Salary payment deadlines in 2020
In accordance with Art. 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, salaries are paid no less than every half month and no later than 15 calendar days from the end of the period for which they were accrued. Specific deadlines are not established in the legislation: they must be specified in the employer’s local regulations: collective agreement, employment contract, internal labor regulations. Taking into account the requirements of the code, you need to pay:
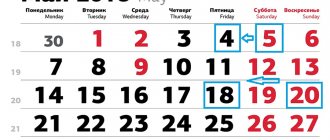
- salary for the first half of the month - no later than the 30th (31st) day of the current month;
- for the second half of the month - no later than the 15th day of the next month.
Paying salaries every half month and twice a month is not the same thing. For example, by paying wages on the 5th and 18th, you pay wages twice a month, but violate the permissible interval between payments - 15 days.
Correct option: salary for the first half of the month is paid on the 25th, and for the second half of the month - on the 10th of the next month.
It is unacceptable to set a salary payment period instead of indicating the exact day (letter of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation dated November 28, 2013 No. 14-2-242). The wording “salaries are paid no later than the 10th and 25th of each month” is similarly unsafe.
If the salary payment date falls on a weekend, it is paid on the day preceding the weekend. In other cases, it is impossible to pay wages before the due date. Although the rights of workers are not violated, the labor inspectorate may, with a small probability, impose a fine for this. The problem is that a violation of the 15-day period may occur, and in addition, local regulations will not correspond to the actual procedures of the company.
The rules of Article 136 of the Labor Code are mandatory for everyone. They cannot be violated even at the request of an employee who wants to receive a salary once a month in full.
The Labor Code establishes the obligation to pay wages at least every half month. This means that you cannot pay less often, but you can please your employees with weekly or even daily payments without restrictions.
Early: is it possible?
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation, as amended in 2020, does not contain a ban on early payment of wages, and liability in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is provided only for delayed payment of wages.
However, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation also requires that wages be paid every half month, and the date of payment itself must be fixed. However, the employer will not make changes to the employment contract or internal labor regulations every time an early payment is made.
Therefore, formally, payment of wages on dates other than those established falls under a violation of wages (Part 1 of Article 142 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) and can be regarded as a violation of labor legislation under the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation (Part 1 of Article 5.27 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
Conclusion: if you pay early, there is a risk that there will be more than half a month between payments.
https://youtu.be/81sPQ0KkDx8
Salary for the first half of the month
The Labor Code does not contain the concept of “advance”. In accordance with the position of Rostrud (letter of Rostrud dated 09/08/2006 N 1557-6), when paying wages for the first half of the month, you must be guided by the information in the time sheet and pay wages according to the time actually worked.
This payment procedure causes difficulties, because... in accordance with the Tax Code and the position of the Ministry of Finance, personal income tax must be calculated based on monthly results, taking into account the provision of standard deductions. In addition, other deductions (for example, alimony) are also calculated from the salary for the entire month. Therefore, it turns out that if you make payments for the first half of the month according to the time actually worked, but without taking into account deductions from your salary, then the salary for the second half of the month will be less, because When calculating, you will need to take into account salary deductions for the entire month.
Therefore, most accountants calculate salaries for the first half of the month in the form of an advance: they set each employee an amount that is approximately half of the amount payable for the month (including deductions) and pay it without dividing it into specific additional payments, allowances and without withholding income tax. And after the end of the month, all types of accruals and deductions are calculated, the total amount payable for the month is determined and the advance payment already paid is subtracted from it. This is the salary for the second half.
Approach each employee individually. If an employee was on vacation for the entire first half of the month, he does not need to pay an advance, because he has already received vacation pay for this period. If the employee did not work for some reason or worked less time, then the amount of the advance must be reduced.
You won't miss anything in payroll
“Accounting is a convenient program. Thanks to the developers. I have been working with Kontur for a long time. And it’s convenient to manage personnel; you’ll never miss anything in payroll. Taxes are calculated on their own. All reports reach the recipient on time. Everything is updated with the times. I really like it, everything is convenient. And when something is unclear, you can call - and they will always come to your aid. Thanks again to the developers."
