Definition
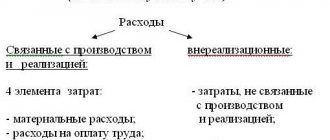
Profit from sales is the difference between the revenue received by the company from the sale of certain products/goods/work and the costs spent on their sale (production, purchase of raw materials, storage, transportation).
At the very start of the company’s activities, the indicator can take a negative value, this indicates an urgent need to increase revenues or reduce expenses, but the most effective way is to take both of these measures at the same time.
To analyze profits from sales, the main accounting documents are used - balance sheet, profit and loss statement, accounting registers.
Revenue from sales of products (works, services).
⇐ PreviousPage 4 of 5Next ⇒
Revenue from sales of products is one of the indicators of the characteristics of the enterprise. Revenue in its general meaning represents the amount of cash or other valuables that a company can receive during a certain period of its activity by selling goods and services. Do not confuse revenue with profit - profit is defined as revenue minus production costs. Revenue from product sales is one of the elements of the enterprise’s total revenue, along with revenue from financial and investment activities. Let us consider in more detail what the term revenue from sales of products means. Revenue (turnover, sales volume) is the amount of cash or other benefits received by a company for a certain period of its activity, mainly through the sale of goods or services to its customers. Revenue is different from profit because profit is revenue minus expenses (costs) that a company incurred in the process of producing its products. Capital gains resulting from an increase in the value of an enterprise's assets for some reason are not included in revenue. For charitable organizations, revenue includes the total value of cash gifts received. Revenue from the sale of products (works, services) includes cash or other property in monetary terms received or to be received as a result of the sale of goods, finished products, works, services at prices and tariffs in accordance with contracts. At the same time, the activity of the enterprise can be characterized in several areas: revenue from core activities, coming from the sale of products (work performed, services rendered); revenue from investment activities, expressed in the form of financial results from the sale of non-current assets, the sale of securities; revenue from financial activities. Total revenue consists of revenue in these three areas. However, the main importance in it is given to revenue from the main activity, which determines the entire meaning of the enterprise’s existence.
Profit and its types.
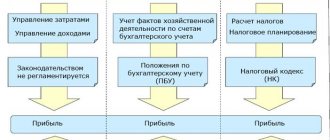
Profit is the main source of financial resources of an enterprise associated with the receipt of gross income. The gross income of an enterprise is the proceeds from the sale of products (works, services) minus material costs, including wages and profit.
Profit is the main assessment indicator of the economic and commercial activities of an enterprise. Profit is always determined in monetary terms.
In conditions of market relations, an enterprise must strive, if not to obtain maximum profit, then at least to the amount of profit that would allow it not only to firmly maintain its position in the market for the sale of goods and services, but also to ensure the dynamic development of production in a competitive environment .
The first type of profit is gross profit. It is defined as the difference between sales revenue and the cost of goods, works, and services sold. Profit from sales is determined taking into account commercial expenses (sales expenses) and administrative expenses (general production and administrative expenses), if administrative expenses are recognized by the organization as expenses for ordinary activities.
The balance sheet profit, which the enterprise must determine, is calculated as follows: the balance of other income and expenses is added (subtracted) to the profit from sales. Next, taxable profit or profit (loss) before tax is determined, in the calculation of which the following must be taken into account (in accordance with tax accounting):
profit, but to which tax has been paid;
profit for which the company has benefits;
profit on which tax is paid in a special manner;
profit that increases the tax base by exceeding normalized expenses (for advertising, personnel training, interest on loans, depreciation, entertainment, etc.).
Net profit (retained earnings), i.e. The profit remaining at the disposal of the enterprise is obtained by deducting income tax from profit before taxation and is used for the following purposes:
production development:
payment of dividends and other income to founders and owners;
contributions to the consumption fund;
payment of penalties for environmental violations, late payments to the budget, inflated prices, concealment of taxable items.
Profitability indicators
Profitability is a relative indicator that determines the level of profitability of a business. Profitability indicators characterize the efficiency of the enterprise as a whole, the profitability of various areas of activity (production, business, investment), cost recovery, etc. They reflect the final results of business more fully than profit, because their value shows the ratio of the effect to cash or resources used. They are used to assess the performance of an enterprise and as a tool in investment policy and pricing.
Profitability indicators can be combined into several groups:
1) indicators characterizing the return on production costs and investment projects;
2) indicators characterizing the profitability of sales;
3) indicators characterizing the profitability of capital and its parts.
All indicators can be calculated on the basis of balance sheet profit, profit from sales of products and net profit.
