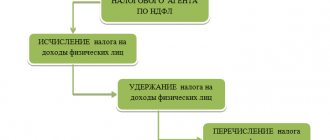
Every accountant of a large company, during his work, is faced with the need to deduct funds from a worker’s salary. Having received such an order, it is very important to carry out this procedure correctly. Current legislation provides a limited list of reasons that can be used as a basis for a legal deduction. Monetary fines and other unauthorized actions may be considered a gross violation of the law. Our article, devoted to the question of how to draw up a sample order to deduct from wages for damage, will help to avoid possible conflicts with hired personnel and regulatory authorities.
The employer can withhold part of their earnings from employees’ wages both voluntarily and compulsorily.
Regulatory documents on regulation of deductions from salaries
Russian legislation firmly regulates official deductions from employee wages:
- types of deductions are described in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (mandatory - these are taxes at the initiative of employers and at the will of the employee himself);
- how enforcement proceedings are carried out, as stated in Federal Law No. 229 of October 2, 2007;
- the salary accruals by which the amount of alimony payments are calculated are specified in Government Decree No. 841 of August 18, 1996.
- the procedure for withholding alimony, transferring compensation for harm to health, for the loss of a breadwinner - these payments, withheld exclusively by court decision, are regulated by Art. 138 Labor Code of the Russian Federation, clause 3, art. 99 of the Law “On Enforcement Proceedings” dated October 2, 2007 No. 229-FZ;
- the procedure for withholding alimony, transferring compensation for harm to health, for the loss of a breadwinner - these payments, withheld exclusively by court decision, are regulated by Art. 138 Labor Code of the Russian Federation, clause 3, art. 99 of the Law “On Enforcement Proceedings” dated October 2, 2007 No. 229-FZ;
- deductions for unworked vacation days, excessive advance payments, results of accounting errors –
- deductions for unworked vacation days, excessively issued advances, results of accounting errors - Art. 137 Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- voluntary deductions from salaries at the request of an employee, their amount is not limited, are regulated by Letter of Rostrud dated September 26, 2012 No. PR/7156-6-1.
When a lien order is not required
A withholding order is not created in the following cases:
- An employee writes an application for a deduction from salary to pay a bank loan on time. This process is not a deduction, unlike deductions based on writs of execution and in the cases listed in Art. 137 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
- For mandatory deductions (court orders and writs of execution - payment of alimony, traffic police fines, taxes, etc.), an order is not needed.
- Deductions of money from wages for unworked vacation days are not carried out if the employee quits for the following reasons:
- clause 8, part 1, art. 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation - refusal to transfer to another job for medical reasons or lack of appropriate work;
- Part 1 Art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation - liquidation of a company, reduction of personnel or staff, change of ownership of the company’s property - regarding its head, his deputies and the chief accountant;
- Part 1 Art. 83 Labor Code of the Russian Federation - conscription for military/alternative service; return to work of the person who previously held this position; recognition as incapable of work based on a medical certificate; death or recognition of an employee as missing; the occurrence of emergency circumstances (catastrophe, natural disaster, military action, etc.).
We invite you to familiarize yourself with: Amount of duty on a court order
https://youtu.be/KGReUxyQiXY
In what cases is it possible to deduct funds from wages?
Labor legislation clearly lists the cases in which the employer has the right to withhold funds:
- At the initiative of the employee himself.
- The employee did not actually work out the money he received. Most companies have adopted an advance payroll system, and this is one of the unpleasant consequences it can lead to.
- A business trip or relocation of an employee was planned (with a budget allocated), but it did not take place.
- If the enterprise has established production standards, and the employee has not met them.
- If the employee is at fault that there was an error in the accounting documents in favor of increasing the funds allocated for his salary.
- If the working year was not completed due to vacation.
- If, as a result of the employee’s actions or inaction, there is downtime at work.
