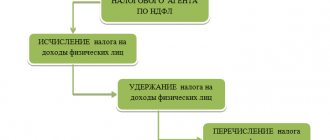
For the time worked, the employee receives a salary already reduced by the amount of deductions.
Dear readers! The article talks about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is individual. If you want to find out how to solve your particular problem , contact a consultant:
+7 (499) 110-56-12 (Moscow)
+7 (812) 317-50-97 (Saint Petersburg)
8 (800) 222-69-48 (Regions)
APPLICATIONS AND CALLS ARE ACCEPTED 24/7 and 7 days a week.
It's fast and FREE !
The law does not reflect such a concept as “deduction from wages”, but only the conditions, requirements and terms of this operation are reflected.
Summarizing all the regulatory information, we can draw a conclusion about the meaning of this term.
A deduction from an employee’s salary is a calculated amount that is formed due to the non-payment of certain amounts to the employee in order to satisfy the legal demands of the employer or other persons.
Normative base
The Labor and Tax Codes of the Russian Federation describe in detail cases of deductions from workers' compensation.
The sequence of retention operations is regulated by federal laws approved by the Government of Russia, including:
| Normative act | Content |
| tax code | Types of deductions |
| No. 229-FZ dated October 2, 2007 | Enforcement procedure |
| Government Decree No. 841 of August 18, 1996 | List of types of wage accruals by which the amount of alimony for the maintenance of minor children is calculated |
You can download the documents here:
Tax Code of the Russian Federation (Part One)
Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two)
Federal Law of October 2, 2007 N 229-FZ
Government Decree No. 841 of July 18, 1996
The employer should focus only on the types of deductions specified in legislative acts. The use of your own types of deductions is equivalent to administrative violations.
How the amount and order of deductions under a writ of execution are determined
When determining the amount of deductions from wages, the employer may take into account the following rules.
1. If alimony is collected, then its amount must be calculated for the entire time from the moment the debtor became obligated to pay it. If during any periods of such an obligation the debtor had no income, then the debt for the corresponding periods is calculated based on the average salary in Russia at the time of debt collection (Part 3 of Article 102 of Law 299-FZ).
Responsibilities for calculating the amount of debt rest with the employer. An exception is the scenario in which the amount of debt is calculated by a bailiff. He determines it on the basis of a court ruling (Part 2 of Article 102 of Law 229-FZ).
2. The amount of deductions should be calculated based on the order of payments under writs of execution, if there are several claimants.
The provisions of Part 1 of Art. 111 of Law 299-FZ establishes that:
- First of all, alimony and damages are paid off;
- secondly, claims related to the debtor’s fulfillment of payment obligations are repaid;
- thirdly, tax claims are paid;
- fourthly, other claims are repaid.
The next debt in line begins to be repaid only if the debt in the previous line is fully repaid.
And if the available amount is not enough to simultaneously repay two different debts of the same priority, then this amount is distributed between the debts in proportion to their size (Part 3 of Article 111 of the Federal Law No. 229). Let us look further at an example of calculating such a distribution taking into account the priority.
In what cases are they carried out?
Mandatory
Withholdings of this type must be carried out in any case and are completely independent of the initiative of the parties and are based only on the norms of the law:
- Personal income tax (NDFL).
- Deductions based on writs of execution.
Personal income tax
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation has a separate chapter for this tax.
Many questions are explained in detail:
- tax base;
- amount of deductions;
- timing of behavior;
- preferential terms for calculating tax for certain segments of the population.
Tax plays an important role in the process of further deductions, since all other deduction operations are carried out only after the calculation of personal income tax.
According to writs of execution
The document received by the organization with the decision of the judicial authority obliges the employer to strictly comply with all requirements.
Mandatory requirements include:
- performance list;
- court order;
- agreement on payment of alimony, certified by a notary;
- decision of the labor dispute commission;
- act of the executive body on administrative violations;
- bailiff's order.
