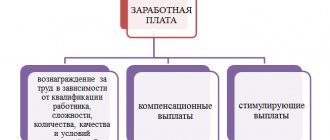
Where and how does the employee labor savings fund disappear?
It's no secret that quite often the salary of one employee turns out to be much lower than the salary of another employee. Moreover, this happens in the absence of objective reasons for this. It happens everywhere and everywhere, regardless of any organizational and legal form of organization, enterprise, institution. Occurs regardless of whether the workers have a trade union organization or a representative of the workers’ collective.
Let's try to figure out why this happens, and, most importantly, why does it live and continue to live? First you need to understand where, where and what money is sent for various payments to employees.
At one time, when I took such a subject as “Financial Law” at the Law Academy, the teacher approached our knowledge loyally. He said: “A lawyer and an accountant are incompatible things.”
He's probably right about something. But as they say, there are always exceptions to every rule. And such exceptions are lawyers with inquisitive minds who always want to get to the truth.
This is me, including about myself. Modest and quiet. So, in any organization, in any enterprise and in any institution, a wage fund (wage fund) is formed.
As a rule, the wage fund consists of: Tariff fund, which includes remuneration of employees according to the staff schedule, taking into account payments for special working conditions. Additional fund for paying bonuses for continuous work experience at a given place. Additional funds for night work , holidays, to replace people going on vacation, etc.
Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Republic of Belarus dated N 04-1-9
Funds not used to pay a one-time health benefit can only be used to pay health benefits to employees who are entitled to these payments, but who have worked for a short time in this government agency.
Law of the Republic of Belarus “On Civil Service in the Republic of Belarus”, Decrees of the President of the Republic of Belarus dated 02/09/2004 N 58, dated 02/12/2004 N 66, dated 12/13/2004 N 77 and 78, Resolution of the Council of Ministers of the Republic of Belarus dated 03/29/2004 N 347 and the resolutions of the Ministry of Labor and Social Protection adopted in furtherance of these decisions, changes were made to the conditions of remuneration for employees of government bodies.
The wage savings fund, where does it go?
Limon Question asked March 24, 2013 at 9:31 pm Hello! I work at Children's Home No. 3 Frunz.
district. Shift work. The employees of the orphanage have a clear assumption that wages are underpaid, because... each group employee performs a double workload (serves children in excess of the norm), accordingly there is a large shortage of employees (m/s, teachers and nannies), this results in good savings in the wage fund.
Where should these savings be spent at the end of the year? Group employees are not given anything; they are always told that there is no money, that all savings are spent on repairs and fines.
A friend of mine works in the accounting department, she calculates wages, and I know that all savings are divided between managers and their associates by calculating various intensities. How legal is this? Pavlov Published on March 24, 2020 at 09:43 pm Published on March 24, 2020 at 09:43 pm If this issue is related to labor law, it is very distant. This question is more likely for economists.
Typically, the labor savings fund consists of salaries for vacant positions and savings on sick leave, which are paid by the Social Insurance Fund.
How the saved money is distributed is a matter of local regulation (for example, in accordance with the regulations adopted by the institution on the procedure for forming and spending the wage savings fund); in some organizations this is not regulated at all, but is at the sole discretion of the manager.
Using payroll savings
Within the limits of savings provided for wages in the institution’s government budget for the current year, it is possible to pay financial incentives to employees.
But this payment must be provided for in the local act of the establishment, for example in the provision on bonuses), then the approval of the founder will not be required.
1. Recommendation: Accounting for expenses for financial assistance to former employees If a local act of a government institution provides for the payment of financial assistance to a former employee or members of his family, it should be remembered that the accounting for this situation has nuances.
Before preparing annual reports, we recommend double-checking whether the accounting is organized correctly. Recipients of budget funds (state institutions) have the right to pay financial assistance to former employees or members of their families only if there are relevant regulations (). Financial assistance is provided on the basis of an order (order) from the head of the institution, which indicates the last name, first name, patronymic of the recipient of assistance, the amount and reason for the payment.
The order is usually issued on the basis of an application from the person receiving financial assistance.
