Art. 180 Labor Code of the Russian Federation: questions and answers
Art. 180 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides guarantees that the employing company is obliged to observe in relation to the specialists whom it intends to lay off. This article is devoted to what is important for an employee to remember so as not to end up illegally without work ahead of time.
Article 180 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
What opportunity does Part 3 of Art. 180 Labor Code of the Russian Federation?
How can a company determine which of the layoff specialists should be offered available vacancies?
What if due to layoffs you were fired not 2, but, for example, 5 months after the warning?
General information
Labor legislation establishes a number of guarantees and compensations for an employee upon dismissal due to:
- personnel changes implying dismissal;
- termination of activities of the legal entity.
Adjustments to the staffing table, expressed in the exclusion of one of the units, do not always provide for the dismissal of an employee occupying a certain position.
According to Art. 180 part 2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer undertakes to offer the hired person occupying a reduced staff position another vacant position, if available.
Retrenchment is the termination of employment relations at the initiative of the employer. Moreover, nothing depends on the employee in such a situation, except in cases where the law directly prohibits the dismissal of certain categories of employees.
The legislation of the Russian Federation establishes regulations for holding such events, for violation of which administrative liability is provided.
https://youtu.be/SUthzDyi4UU
Article 180 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Article 180 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides that if an organization intends to cease to exist or lay off working specialists, it should first of all take care of compliance with certain guarantees for full-time employees.
In particular, before downsizing an employee (i.e., firing), the company must first offer him other available vacancies, even if they do not correspond to his profile.
Each of the laid-off employees must be notified no later than 2 months before this specialist is dismissed.
If there is a threat of mass layoffs in the company, by virtue of Art. 180 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, certain measures should be taken to reduce the negative consequences of such dismissal.
In addition, laid-off employees are entitled to certain compensation.
Employee notification
Part 2 of Article 180 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation stipulates that the employer undertakes to inform the employee in writing about the termination of labor relations in connection with personnel changes or termination of the activities of a legal entity through liquidation.
The chronology of the actions of the head of the enterprise is as follows:
- coordination of upcoming events aimed at changing the staffing table or liquidating the enterprise;
- compiling a list of persons subject to dismissal, as well as conducting an analysis to determine the availability of benefits or preferences for specific employees;
- informing the employee in advance about the upcoming termination of the employment contract - 2 months before the actual termination of the employment contract;
- granting the right to occupy a vacant position to dismissed employees;
- transfer of information about the upcoming layoff to the territorial employment center or trade union organization;
- obtaining approval from the trade union;
- actual dismissal with provision of final payment.
Part 3 of Article 180 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation gives the employee the right to resign before the expiration of 2 months after familiarization with the order of the upcoming reduction, with receipt of compensation in the amount of average earnings for the remaining period before the termination of the employment contract.
Notification of the upcoming layoff is communicated personally to each employee against his signature in the order document. Article 180 of the Labor Code establishes this requirement. If the employee does not agree or refuses to sign the document, a corresponding act is drawn up about this.
This obligation is established by the Labor Code, namely Article 180.
What if due to layoffs you were fired not 2, but, for example, 5 months after the warning?
In order to warn the company’s specialists about the impending reduction, Art. 180 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation gives the employer 2 months. But this does not mean at all that after an employee has received a warning, he must be fired within 2 months. The Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not contain a corresponding imperative norm.
So a specialist who has not been laid off 2 months after receiving a warning cannot relax.
The company has the right to terminate the employment contract with him even after the end of the specified period. At the same time, the courts proceed from the legality of dismissal, which laid-off workers often unsuccessfully try to challenge (rulings of the Moscow City Court dated November 6, 2015 in case No. 33-40687/2015, dated February 12, 2014 in case No. 33-6931/2014, etc.). You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Full and free access to the system for 2 days.
Stages of dismissal
The employer performs a number of sequential actions when carrying out the employee reduction procedure:
- change in staffing. At the same time, it is impossible to eliminate the position and immediately re-establish it;
- preparation of an order;
- creation of a special commission whose powers include carrying out measures to reduce employees;
- familiarization of dismissed employees with the order;
- actual dismissal.
Not only the dismissed employees, but also the representative of the trade union organization, as well as the territorial employment center are notified in advance of the upcoming reduction. The notice period is 2 months before dismissal. If the reduction is massive, the period increases to 3 months.