The administration of the enterprise must make all deductions according to executive documents within the agreed period and in full, based on the standards reflected in legislative acts.
It is important to carry out deductions in the required amount without violating labor laws.
At the request (initiative) of the employee
The employee’s own desire serves as the basis for making deductions of a certain nature:
- payment of union dues;
- voluntary donations to charitable foundations;
- repayment of loans;
- payment of insurances.
At the written request of an employee, the enterprise administration makes deductions from wages.
Economic services are required to make appropriate calculations monthly and absolutely free of charge, in accordance with the approved collective agreement.
Union dues
The rules for payment of contributions are confirmed by Federal Law No. 10-FZ of January 12, 1996.
Federal Law of January 12, 1996 N 10-FZ
The employer is obliged monthly, within the time limits established by law, to transfer contributions to members of the trade union society, based on a written application from employees.
Loans
When receiving a loan from a “native” enterprise or from a third-party microfinance organization, a citizen has the right to choose any repayment method:
- directly depositing funds into the cash desk of the microfinance organization;
- write a statement at your place of work requesting monthly transfers of certain amounts to the account of the lending company.
What sections does the Labor Remuneration Regulation contain? Read about it in our article. How to calculate the salary of a minor? Find out here.
At the initiative of the employer
This type of deduction has a special status: it is the employer’s right, not an obligation.
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation considers several areas of deductions at the initiative of the enterprise administration:
- return of advance payment for wages not earned by the employee in due time;
- closing a travel advance, the balance of which was not returned within three days;
- return of overpaid wages, the reasons for the payment of which may be a counting error, failure to comply with labor standards or unlawful acts of the employee;
- refund of unearned vacation pay;
- compensation for material damage;
- covering shortages of material assets;
- reimbursement of administrative fines;
- the cost of self-produced products used for personal needs;
- reimbursement of cellular communication services;
- payment of the cost of excess fuel consumption;
- for passing a medical examination.
Deductions at the initiative of the employer are lawful only if two conditions are met:
- the time period does not exceed one month;
- the employee agrees with the deductions being made.
If one of the conditions is missing, the employer cannot independently make the necessary deductions; all controversial issues must be resolved in the courtroom.
Material damage
An employee’s financial liability arises when it is discovered that damage has been caused to the employer’s property as a result of:
- improper action during the performance of a production task;
- detecting a direct relationship between the employee’s behavior and the detected material damage;
- unless the perpetrator disputes the fact.
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that the cost of property damage must be compulsorily compensated to the employer.
Compensation includes not only the cost of the actual reduction of the employer's property, but also the necessary costs to eliminate the damage caused.
An employee who causes damage to the employer’s property provides a written explanation of what happened.
If there is a refusal to write an explanatory note, an act is drawn up, confirmed by the signatures of two witnesses.
Reimbursement from salary is carried out according to the order of the manager if:
- the amount of damage does not exceed the average salary;
- the document is executed no later than one month from the date of discovery of damage to property;
- the employee agrees with the punishment.
Otherwise, the decision must be made at a court hearing.
For cellular communications
Production needs often lead to the active use of cellular communications by employees of an organization.
Permitted standards are fixed in local regulations, which employees are introduced to “under signature.” Identified excess expenses are withheld from employee salaries.
An order is issued for the enterprise, in which all detected amounts of overspending are displayed individually for the “guilty” ones.
Confirmation that employees are familiar with the decision must be provided in writing.
For the financially responsible person in case of shortage
Based on the results of the audit, an inventory sheet is drawn up, which records the fact of a shortage of commodity assets.
Compensation for shortfalls occurs under the same conditions as compensation for material damage, regardless of the type of liability (full or limited).
For products
The order for the enterprise fixes the possibility of purchasing products of its own production for employees at a discounted price.
All full-time employees must be familiarized with the document in writing.
In case of excessive consumption of fuel and lubricants
The use of a vehicle for production purposes is confirmed by a vehicle route sheet.