The former employee must attach relevant supporting documents to the application for payment. But in some cases, the initiative may come from the management of the institution.
For example, when the reason for payment is the occurrence of certain circumstances (death, illness, fire, etc.). Financial assistance is usually paid to employees
We recommend reading: What payments are there for a second child in Moscow
What is the formula and how is the wage fund calculated?
Any hired labor, being the main activity of a person, must be paid.
In other words, the end result of any work is receiving a reward for it. When finding employment, an employee expects a certain payment, agreed upon in advance and reflected in the relevant documentation. Remuneration involves not only the regular receipt of wages by employees. In enterprises that care about their staff, employees usually receive not only the amounts intended to be paid according to the salary or tariff schedule, but also additional funds provided for by the internal policy and/or industry characteristics of the organization.
How to calculate the amount of payroll savings
/ / According to the calculations obtained in Table 9 “Determination of relative savings or overexpenditure of the wage fund in 2010”, it is clear that in general for the economy and in comparison with the plan, there is a saving in the wage fund of workers in the main production due to a decrease in the average annual wage and the number of employees.
Stimulating the growth of labor productivity is also achieved as a result of expanding the team's morale to use savings in the wage fund. The resulting savings are used for additional payments to workers, engineering and technical workers and employees in the amount of up to 50% of the tariff rate (official salary) for combining professions or an increase in the volume of work performed due to a reduction in numbers compared to the approved and standards; additional wages for workers, engineers -technical workers and employees for high professional skills a one-time remuneration for the implementation of technically obos [p.95] Payroll tax rates depend on the civil legal form of the business entity.
An employer who is an individual entrepreneur pays payroll taxes not only for his employees, but also for himself.
Affects the amount and form of payments and the citizenship of the employee. The personal income tax rate levied on a citizen of the Russian Federation in 2016 is 13%, on a non-resident - 30%. Accounting at the Sterlitamak CHPP is carried out in accordance with the Law “On Accounting” dated November 21, 1996 No. 129-FZ, Regulations on Accounting and Reporting in the Russian Federation dated July 29, 1998.
Analysis of the labor fund and wages
In the organization, the wage fund in 2003 compared to 2001 increased by 396 thousand rubles. and compared to 2001 - by 804.4 thousand rubles, including for each article. Having studied the structure of the fund, we can say that the largest share in the structure of the fund falls on time-based payment.
Comparing the average monthly wages by employee category for 2004, we can say that the highest wages are for managers - 3,452.9 rubles, which is explained by higher official salaries. The lowest salary level for employees is 1119.3 rubles, which indicates the lowest salaries in the meat processing plant ( Appendix
8
)
Conclusion.
Distribution of the salary savings fund for the year
Working as a teacher in a kindergarten, while on vacation From 10.11 to 15.12, the employer paid the teachers money from the wage savings fund, but they did not pay me, arguing that in the month of December I did not work a single day, is this legal? ?
January 12, 2020, 05:13, question No. 680923 Anna, Dalnegorsk Clarification of the client while on vacation from November 10, 2014 to January 15, 2015 January 12, 2020, 05:49 Collapse Online legal consultation Response on the website within 15 minutes Answers from lawyers ( 2) 139 answers 55 reviews Chat Free assessment of your situation Lawyer, Tyumen Free assessment of your situation Good afternoon, Anna!
If money was distributed from annual wage fund savings, then all employees must be paid in proportion to the time worked for the year. This is logical. But in fact - you need to familiarize yourself with the normative act (Regulations) regulating the distribution of saved funds. Try contacting the Education Department of your kindergarten for clarification.
Best regards, Elena Strakhova. January 12, 2020, 09:08 0 0 3647 replies 1090 reviews Chat Free assessment of your situation Petin Dmitry Lawyer,
Engels Free assessment of your situation
- 3647responses
- 1090 reviews
Good afternoon.
To answer your question, you need to know your local regulations regarding the distribution of these funds. If it is impossible to post for review
The procedure for determining wage fund savings using examples
/ / 2.3.
