Volume of production in the balance sheet
How are export customs duties reflected in the Statement of Financial Results? In Note 5 in Appendix No. 1 to Order No. 66n of the Ministry of Finance of Russia, export customs duties are not listed among the amounts excluded when forming the revenue indicator, along with VAT and excise taxes. According to the clarifications of the Ministry of Finance of Russia, contained in Letter dated January 09, 2013 N 07-02-18/01, export customs duties paid by an organization in connection with the movement of goods across the customs border do not reduce the revenue reflected in the Statement of Financial Results.
FAQ
Question No. 1. What are the limitations when calculating the indicator?
Answer. Depreciation is included in the calculation of earnings before taxes and can lead to different results when comparing companies in different industries. If an investor compares a company with a significant amount of fixed assets to a company that has few fixed assets, depreciation expense can hurt a company with fixed assets because the expense reduces profits.
Additionally, companies with a large amount of debt are likely to have high interest costs. Earnings before taxes reduce a company's earnings potential, especially if the company had a lot of debt. If debt is not included in the analysis, the problem may be that the firm will increase its debt due to lack of cash flow or poor sales performance.
Question No. 2. What is the indicator used for?
Answer. Profit before taxes takes into account all the profits a company generates, whether from core activities or non-core activities. The indicator calculation was invented to account for the constantly changing tax expenses of a company. It gives company owners and investors a good idea of how much profit a company makes without taking into account payments to the budget.
Question No. 3. Where is the value reflected?
https://youtu.be/XU_CzO2XusA
Answer. Profit before tax is indicated exclusively in the income statement on line 2300.
Which line shows profit from sales in the balance sheet?
Every year, companies prepare financial statements. Using data from the balance sheet and profit and loss report, you can determine the effectiveness of the organization’s activities, as well as calculate the main planned indicators. Provided that management and the finance department understand the meaning of terms such as profit, revenue and sales on the balance sheet.
Terminology The volume of product sales on the balance sheet is the amount of revenue received for the sale of goods in the reporting period.
In this case, the form of calculations does not matter. Products can be sold on credit, for cash, with deferred payment or at a discount. Therefore, for a more accurate calculation, the formula for calculating net sales in the balance sheet is used, when the revenue received is adjusted by the amount of goods shipped on credit. Sales volume reflects the amount of funds received by the company.
Therefore, it should be calculated by all organizations.
Analysis of balance sheet profit.
Analysis of an enterprise's balance sheet profit begins with an assessment of the plan's implementation in fact and in comparison with the previous reporting period. The assessment is given as a general and composite assessment; the latter involves an analysis of the components of the profit indicator by element.
The main objectives of the analysis of balance sheet profit are:
- identifying the reasons and factors for non-fulfillment of the profit plan;
- identification of weaknesses of economic activity, unprofitable links;
- finding sources of losses;
- creating lists of reserves to further increase profits/reduce losses.
In the process of analysis, the structure of balance sheet profit, its composition, and the dynamics of plan implementation during the reporting period are studied. When studying indicators over time, inflation factors changing its outcome are taken into account, revenue is adjusted by the index of the weighted average increase in product prices in the industry, and the cost of goods, works, and services sold is, as a rule, reduced by the difference in prices of resources consumed and used in production for the analyzed period.
IV. balance sheet (form No. 1)
The presence of a balance will mean that the formation of the entry for writing off profit (loss) was made with an error. When reforming the balance, it is necessary to close the 90th account.
This event involves writing off the balance of all subaccounts to account 90 to account 90. 9. These can be operations such as (if there is turnover during the year):
- Dt 90. 1 Kt 90. 9 - for writing off revenue turnover during the year;
- Dt 90. 9 Kt 90. 2 - for writing off turnover at cost;
- Dt 90. 9 Kt 90. 3 (90. 4) - for writing off turnover based on accrued VAT or excise taxes.
The balance on account 90.9 (as well as on account 90 as a whole) should become zero automatically after the above operations. If this does not happen, you should look for an error in the wiring. Read more about balance sheet reformation in the material “How and when to carry out balance sheet reformation.”
