The dismissal of an employee, according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (Article 140), is accompanied by a full settlement with him. All amounts due must be paid on the date of termination. However, there are always many questions regarding bonus payments. At the time of dismissal, the amount of the bonus may not yet be determined. How to calculate dismissal pay in this case? Is it necessary to pay a bonus to an employee who no longer intends to work for the organization? A bonus is an incentive payment. Does it make sense to use it in this case? How to avoid breaking the law and sanctions from regulatory authorities?
General issues of bonuses for resigning employees
Forms of remuneration in an organization, the system of this payment (SOT) can include not only payments for the performance of their duties by employees, but also be of an incentive, bonus nature. The payment of bonuses is regulated by all-Russian legislation and local regulations relating to labor relations (LRA).
The Labor Code does not consider bonus issues in detail, indicating only that in the event of controversial situations, the employer must pay the employee an undisputed amount. To avoid problematic issues, bonuses and their payment are described in detail in the organization’s regulatory documents. The procedure for calculating and paying bonuses in the organization is prescribed:
- in a collective agreement;
- in the employment contract (agreement) with the employee;
- in the Regulations on remuneration;
- in orders and regulations on individual bonuses for individual employees.
It is advisable to reflect the bonus payment procedure in the individual agreement of the parties, while at the same time specifying detailed conditions for such payments in the collective agreement or Regulations.
All bonus amounts due to the employee according to regulatory documents must be paid upon his dismissal. The amounts of accrued bonuses are included in the amount of dismissal payments (for example, compensation for unused vacation), in accordance with the current government Decree No. 922 of 12/24/07 on average earnings. According to Federal Law No. 272 and subsequent clarifications of the Ministry of Labor (see Letter No. 14-1/B-800 dated 08/23/16), payment of bonuses must be completed no later than the 15th day after the period for which it was accrued, and LNA must contain appropriate wording regarding deadlines.
Arbitrage practice
Judicial practice regarding the payment of bonuses after the dismissal of an employee is ambiguous.
On the one hand, the condition stated in the employment contract that only employees who have an employment relationship with the employer receive bonuses for achievements is recognized as discriminatory and contrary to the norms of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (Decision No. 33-3855/15 of the Stavropol Regional Court of June 30, 2015).
On the other hand, it is noted that bonuses are an incentive payment for employees who continue to work, so there is no discrimination here (Appeal ruling of the Perm Regional Court dated November 18, 2013 No. 33-10685/2013).
Each employee independently decides what to do if the dismissal bonus is not paid, whether to go to court or not. It is important to remember: if the employee wins the dispute, the former employer will have to pay the required bonus, pay legal costs and compensate for possible moral damages plus interest for each day of late payment.
If the amount paid upon dismissal, in the opinion of the employer, turns out to be excess, then the former employer will have to go to court, since it is possible to seize the excess from the former employee only by a court decision.
Premium accounting
Accounting for bonuses to a dismissed employee is kept in the accounts for wages, other payments and those corresponding to them. The bonus is calculated on the debit of production and similar accounts: D 20, 23, 25, 26, 44, etc. K 70.76 . Payment is made in the usual manner, through a cashier or bank: D 70, 76 K 50.51 .
Annual and quarterly bonuses are subject to personal income tax (Article 208-1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) and are reflected by the posting: Dt 70, 76 Kt 68/NDFL .
On a note! There is Art. 217-7 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which contains a mention of non-taxable bonuses (for example, for outstanding achievements in science or cultural activities), in addition, bonuses of 4,000 rubles or less specified in Art. 217-28 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The inclusion of bonus payments not specified in the LNA in the calculation of income tax to reduce the base is illegal (Article 270-21 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Premiums are subject to insurance charges, according to Art. 420 Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Art. 20.1-1 Federal Law No. 125 dated July 24, 1998. Costs for them are recorded as standard: Dt 20, 23, etc. K69 (according to accounting subaccounts) .
Bonus after dismissal: calculation, payment - Kontur.Accounting
Compensation payments after the dismissal of an employee are of great interest to him. Employers often refuse to pay bonuses after an employee leaves. Next, we will try to figure out whether it is necessary to pay a bonus after dismissal or not.