The standard consumption of fuel and lubricants is determined by calculation based on the mileage recorded in the voucher.
Excessive fuel consumption, by order of the manager, is reimbursed by the driver from his salary.
For a medical examination
Mandatory periodic medical examinations of public catering or food retail workers are carried out by enterprise administrations in a collective manner.
Payment for the organized event is transferred by bank transfer to the bank account of the medical institution.
An employee who quits without working for 6 months after a medical examination is reimbursed for the cost of medical services upon final payment.
Excess amounts paid
Wages paid in an unreasonably increased amount are subject to mandatory refund.
They can arise in various ways:
| Variety | Cause |
| Counting error |
|
| Failure by an employee to fulfill a production task |
|
| Illegal actions of an employee |
|
Fines
Administrative sanctions are withheld from the employee’s salary based on the order of the manager.
Unearned advance
The written consent of the employee and execution of the transaction no later than a month from the date of issuance of the advance are essential conditions for the return of the amounts of the unpaid advance.
The basis is the order (order) of the manager.
For unworked vacation days
Dismissal of an employee before the end of the period for which vacation pay was accrued to him entails recalculation and further deduction of previously issued amounts.
There are several exceptions to this rule; vacation pay is not refunded:
- the employee refuses to be transferred to another place of work for health reasons (the basis is a medical report in the established form);
- personnel reduction procedure;
- change in the composition of the owners of the enterprise;
- the employee is called up for military service;
- the employee is reinstated at his previous place of work by decision of the labor inspectorate;
- incapacity of a citizen;
- due to the death of an employee;
- force majeure circumstances, the occurrence of which prevents the performance of official duties.
Economic services recalculate accrued vacation pay, taking into account how many days of vacation it is necessary to make deductions for.
D(on) = D(sp) – (Dl/12 * Mo)
Values:
- D(on) – unworked calendar days of vacation;
- D(isp) – used calendar days of vacation;
- Dl – duration of annual paid leave;
- Mo – worked months of the last calendar year.
In accounting, a reversal of the vacation pay amount is recorded. The adjustment to the withholding of insurance premiums is reflected in the reporting period of the employee's dismissal.
In what cases is a payroll slip required? Read our article. You can find information about payroll calculations on holidays here.
Is alimony deducted from salary advances? Information is here.
Deductions from wages at the initiative of the employer
The initiative to make deductions from an employee’s salary can come not only from the employee, but also from the employer. In accordance with Russian law, an employer can make deductions from an employee’s income in such situations, for example, if the employee has not worked off the advance payment he received. In addition, the employer can deduct from the employee’s salary in the following situations:
| Reason for retention | A comment |
| The employee was fired in a year for which he already had vacation | It is worth considering that in this case, deduction cannot be made if the employee is forced to resign due to:
|
| In case of downtime or failure to comply with labor standards | Such deduction is possible only after the employer goes to court. If the court finds that it is the employee’s fault, then the retention period will be the date the court decision comes into force |
| Funds were paid due to incorrect calculation | Excess amounts of money paid to an employee are any funds that were received by him as part of his employment relationship with the employer. If the employee refuses to return the money voluntarily, the employer has the right to go to court (such behavior of the employee may be regarded by the court as unjust enrichment) |
| The working days were not worked by the employee upon his dismissal | The employer has the right to deduct the employee's debt from the payments due to him upon dismissal. But in some cases, the employer cannot withhold funds from the salary (without the employee’s consent) when dismissing an employee in the following cases:
It is necessary to issue a deduction order and calculate vacation pay |
The procedure for deducting from an employee's salary
The procedure for deductions from an employee’s salary is the same:
1. The accountant determines the type of deduction from the employee’s salary. 2. The availability of documents that are the basis for the withholding is checked. 3. Withhold tax on personal income.
After personal income tax has been withheld, all other deductions can be made from the employee’s salary.
What income is not generated from?
