and insurance premiums. Therefore, they closely monitor such companies and try to grab any clue to turn the situation in their favor.
Even small shortcomings in the agreement with the individual entrepreneur provoke lengthy and serious proceedings, attempts to collect lost taxes from the LLC.
Tax authorities especially often try to reclassify a civil contract concluded between an LLC and an individual entrepreneur into an employment agreement drawn up with ordinary employees.
To start this procedure, the following reasons are sufficient:
- the manager acts according to the job description and strictly observes the work schedule at the enterprise;
- the work of an entrepreneur does not have an independent economic purpose;
- the Company's charter does not contain a clause giving permission to transfer management to an outside person;
- the compilation of individual entrepreneur reports is carried out by the company's chief accountant;
- the services specified in the agreement between the individual entrepreneur and the LLC are not included in the list of OKVED codes.
The tax inspectorate does not miss the opportunity to check the organization and find at least some loophole in order to collect the maximum taxes.
Responsibilities of an external manager
The main characteristic of external management as a bankruptcy procedure is the termination of the powers of the current management of the enterprise. At the same time, the external manager has a wide range of responsibilities, which includes the disposal of the debtor’s property. The existing management bodies of the enterprise are deprived of the right to make independent decisions without the consent of the external manager or to influence his decision-making. The manager also performs all functions of managing the organization, controls the processes of inventory and property disposal, maintains accounting, financial, statistical records and reporting, a register of creditor claims, and takes measures to collect receivables. Moreover, he is engaged in carrying out health measures aimed at restoring solvency and carried out in the course of business activities. For this purpose, a management plan is drawn up.
Governing bodies of an individual entrepreneur: what is the secret?
Management bodies are considered to be those bodies that make certain decisions and monitor their implementation without fail. Management bodies act exclusively within their competence when making management decisions. Management bodies, as a rule, are elected and appointed.
Currently, an individual entrepreneur is one of the most common forms of doing business. Registration in this status allows newcomers to avoid unnecessary hassle with taxation and the registration procedure itself. At the same time, this status gives entrepreneurs quite extensive rights that are not inherent to ordinary citizens - individuals. These rights are vested in him by state bodies using legislative and regulatory acts. For example, some types of activities of an entrepreneur are subject to licensing; acting as an employer, an individual entrepreneur is obliged to follow the norms of the Labor Code when hiring or firing employees. Individual entrepreneurs are guided by these same standards when maintaining work books, applying for vacations, and so on. And one of these advantages is the fact that the management bodies of an individual entrepreneur are the entrepreneur himself, since he carries out his activities at his own peril and risk.
Doing business is always carried out with the sole purpose of making a profit. This is possible with a fairly efficient level of management and adequate planning of activities. It is the entrepreneur who independently plans activities. A business plan in this case serves as a document that allows you to adequately build a business model, reduce the risks associated with it, and ultimately increase profits. The management bodies of an individual entrepreneur are represented by the individual entrepreneur himself. He manages his activities in the case of one employee working in a specific individual entrepreneur. If an entrepreneur hires employees, then in carrying out their activities he is the governing body, since he himself determines the business strategy. It is his instructions that hired workers follow when performing it as employees of individual entrepreneurs.
Any organization or enterprise registered as a legal entity must have its own system of governing bodies. This can be one person, who is also the founder, who independently carries out management. But management can also be entrusted to the meeting of founders, the board of directors. This is a more complex system of governing bodies, but also more effective: several people are capable of quickly making a decision or resolving a controversial situation. The number of people in the management bodies of a legal entity depends on the total number of employees, as well as on the form of business management - LLC, CJSC and others.
Thus, the governing bodies of an individual entrepreneur are the individual entrepreneur himself in the status of an individual. But, in addition to the sole management of its business entity, an individual entrepreneur in some situations comes into contact with government authorities. Taxation of entrepreneurs is managed by state tax authorities. The same structure registers an individual entrepreneur and issues him a certificate. The State Antimonopoly Committee also works closely with entrepreneurs to ensure that they establish an adequate cost for a product or service.