Violation of the current regulations on carrying out measures aimed at reducing staff is grounds for legal proceedings. Ultimately, the court may declare the actions illegal and reinstate the dismissed employee with the obligation to pay compensation for days absent from work.
It is important to take into account the nuances of the employee reduction procedure provided for in 2020 by the law of the Russian Federation, since the slightest deviation from the established regulations will lead not only to the obligation to restore the violated right to work, but also to the imposition of penalties, up to the complete suspension of the enterprise’s activities.
Collective agreement
In Art. 180 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, this act is mentioned among the documents establishing additional requirements for the employer. The collective agreement prescribes measures aimed at reducing the number of laid-off employees and ensuring their employment. The relevant section may include:
- Measures to reduce working hours without changing the number of personnel.
- Compensation and benefits for employees whose contract is terminated. They are established in addition to those determined by law.
- Rules for organizing professional training and advanced training before the deadline for termination of employment relations.
- Other measures to ensure social protection for employees.
In the event of a short-term decrease in production volume, measures can be taken to prevent staff reductions. For example, this could be a temporary suspension of hiring employees for vacant positions.
Another comment on Art. 180 Labor Code of the Russian Federation
1. When carrying out measures to reduce the number or staff of an organization’s employees, it is necessary to take into account those restrictions and additional guarantees that are provided for by the current labor legislation for certain categories of workers, including: a) a ban on the dismissal of certain categories of workers under certain conditions; b) the possibility of terminating an employment contract with certain categories of employees only with the consent of the subjects specified in the law; c) the preferential right to remain at work for certain categories of employees, including those in respect of whom this right is established by a collective agreement (see Article 179 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and the commentary thereto).
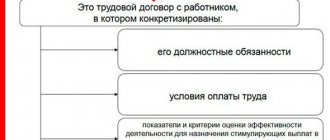
2. By virtue of Part 1 of Art. 180 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, when carrying out measures to reduce the number or staff of an organization’s employees, the employer is obliged to offer the employee another available job (vacant position) that corresponds to the employee’s qualifications.
Work that corresponds to the employee’s qualifications should be understood as any other work that the employee is able to perform due to his actual qualifications, including work of lower qualifications compared to what the employee previously performed.
In practice, the employer presents the employee with a list of available vacancies simultaneously with a warning about the upcoming dismissal.
Termination of an employment contract due to a reduction in the number or staff of an organization's employees is possible only if the employer does not have a job that would correspond to the employee's qualifications, or if the employee refuses to be transferred to another job. At the same time, the employer is obliged to offer vacancies that the employer has in other localities, if this is provided for by the collective agreement, agreement, or employment contract (see Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and the commentary thereto).
3. As follows from Part 3 of Art. 180 of the Labor Code, the employer has the right, with the written consent of the employee, to terminate the employment contract with him without notice of dismissal two months in advance, while simultaneously paying additional compensation in the amount of the employee’s average earnings, calculated in proportion to the time remaining before the expiration of the notice of dismissal.
The employee’s written consent to terminate the employment contract without working out the established two-month period can be expressed by reading the relevant order of the employer against receipt or by a separate written document (employee statement), in which he expresses his consent to dismissal without working out the specified period.
Along with the obligation to warn about the impending dismissal of an employee, the employer is obliged to notify the relevant trade union and government bodies about the dismissal in advance (see.
Art. Art. 81, 82 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and commentary thereto).
4. The rules established by Art. 180 of the Labor Code, apply only to cases of reduction in the number or staff of an organization’s employees, as well as liquidation of an employer - a legal entity. Guarantees and compensation to employees in the event of termination of the activities of an individual employer, as well as in the event of a reduction in the number or staff of employees employed by him, are established in accordance with the procedure of individual contractual or collective contractual regulation.
Current version of Art. 180 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation with comments and additions for 2018
When carrying out measures to reduce the number or staff of an organization’s employees, the employer is obliged to offer the employee another available job (vacant position) in accordance with part three of Article 81 of this Code. Employees are warned by the employer personally and against signature at least two months before dismissal about the upcoming dismissal due to the liquidation of the organization, reduction in the number or staff of the organization's employees.
The employer, with the written consent of the employee, has the right to terminate the employment contract with him before the expiration of the period specified in part two of this article, paying him additional compensation in the amount of the employee’s average earnings, calculated in proportion to the time remaining before the expiration of the notice of dismissal.
If there is a threat of mass layoffs, the employer, taking into account the opinion of the elected body of the primary trade union organization, takes the necessary measures provided for by this Code, other federal laws, a collective agreement, and an agreement.