Natalia Abbasova, accountant, senior Veshenskaya, Rostov region.
Responsibility
It’s better to pay your salary at least every half month (Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Inspectors have the right to fine the employer for the first violation in the amount of up to 50,000 rubles. The manager as an official faces a fine of up to 20,000 rubles. For repeated violations, the fines are higher, and directors may be disqualified. There are court decisions that confirm the legality of fines (appeal ruling of the Saratov Regional Court dated April 2, 2015 in case No. 33-1840/2015).
There are also other sanctions for violating the terms of payment of wages. For days when the interval of half a month between the payment of the advance and the final payment of wages exceeded, the employee is entitled to compensation (Article 236 of the Labor Code).
Early payment of wages is not expressly prohibited in the Labor Code. It is safer to pay wages ahead of schedule not regularly, but on a one-time basis. Indicate in the wage regulations the possibility of early payment at the request of the employee.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Responsibility for violation of terms of payment of advance payment and salary
Late payment
Article 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for financial liability for non-payment of wages on time. Interest is accrued daily on the amount that has been withheld. From October 3, 2020, their size was increased to 1/150 of the discount rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation per day, including the day after the established payment deadline and the day of actual settlement. This is the minimum amount of compensation, but the employer can increase it on its own initiative. Compensation is paid along with payment of the delayed amount.
Compensation is awarded regardless of whether the employer is at fault for violating payment deadlines.
In addition to financial liability, there is administrative liability for late wages - a warning or a fine.
| Who will be fined | Primary penalty | Repeated fine |
| Executive | 1,000 - 5,000 rubles | 10,000 - 20,000 rubles |
| Guilty IP | 1,000 - 5,000 rubles | 10,000 - 20,000 rubles |
| Guilty legal entity | 30,000 - 50,000 rubles | 50,000 - 70,000 rubles |
A repeated violation is considered non-payment of wages within a year from the date of entry into force of the decision on the first fine.
An employee has every right to boycott a negligent employer. Article 142 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, if wages are delayed by more than 15 days, allows:
- notify the employer in writing of the delay;
- not showing up for work until you receive your paycheck;
- coming to work and messing around in the workplace.
You must return to work no later than the next working day after the employer informs you in writing that it is ready to pay wages on the day the employee returns.
Not every employee can afford such behavior. Civil servants, rescue workers, employees of defense enterprises and law enforcement agencies are required to report to work and perform official duties.
According to Art. 142 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, during the suspension of work the employee retains his average earnings. Therefore, the manager must also pay the worker for downtime.
Payment ahead of schedule
If an employer unreasonably pays wages ahead of schedule, then he violates Article 142 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. This can be assessed as a violation of labor legislation and punished in accordance with Part 1 of Art. 5.27 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, similar to salary delays.
| Who will be fined | Primary penalty | Repeated fine |
| Executive | 1,000 - 5,000 rubles | 10,000 - 20,000 rubles |
| Guilty IP | 1,000 - 5,000 rubles | 10,000 - 20,000 rubles |
| Guilty legal entity | 30,000 - 50,000 rubles | 50,000 - 70,000 rubles |
The likelihood of being held accountable for such a violation is extremely low, because no one’s rights are violated. If your employees don't hate you, they certainly won't complain. But in order to avoid violating the provisions of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, we recommend that salaries be transferred strictly on the dates established by local regulations.
Commentary on Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
1. The general rules for payment of wages are regulated by Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
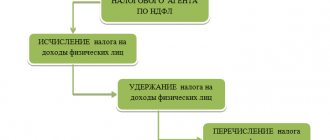
Part 1 of the commented article imposes on the employer the obligation to notify each employee in writing: - about the components of the wages due to him for the corresponding period; — about the amounts of other amounts accrued to the employee; - about the amounts and reasons for the deductions made; - about the total amount of money to be paid.
Notification is carried out by issuing a pay slip, the form of which is approved by the employer, taking into account the opinion of the representative body of employees.
The list of information established by Part 1 of the commented article is required for inclusion in the pay slip.
