Dismissal: P
Indeed, the question of which article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation should be referred to when dismissing an employee at his own request arises very often. The answer to this was given in the Rules for maintaining and storing work books, producing work book forms and providing them to employers, approved. Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated April 16, 2003 No. 225 “On work books”.
Clause 15 of the Rules establishes that upon termination of an employment contract on the grounds provided for in Art. 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (except for cases of termination of an employment contract at the initiative of the employer and due to circumstances beyond the will of the parties (clauses 4 and 10 of this article)), an entry about dismissal (termination of the employment contract) is made in the work book with reference to the relevant paragraph the specified article.
What difficulties may arise during dismissal under the Labor Code of the Russian Federation 2020
Upon dismissal, problems may arise that the employee has the right to solve with the help of the labor inspectorate or court. There are frequent cases of unlawful termination of employment relations at the initiative of the employer; sometimes pressure is placed on the employee in order to force him to write a statement of his own free will.
Read how to receive alimony to parents from children, judicial practice. How to avoid paying alimony legally in Russia? More details here.
Various unpleasant situations may arise:
- management does not accept the application, then it must be sent by mail
- they refuse to accept an application for withdrawal of a resignation letter submitted earlier - this will also have to be sent by mail
- fired without being allowed to work the allotted time - there is a reason to go to court
- management puts pressure or directly suggests writing a statement in an amicable way - you need to contact a lawyer and go to court (Article 391 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation - resolving labor disputes, considering applications from people who believe that they are being discriminated against)
- fired or transferred to a low-paid position - to court (Article 394 - consideration of the legality of dismissal or transfer to another job)
- withheld part of the money during settlement - to the court (Article 395 - protection of the interests of the employee if he disagrees with the amounts paid to him).
To resolve labor disputes, there are special authorities where a citizen can apply. According to Article 393 of the Labor Code, legal assistance in case of wrongful dismissal or other claims is free. The article lists cases when filing a claim for an individual does not mean expenses.
All these cases are of a civil nature and may relate to failure to comply with the accepted terms of the contract or other aspects of the labor relationship.
Article 80 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Upon expiration of the notice period for dismissal, the employee has the right to stop working. On the last day of work, the employer is obliged to issue the employee a work book and other documents related to the work, upon the employee’s written application, and make a final payment to him.
An employee has the right to terminate an employment contract by notifying the employer in writing no later than two weeks in advance, unless a different period is established by this Code or other federal law. The specified period begins the next day after the employer receives the employee’s resignation letter.
Dismissal procedure
Upon completion of work at his own request, the employee must submit an application to his immediate supervisor. The document must indicate that he is asking to be relieved of his position from a certain date; there is no need to describe the reason why the employee wants to leave - the wording “at his own request” will be sufficient.
Based on this application, an order is issued to the enterprise and after a certain time the employee stops working, a final settlement is made with him: they issue a work book and other documents at his request (for example, a certificate of average salary, information about the insurance period, etc. ), as well as all the cash he should receive.
Part 3 Article 80 Labor Code of the Russian Federation With Comments 2020 Dismissal
An employee has the right to terminate an employment contract by notifying the employer in writing no later than two weeks in advance, unless a different period is established by this Code or other federal law. The specified period begins the next day after the employer receives the employee’s resignation letter.
c) based on the content of part four of Article 80 and part four of Article 127 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, an employee who has warned the employer about termination of the employment contract has the right, before the expiration of the warning period (and when granting leave with subsequent dismissal - before the day the leave begins) to withdraw his application and dismissal in this case is not carried out, provided that another employee is not invited in writing to take his place...
Labor Code of the Russian Federation 2019- 2019 dismissal
Labor Code - current edition, relevance 2020 The latest edition came into force on 10/03/2019 The current version is posted on the website. Next update: 01/01/2019 The Labor Code of the Russian Federation is a set of basic rules governing the relationship between employee and employer. This document is fundamental along with federal laws and other regulatory legal acts and is subject to constant changes in connection with changing conditions of labor relations.
Articles of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation Labor Code 2020 comments, changes, articles The Labor Code 2020 (Labor Code of the Russian Federation) regulates all labor relations on the territory of the Russian Federation. On its pages, in the articles of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation 2019, you will find answers to all kinds of questions and ways to solve numerous situations that arise in the process of labor relations.
Article 80
Dismissal of an employee at his own request before the expiration of the notice period is possible both by agreement of the parties and in the presence of valid reasons (retirement, enrollment in studies, etc.), as well as in cases of established violation by the employer of the labor rights of employees (see paragraph 22 PPVS of the Russian Federation dated March 17, 2004 No. 2).