Employee rights
If the reason for the termination of the employment relationship is the liquidation of the company, then employees are given the authority to contact employment centers, where they are registered. When a person cannot be employed within the period established by the legislator, CZN specialists issue a document giving the right to further receive compensation.
After receiving the document, the employee will need to take the work book and contact the commission conducting the liquidation. An application for payment of compensation is drawn up. If the employer refuses to pay, the decision is appealed, since the rights of employees are reflected in the laws.
Notice of dismissal (Part 2)
Second part of Art. 180 states that the employer is obliged to notify workers of dismissal or reduction 2 calendar months in advance.
Mandatory notification requirements:
- Written form.
- An exact indication of the date of termination of the employment contract.
- The employee's familiarization is confirmed by a signature indicating the exact date of familiarization.
If an employee refuses to confirm familiarization in writing, the employer must draw up a statement of refusal.
2 months begin to count from the next day after notification. The employer has the right, on his own initiative, to postpone the period of suspension from work to a later date. Increasing the notice period increases the likelihood of employees being hired.
The employee has the right to go to court and change the date of dismissal if the notice period has not been met. In this case, the period of shifting the date of dismissal must be paid based on the average salary.
An employee who was on sick leave during the notice period, but before its end, does not have the right to postpone the date of reduction, taking into account the period of temporary disability. But if the employee is on sick leave by the end of the notice period, then the employment contract with him is terminated only after the sick leave is closed.
Compensation for layoffs
When a person gets acquainted with the order according to which the number of workers is being reduced and puts his signature on all acts, he can begin to look for a new job. The date reflected in the documentation as the day of dismissal becomes the last working day in the company. When the decision to dismiss was made by the management of the organization, they are obliged to pay employees:
- compensation related to unused rest days;
- severance pay;
- other financial debts.
Debts may be related to the payment of wages, bonuses, and other things. According to the law, payments are made on the last day that a person works at the enterprise. It is no longer possible to pay later. The salary for the last month worked is issued the day before the employment relationship with the employee is terminated.
The company will pay compensation for a two-month period only if the former employee has not found another job. In a situation where a person works, but the employment relationship has not been formalized, the right to receive compensation is not lost.
For the first month, a person is entitled to an amount equal to his average monthly earnings. In the second month, calculations are made differently. The number of days worked is multiplied by the average daily earnings.
Some situations require an extension of payments into the third month after the layoff. Another condition is that the dismissed citizen does not return to work. This fact must be confirmed with the help of a certificate issued by the CZN.
In a situation where a person did not use vacation before terminating the employment relationship, this is compensated with money. The amount is equal to what should be paid as holiday pay.
For information on severance pay in case of staff reduction, see here:
Explanations
Art. 180 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation imposes on the employer the obligation to ensure internal employment of employees who are laid off. Among the criteria that apply to other work, it is established that a vacant position must be offered. Other requirements are set forth in Article 81 (Part 3) of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The employer has the right to offer the employee to perform the professional duties of a temporarily absent employee due to a long illness, being on a business trip, parental leave, etc. In this case, the manager must explain to the employee his responsibilities and notify him of the amount of earnings. This proposal must come from the employer not only directly on the day of notification of the upcoming layoff, but also during the period allotted for warning if positions suitable for the employee become vacant at the enterprise. Failure to comply with this requirement indicates that the manager is not properly complying with his duties regarding the employment of personnel.
Responsibilities of the employer during layoffs and liquidation
The Labor Code determines the actions of the manager when dismissing employees due to the termination of the enterprise's activities or a decrease in the number of personnel. The employer must promptly warn citizens about unscheduled terminations of contracts. The main responsibility of a company director is to offer employees new vacant positions. When reducing staff, the manager must find for an individual an equivalent specialty in a given institution or a lower position.
It is important to know! Cancellation of the contract occurs if the employee refuses to be transferred to another position. Article 180 of the Labor Code regulates the employer’s obligation, in the event of a mass layoff, to notify the trade union organization and take measures determined by the collective agreement or internal regulations.
Guarantees and compensation
Upon termination of a contract, the manager must pay severance pay to employees. Additional monetary compensation upon cancellation of the agreement due to liquidation of the enterprise:
- income for the period worked before dismissal;
- payment of unused days of annual leave;
- additional compensation for early termination of an employment contract;
- severance pay in the amount of average monthly profit;
- repayment of debts, including unaccrued bonuses, payment for business trips.