Net sales in the balance sheet: line. sales volume on the balance sheet: how to calculate?
The organization may have other unforeseen expenses (p. 2350) and income (p. 2340).
This way you can calculate net profit or net sales in the balance sheet: Line 2400 = 2110 – (2120 + 2210 + 2220) + 2340 – 2350 – 2410, where 2410 is the amount of income tax.
| Dear visitors! The site offers standard solutions to problems, but each case is individual and has its own nuances. |
| If you want to find out how to solve your particular problem, call toll-free ext. 504 (consultation free) |
Net sales on the balance sheet can be calculated by subtracting retained earnings (uncovered loss) at the end of the period from the value at the beginning of the period. A positive difference indicates a net profit, and a negative difference indicates losses.
Revenue. line 2110
PBU 9/99): - receipts from sales of products; — proceeds from the sale of goods; — receipts for work performed; — receipts for services rendered; — rent (in organizations whose activity is the provision of their assets for temporary possession and (or) use); — license payments (including royalties) (in organizations whose subject of activity is the provision of rights to use the results of intellectual activity); — income from participation in the authorized capital of other organizations (in organizations whose subject of activity is such participation); - other income recognized by the organization as income from ordinary activities based on the nature of its activities, the type of income and the conditions for their receipt (for example, for pawnshops, interest on loans provided is income from ordinary activities). But regardless of how the release of finished products is reflected in accounting, finished products in the warehouse in the balance sheet are indicated on line 1210 “Inventories (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n). If the amount of finished products in the organization's total reserves is significant, the organization must reflect information about product output in a separate line in the balance sheet or indicate the relevant information in the notes to the balance sheet.
Of course, finished products are reflected in accounting on line 1210 only in terms of product warehouse balances. How are sold finished products reflected in the balance sheet? Volume of product sales in the balance sheet: line There is no separate line for revenue from product sales in the balance sheet.
And this is not surprising. After all, the balance sheet reflects the assets and liabilities of the organization as of the reporting date (clause 18 of PBU 4/99).
Formula for calculating net profit on balance sheet
In the standard form of the balance sheet, approved by the order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia “On forms of financial statements of organizations” dated 07/02/2010 No. 66n, there is no net profit indicator. But in Section III “Capital and Reserves” of the balance sheet, line 1370 reflects retained earnings (uncovered loss), part of which is the net profit (loss) of the current period.
We invite you to read: Salary in an employment contract with or without personal income tax
Most businessmen start their companies out of a desire to make a profit. There are several metrics that business owners can use to determine the performance of their business. One such indicator is profit before tax.
The purpose of calculating this indicator is to determine the total amount of profit of the company, on the basis of which the amount of tax payments can be finally determined.
The profitability of a company can be calculated using the profit before tax indicator. The significance of this indicator in efficiency calculations is very high.
Profit before taxes covers all income earned, regardless of where it comes from. It includes sales, commissions, income from other services and interest income. All expenses are subsequently deducted except for income taxes. Alternatively, the indicator can be calculated by taking the organization's net profit and adding income tax.
PN = V – S – KR – UR DU PP – PU PD – PR,
where PN – profit before tax, etc.;
B – sales revenue, t.r.;
C – cost, t.r.;
KR – commercial costs, t.r.;
UR – management costs, t.r.;
DI – income from participation in the activities of other companies, etc.;
PP – interest to be received, etc.;
PU – interest to be paid, etc.;
PD – other income, t.r.;
PR - other expenses, t.r.
Page 2300 = page 2110 – page 2120 – page 2210 – page 2220 page 2310 page 2320 – page 2330 page 2340 – page 2350
Algorithm for calculating profit before tax:
- collection of all financial data on the income received by the company. Revenue can come from various sources such as rental income, discounts received, and general sales. Other unique sources of income include service income, interest earned on bank accounts, and bonuses;
- determination of all expenses. These include: rent, debt, utilities and cost of goods sold;
- subtracting expenses from income received to obtain gross profit;
- determination of commercial and administrative expenses;
- subtracting the amount of selling and administrative expenses from gross profit to obtain profit from sales;
- adding to the profit from sales the amounts of income from participation in other companies, the amount of interest received and other income;
- subtracting interest payable and other expenses from the resulting amount;
- formation of profit before tax indicator.