Funds in the amount of 10 percent of the planned wage fund are provided for the establishment of bonuses for managers, specialists and employees for high creative achievements in work, the complexity and intensity of work, as well as for the performance of particularly important (urgent) work. Using this indicator, wage costs for employees of different structural divisions and categories are analyzed, costs are adjusted and optimized, and rates, salaries, and prices are adjusted. It is from the amount of the fund that all payments provided for by law are calculated: pension contributions, insurance contributions, etc.
d. You can save on taxes by replacing part of the cash payments with real ones. Tax legislation allows tax-free gifts whose value does not exceed 4,000 rubles.
There is no need to pay taxes on the same amount of funds if they are registered as financial assistance. A multi-shift mode is considered to be a mode when during the day work is organized in 2 or more shifts, the duration of each of which is not less than the duration of working hours established by law.
In this case, workers alternate shifts evenly every other week at the hours determined by the schedule. 2.1. The period for the formation and use of payroll savings is the calendar year from January to December inclusive.
The source of additional payment for combining professions (positions) is the savings in the wage fund obtained from the release of the number of workers in comparison with inter-industry and sectoral staffing standards, staffing approved on the basis of standard staffing levels, service standards, production (time) standards, as well as labor standards. costs approved by a higher organization, and at newly commissioned enterprises, facilities and workshops - all wage fund savings obtained as a result of performing work with a smaller number of personnel compared to the design one.
[p.16] Salary fund savings, rub. [p.80] Salary fund savings, rub., per year [p.81]
The value of the CTU is determined in accordance with the Basic Methodological Provisions for the distribution of the total part of team earnings using the labor participation coefficient. The team's wages, paid for the results of the team's work and distributed with the help of the CTU, include piecework earnings and bonuses, part of the savings in the wage fund of temporary workers obtained as a result of the release of personnel and not used for additional payments or allowances to tariff rates and salaries for individual members of the team for combination of professions. [p.217]
In the tenth five-year plan, much attention was paid to incentives for reducing unit labor costs. Linear rates for this indicator were at an extremely high level. They provided contributions to the material incentive fund of up to 60% of the amount of savings in the wage fund obtained as a result of reducing the labor intensity of servicing wells in oil producing associations. This contributed to an increase in labor productivity and a reduction in unit labor costs in the industry by 19.4%. In the Eleventh Five-Year Plan, the role of this fund-forming indicator was strengthened due to the fact that unit labor costs in the industry are planned to be reduced by 18% by 1985. [p.248]
The effectiveness of methods for stimulating the achievement of high performance in the enterprise as a whole, the development of the creative initiative of workers, and increasing the interest of each employee in improving the results of their work and the team as a whole depend on the chosen forms of remuneration. Therefore, the USSR Law on State Enterprises (Associations) states that an enterprise is obliged to use wages as the most important means of stimulating the growth of its productivity, accelerating scientific and technological progress, improving product quality and increasing production efficiency. At the same time, the enterprise has the right to independently determine the forms and systems of remuneration, introduce various forms of additional payments within the limits of wage fund savings, establish official salaries, and determine bonus systems. [p.84]
Stimulating the growth of labor productivity is facilitated by the transition to normative wage planning and the expansion of the rights of enterprises to use savings in the wage fund against the standard, the introduction of wages taking into account the KTU, material incentives for increasing production output with a smaller number of industrial personnel, wages based on final results, etc. [c .95]
To reward individual workers for high production performance, exemplary work and successful completion of tasks, a foreman fund is created in the amount of 3% of the planned wage fund for the site, if there is a wage fund savings at this site. The part of the fund not spent in a given month can be used over the next three months. [p.96]
Analysis of the implementation of the wage plan helps to increase the efficiency of spending funds allocated to pay employees. The analysis begins with determining the absolute and relative overexpenditure (or savings) of the wage fund (Table 4.6). [p.251]
From the calculation it follows that the company has relative savings in wages, which should be assessed positively. [p.252]
In our example, as a result of reducing the number of personnel, wage fund savings amounted to 8.48 thousand rubles, and due to an increase in average earnings, the overexpenditure amounted to 12.28 thousand rubles. As a result, the absolute overexpenditure is 3.8 thousand rubles. (12.28—8.48). [p.252]