We recommend reading: How Much Can Bailiffs Calculate Benefits From the Exchange
In cases where the employee’s application for dismissal on his initiative (at his own request) is due to the impossibility of continuing his work (enrollment in an educational organization, retirement and other cases), as well as in cases of established violation by the employer of labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts, containing labor law norms, local regulations, terms of a collective agreement, agreement or employment contract, the employer is obliged to terminate the employment contract within the period specified in the employee’s application.
advant24.ru
Registration of dismissal from work……………………………………………………… 30 5.1 Statement of resignation……………………………………………………… ………….
30 5.2 Order of dismissal……………………………………………………………….
31 5.3 Submission of termination of the employment contract………………………… 32 5.4 Minutes of the elected trade union body…………………………………… 32 5.5 Records upon dismissal from work……………… ……………………………………………………… 33 Conclusion………………………………………………………………………………………… . But there are also cases when the employees of a given employer are not united in any primary trade union organizations or none of the existing primary trade union organizations unites more than 1/2 of the workers
Article 280
The head of the organization is subject to the general rule established by Part 3 of Art. 80 of the Labor Code, according to which, when dismissing for good reasons established by law, the employer must dismiss the employee within the period for which he requests. He is also subject to other conditions for terminating an employment contract at his own request, provided for in Art. 80 TK.
The longer notice period for the head of the employer's organization about the upcoming termination of the employment contract (as a general rule, 14 calendar days) is due to the special position of the head compared to other employees of the organization and is explained by the fact that the owner of the property may need more time to replace the outgoing head of the organization.
Terms of termination of employment relationships
If an employee expects to return to another job after dismissal, he must submit his application within the following time frame:
- two weeks before the date of dismissal in general}
- three days before the date of dismissal, if he performed temporary or seasonal work, or was on a probationary period}
- one month before the date of dismissal, if we are talking about the heads of the organization (he is obliged to notify the owner of his decision)}
- at any time if the employer violates the agreed working conditions, as well as if the employee can no longer continue to work for good reason. These include illness, injury, moving to another area, enrollment in an educational institution, and the like.
It must be remembered that, according to the Labor Code, voluntary dismissal is not considered achieved if the employee continues to go to work after the specified two weeks. In this case, according to the law, it turns out that he has changed his mind about quitting, and if in fact this is not the case, he will have to write a new application and work for a new fourteen days.
Termination of an employment contract, clause 3, article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation: dismissal at will
There are situations when an employee is forced to write a letter of resignation of his own free will. The reasons, of course, are purely individual. The new director is selecting personnel, the employee is no longer happy, there is a reorganization, pregnant women are often forced to do this, etc. The Labor Code has two paragraphs of Article 77, which seem equivalent to ordinary citizens:
To cancel an application that has already been submitted, you must write and also officially register a new one in accordance with all the rules. No matter how good the relationship between him and the employer may seem to the employee, it is important to know the main rule: the application for refusal of dismissal must be submitted officially, i.e. in writing through a secretary or by mail.
Article 31 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, entry into the labor force, what is the problem?
During the notice period, the administration may dismiss the employee,
if he has committed an offense that is grounds for dismissal (appeared
drunk at work, etc.).
§8. Upon dismissal of a temporary and seasonal employee at his own request
warning period is three days.
§9. The warning period is calculated in accordance with Art. 221 Labor Code (see comment
to her) from the next day after the employee submits the application. If the last one
the day of the notice period falls on a non-working day, then the day of the end
The notice period is considered to be the next working day following it.
Article 80
It should be borne in mind that the employee’s demand in question has legal significance only at the time of expiration of the working period. If the employment contract was not terminated upon expiration of the working period, the employee continued to work, and subsequently demanded termination of the employment contract with him with reference to Part 6 of the commented Article 80 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, such a requirement cannot be considered legal: the employment contract must be terminated according to the rules established by the commented article, including working out the established notice period for dismissal.
We recommend reading: Social Travel Card and Reduced Ticket Rate
In practice, there are often cases when an employer delays making payments to an employee and issuing a work book to him, citing the fact that the employee did not fill out the so-called bypass sheet, did not hand over the material assets he accepted, etc. This type of practice is not provided for by labor legislation and is therefore illegal. Moreover, after the expiration of the notice period for dismissal, the employee has the right to stop working, and the employer is obliged to issue him a work book on the day of dismissal (last day of work) and, upon the written request of the employee, copies of documents related to the work, as well as pay all amounts due to him from the employer (see Articles 62, 140 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and commentary thereto).