Citizens who have entered into a fixed-term contract of up to 2 months, as well as external part-time workers, do not receive additional funds. Seasonal workers are paid severance pay, the amount of which is the average earnings for 2 weeks.
If, after dismissal, the employee does not find an equivalent position, the manager is obliged to pay compensation within 60 days based on a written application and a copy of the work record book. The subsidy includes salary, bonuses, allowances, financial assistance for the birth of a child, death of a close relative, and retirement. The payment period can be increased to three months upon presentation of a certificate from the employment center confirming timely registration and the absence of vacancies. Severance pay before subsequent employment is not provided to pensioners who, by law, do not have the right to register with the labor exchange. The provided accruals are not subject to personal income tax or insurance premiums.
Citizens have the right to receive temporary disability benefits if a deterioration in their health status was recorded within 30 days after termination of the contract. Upon liquidation of an enterprise, compensation is calculated by the Social Insurance Fund based on the documents presented:
- sick leave certified by a medical professional;
- income certificate for calculating benefits;
- paper confirming insurance experience;
- written statement.
Pregnant women and women on maternity leave have the right to receive child care benefits within 12 months after the liquidation of the enterprise. To calculate compensation, employees must register with the employment service. Funds are paid by the territorial body of social protection of the population. The benefit is due upon presentation of a written application, a certificate of incapacity for work, a antenatal clinic certified by a doctor, an extract from the work record book, or a certificate of recognition of the citizen as unemployed.
Commentary on Article 180 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
1. When carrying out measures to reduce the number or staff of employees, the employer (organization, individual entrepreneur) is obliged to offer the employee another available job.
This rule corresponds to Part 3 of Art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, according to which dismissal on this basis is allowed only if it is found impossible to transfer the employee with his written consent to another job available to the employer. This can be either a vacant position or job, or a vacant lower position or lower-paid job that corresponds to the employee’s qualifications, which the employee can perform taking into account his state of health. When deciding whether to transfer an employee to another job, it is also necessary to take into account the employee’s real ability to perform the work offered to him, taking into account his education, qualifications, and work experience (clause 29 of the resolution of the Plenum of the RF Armed Forces on the application of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation by courts).
The employer must notify the employee of the availability of such a vacancy. At the same time, the employer is not obliged to offer the employee absolutely all available vacancies that do not meet the above criteria. Likewise, labor legislation does not provide for the obligation of an employer who has decided to reduce staff to send an employee for retraining to subsequently fill vacant positions that do not correspond to the employee’s qualifications (see the appeal ruling of the Moscow City Court dated December 12, 2012 in case No. 11-27662) .
The employer must offer the employee vacancies that meet the specified requirements that are available in the given area. The employer is obliged to offer vacancies in other localities only if this is provided for by the collective agreement, agreements, or employment contract.
Thus, in the appeal ruling of the Moscow City Court dated December 24, 2012 in case No. 11-25754, it is stated that since there are no such conditions in the collective agreement, agreement or in the employment contract of the parties, the employer has the right not to offer the employee vacancies in another location (even if they existed).
The Federal Law “On the State Civil Service of the Russian Federation” provides special guarantees for state civil servants. In accordance with Part 1 of Art. 31 of this law, when civil service positions are reduced or a state body is abolished, public service relations with a civil servant continue if the civil servant filling a reduced civil service position in a state body or a civil service position in a state body being abolished is given, with his written consent, another civil position service in the same state body or in the state body to which the functions of the abolished state body were transferred, or in another state body, taking into account: - the level of his qualifications, professional education and length of service in the civil service or work (service) in the specialty, area of training; - the level of his professional education and length of service in the civil service or work (service) in his specialty, area of training, provided that he receives additional professional education corresponding to the field of activity for this position in the civil service.
In development of these provisions, Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of September 19, 2013 N 822 approved the Rules for providing a state civil servant in the absence of vacant positions in a state body in which the positions of the state civil service are being reduced, or in a state body to which the functions of an abolished state body have been transferred, a vacant position state civil service in other government bodies.
2. Employees must be notified by the employer of the upcoming dismissal due to the liquidation of the organization or staff reduction at least two months before the upcoming dismissal. Thus, a warning to the employee indicating the date of the expected layoff can take place, for example, three or four months in advance.