Unused wage fund savings can be transferred to the material incentive fund at the end of the year only if there is a corresponding excess profit. It is advisable to give the enterprise the right to transfer wage fund savings to the material incentive fund at the expense of the total actual profit before its distribution. [p.130]
The task of analyzing the level of qualifications of workers also includes studying the reasons for deviations of the established categories of workers for each profession from the staffing table or from the category of work performed in order to bring them into compliance. Current practice indicates that the use of workers in jobs charged according to other categories is undesirable. Additional payments for the performance of work of low grades by workers of higher grades increase labor costs per unit of output and cause unproductive expenses on wages, and the performance of more complex work that does not correspond to the qualifications of workers leads to a decrease in product quality, an increase in the level of defects and unjustified savings of the fund wages. [p.81]
Relative savings of the wage fund and Roma perishable-production personnel-.in for the previous (1986) year [p.96]
At the end of the year, unused wage fund savings received against the established standard or planned wage fund are transferred to the FMP of enterprises, subject to the implementation of the production plan and targets for increasing labor productivity. If the wage fund is overspent, FMP funds are allocated to cover it (within the limits of wage fund savings transferred to this fund in the previous year). [p.335]
The above-tariff part usually includes piecework and all types of collective bonuses from the wage fund and the material incentive fund for the current bonus payment for combining professions, expanding service areas and increasing the volume of work performed, determined as a whole for the team; wage fund savings obtained from release of personnel and not used for additional payments for combining professions, expanding service areas and increasing the volume of work performed, one-time rewards for revising standards at the initiative of the team and other types of collective payment. [p.169]
The Ministry has been given the right to establish bonuses to the official salaries of enterprise managers by saving wages. [p.132]
According to the second method of forming the general wage fund of an enterprise, the base fund for a given year is the wage fund for the previous year, which increases by the amount of relative savings in the wage fund and decreases by the amount exceeding [p.133]
In order to increase the interest of departmental labor collectives in increasing labor productivity and reducing numbers, they can use part of the savings in the wage fund for additional payments and allowances, which will be canceled if work deteriorates. [p.322]
It should be noted that the introduction of these increased tariff rates is carried out due to savings in the wage fund obtained from a reduction in the labor intensity of work as a result of the revision of time standards (for piecework payment) or the release of temporary workers as a result of the transition to work according to standardized tasks, calculated on the basis of technical reasonable norms and standards for labor. [p.241]
If the wage fund is overspent, funds from the material incentive fund are allocated to cover it (within the limits of wage fund savings transferred to this fund in the previous year). [p.237]
The Kuibyshev synthetic rubber plant was the first to adopt the Shchekino experiment. As a result, in the first half of 1969, wage fund savings of 89.9 thousand rubles were achieved, 423 people were released, average wages and labor productivity increased by 1.4%. [p.317]
In the Bashkir experiment, 30% of the wage fund savings received at enterprises as a result of the release of workers was transferred to a centralized association fund, where it was redistributed between factories taking into account coefficients characterizing the level of rationing and growth in labor productivity. In 1969 (the first year of the experiment), 1,659 people were released from existing production facilities, including engineers and office workers—146 workers—1,513. [p.317]
If there are savings in the wage fund for the enterprise as a whole, the head of the enterprise has the right to pay bonuses in full to the management employees of the enterprise, services and workshops who have improved their work, but have not yet compensated for the overexpenditure of the wage fund committed during the previous period. [p.333]
Salary fund savings, thousand rubles. 450 380 [p.76]
The Bashkir experiment was that 30% of the wage fund savings obtained in enterprises as a result of the release of workers was transferred to a centralized association fund. The association redistributed this fund between factories, taking into account coefficients characterizing the level of rationing and. growth in labor productivity. [p.237]
According to the Resolution (1979) of the Central Committee of the CPSU and the Council of Ministers of the USSR, unused savings from the wage fund against the standard or plan are transferred to the material incentive fund. [p.245]
Experience using the KVO method is widely distributed among industry enterprises. The number of laid-off workers since the beginning of its implementation amounted to 1,508 people, wage fund savings amounted to 3,074.4 thousand rubles. [p.101]