Deductions are made from all income groups received by employees.
There are a number of additional payments established by law that cannot be taken into account when deducting from employees’ wages:
- Accrued to compensate for damage caused to health (does not apply to deductions of alimony for the maintenance of minor children).
- Compensation for injuries received during the performance of government or production tasks (in the event of the death of a direct participant in the events, this type of additional payment applies to members of his family).
- Additional payments related to labor regulations, including business trips or transfer to work in another location.
- Insurance payments for compulsory social insurance, except for sick leave due to temporary disability.
- Partial or full reimbursement of the cost of sanatorium vouchers for employees and their children.
- Accruals for the purpose of eliminating the consequences of natural disasters and emergency situations.
- Elimination of consequences of terrorist attacks.
- Payments due to the loss of family members.
- Humanitarian assistance provided.
All of the above types of surcharges are not subject to personal income tax.
General procedure
Deductions from an employee’s earnings to repay his debt to the employer are carried out for the purpose of:
- Compensation for unearned advances provided to an employee on account of their salary.
- Repayment of unspent and not returned in a timely manner advance payment provided to an employee in connection with a transfer to another location for another job or a business trip or in other cases.
- Refund of amounts paid to an employee in connection with accounting errors made, if the employee is found guilty of failure to comply with labor standards or idle time. In the latter case, the basis is the decision of the body authorized to consider individual labor disputes.
According to the provisions of Part 2 of Art. 137 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, deductions are allowed upon dismissal of an employee before the end of the year for which paid leave was provided. Deductions are made for days not worked. An exception to the rule, according to Art. 137 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, there are cases of termination of the contract on the grounds established in Article 77 (Part 1, Clause 8), Art. 81 (part 1 clause 1, 2, 4), art. 83 (clauses 1, 2, 5, 6, 7).
How to make deductions from wages?
General order and stages of calculation
Deductions from wages for all types of areas are calculated every month within certain periods corresponding to the accrual period.
The retention calculation process follows basic accounting rules:
- Payment is calculated for all types of earnings, as well as all available additional payments and charges, excluding amounts that are not accepted for calculating deductions.
- Personal income tax is calculated.
- The remaining amounts of deductions are determined, which remain at the disposal of the employer or are transferred to third parties within three days after payment of wages.
Documenting
The package of required documents depends on the type of deduction.
To calculate personal income tax:
- Employee's application for standard deductions.
- Copies of children's birth certificates.
- Certificates from the place of study of children.
Application form for deduction:
Application for tax deduction
For deductions under executive documents:
- Judgment.
- Performance list.
- Decree of the bailiffs.
- Agreement on payment of alimony, certified by a notary.
- Act of executive bodies on administrative penalties.
- Decision of the labor dispute commission.
For payments decided by the employer:
- order;
- written consent of the employee.
Example of an order:
Order to deduct from salary
Deductions at the initiative of an employee: a statement by a person who has expressed a voluntary desire to pay.
Application for deductions to the trade union
Sequence
Initially, income tax is excluded from wages. Then a certain sequence of fulfillment of the requirements, fixed in Art. 111 of Federal Law No. 229-FZ.
| Sequence | Claim |
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 | Mandatory payments to budgets of various levels and extra-budgetary funds |
| 4 | Other deductions |
The presence of requirements of various types presupposes the following retention order: passing all calculations in chronological order.
Each subsequent queue begins to be satisfied after full payment of the requirements of the previous queue.
Size limitation
The maximum possible amount of deductions from an employee’s salary in favor of third parties is established by law, which are mandatory:
| Maximum percentage | Conditions |
| 70 |
|
| 50 | Cases provided for in federal legislation |
| 20 | Other conditions |
The 20% amount of deductions does not require the written consent of the employee in cases occurring at the initiative of the employer.
Mandatory deductions from salary
As we have already noted, mandatory deductions from an employee’s salary according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation are personal income tax, as well as alimony. Let's look at each type in more detail.