Profitability is defined as the ratio of profit to the capital invested to obtain this profit:
The following profitability indicators are widely used in practice:
1. Profitability of core activities
Shows how much profit the company makes from each ruble spent on the production and sale of products. It can be calculated for the enterprise as a whole, its individual divisions and types of products.
According to this indicator, enterprises are divided into:
- low-profit: R2 is 1-5%;
- average profitability: R2 is 5-20%;
- highly profitable: R2 is 20-30%;
— extremely profitable: R2 is more than 30%
The payback of investment projects is determined in a similar way; the received or expected amount of profit from the project relates to the amount of investment in this project.
2. A general indicator characterizing the profitability of sales is the profitability of sales (turnover)
Characterizes the efficiency of entrepreneurial activity, how much profit from sales the enterprise has per ruble of sales. This indicator is widely used in a market economy. It is calculated for the enterprise as a whole and for individual types of products.
The efficiency of using capital and its parts can be assessed using indicators of return on capital.
3. Economic profitability
Shows the efficiency of using all the organization’s assets.
4. Return on equity on net profit
Shows the efficiency of using the enterprise's own capital.
Similarly, the profitability of borrowed, permanent, fixed, working capital, etc. can be calculated.
In the process of analysis, it is necessary to study the dynamics of the listed profitability indicators, the implementation of the plan at their level and conduct inter-farm comparisons with competing enterprises.
⇐ Previous4Next ⇒
Recommended pages:
Use the site search:
Profit concepts
The concept of profit from the sale of products refers to the totality of funds representing income minus basic costs.
There are economic and accounting income, the difference that exists between them is due to the fact that there are several concepts of this definition.
For example, accounting income is total income less explicit accounting costs. As for the economic indicator, not only explicit, but also implicit costs are subtracted from the total income. That is, based on the data, it can be noted that the economic profit parameter is defined as the difference between the parameters of accounting profit and costs (implicit).
Normal profit
It comes from putting entrepreneurial skills and talents into practice. The indicator appears in a situation where total income equals total economic costs. Then the indicator takes on a zero value.
Net economic profit
If, from the total number of ways to use resources, a company chooses the most effective one, then income takes on a value greater than costs, and a positive indicator arises. Based on the ratio of the main elements of competition, the parameter can be maintained for a certain period of time.
The concept of profit from the sale of products refers to the totality of funds representing income minus basic costs.
Calculation formula
To calculate the coefficient, use the formula:
ROS = PR / V * 100%,
where ROS is the profitability of products sold, %
PR – profit from sales, t.r.;
B – revenue (net sales), t.r.
The formula for the lines of the income statement looks like this:
ROS = page 2200/page 2110 * 100%
Important! The formula does not take into account non-operating activities such as taxes and financing structure. For example, income taxes and interest expenses are not included in the formula because they are not considered operating expenses. This allows investors and lenders to understand the underlying operations of the business and focus on whether the underlying operations are profitable or not.
ROS is calculated as a company's operating profit for a given period divided by its net sales (revenue).
The calculation shows how efficiently a company produces its core products and services and how its management manages the business. Thus, ROS is used as an indicator of efficiency and profitability.
Factors affecting profit
The indicator is determined by several elements that have a serious impact on its value.
- The amount of income (revenue) received by the company through sales of products: the higher the value this indicator takes, the greater the value the profit ultimately receives.
- Revenue is nothing more than the product’s unit price multiplied by the volume of product sold.
A caveat: usually this indicator reaches its greatest value with a wide range of products offered.
- Full cost, which is the determining indicator in the area of sales costs. This indicator refers to the costs that were incurred by the company in order to first produce (or purchase - in the case of a trading enterprise) these products and then sell them. The goal of organizations is to minimize these costs by finding good suppliers and reducing logistics and service costs.
Thus, profit is an indicator influenced by certain factors that are important to take into account in any case.
Calculation
There are several methods that allow you to effectively and quickly calculate profit from sales of products, this is the formula: P = B - C floor.
- P - represented directly by the indicator under consideration,
- B – revenue,
- From floor - represents the full cost, that is, the main costs incurred to produce this product.
Another effective and useful method, often used to calculate the indicator in question , is the following formula: P = C * Ob - Seb. = About * (C – Seb).
- P - again, this is the indicator we directly need,
- About – the volume of products that were sold,
- P – the price that the enterprise set for 1 unit of product,
- Seb is the cost.
So, the formation and determination of profit is influenced by first and second order factors . Several of the first include:
- Volume of goods/products that were sold;
- The cost that is taken specifically per unit of the product sold;
- Assortment policy in the general product policy of the organization.