In addition to these situations (they can be challenged), there are cases of mandatory retention. Specifically, these are court orders. If an employee is a debtor of alimony payments, a defaulter of traffic police fines, etc., then his salary must be reduced by the appropriate amount.
The only exception to the rule is the last “peaceful” month of cooperation between employer and employee. That is, the employee leaves, but only due to a reduction in staff, being sent to military service, due to the return to work of the previous employee, etc.
Withholdings from the employer
The employer also has the right to make certain deductions from the employee’s salary:
- Compensation for an advance that was not worked out. Today, employers must pay wages by providing an advance and a final amount. In fact, a division of remuneration into parts is being formed, since the law establishes the need to pay for labor at least once every two weeks. The essence of the advance is that it is issued in advance, two weeks before the process of issuing the main salary will be carried out. Employers do not always take vacations into account, and there is also no possibility of accounting for vacations without pay; accordingly, subsequent hours worked may not cover the previously issued advance amount. In order to compensate for losses that are formed in this way, the employer is obliged to draw up an order on the basis of which the process of withholding part of the salary will be carried out;
- In addition, the employer can carry out the procedure for actually collecting an advance payment that was issued to reimburse expenses related directly to a business trip or work in another area. When an employee is sent on a business trip, he receives a certain amount of funds from the company's cash desk. After finishing work, he is obliged to provide documents that reflect all his financial losses. If the amount of funds determined by documents is less than the amount that was actually received by the employee to fulfill professional obligations, then the possibility arises of legal deduction of this amount with subsequent accrued salary. However, many enterprises establish a rule that determines the possibility of returning the excess advance amount in cash equivalent. An employee arrives from a business trip, submits all reports, and then hands over the funds that turned out to be excessively issued. If the employee does not perform such actions, the funds will be calculated from his salary. The employer is required to draw up a special order to withhold contributions;
- An employer may impose a fine due to the fact that an employee refuses to perform functional or job duties. There may also be deductions that are associated with the occurrence of counting errors. In all cases, counting errors are legally compensated from the employee’s salary. For example, if the employee was mistakenly accrued a more significant salary, or additional payments, then in this case the deduction will be equal to the calculation error. When an employee violates professional and functional obligations, a fine may also be imposed. If such situations arise, the employer draws up an order. The absence of an order results in the inability to retain an employee from the salary. All circumstances of the situation are described quite clearly and accurately;
- Deduction is formed for unworked vacation days. If the employer terminates the employment contract, and all vacation payments have already been made by the employer, the possibility of making deductions is established. But, in certain cases, such compensation will not be possible. For example, if an employee is called up for military service, if the employee is being laid off, or the enterprise is being liquidated;
- It should also be noted the possibility of deductions that are formed due to material damage. There are persons who bear financial responsibility, and if a situation arises where an employee violates his authority, the employer can use a deduction structure that relates to material damage. As you understand, a prerequisite for payments is the drawing up of an order that forms a detailed description of the nuances of subsequent deductions from the employee’s salary.
There are many options for deductions that can be formed based on the order of the employer. An appropriate document must be drawn up, the need to describe all the nuances of the situation is formed. If the employer does not make the process of returning material damage within a month, since the employee’s salary is not enough for recovery, then the opportunity is formed to file an application to the court, after which compensation will be carried out by obtaining a court decision. In most cases, the financial liability is quite significant, and you have to go to court. The court issues an order or a writ of execution, after which all necessary payments are made within the established amount from each employee’s salary. There is no need to draw up a separate order for each deduction, since the basis will be an executive-type sheet.
What percentage of funds should be retained?
In most situations, it is enough to keep 20%. This applies to property damage, shortages, etc. If there is more than one writ of execution, then it is permissible to withhold up to 50% of the total amount issued for the month. Labor legislation provides for cases when up to 70% of wages are deducted. This:
- alimony payments;
- if a crime was committed, resulting in material damage;
- there has been a death of the breadwinner;
- the employee was subject to punishment in the form of corrective labor.