The laws do not clearly state that payment of bonuses after the dismissal of an employee is mandatory. Many employers deliberately say that there are no direct instructions from the state regarding the payment of bonuses, thereby depriving workers of compensation. However, an employee who has not violated the employment contract may qualify for a bonus after dismissal.
The bonus is calculated in accordance with Article 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. This document states that if a person is fired, this should not deprive him of the right to receive the compensation he deserves.
There are conditions for paying bonuses after an employee leaves the organization:
- the employee must work during the remuneration period;
- compliance with the terms of the employment contract;
- the absence in the regulatory act on bonuses of a clause that bonuses are not accrued after dismissal.
The annual bonus is calculated for a full calendar year. When an accountant calculates remuneration, he must take into account many factors: dismissal at his own request or by agreement of the parties; actual time worked; employee experience.
Upon dismissal of one's own free will: if a person worked well and had no reprimands or fines, the annual remuneration is accrued regardless of whether he quit or not. Incentives are calculated based on the company's performance in the new billing period. The employee has the right to apply to the arbitration court after three months after non-payment of the amount due.
When dismissing by agreement of the parties: this dismissal option is a peaceful agreement between the resigning employee and the manager.
You need to draw up a document in which all payments will be spelled out: salary, incentive bonuses, bonuses.
If the employee quit before the order for annual compensation was issued, this fact must be stated in the agreement, as well as the procedure for receiving the bonus after dismissal and the amount of the amount.
The bonus accrued to the dismissed employee will be included in labor costs in the month of accrual (in order to be included in expenses, it is important that such a bonus is mentioned in the employment contract or local act). Issue an order in form T-11, the accounting department will accrue the money, give it to the employee and reflect it in the accounting records:
- The accrual is reflected in correspondence with account 76: Dt 20 (23, 25, 26, 44) Kt 76.
- We also make entries for calculating personal income tax on the premium: Dt 76 Kt 68.
- The payment is reflected in the posting Dt 76 Kt 50 (51).
- Insurance contributions for pension, medical and social insurance are paid from the premium - using standard entries for expenses, the amounts are divided into the corresponding subaccounts of account 69: Dt 20 (23, 25, 26, 44) Kt 69.
Incentives are awarded after the employee has familiarized himself with the regulatory act against signature. If he does not agree with the amount of compensation, he will have to write a statement to the head of the organization with the reason and nature of the claim.
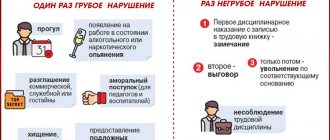
After an employee's dismissal, payment of incentives is not required. The manager may refuse to pay compensation. In such a situation, the case may go to court, and the court will be on the side of the employer under the following conditions:
- a note in the employment contract about restrictions on the accrual of incentives to a dismissed employee (although some courts in this case take the employee’s side);
- documented disciplinary sanctions, fines, violations of labor discipline by workers during work, which relate to the calculation of compensation;
- the scope of work according to which bonuses are due has not been completed;
- the employee who went to court does not have documents confirming the fact of working in the organization;
- malicious violation of an employment contract by an employee.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with How to achieve not being fired on your own, but getting laid off
If the compensation was paid not as financial assistance, but as a bonus, it relates to the employee’s income. Then the accounting department is obliged to attribute these funds to the wage fund and make payments for personal income tax deductions, contributions to the Pension Fund, Social Insurance Fund, and Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund. Premiums are subject to the following charges:
- Personal income tax - 13% if the employee is a resident of the Russian Federation; if compensation is paid to a foreign citizen, then the rate will be 30%;
- PFR-22%;
- Social Insurance Fund - 2.9%;
- Compulsory medical insurance - 5.1%.
When calculating remuneration already paid, an error may be discovered that leads to an overestimation or underestimation of its amount. Errors can be counting or they are associated with incorrect application of accrual rules.
If an error led to an underestimation of the premium, it can be corrected by adding the required amount of incentives. If the amount of the bonus paid is too high, the employer who wants to return the overpaid money must go to court. The court's decision will be positive if it can be proven that a counting error was made.