Features of dismissal under Article 33
The definition of “dismissed under Article 33” still means for most of the adult population the dismissal of a person for systematic absence from work or drunkenness. However, not many people know that after the Labor Code of the Russian Federation came into force on December 30, 2002, the numbering shifted and this article contains completely different provisions that are not related to the exclusion of an employee from the organization’s staff.
The new Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes in the specified article the relationship between the employer and the employee, allows solving issues of labor protection, professional training, advanced training, and payment rules. Separate parts are devoted to the activities of citizens of certain categories. These are minor children, specialists with pedagogical education, people whose professional activities are carried out at home.
The meaning of the expression “dismissed under Article 33”
In all Soviet republics and the RSFSR, in the labor code, it was Article 33 that aroused special interest among working people, since it reflected multiple reasons that gave the employer the authority, represented by an employee of the management or administration of the enterprise, to initiate the termination of the employment agreement with its staff, that is, to fire. The reasons cited were mainly absenteeism, drunkenness, and regular violations of labor discipline.
The corresponding entry appeared on the page of the employee’s work book and implied a negative meaning, subsequently becoming an obstacle to subsequent employment. And although there was practically no lack of work in the Soviet Union, personnel department employees were prejudiced against applicants who were fired “under the article.”
However, the list of grounds included many items, many of which did not record violations by the staff. Termination of an employment contract with an employee could be initiated at the request of the administration due to the likely cessation of the enterprise's activities or a decrease in the number of working people.
Contents of the article on the Labor Code
During Soviet times, Article 33 of the Labor Code provided the opportunity to indicate the following reasons for dismissal:
- reduction in the number of employees or liquidation of an organization/enterprise;
- inadequacy for the position held;
- health problems;
- regular violations of labor regulations and behavior;
- absenteeism, absences from work without indicating a valid reason, confirmed by a document;
- long-term disability due to illness not related to pregnancy or work injuries;
- the appearance of an employee at the workplace after he was fired;
- presence at the workplace while intoxicated, drinking alcohol;
- theft or theft, the fact of which was confirmed by a relevant document from the court.
At the same time, this article contained a whole list of reasons on the basis of which the administration was entitled to reduce the position of an employee and give a full payment without his consent.
Article 33 in the modern version of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Today, the improved Article 33 of the latest edition of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation has been moved to a section that reflects provisions on issues related to social partnership in the world of work. It was called “Representatives of Employers” and now consists of two parts, while regulating the following relations.
- Cooperation between the administration and the working personnel of the enterprise in the development and creation of collective agreements or during negotiations. Both the manager himself and his authorized representative can act on behalf of the employer. If the organization is a government agency, then the government agency is authorized to represent it.
- Interaction with employee associations in the event of disputes or other organizational issues of a collective nature related to the conclusion or amendment of labor agreements. In this case, their union acts on behalf of the employers.
As can be seen, in Art. 33 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation says nothing about the dismissal of working personnel.
Article 80 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, dismissal at will with comments
There is one exception to this rule, when the reduction of the period is due to valid reasons, the list of which is given in Part 3 of the commented article. Among such cases, one can indicate the entry of an employee into military service under a contract (see Article 83 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and the commentary thereto).
An employee’s absence from work for valid reasons (for example, due to temporary incapacity for work) is not grounds for extending the period of service upon dismissal of his own free will. At the same time, the employee’s refusal to dismiss may be declared by the employee during his absence from work for the specified reasons.
Reasons for dismissal according to Article 81 of the Labor Code
Dismissal under Article 33 of the old-style Labor Code of the Russian Federation has not been carried out since 2002. If it is necessary to terminate the employment agreement, the administration representative must rely on the list of grounds reflected in Art. 81. And when staff are intimidated by the thirty-third, it should be understood that this is just a habit that has been formed over many years.
It is important to know! The new article displays a wide range of reasons for terminating a cooperation agreement. But in all cases, the initiative belongs to the employer’s organization; the employee’s wishes are not taken into account.
According to the new additions, the contract can be canceled if the following circumstances arise:
- the company or organization ceases its activities and is liquidated;
- a reduction in the number of employees is planned - staff reduction;
- a fact of non-compliance with the position held, identified by the certification method, was established;
- there was a change in management;
- neglect of direct official duties was recorded, confirmed by fact;
- absenteeism occurs: absence from work all day or more than 4 hours;
- the fact of inappropriate behavior at work, appearing in an intoxicated state has been revealed, the person has been convicted of drug addiction;
- theft occurred, deliberate damage and destruction of property was revealed (regardless of size);
- illegal activity was discovered that resulted in material losses;
- the commission of immoral acts by employees engaged in educational work has been proven;
- the provision of false documents during employment was discovered, which was actually revealed;
- non-conservation or deliberate dissemination of state or commercial secrets was recorded.