If the employer does not have this information and withholds, for example, 100% of wages for any violation, then the negligent employee has the right to even go to court regarding this incident. If everything is formalized properly, he will win the case regarding the violation of his rights. In any case, both parties should be aware that 20% is that part of the salary that can be withheld by the employer from the employee for valid reasons. And for the rest it will be necessary to look for reasons in the labor code.
Nuances of retention
When making a positive decision on an employee’s application, an enterprise must proceed from the order of deductions established by the laws of the Russian Federation. First, personal income tax is paid on the employee’s income, then the requirements for alimony payments, payments to the person who suffered health damage, criminal fines, and compensation for slander are satisfied. Then the FSSP writs of execution are considered, and the financially responsible person compensates for the damage to his enterprise.
Exceptions to the rules
If an agreement on financial liability has been concluded, the employer has the right to recover the entire amount from the employee. By mutual agreement, you can pay in installments, deducting gradually from each subsequent salary.
The same is done if, during the trial, the employee was found guilty of any administrative offense that resulted in material damage to the organization.
The employee may also express a desire not to receive part of the funds. He can, for example, transfer his finances immediately to repay the loan, to a charitable organization, trade union, insurance fund, etc. It is worth keeping in mind that in order to carry out such actions, the company’s accounting service will need to have a written statement from the employee himself. It must clearly indicate that this is his initiative and he fully agrees with these actions.
What documents are needed?
The accounting department makes deductions based on a written order from management.
The order is issued on the basis of:
- an inventory (audit) act during which a shortage was discovered;
- written explanation of the guilty person;
- a written obligation to compensate the financially responsible person for damages.
Important! An agreement on full or partial financial liability must be concluded with the person who is responsible for the inventory items.
The deficiency can only be recovered from the guilty party.
Article 248 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that damages not exceeding average earnings can be recovered by decision of the employer.
Shortages exceeding this limit, according to the provisions of the same article, are recovered through the court.
However, in practice, it is more profitable for the guilty party to admit the damage and give an obligation to compensate for the harm.
The risk that the employee who paid the damage will later challenge these deductions in court on a formal matter (the article says that such amounts can only be recovered by the court) is extremely low.
Therefore, procedures where deductions are made based on a written commitment from the guilty employee are common.
Preparation
Before proceeding with the execution of the order, it is necessary to document the damage (if the withholding occurs at the initiative of the employer and in connection with the damage incurred). Such documents may be inventory reports, a special act on damage to company property, or other materials. If we are talking about an accident, then the supporting documents can be acts from the insurance company, car service receipts, invoices for the purchase of parts, etc.
An important point: the payment documents presented to the employee must indicate the full amount of wages. It includes the bonus part, compensation, for length of service, etc. And deductions will be calculated from this total amount.
When is drafting required?
He prepares, if the need arises, to withhold certain amounts from the employee’s salary ( Article 130). TK.
If the employee himself made a statement about this, the immediate basis is such a statement.
A person may need voluntary withholding to pay for housing and communal services, bank loans, trade union and other dues, pension contributions, child support, voluntarily agreed upon by the ex-spouse.
A special case is to repay a loan issued to a worker by an organization.
If the withholding must be carried out involuntarily, in addition to the desire of the employee and without his application, the basis may be the fact of debt to the organization in the following cases:
— non-payment or failure to spend the advance;
- amounts paid to him unjustifiably (accounting errors);
— recovery of damage caused to the organization, Article 248.
The receipt of a writ of execution or a court order is not a reason for drawing up an order to deduct from wages. It is made directly on the basis of these documents.
As can be seen from the Federal Law on Enforcement Proceedings, the employer is obliged to transfer funds in the specified amount to the claimant within three days, and at the expense of the debtor (3rd part of Article 98).