Withholding of alimony from wages
Please note that alimony can be withheld solely on a documentary basis. The retention order is regulated by:
1. Law on enforcement proceedings. 2. Family Code of the Russian Federation.
Alimony may be withheld in relation to:
- children who have not reached the age of majority;
- other adult family members (if they do not have the ability to work).
The grounds for paying alimony are as follows:
- by court decision (if there is a court order or writ of execution);
- upon agreement on this issue by the child’s parents (a notarized agreement must be drawn up);
- employee's statement - voluntary alimony. The main feature of voluntary alimony is the absence of legal restrictions on its amount.
Original documents must be submitted to the accounting department of the enterprise.
The following amounts of alimony are withheld for the maintenance of minor children (Family Code, Article 81):
| Amount of children | Part of the employee's income (per month) | |
| 1 | 25% | 1/4 |
| 2 | 33% | 1/3 |
| 3 (or more) | 50% | 1/2 |
Please note that at the discretion of the court, the size of these shares may be increased or decreased. The court takes into account the financial situation, as well as other circumstances of the parties.
In general, the deduction from an employee's salary for alimony will be calculated from the amount that remains after taxes are paid.
Within three days after the employee’s salary has been paid, the company must transfer alimony to the claimant.
If a company employee receives several writs of execution, then the amount of deductions (total) cannot be more than 70%.
If the legal basis for paying alimony is an agreement between the payer and the recipient or a voluntary application of the employee, then the maximum deduction of alimony from wages is not limited in any way (Clause 1 of Article 103 of the RF IC, Article 110 of the RF IC). Moreover, if the agreement is drawn up for alimony for a minor child, then the amount specified in it should not be less than that determined when alimony is assigned by the court (Clause 2 of Article 103 of the RF IC).
If the company has an employee who has alimony debts and changes his place of work, the organization must notify the bailiff about this. Then the company is obliged to return the enforcement document to the bailiff, which should contain a note indicating what penalties were imposed on the employee.
Withholding personal income tax from wages
When the salary is actually paid, the amount of personal income tax that was accrued must be withheld from the taxpayer’s income. This provision is provided for by the Tax Code (clause 4, article 226).
When the actual payment occurs, withholding can be made from any funds that are paid to the taxpayer by the withholding agent. In this case, the amount of withholding cannot exceed 50% of the amount that must be paid.
The withheld personal income tax must be transferred no later than the day when the bank received the money to pay the employee’s income.
Calculation using examples
Prima LLC received writs of execution against employee P.S. Lvov:
- Alimony for the maintenance of 2 minor children in the amount of 33% of income.
- For compensation of damage caused to the health of an individual - 12,000 rubles. per month.
The employee's salary is 25,000 rubles per month.
Accepted enforcement documents belong to the first stage, the amount of deductions in which is possible up to 70% of earnings.
The standard deduction for the first and second child is 1,400 rubles each.
25,000 + 15% * 25,000 = 28,750 rub. salary accrued
13% * (28750 – 1400 – 1400)= 3374 rub. Personal income tax
33% * (28750 – 3374) = 8374.08 rub. alimony amount calculated
8374.08 + 12000 = 20374.08 rub. summary amount of deductions according to writs of execution
70% * (28750 – 3374) = 17763.20 rub. permissible amount of deductions
The final amount of deductions exceeds the maximum possible amount, so it is necessary to find the percentage of required payments:
20374,08 – 100%
8374,08 — 41,1%
12000 — 58,9%
Actual amounts of deductions for the current month:
17763.20 * 41.1% = 7300.68 rub. alimony to be transferred
17763.20 * 58.9% = 10462.52 rubles. damage to health
The following amounts are transferred to the next month:
8374.08 – 7300.68 = 1073.40 rubles. for alimony
12000 - 10462.53 = 1537.47 rubles. for compensation for harm to health
28750 – 3374 -7300.68 – 10462.52 = 7612.80 rub. salary was issued to the employee
Accounting entries
The withholding procedure for requirements is reflected in accounting according to the Chart of Accounts and the Instructions for its application.