The warning is issued to the employee personally, against his personal signature. As a rule, the employer presents the employee with an individual warning letter, the second copy of which bears the date of the actual warning of the employee and his signature.
If an employee is absent from work (for example, due to a long vacation), it is advisable to send him a warning by registered mail with acknowledgment of receipt. From the date the employee receives the warning, a two-month period will begin, after which the employer has the right to issue an order to dismiss the employee under clause 1, part 2 of Art. 81 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
In general, the employer should keep in mind that, in accordance with the explanations given in paragraph 29 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation on the application by the courts of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, termination of an employment contract with an employee on this basis is possible only if he did not have a preemptive right to remaining at work and was duly warned about the upcoming dismissal.
3. The employer, with the written consent of the employee, has the right to terminate the employment contract with him before the expiration of a two-month period. At the same time, the condition that it is mandatory to officially warn the employee about the upcoming layoff, even if there is such an agreement, remains in force.
In this case, the employer is obliged to pay the employee additional compensation in the amount of his average earnings, which is calculated in proportion to the time remaining before the expiration of the period specified in the notice of dismissal.
It must be emphasized that this option is possible only with the mutual consent of the employee and employer.
According to the explanations given in the Review of Legislation and Judicial Practice of the RF Armed Forces for the first quarter of 2007, approved by the resolution of the Presidium of the RF Armed Forces dated May 30, 2007 (issue 18), the guarantee established by Art. 180 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation regarding the payment of additional monetary compensation also applies to a civil servant subject to dismissal from the civil service due to a reduction in the position he is filling.
4. To make a decision on reducing the number (staff) in relation to employees who are members of a trade union, a number of features are provided.
According to Art. 373 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation when making a decision on the possible termination of an employment contract with such employees under clause 2, part 1 of art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer is obliged to send to the elected body of the primary trade union organization the corresponding draft order and copies of documents that are the basis for making this decision. The said body, within seven days, expresses its reasoned opinion to the employer in writing.
Also in accordance with Art. 374 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, dismissal on this basis of heads (their deputies) of elected collegial bodies of primary trade union organizations, elected collegial bodies of trade union organizations of structural divisions of organizations (not lower than shop floors and equivalent to them), which are not released from their main work, is allowed, in addition to the general procedure for dismissal, only with the prior consent of the relevant higher elected trade union body. The same applies to cases of termination of an employment contract under clause 2, part 1 of Art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation with the head of the elected body of the primary trade union organization and his deputies for two years after the end of their term of office.
Provided by Art. Art. 373, 374 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the procedure for dismissing workers from these categories is mandatory for the employer. Thus, according to the appeal ruling of the Kemerovo Regional Court dated September 5, 2012, in case No. 33-8392, the claim for declaring the dismissal illegal, reinstatement, recovery of wages for the period of forced absence, compensation for moral damage and expenses for the services of a representative was granted, since the issue of the preferential right to remain at work in relation to the employee was resolved without taking into account the reasoned opinion of the elected body of the primary trade union organization.
Also Art. 82 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation contains a condition that is subject to application regardless of whether the employees subject to dismissal under clause 2, part 1 of art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, members of the trade union. In any case, when making a decision to reduce the number or staff of employees of an organization, individual entrepreneur and the possible termination of employment contracts with employees on this basis, the employer must notify in writing the elected body of the primary trade union organization (if there is one at the enterprise) no later than two months before the start of activities related to the reduction.
In the event that such a decision by the employer to reduce the number (staff) of employees may lead to mass dismissal of workers, the notification is made no later than three months before the start of the relevant measures. The criteria for mass layoffs when reducing the number or staff of an enterprise's employees are determined by clause "b" part 1 of the Regulations on the organization of work to promote employment in conditions of mass layoffs, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of February 5, 1993 N 99 "On the organization of work to promote employment in conditions of mass release."
Also, according to Part 2 of Art. 25 of the Law of the Russian Federation “On Employment of the Population in the Russian Federation” when making a decision to reduce the number or staff of employees of an organization, an individual entrepreneur and the possible termination of employment contracts between employer and organization no later than two months, and an individual entrepreneur no later than two weeks before the start of the relevant activities must be reported in writing to the employment service authorities. In such a message, the employer indicates the position, profession, specialty and qualification requirements for them, as well as the terms of remuneration for each specific employee. If a decision to reduce the number or staff of an organization’s employees may lead to mass layoffs of workers, the employer notifies the employment service authorities of this no later than three months before the start of the relevant measures.