Components of an order
It is advisable to print the text of the order on the organization’s letterhead. The paper must contain:
- Date of preparation;
- city (place);
- order number;
- reason for withholding funds;
- what percentage of the salary is the amount of withheld funds;
- the amount of the withheld amount in rubles;
- hold date;
- grounds for withholding (supporting documents);
- signature of the head of the organization;
- signature of the employee whose salary is being withheld.
In most cases, the written consent of the employee will be required to draw up an order to withhold funds from wages. This is the only way to achieve legal literacy in matters of the relationship between employer and employee. In the absence of mutual agreements, they resort to recourse to the courts, but this rarely happens.
Sample order
Experts in the field of office management recommend using letterhead for printing administrative acts. The header of the document must contain information about the place and date of issue of the order. Also in this part of the form you should indicate the registration number of the act. The content of the order contains the following information:
- Grounds for partial deprivation of earnings.
- The percentage of the total amount earned and the amount of funds withheld.
- Specific amount of withholding in national currency.
- Date of the procedure.
- A list of documents used to confirm the legality of management’s actions.
The completed act must be certified by the signature of the worker and the head of the company.
There is no standard form for this order; it can be drawn up in any form
An order for deduction from wages, a sample of which is given above, must contain the employee’s signature. Otherwise, the decision may be challenged through legal action.
Order to stop withholding
When the employee himself requests deductions from wages in writing, this is a special case when the limits and restrictions of the Labor Code, which largely protect the interests of personnel, cease to apply. To begin such deductions, an order is needed.
But if an employee decides to stop voluntary transfers through salary deductions, this is his right. To accomplish this, another order is needed to cancel the first one. To do this, the employee needs to perform one of two actions:
- write another statement - a request to stop withholding funds from his salary for the specified purposes;
- When writing the initial application, indicate the period after which it will no longer be valid and funds will need to stop being transferred.
Cases of preparation for the collection of funds from an employee’s salary
An order is prepared when it becomes necessary to deduct certain amounts from an employee’s salary in accordance with Article 130 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
When a subordinate independently fills out an application for withholding due to any circumstances, this document is the basis for drawing up the order.
Voluntary withholding is used by employees to pay utility bills, loans from commercial banks, trade union dues, additional contributions to the funded part of a pension to the Pension Fund, alimony for a minor, and contributions to charitable foundations.
A special case is the repayment of a loan issued by an organization where the employee is on staff.
If a deduction arises without fail, except at the request of the employee and without his request on paper, the basis may be the currently existing debt to the company for the following reasons:
- non-working;
- non-use of the advance payment and failure to return the accountable amount - a sample application for the collection of accountable money;
- amounts paid to him erroneously (calculation errors) - the procedure for withholding excess amounts.
Some accrued amounts of an employee's income cannot be recovered. They are outlined in Article 101 of the 229th Federal Law (payments related to a business trip, transfer to perform work functions in another area, the birth of a child, the loss of a close relative).
This limitation must be taken into account when placing an order.
The receipt of a writ of execution (court order) in the accounting department of an enterprise does not serve as a reason for issuing an order to deduct a subordinate from the wages.
The deduction of amounts recorded in the court form is made directly on the basis of the documents provided.
In accordance with the Law on Enforcement Proceedings, the employer has the obligation to transfer funds in the required amount to the claimant (at the expense of the debtor) within 3 days.
Issues of withholding money from employee income relate exclusively to federal laws. Local legislative acts do not resolve such issues.
For example, for violating the work schedule (being late to the workplace), smoking in a prohibited place, the company management may hold a subordinate accountable in the form of a fine.
It should be understood that the administration of the company can make deductions at the request of a subordinate, but this is not its responsibility. This point is considered by the director of the enterprise.
Making an order
The document must be correctly drafted to give it legal force. Its design should not attract the attention of supervisory government bodies.
There is no standard form for this order; it can be drawn up in any form.
The document must indicate: the amount of the penalty, the basis for the procedure, and the employee’s data.