We also note that by Decree of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated January 5, 2004 N 1, unified forms of primary accounting documentation for labor accounting and payment were approved, including forms of payroll, payroll, payroll, payroll register. However, from January 1, 2013, these forms are not mandatory for use (see information from the Ministry of Finance of Russia N PZ-10/2012 “On the entry into force on January 1, 2013 of the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 N 402-FZ “On Accounting” ").
2. As a general rule, wages are paid to the employee at the place where he performs the work, that is, directly at the location of his workplace, determined by the employment contract. However, payment of wages may be transferred to the credit institution specified in the employee’s application.
It should be noted that in accordance with the Federal Law of November 4, 2014 N 333-FZ “On amendments to certain legislative acts of the Russian Federation regarding the exclusion of provisions establishing advantages for certain business entities,” Part 3 of the commented article was supplemented with a provision in according to which the employee is given the right to change the credit institution to which the wages should be transferred by notifying the employer in writing about the change in the details for transferring wages no later than five working days before the day of payment of wages. This provision, on the one hand, guarantees the employee’s right to freely choose and change the credit institution to which his wages are transferred. On the other hand, a guarantee is established for the employer of his notification of a change of employee from a credit institution, and within a time period that allows for the necessary changes to be made in the relevant accounting documents.
The terms of the transfer are determined in the collective agreement or employment contract. The place and timing of payment of wages in non-monetary form are also determined by the collective agreement or employment contract.
3. According to Art. 5 of ILO Convention No. 95 Relating to the Protection of Wages (1949), wages will be paid directly to the worker concerned unless national law, a collective agreement or an award of an arbitration body provides otherwise and unless the worker concerned agrees to another method.
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for a similar provision in Part 5 of Art. 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which establishes that wages are paid directly to the employee.
An exception to this rule is cases when a different method of payment is provided for by federal law or an employment contract.
The Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation indicated that the norms of Parts 3 and 5 of Art. 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation represent guarantees of the implementation of the employee’s right to timely and full payment of wages, as enshrined in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Provisions part 3, 5 art. 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation are aimed at ensuring the coordination of the interests of the parties to an employment contract when determining the rules for the payment of wages, at creating conditions for the unhindered receipt of wages personally by the employee in a way convenient for him, which corresponds to the provisions of ILO Convention No. 95 (see the definition of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation of April 21, 2005 No. 143-O).
4. In accordance with Part 6 of Art. 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, wages are paid at least every half month on the day established by the internal labor regulations, collective agreement, or employment contract. The Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not establish specific terms for payment of wages, as well as the size of the advance.
The letter of Rostrud dated September 8, 2006 N 1557-6 “Calculation of advances on wages” states that, taking into account the provisions of the resolution of the Council of Ministers of the USSR dated May 23, 1957 N 566 “On the procedure for paying wages to workers for the first half of the month”, which is in force to the extent that does not contradict the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, specific terms for payment of wages, including advance payments (specific dates of the calendar month), as well as the size of the advance payment, must be determined by the internal labor regulations, a collective agreement, and an employment contract. Thus, in addition to the formal fulfillment of the requirements of Art. 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation on the payment of wages at least 2 times a month, the employer, when determining the amount of the advance, should take into account the time actually worked by the employee (actually completed work).
A different period for payment of wages can be established for certain categories of employees only by federal law (Part 7 of Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). For example, upon termination of an employment contract, payment of all amounts due to the employee from the employer is made on the day the employee is dismissed. If the employee did not work on the day of dismissal, then the corresponding amounts must be paid no later than the next day after the dismissed employee submits a request for payment.
If the salary day coincides with a weekend or non-working holiday, it is paid on the eve of this day.
Payment for vacation is made no later than 3 days before it starts.
For the employer’s delay in paying wages and other payments due to the employee, Art. 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for financial liability.
Thus, if the employer violates the established deadline for payment of wages, vacation pay, dismissal payments and (or) other payments due to the employee, the employer is obliged to pay them with interest (monetary compensation) in the amount of not less than one three hundredth of the refinancing rate in force at that time of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation from amounts not paid on time for each day of delay starting from the next day after the established payment deadline until the day of actual settlement inclusive.
Payment methods and location
The employer must notify the employee of the wages accrued to him, indicating all the data established by law. The employee is notified against signature by handing over a written document - a payslip, which he receives after his salary is issued.