For the purpose of synthetic and analytical accounting of mandatory deductions, it is recommended to open separate sub-accounts account 76.
| Dt | CT | Posting Contents |
| 44; 20 | 70 | Salary accrued |
| 70 | 68 | Personal income tax calculated |
| 70 | 76 | Deductions were made on writs of execution |
| 76 | 51 | Alimony amounts listed |
| 71 | 50 | An advance was issued from the cash register for a business trip |
| 20;44 | 71 | An advance report on the business trip was carried out |
| 94 | 71 | The amount of advance payment for a business trip not returned on time is reflected as a shortage |
| 70 | 94 | Withholding the balance of accountable amounts |
Control and accounting
The chief accountant of the enterprise exercises full control over the correctness of accounting at the enterprise.
The Chart of Accounts includes all the necessary synthetic accounts with the necessary breakdown of analytics into subaccounts.
Particular attention is paid to issues of control over the accounting of deductions from the wages of company employees.
What is piecework wages? Read our article. How to calculate wage arrears? Find out here.
Conditions for making deductions
Moreover, in all of the above cases, except for the case of returning a previously issued advance against future wages, deductions are made in the following order:
- the decision to make a deduction must be made no later than a month from the date of: return of the advance, repayment of debt or incorrectly accrued payments;
- a mandatory condition for making a deduction based on an order from management is the consent of the employee and the absence of objections on his part regarding the grounds and amount of deductions.
Nuances
If there is a child
Personal income tax is calculated taking into account the standard deduction for children. All other deductions are made on a general basis.
For a deceased employee
The uncollected amount of the deceased employee's salary is received by his family members.
At the same time, the organization does not have the obligation to transfer personal income tax from the income of a deceased citizen.
State employees
Deductions from wages are regulated by law and are subject to generally accepted rules applicable in commercial organizations.
https://youtu.be/xdJN66XpwFQ
Deductions from wages at the initiative of the employee
Withholding by agreement after loan issuance
A loan agreement is the basis for deducting a sum of money from an employee’s salary. The document must be concluded between the employee and the employer. The agreement reflects the following provisions:
- the size of the loan provided to the employee;
- loan term (period during which the debt must be repaid);
- the amount of interest under the terms of the agreement;
- procedure for returning funds.
Due to the fact that the deduction of money under the loan agreement will be carried out from the employee’s salary, the latter should fill out an application containing approximately the following wording:
“I ask you to withhold 1,500 rubles monthly to repay the loan.”
Withholding additional insurance contributions for the funded part of the pension
This type of deduction is permissible solely on the basis of an employee’s application (in writing). The document must indicate the following points:
1. How much should insurance premiums be withheld each month? 2. How should they be calculated?
After the employer receives the application completed by the employee, he is obliged to withhold and also transfer additional insurance contributions to the funded part of the employee’s labor pension.
The organization must begin deducting the amount specified in the application from the salary and transferring it to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation on the 1st day of the month following the month of receiving the application from the employee.
Deduction for mobile phone usage
This form of deduction from an employee’s salary is relevant if the company has an established limit on expenses for using mobile communication services. Thus, if the limit is exceeded, the employee will have to compensate for this excess from his own funds.
Deduction from wages for cellular communications will be based on the local act of the enterprise. For example, such a document could be the Regulations on Remuneration. It must contain the procedure for compensation for communication services employees.
In addition, the employee can write an application requesting that funds be withheld from his income to compensate for mobile communication services.
Such withholding can be interpreted as recovery of damages. The procedure for collecting damages is described in Art. 248 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Reimbursement for “non-targeted expenses” can be made in three ways:
- The employee voluntarily compensates for the damage.
- The amounts are withheld by the employer.
- The debt is collected in court.