Certain paragraphs of Part 2 of Art. 81 contain provisions prohibiting termination of employment agreements with employees who are on vacation or sick leave. However, the commentary states that in the event of termination of the enterprise's activities due to its liquidation, these restrictions cease to apply. If this situation arises, the employer is obliged to try to find minimum wage jobs for its staff.
Advice! Any point used by the employer as a basis for severing the employment relationship must be proven and supported by documents. Otherwise, the employee has the right to defend his innocence and reputation.
Articles-analogs 81 Art. Labor Code of the Russian Federation and 33 Labor Code: general points
Analysis of the provisions contained in Art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, allows us to conclude that most of the points were transferred from the previous Article 33, having undergone minor changes and modifications. In particular, the following reasons for dismissal remained.
- Termination of the company's activities and reduction of staff. In the new version, these two points were broken down and became independent.
- Inconsistency with official position due to lack of qualifications. But this must now be confirmed by the conclusions of the certification commission.
- Systematic violations of norms of behavior at work.
- Absenteeism. This term has now been clearly defined and the time away from work has been increased.
- Inadequate condition. Appearing at work after consuming alcohol, drugs or taking them during work.
- Committing theft. The fact of such an action must be confirmed by the judicial authorities and recorded in a written decision. In addition, grounds such as intentional damage to property, which is expressed in embezzlement or damage, have appeared.
At the same time, the requirement for the manager remained in force, obliging him to employ his employees in the event of an inevitable reduction in staff and ensure timely payment of wages.
2002 changes
Along with the old clauses, new provisions appeared in Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which made it possible to make it more capacious and functional. Thus, the improved version was supplemented with the following reasons.
- A change in the owner of the company, which involves the dismissal of management personnel, deputies, and the chief accountant.
- Committing a gross or severe violation of labor discipline (even once) in the form of being present at the workplace in a state of intoxication, drinking alcohol during the day, theft, embezzlement.
- Failure to comply with the condition of non-disclosure of state or commercial secrets, which entailed serious consequences for the organization or the owner of the company.
The list of reasons that allow severing employment relations with staff without their consent also includes immoral actions and deeds, provision of incorrect data, false documents when applying for a job or during the period of employment.
It is important to know! Despite some changes and a number of additions to Art. 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, most of the provisions, as before, are related to violations of labor behavior of employees.
AutoJurist legal assistance
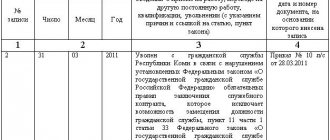
In the first column the record number following the previous one is entered, in the second - the date of dismissal, which must correspond to the date of termination of the agreement, in the third column, based on Art. 80 part 3 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the reason for dismissal and information about the authorized person is indicated; the fourth column must indicate information about the document based on which the employee was dismissed. After the employee has received his work permit, he must sign the work log book.
If the plaintiff claims that the employer forced him to submit a resignation letter of his own free will, then this circumstance is subject to verification and the responsibility to prove it rests with the employee; b) the employment contract can be terminated at the initiative of the employee and before the expiration of the two-week notice period for dismissal by agreement between the employee and the employer. If the employee’s application is due to the impossibility of continuing his work, as well as in cases of established violation by the employer of labor legislation, etc.
What is it for?
There are often cases when the employer is not against such dismissal. But he had no reason to do it himself. And then the employee himself brings such a letter of resignation under clause 3 of Art. 77 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Then after some time the employee announces that he has changed his mind. The director, knowing the legislation, says with joy on his face that “I understand everything, continue working.”
After a two-week period from the date of writing the application, a dismissal order is issued in accordance with clause 3 of Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation - at one’s own request.
There is no use going to court. Legally, the director did everything correctly. One of the principles of law was at work here: “Most moral principles become legal norms, but not all.”
When refusing an application of your own free will, there is one very important nuance. If, from the moment the employee was fired until his refusal, a written invitation was sent to another person to accept this position, then it will no longer be possible to cancel it.
Here the law will be on the side of the future employee, i.e. someone who has already been invited. Because Now no one has the right to refuse him employment.
Therefore, it is necessary to weigh everything carefully before writing a letter of resignation. There are times when there is no way back.
Article 127 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
1. When an employee is dismissed, regardless of the grounds for dismissal, he is paid monetary compensation for all unused vacations; When an employee enters a new place of work, the length of service required to obtain the right to annual paid leave begins to flow over again.
We recommend reading: Article 228 part 4 pregnant 2019
When granting leave with subsequent dismissal upon termination of the employment contract at the initiative of the employee, this employee has the right to withdraw his resignation letter before the start date of the leave, unless another employee is invited to take his place by transfer.