Today, employers can pay wages in cash in two ways:
- in cash, by issuing funds at the organization’s cash desk;
- transfer of the established amount of salary to the employee’s current account in any banking organization.
Payment of wages at the organization's cash desks is carried out with the obligatory maintenance of cash documents to confirm the intended use of the funds received by the employer. Funds to pay employees' salaries are transferred by banking organizations with which the company cooperates. They can only be used to pay salaries and cannot be spent on other purposes.
Small enterprises that have constant revenue can issue salaries from the funds received, however, in such circumstances, coordination with the banking organization is necessary.
Salaries are paid in accordance with the requirements established by law, therefore:
- for large organizations, a payroll form No. T-53 has been established if the transfers are permanent;
- for small enterprises and small businesses - No. T-49, in case of payment of salaries to permanent employees;
- for any enterprises that pay employees a one-time remuneration - No. KO-2.
Paying wages by transferring a set amount to the employee's current account is a potentially new phenomenon in business. Every year, more and more employers are switching to such a calculation system, as it can significantly save the time of accounting workers. The rules and features of the transfer of remuneration for labor are regulated by a collective or labor agreement between employees and the management of the organization. The employee can independently determine the banking organization to which his salary will be transferred, thereby establishing the place where the funds will be received.
Norms and procedure for determining deadlines
Specific terms for payment of wages at many enterprises are reflected in the Labor Regulations and in the Regulations on Remuneration. The law on salary payment deadlines in 2020 does not prohibit this.
In turn, the employer must familiarize employees with the changes made to local regulations against signature.
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation and Federal Law No. 272 of July 3, 2020 on introducing adjustments to the laws of the Russian Federation to increase the responsibility of employers for violations of the labor code relating to the calculation of wages in 2020 regulates the procedure and periods for payment of wages.
According to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and Federal Law No. 272, the manager sets the date for issuing salaries to employees in 2019 independently.
Where should I indicate?
The manager of the company indicates the timing of the advance payment and the payment periods for the rest of the salary in the following documents:
- Labor contract. The employer prescribes salary accrual periods here. He can also prescribe the issuance periods, describe them in another act, and leave a link to the document in the contract;
- Rules of routine. The head of the company must indicate the periods for calculating salaries in the rules of procedure, and in other documents leave a link to this provision. The fact is that all employees follow the rules of the work schedule, but the employment contract is followed only by a specific employee. The company may not have a collective agreement;
- Collective agreement. In this document, the head of the enterprise indicates the point in which the periods for accrual of salary are entered. In such a situation, in the employment contract, the director of the company makes reference to a specific provision of the collective agreement.
When paying an employee his salary, the accountant indicates the following information on the pay slip:
- the main part of the salary, which is accrued for a specific month;
- the size and basis of the deductions, if any;
- monetary compensation, vacation pay, severance pay, etc.
When officially employed, a citizen may demand compliance with his own labor rights. One of the employer’s obligations is to pay wages for the time actually worked by the citizen.
There are some features that need to be remembered when making calculations. It must be done every six months.
In addition, the accountant should not forget about preparing payment documents. It is also necessary to carefully prepare reports.
If mistakes are made, serious problems can arise. They relate to relationships with the tax service. The basic rule is to transfer the advance for the period already worked.
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not provide for a specific indication of the amount of interest in accordance with which the advance payment should be calculated. But it is indicated in Resolution of the Council of Ministers of the SSS No. 566, which was issued on May 23, 1957.
On February 3, 2020, Letter No. 14-1/10/B-660 of the Ministry of Labor was issued. It reflects that the calculation is based on the time actually worked by the employee for the first half of the month. You can also focus on fulfilling work standards if the accounting department identifies this criterion.
The employer is responsible for paying wages every half month. The amount can be fixed or be a percentage of salary. The final decision is made by the employer. It must be reflected in the collective agreement or the Regulations on remuneration.
Most often, payments of half of the salary are provided. But in practice, employers decide to give a smaller portion in the form of an advance. This is due to the fact that allowances and bonuses are transferred along with the main payment.