At the same time, an individual entrepreneur as an individual is not prohibited by law from holding any positions in other organizations and enterprises. As an employee, the entrepreneur will be subordinate to the management body of the enterprise with which he will enter into an employment or civil law contract. Occupying a leadership position in an enterprise or LLC (legal entity), an entrepreneur can himself be a member of the management bodies of a given business entity - be a founder, be a member of the board of directors, etc.
External manager work plan
External management as a bankruptcy procedure involves the implementation of a work plan, which is drawn up within a month. The external manager must reflect in the plan the following points:
- The procedure and conditions for the implementation of measures aimed at restoring the viability of the enterprise.
- Financing.
- Planned expected expenses of the organization.
- The period during which it is planned to restore solvency.
- Reasoning for the chosen recovery period.
- Separation of powers between committees and creditors.
The execution of the plan is controlled by creditors and must be strictly followed.
What measures can the manager take?
External administration as a bankruptcy procedure involves the application of the following measures to the debtor:
- Changing the nature of production activities.
- Completion of the work of divisions and branches of the enterprise that are recognized as unprofitable.
- Collection of accounts receivable.
- Sales of property assets of the organization.
- Replenishment of the authorized capital with funds from third parties and founders.
- Replacement of assets and other measures within the framework of the law.
Measures can be taken either separately or in combination.
Can an individual entrepreneur have a director or general director?
An individual entrepreneur is the sole full-fledged manager of his enterprise. He does not need to call himself director or general manager. But it happens when, due to family circumstances or illness, an individual entrepreneur cannot coordinate the activities of his organization himself. Then he has the right to hire an employee as a director who will be able to act within the framework of the issued power of attorney.
There cannot be a position of “CEO of an individual entrepreneur.” The functions that are assigned to the general director of an LLC are performed in an individual enterprise only by the owner of the individual entrepreneur, and no one else.
Wellness events: features of implementation
External management as a bankruptcy procedure has features of implementing health measures:
- The notification period for the head of the organization about the introduction of external management is 1 day.
- The founders are notified of the procedure.
- Within a 10-day period from the start of the procedure, an application for publication of this information is sent.
- The manager receives an order to transfer all documentation to him.
- Documents are transferred within 3 days after the manager takes office.
- The first meeting of creditors is scheduled within 31 days after the start of the procedure.
- The FSSP, the Federal Tax Service, and banks are informed about health-improving activities.
- Relevant requests are sent to the control authorities.
- A general meeting of all employees of the enterprise is organized.
- An accountant and auditor are involved in the work of the organization.
- An inventory is organized.
- The financial position of the enterprise is analyzed.
- The property of third parties is returned to them.
- A list of creditors' claims is compiled and considered.
- A meeting of creditors is organized.
- An interim and final report is drawn up and announced at the meeting of creditors.
- The plan is submitted to the arbitration court.
- Property objects are being sold.
Result of the procedure
External management as a bankruptcy procedure, as judicial practice shows, does not always have good results. The reason for this is the low level of professionalism of the external manager. This is because he is a third party and does not have the necessary skills to use legal measures to solve the organization's problems.
Moreover, the activities of the external manager can be significantly influenced by external factors - direct (entry into force of changes in existing legislative acts, competition, taxation system) and indirect (political situation in the country, changing trends in international relations, rapid inflation, natural disasters) character. Often the reason for the low efficiency of external management is the desire of creditors to establish financial control over the debtor, ruin him, and reclaim his movable and immovable property.
External management as a bankruptcy procedure is introduced with the aim of restoring the solvency of the debtor organization. The manager, who is vested with almost all the powers of a manager, is directly involved in its course. The main characteristic of external management as a bankruptcy procedure is that not only interaction with debtors occurs, but also the activities of the enterprise itself are reorganized. When solvency has been restored, the manager fulfills his duties until new management arrives. Otherwise, the commencement of bankruptcy proceedings is announced.
Why do they do this?
A managing individual entrepreneur is the optimal solution for the company. Owners of companies prefer to appoint individual entrepreneurs primarily in order to save on paying taxes. After all, a legal entity has the right not to make insurance payments for this citizen.
An entrepreneur also has the right to choose a simplified taxation system. According to it, he pays a tax of only 6%, not 13% as paid by hired directors of companies. And the amounts of insurance premiums for individual entrepreneurs are fixed and quite reasonable even for average earnings. You have to pay a lot more for a regular director.