In addition, fill out the following information:
- details of the enterprise;
- title of the document (order, instruction);
- number and date of document preparation;
- signature of the head of the enterprise, chief accountant.
If the write-off is voluntary, then this fact must be recorded in the text part of the order. The employee’s statement is indicated as the basis for the order.
At the bottom, the employee puts his introductory signature.
When preparing a draft order to deduct the required amounts from an employee’s salary, it is especially important to pay attention to the timing. They are provided for in Article 137 and Article 248 of the Labor Code.
Article 248 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for the recovery of damages by order to deduct missing amounts from wages no later than 1 month from the date of discovery of the loss.
An employer who violates this requirement allows the employee to go to the courts and challenge the legality of the withholding.
A similar condition is contained in Article 137 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation: the decision to return the advance or incorrectly paid amounts is made within 1 month from the date of payment.
If facts of theft, abuse and damage to company property are discovered, a commission is created that will identify the causes of damage and the amount of loss incurred.
order to withhold an accountable amount from an employee’s salary – word.
Example of a request to terminate deductions
Written if the date of termination of deductions was not indicated in the first application.
Director of Felix-M LLC Kolobkov P.A. caretaker N.L. Solovykhina
STATEMENT
I ask you to stop deducting 8,000 rubles from my salary starting September 12, 2020. in favor of Solovykhina E.N., since the girl for whose maintenance these funds were transferred became an adult.
I am attaching a copy of the birth certificate of E.N. Solovykhina to the application.
01.08.2020
/Solovykhin/ N.L. Solovykhin
Amount of mandatory deductions
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation limits the cases of collection from wages and the amount of such penalties:
- the total amount of monthly penalties should not exceed 20% of the entire monthly salary and 50% in certain cases provided for by law;
- if penalties are carried out on several writs of execution, the employee must have at least ½ of the salary left;
- penalties do not exceed 70% for persons paying alimony, serving correctional labor, compensating for harm caused to health, etc.
If an employee of an enterprise obligated to pay alimony does not come to an agreement with the other party, the following deductions are made from his salary:
- half of the salary if there are more than three children;
- one third of the salary for two children;
- one fourth of the salary for one child.
Collecting wages from employees is a rather labor-intensive process. Stages of calculating deductions:
- the manager determines the type of retention;
- establishes the basis for collection;
- draws up documents confirming the reasons for withholding;
- sends them to the employee for review;
- determines dimensions and adjusts in accordance with current legislation.
The main thing is not to forget to support each step with written evidence, so that in the event of an employee’s disagreement or an unplanned inspection, the manager has evidence that he is right.
You can find out more information about the procedure and on what grounds for deductions from an employee’s salary in this video:
Why should an employee write an application for retention?
There are two main categories of reasons for writing a statement:
1. The employer has grounds to deduct the following amounts from the employee’s salary:
- to pay off technical debt to the employer - due to overpayments, accounting errors and other similar scenarios (Article 137 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- to compensate for damage caused to the employer (Article 248 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
If we talk about technical debts under Art. 137 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, then for deductions for most of them, the employer is obliged to make sure that the employee does not dispute such deductions.
Exceptions:
- retention of unearned advance payment, which is written off without application (more on this later in the article);
- withholding of overpayment due to a court-established unlawful action of an employee (a court decision is required).
Compensation for damage under Art. 248 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not require the consent of the employee if the amount of damage does not exceed the average salary of a person per month (more on this later in the article). However, the parties have the right to agree on a larger amount of compensation in writing. For example, an employee can write an application to withhold agreed amounts.
2. The employee’s voluntary decision to make deductions from wages.
Such deductions may be related, for example:
- with voluntary payment of alimony;
- transfer of contributions to the trade union;
- employee participation in additional pension and health insurance programs.
Deductions can, in principle, be anything - the law does not provide for any restrictions here.
Let's now talk in more detail about when the application in question is not required - in the context of the scenarios we noted above.