Analysis of the implementation of labor standards, changes in technical, organizational, economic and psychophysiological working conditions serve as the basis for revising the standards. To stimulate workers' initiative to revise standards, up to 50% of the resulting wage fund savings are used for additional payments to workers for three to six months, with the largest additional payments being received by workers whose work is standardized according to intersectoral and industry standards. [p.115]
Stimulating the growth of labor productivity is also achieved as a result of expanding the team's morale to use savings in the wage fund. The resulting savings are used for additional payments to workers, engineering and technical workers and employees in the amount of up to 50% of the tariff rate (official salary) for combining professions or an increase in the volume of work performed due to a reduction in numbers compared to the approved and standards; additional wages for workers, engineers -technical workers and employees for high professional skills a one-time remuneration for the implementation of technical equipment [p.95]
The basic wage fund for a given year is the wage fund as reported for the previous year, increased by the relative savings in the wage fund or reduced by its relative overexpenditure. [p.249]
The analysis usually begins with establishing the amount of savings (I overexpenditure) on the wage fund of industrial production personnel. To determine the absolute deviation, it is necessary to compare the actual accrued amount of wages with its planned fund. An excess of the actually accrued amount of wages against its fund according to the plan means an absolute overexpenditure, and vice versa, if the actually accrued wages are less than the planned fund, the difference indicates the presence of absolute savings in the wage fund. It is necessary to establish what factors caused the overexpenditure or savings on the wage fund. [p.94]
From the table 4.10 it is established that the basic wage fund for industrial and production personnel, due to relative savings in the wage fund, increased to G>782.3 thousand rubles. (5769.0+13.3). [p.95]
Of significant importance is the analysis of the validity of the quarterly distribution of the annual base wage fund, taking into account changes in the structure and labor intensity of products in comparison with the previous year. From the practice of industrial enterprises, it follows that in a number of enterprises that were transferred to new working conditions, due to an overestimation of the basic wage fund in the plans for individual quarters of the year, violations of the proportions between the growth rates of labor productivity and average wages were allowed. This led to the fact that enterprises had unjustified savings in the wage fund, which served as a source of allowances and additional payments to the salaries and tariff rates of employees. Analysis of the actual use of the wage fund in [p.95]
Relative overexpenditure (I-) or savings (-) of the wage fund 1II1II (ip. Г> - p. 5) [p.97]
The economic effect of reducing unit labor costs is not limited to industrial production indicators. The release of some industrial production personnel makes it possible to reduce the number of employees in service farms of the non-industrial group and capital investments in non-industrial construction in new oil regions of the country. The importance of reducing unit labor costs for increasing production efficiency in the oil industry required a corresponding strengthening of material incentives in this direction. For this purpose, about 10% of the entire material incentive fund created in the industry was formed according to the standards of deductions from the mass of the estimated profit for each percent reduction in unit labor costs. Thus, about 60 kopecks were sent to the material incentive fund. from every ruble of relative savings in the wage fund, which made oil producing enterprises interested in implementing measures to automate production and reduce labor costs. [p.141]
The strengthening of the material interest of enterprises in saving living labor is facilitated by the cheek method being introduced at oil refineries. The wage fund savings achieved in this way are used for [p.244]
In the chemical industry, advanced methods of organizing production and material incentives arose and were developed. The Tekin method, which involves increasing production output while reducing the number of employees, has become most famous. The savings in the wage fund received from the release of personnel are spent on additional payments for increasing the volume and improving the quality of work, paying one-time bonuses for the development and implementation of measures to increase labor productivity and reduce the number of industrial production personnel. The release of workers is carried out by expanding service areas, increasing production standards, combining professions and mastering related ones, etc. The Shchekin method has found widespread use, first in the nitrogen enterprises, and then throughout the chemical industry. It was further developed in the Polotsk production association Polymir, where a method of comprehensive equipment maintenance was developed and implemented. [p.76]
Payroll savings
Contents Economic mechanism Regulations for school accounting services, reporting forms (report on wage fund savings, report on the use of cost estimates).