Nuances and judicial practice
Regardless of who is the initiator of the severance of labor relations, it is necessary to strictly observe the norms provided for by the current legislation of Ukraine. If the provisions of the Labor Code are violated by the employer, the dismissed employee may apply to the judicial authorities to protect his own interests. By a court decision, the dismissal may be annulled, which will oblige the director of the organization to reinstate the employee in his position. In addition, a person may demand payment of monetary compensation for the period when he cannot work due to a manager’s mistake. These violations may include failure to offer an employee a vacant position during a layoff or untimely notification of an upcoming layoff, or untimely issuance of a work book, which led to a violation of the employee’s rights.
The current legislation of Ukraine, in particular the Labor Code, provides many options for terminating an employment contract. At the same time, the initiator of termination of cooperation can be not only the head of the organization, but also the employee himself. After the termination of an employment contract, a person must be provided with funds, the amount of which is regulated by the collective agreement and articles of the Labor Code, in particular Article 44.
Article 140 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
The Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation explained that Part 2 of Art. 140 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, imposing such an obligation on the employer, thereby protects the labor rights of dismissed workers and cannot be considered as violating the constitutional rights of the applicants (see the definition of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation of February 21, 2008 N 74-О-О).
1. Upon termination of an employment contract, the employee must be paid all amounts due to him: wages for the current month; wages for the previous pay period, if they were not paid on time, as well as monetary compensation for delayed payment of wages; compensation for unused vacation; severance pay; guarantee and compensation payments; amounts due to the employee on the basis of a collective agreement. The day of payment of all amounts due to the employee is the day of dismissal, which is considered the last day of work.
"Correct" article
Despite the basic basic principles of legal acts, namely “absolute clarity in wording,” misunderstandings very often arise. Under what article should dismissal be made? Clause 3 Art. 77 or art. 80 Labor Code of the Russian Federation?
But in fact there is no problem in understanding here. One is considered procedural (how to legally change jobs correctly), and clause 3 of Art. 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation – normative, i.e. indicates the fact itself.
Almost everyone knows that you need to work for 2 weeks before leaving the organization. Let us immediately clarify one very important nuance.
Dismissal (clause 3 of Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) does not provide for any work.
You just need to notify the employer no later than this period. Of course, during this period you will have to perform your functions at the enterprise. Hence the erroneous opinion. But let us clarify that compulsory work for half a month is optional.
You can go on sick leave or vacation, warning your employer about future dismissal. In this case, there can be no processing.
Nuances of dismissal from work under the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
Hello. Please tell me, in the event of my dismissal from work at my own request (Article 80 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), if I do not want to work the 2 weeks provided for in such cases, can I indicate as the reason for dismissal - “at my own request, in connection with the release on retire"? And can I take advantage of this opportunity if I am a foreign citizen and my pension was assigned in another state (Ukraine), but I work officially in the Russian Federation?
Hello Dmitry! Part 3 of Art. 80 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes cases when an employer is obliged to terminate an employment contract within the period specified in the employee’s application. One such case is the inability of an employee to continue working due to retirement. Provisions of Art. 80 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation also applies to employees who are foreign citizens.
07 Feb 2020 juristsib 1462
Share this post
- Related Posts
- Application for payment of a lump sum benefit upon the birth of a child 2020 father
- How to Correctly Fill out Sheet D1 of Personal Income Tax Declaration 3 for 2020
- When can you get a tax deduction when buying an apartment with a mortgage 2020
- Is it necessary to pay for kindergarten if the child does not attend due to illness in 2020
Labor Code of the Russian Federation with amendments and additions for 2020 dismissal
disputes Probationary period This is interesting: Will there be an increase in salaries for public sector employees? Where will those who have raised their retirement age work? How do we rest in 2020? The minimum wage will be raised again, but from the new year 2020. There will be an increase in the retirement age. Parents with many children will now be able to rest not according to a schedule, but at any time. To undergo a medical examination, employees will be given an additional day off. How much does a cashier earn in Russia? Increasing pensions in Russia - myth or reality?
- 2.1 Dismissal from the civil service
- 2 Articles of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation on dismissal
- 2.1 Dismissal from the civil service
- 2.2 Article 71 – result of the employment test
- 2.3 Article 77 – general grounds for termination of an employment contract
- 2.2 Article 71 – result of the employment test
- 1.1 The procedure for dismissal under the article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation 2019
- 2.3 Article 77 – general grounds for termination of an employment contract
- 1 Dismissal - Labor Code of the Russian Federation 2020 with comments
- 1.1 The procedure for dismissal under the article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation 2019