If any other error was made when calculating remuneration, the former employee has the right not to return the excess amount paid to him.
Author of the article: Alexandra Averyanova
What important changes have occurred in the calculation of insurance premiums and personal income tax, how the size of the minimum wage and benefits at the expense of the Social Insurance Fund have changed.
Let's talk about how often salaries are paid to employees and why the law does not contain the concept of “advance”.
In Russia, the minimum wage has been increasing since January 2020. In the article we will look at how this indicator has changed over the past few years and how it relates to the cost of living.
When paying a bonus to an employee after dismissal, he may be paid either less or more money than expected. As a rule, this happens due to incorrect calculations by the accounting department.
If the employee received less than the required amount, the employer can make another payment. However, in this case, insurance and tax will be paid in two payments.
If the company has paid excess funds and the employee does not want to return them, justice can only be restored through the courts. In this case, you will have to prove the mistake made by the accountant in the calculations.
If the situation is the opposite, and the employer completely refuses to pay the due bonus after dismissal, he must remember the liability that he may incur for non-payment (according to parts 1 and 2 of Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
Expert opinion
Irina Vasilyeva
Civil law expert
Before going to court, it is advisable for the employee to try to resolve the issue peacefully.
The employee quits, and the amount of the bonus has not yet been determined
If the size of the bonus is known at the time of dismissal, the accounting accountant does not have any problems; he includes it in the calculation of dismissal amounts. If the amount of bonuses is not determined at the time of dismissal, you should recalculate later and adjust the amount due to the former employee. It is obligatory to make an additional payment, recording its receipt by the employee in any legal way. Otherwise, there is a high probability of going to court. The timing of payment of bonuses to employees after their dismissal must be prescribed by the LNA (Article 8 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) - Regulations on Labor Protection, bonuses, etc. The specified position is contained in Letters of the Ministry of Finance, for example, No. 03-03-04/1/294 dated 25-10 -05, recommendations of Razgulin S.V., state adviser 3rd class, arbitration judicial practice.
Prize as a legal concept
According to the norms of Article 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the salary structure of a staff unit may include the following components:
- tariff rate;
- compensation charges (work in difficult conditions, harmfulness, etc.);
- incentive payments (bonus, allowance).
Motivating employees to increase their desire to work more efficiently is an important component of the company’s overall success in achieving planned goals. Based on this, bonuses can be of the following types:
- regular (every month) or periodic (usually paid on holidays or quarterly);
- for conscientious performance of official duties;
- for achieving and exceeding planned targets;
- as an assessment for completing particularly serious and important tasks;
- annual (based on the results of the enterprise’s work for 12 months);
- for complexity and tension.
Incentive payments are a pleasant bonus for every employee, but in order to calculate additional payments, it is necessary to secure the possibility of bonuses for colleagues in legal documents, in particular:
- in regulations for a particular industry;
- an individual employment contract with an employee;
- collective agreement at the enterprise.
Mistakes and Consequences
Errors that arise during the calculation of bonuses can be divided into 3 categories:
- arithmetic;
- arising as a result of incorrect application of established calculation rules;
- relating to tax accounting.
The latter have already been discussed: they arise, for example, if a premium that is not legally fixed is included in the calculation of the income tax base in order to reduce it. Such actions are considered by the Federal Tax Service as a reason to apply fines and sanctions when checking payments.
Accounting errors lead to incorrect payment of funds to the former employee during settlement. An underestimated amount of the bonus can be recalculated and an additional payment made, while an overestimated amount of the bonus paid represents a problem for the organization, since it can be resolved in court. According to Art. 137 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the overpaid amount can be withheld from an employee, but the specified citizen is not actually an employee. In addition, the already mentioned Art. 140 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation speaks of the possibility for an employee to challenge the amounts paid. It is therefore advisable to resolve this dispute out of court.
Errors of a different nature, in addition to arithmetic, that overstate bonus payments to a dismissed employee, are resolved only at the expense of the organization (Civil Code of the Russian Federation, Art. 1109). In any case, the court will be on the side of the dismissed citizen.
Is it possible not to pay a bonus upon dismissal?