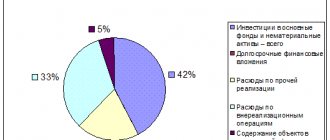
In addition to this parameter, in practice one can often find profits not only from the sale of products, but also from fixed assets and other types of company property.
This indicator acts as a certain financial result, which has no connection with the main types and activities of the company. In addition, this parameter usually reflects the amount of income that was received.
Preparation of accounting entries
Account 90 “Sales” is used to record revenue from sales of products. The account consists of several sub-accounts. Postings for revenue from sales of products are compiled in order to determine the financial result from sales. The mandatory conditions under which revenue is recognized in accounting are given in PBU 9/99.
In accounting, profit from sales involves several accounts:
- 50 "Cashier";
- 41 "Products";
- 44 “Sales expenses”;
- 90.1 Revenue;
- 90.2 Cost of sales;
- 90.7 Selling expenses;
- 90.9 Profit/loss from sales
What transactions need to be made to get a financial result, i.e. profit margin.
They will be as follows:
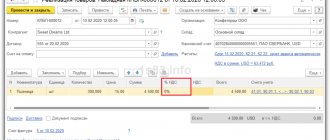
- 50 /90.1 - 900 thousand rubles. – proceeds from sales in cash are entered into the company’s cash desk;
- 90.2 /41 - 790 thousand rubles. – the cost of sales is written off;
- 90.7 /44 - 68 thousand rubles. – sales expenses are written off.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with how long before the visa expires you can enter Schengen, the validity period of the visa
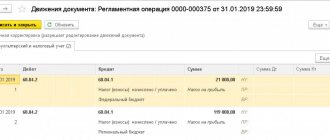
Next, to obtain a financial result, you need to write off the amount of revenue and expenses to account 90.9.
Here's how to do it:
- 90.1 / 90.9 - 900 thousand rubles.
- 90.9 / 90.2 - 790 thousand rubles.
- 90.9 / 90.7 — 68 thousand rubles.
During the postings, we determine that the turnover on the credit of account 90.9 is 900 thousand rubles, i.e. the amount of sales revenue. 858 thousand rubles must be reflected in debit. (790 thousand rubles. 68 thousand rubles). Thus, at the end of the reporting period, the credit balance was 42 thousand rubles, indicating profit from sales.
Profit from sales using documentation
This indicator is one of the most important parameters of any company’s activities, since certain performance results depend on it. This indicator is calculated not only by year and quarter, but also by month. This will require certain data, which is usually entered into accounting records and reflected there.
The goal of organizations is to minimize these costs by finding good suppliers and reducing logistics and service costs.
Instructions for finding the parameter
If you use the above data to search for profit indicators, then the basic information can be easily found in the financial statements. Line 010 displays the revenue received by the company from the sale, where it already appears without VAT.
If there is a need to calculate an indicator for a certain month, then to determine it you need to take the total amount; it is shown in line 90.1.
At the next stage, the products, works, goods and services sold are determined. In the report, this line is called 020 and is shown as cost, that is, as costs that were incurred for production and sale. Based on the profit reporting data, commercial and administrative expenses are calculated.
The amount of expenses of the commercial part is determined by the debit of account 44, which assumes sales expenses.
Profit in this case is always calculated using the general formula: P = B – C – KR – UR;
- B – in this case represents the proceeds received from the sale,
- C – selling costs (cost),
- KR - other expenses for commercial activities,
- UR – management costs.
So, we looked at how to calculate profit from sales. You can do this through price and volume, or you can do it using basic accounting documents that are available in any company.
Determination of sales indicators
Products
Revenue is the amount of money received from the sale of goods, both self-produced and purchased for resale.
Profit from sales is a value representing the difference between revenue received from the sale of core activities and the cost of goods sold, commercial and administrative expenses.
Works
Revenue - the amount of money received from the organization's performance of work, represents the volume of work performed multiplied by the tariff.
Profit from sales is the amount of money received from performing work, minus the full cost of work.
Services
Revenue - the amount of money received by an organization from the provision of services, represents the volume of services performed by the organization multiplied by the tariff.
Profit from sales is the amount of money received from the provision of services, minus the full cost of the services provided.
Fixed assets
Revenue is the amount of money received from the sale of fixed assets.
Profit is the amount of cash received from the sale of fixed assets minus the costs of selling these assets and their residual value.
Fixed assets can be buildings, structures, equipment, machinery, vehicles, tools, devices, that is, all the property that is used by the enterprise in the process of selling products or services.