In this case, calculation of payroll savings for December is made no later than December 10 on the basis of primary documents available on this date confirming the availability of savings. In Russian legislation, the formula for calculating the payroll is not clearly established.
Analysis of types of financial statements. Regulatory - per capita financing. Lecture 3 Regulations on accounting services for schools, reporting forms (report on wage fund savings, report on execution of cost estimates).
We recommend reading: Deadlines for filing income tax returns
All organizations of any organizational and legal form of ownership are required to prepare financial statements based on synthetic and analytical accounting data, which is the final stage of the accounting process.
Accounting statements in established forms contain a system of comparable and reliable information about sold products, works and services, the costs of their production, the property and financial position of the organization and the results of its economic activities.
The financial statements consist of - a balance sheet, - a profit and loss statement, appendices thereto and an explanatory note, - as well as an auditor's report confirming the reliability of the organization's financial statements, if they are subject to mandatory audit in accordance with federal laws. If, when preparing financial statements, based on the rules of PBU 4/99, the organization reveals insufficient data to form a complete picture of the financial position of the organization, the financial results of its activities and changes in its financial position,
How to save on employee benefits
The need to save on employee benefits may arise in many cases. In this article we will look at ways to reduce such costs.
One of the mandatory clauses of an employment contract is the condition on remuneration (Part 2 of Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). It cannot be changed only at the request of the employer (Art.
72 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). If it is necessary to minimize labor costs, the employer, without violating labor legislation, can unilaterally: - change the structure of the wage fund (if the wage system is established by a local regulation and not a collective agreement); — to reduce the number of employees; - attract cheaper labor; — reduce the production load on workers. The tax burden on the payroll fund is reduced through the use of outsourcing, outstaffing and a simplified taxation system. TO WHAT MAXIMUM WAGES CAN BE REDUCED Labor legislation provides for two restrictions that the employer must remember when setting wages for his employees.
Let's talk about this in more detail. Minimum wage The monthly salary of an employee who has fully worked for this period and fulfilled his job duties cannot be lower than the minimum wage (Part.
3 tbsp. 133 Labor Code of the Russian Federation). From September 1, 2007, constituent entities of the Russian Federation have the right to establish their own minimum wage (Part 1 of Article 133.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). It cannot be lower than the minimum wage established by Federal Law No. 82-FZ dated June 19, 2000 “On the minimum wage.”
Optimization and savings of wages and salaries fund funds: how to make a reduction, and what are the reduction reserves?
Free legal advice: All Russia » » » » Good news for employers and not so good for their employees. State Duma deputies rejected a bill on a special wage fund, which would have been used to pay off the debts of insolvent employers.
The state was asked to guarantee payments.
From October 1, 2020, the minimum wage for Muscovites will increase by 261 rubles. Employers will have to pay employees from the capital at least 17,561 rubles. Finding opportunities at an enterprise to increase wages requires the mobilization of all technical, organizational, economic and social factors to increase production efficiency and comprehensively improve the organization of wages.
– wage fund savings obtained through the implementation of additional measures to increase labor productivity, reduce labor intensity, reduce the number of personnel, reduce lost working time, and increase production volume; – wage fund savings achieved as a result of measures to improve the organization of wages (revision of labor costs and prices, bonus payments, allowances and additional payments). With time-based wages, the wages are set depending on the quantity
Legitimate savings. How to optimize the salary fund?
Every entrepreneur strives to increase the profitability of his business, for which there are two logical ways - increasing income and reducing costs.
Today we will talk about one of the largest expense items for most enterprises - salary fund .
Often, company management understands by optimizing wages to be a banal staff reduction, pressure on employees, and even a requirement to “leave of their own free will.” Although there are legal and much less sensitive optimization methods for personnel.