All grounds for which the premium is paid must be specified in local acts agreed upon by each other. If there are vague formulations or contradictions, the emergence of a conflict in the event of a refusal to pay a bonus to a resigning employee is inevitable. Thus, the wording: “The manager has the right to pay incentive payments to employees - bonuses” is not obligatory for payment, and the phrase “The manager must pay bonuses” fixes the mandatory nature of such payments.
Cases of deprivation of a bonus in the LNA must also be clearly stated. Every employee must be familiar with the labor regulations adopted by the organization. Consent must be recorded with his signature.
Failure to pay the bonus specified in the LNA to a dismissed employee on the basis of a disciplinary sanction is not recommended. If you go to court, most likely, such a decision by the organization’s management will be declared illegal.
On a note! The period for going to court is 3 months from the moment the employee became aware of a violation of his rights, i.e. from the date of receipt of settlement amounts from the organization.
At the discretion of the parties
The bonus is part of the earnings of the working staff, designed to stimulate the labor process. The decision on monetary compensation usually occurs upon completion of a production plan, so payment may be monthly. The regularity of accruals is regulated by the internal documents of the enterprise.
The right to material remuneration based on the results of the previous year arises for all persons who worked for the benefit of the employer, including those dismissed, with the onset of the new calendar year.
In this case, the essential conditions of the bonus payment procedure for employees are taken into account. If an employee upon dismissal was not paid a legally due bonus, he has the right to appeal to higher supervisory authorities after the expiration of the three-month period given to the employer to fulfill the direct obligation.
The legality of the parties' actions is also interpreted by clarifications of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation. The right to receive bonuses for the previous period by citizens after dismissal is confirmed on an equal basis with other employees.
Termination of an employment contract by mutual consent implies the termination of employment relations peacefully. The parties need to:
- draw up a written document;
- discuss all the details.
Particular attention should be paid to the procedure for paying cash benefits.
The absence of a valid order on bonuses for the period worked does not deprive the opportunity to receive financial compensation in the future. During the process of drawing up an agreement, all rules must be followed and legal provisions taken into account. Contradictions with the provisions of labor legislation are not permitted.
Precision of presentation is encouraged. The best option involves designating specific payment amounts.
The presence of a system of annual bonuses involves the accrual of separate compensation to the employee in the event of dismissal due to retirement.
The intended purpose of the monetary payment determines the taxation procedure. Financial assistance in the amount of up to 4,000 rubles. does not oblige to charge a tax fee.
Main
- The bonus to the dismissed employee must be paid in the vast majority of cases. Non-payment of bonuses must be recorded in the organization’s local acts relating to labor relations, otherwise legal disputes with the former employee are likely, not in favor of the organization.
- Errors made in the direction of overestimating payments to a dismissed person can be corrected at the expense of the former employee only if they are of an arithmetic nature, in court.
- Quarterly and annual premiums are subject to personal income tax, insurance premiums and are included in the calculation of income tax only if they are registered in the LNA.
- Postings reflecting bonus payments are made in a similar way to taking into account wages.
Procedure for paying a dismissed employee
After issuing a work book to an employee and accruing settlement funds, you can also pay additional remuneration. If an employee expects to receive bonuses after completing work at a particular enterprise, he should know that incentive accruals are calculated in a certain order.
The sequence of paying bonuses to a dismissed employee is as follows:
- an order of form T-11 or T-11a (or other regulatory act) is created to assign a bonus to the employee;
- the accounting department calculates the established amount of money: the amount of the subsidy due in this case depends on the size of the period for which compensation is calculated (can be a month, a quarter or one year);
- providing a sum of money to an employee: an employee can receive bonuses during dismissal. However, in most cases, the bonus is paid to the dismissed employee after full payment. In the second case, funds are paid separately.
The incentive is awarded after the employee has read the contents of the regulatory act and paid for it. If an employee is not satisfied with the amount, he can draw up a written statement addressed to the head of the enterprise indicating the existing claims.
Dear readers! Our articles talk about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is unique. If you want to find out how to solve your particular problem, please use the online consultant form on the right or call:
7; 8
It's fast and free!