The first step is staff analysis
Before taking any action in the field of business management, it is necessary to understand what is causing the current difficulties in staffing and employee costs. It is necessary to conduct a financial and economic analysis of economic activity, based on the results of which it is necessary to determine optimization methods and its goals.
— If the company is in a critical condition and cannot maintain the current staff, it will not be enough to reduce costs for each employee, this will require a real reduction in the number of personnel (Clause 2, Part 1, Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
— If the company is in a stable state, growth potential is visible, there is no need to reduce the number of employees, it is quite possible to optimize the organizational structure of the company, increasing the quality of administration and optimizing costs for each employee (application of Article 74 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
Optimization without shortcuts:
Compensation payments
The employer has the right to compensate employees for food expenses, cellular communications, transportation costs, and so on (Chapter 34 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Compensations can make up a significant portion of the money paid to employees, but in the event of claims and questions from supervisory authorities, they will have to prove the validity of the compensation.
Compensations can be specified in employment contracts, which means they can be taken into account when calculating taxes, as expenses, as labor costs (clause 25 of Article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). However, compensation will be subject to the same taxes and insurance premiums as regular salary.
If compensation is not provided for in the contract, but is specified in the internal acts of the organization, such as an order of the manager, the payment is considered not related to wages and is not subject to insurance contributions. Thus, if part of the costs for employees consists of compensation, the employer can save on insurance contributions to the Russian Pension Fund (22%), the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund (5.1%) and the Social Insurance Fund (2.9%). In total, if an employee receives 5,000 rubles as compensation, the employer saves 30%—1,500 rubles in insurance premiums.
Risks! Compensations should not lead to a significant reduction in salaries. If, as a result of such optimization, employee salaries turn out to be significantly lower than the market average, and the amount of costs turns out to be unreasonable, the tax office may interpret this as an evasion of responsibility, threatening serious fines.
Registration of employees as individual entrepreneurs
This operating model allows the company to save not only on insurance payments (30%), but also on personal income tax (13%). However, it is quite risky, since supervisory authorities and the court may qualify cooperation with a large number of individual entrepreneurs as an attempt to evade taxes.
However, it is quite applicable for employees who traditionally work in outsourcing and offer their services to other companies and individuals: accountants, lawyers, authors, sales people, drivers, and so on. To prove the legality of such optimization, individual entrepreneurs must have different partners and not depend on one company - the customer of the services.
Replacing a director with a manager of an individual entrepreneur
The essence of saving in this case is no different from the previous point. The director of the company is paid a salary, subject to insurance contributions and personal income tax. An individual entrepreneur independently pays taxes, which range from 6% (USN). However, tax authorities can re-qualify such relationships if they see in the agreement with the manager the guarantees and standards characteristic of an employment contract: working week, vacations and business trips.
To minimize such risks, the contract with the manager should be as different as possible from the labor contract:
- exclude vacation, sick leave, employment and working conditions and other guarantees related to labor law;
— the manager’s remuneration should not be fixed, it depends on the organization’s profit;
— the purpose of concluding an agreement is to overcome the crisis, achieve a certain level of profit, optimize the organization’s work, etc.
Renting personal transport and office equipment from employees
Rental payments are not subject to any types of insurance premiums. And if an employee uses a personal car or his own computer for work, they may well become the object of rent from the employer. In this case, the only payment above the rental amount will be personal income tax.
All the indicated optimization methods without reduction have serious risks. First of all, this is retraining in labor relations and payments. If the tax office proves through the court that the employer avoided responsibility to employees and the state, this threatens with serious fines. However, if these measures are justified, the auditors will not be able to find fault with them. What does switching to individual entrepreneurs or compensation do for employees instead of part of their salary? Opportunities open up for individual entrepreneurs to collaborate with new customers and go on an independent business journey. In addition, by supporting the company, employees will help avoid unwanted layoffs, and reducing the company's costs may mean that it can use some of the funds directly to support staff. However, in all optimization methods it is worth knowing when to stop and not cross the line, which takes you beyond the limits of legal methods of cooperation.
Especially for HONEST BUSINESS
Vavina Elena
The editor's opinion may differ from the author's opinion