The scheme for calculating the indicator is presented more clearly in the figure here.
For an example of calculation, let's take a conditional company with the following initial data presented in the table below.
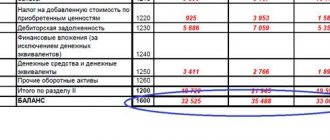
| Index | 2017, t.r. | 2018, t.r. |
| Revenue | 547800 | 654700 |
| Expenses | 321470 | 455900 |
| Business expenses | 12455 | 17855 |
| Administrative expenses | 9875 | 9777 |
| Income from participation | 5446 | 6511 |
| Interest receivable | 7885 | 8444 |
| Interest payable | 15477 | 19745 |
| Other income | 5423 | 2144 |
| other expenses | 7895 | 6744 |
To calculate the profit from sales, we use the table below.
| Index | 2017, t.r. | 2018, t.r. | Absolute deviation, t.r. | Rate of change, % |
| Revenue | 547800 | 654700 | 106900 | 119,5 |
| Expenses | 321470 | 455900 | 134430 | 141,8 |
| Gross profit | 226330 | 198800 | -27530 | 87,8 |
| Business expenses | 12455 | 17855 | 5400 | 143,4 |
| Administrative expenses | 9875 | 9777 | -98 | 99,0 |
| Profit from sales | 204000 | 171168 | -32832 | 83,9 |
| Income from participation | 5446 | 6511 | 1065 | 119,6 |
| Interest receivable | 7885 | 8444 | 559 | 107,1 |
| Interest payable | 15477 | 19745 | 4268 | 127,6 |
| Other income | 5423 | 2144 | -3279 | 39,5 |
| other expenses | 7895 | 6744 | -1151 | 85,4 |
| Profit before tax | 199382 | 161778 | -37604 | 81,1 |
As can be seen from the table, by 2020 there is a decrease in profit before tax by 37,604 tr. or by 18.9%. This decrease is due to the fact that the growth rate of revenue (19.5%) was lower than the growth rate of expenses (41.8%). Along with the decrease in profit before tax, one can also see a decrease in gross profit by 27,530 tr., profit from sales by 32,832 tr.
Revenue from net sales in the balance sheet is a line
Asset items are arranged in order of increasing liquidity, i.e. depending on how quickly the property can be converted into cash. The liability side of the balance sheet shows how much money was invested in the economic activities of the organization and who and in what form participated in the creation of the organization’s property.
Balance sheet liability items are arranged in order of increasing urgency of repayment of obligations. When drawing up a balance sheet, the following rules must be observed: the balance sheet data at the beginning of the year must correspond to the data at the end of last year; offset between items of assets and liabilities, items of profit and loss is not allowed, except in cases where such offset is provided for by the relevant accounting provisions; individual indicators are reflected in the net assessment, i.e. Composition of financial statements Statement of financial results for analysis of business activities Profit from sales in the balance sheet: which line Where can you see the indicator of profit from sales in the SMP report Which accounting entry reflects profit from the sale of products Results Composition of financial statements Law “On Accounting dated 06.12 2011 No. 402-FZ provides for the following package of forms, which is included in the financial statements of a legal entity:
- balance sheet;
- income statement;
- applications.
The balance sheet is a reflection of the state of the enterprise as of the reporting date, and the financial results report shows the results of its activities for the reporting period. From this it becomes clear that in the balance sheet it will be possible to find only the accumulated profit or loss for a specific date.
Revenue from net sales in the balance sheet is the 2020 line
And in production, the cost of finished products will be written off as Dt 90. 2 Kt 43.
- VAT for any type of activity will be charged by posting Dt 90. 3 Kt 68.
- Profit from sales will be reflected in the accounting record Dt 90. 9 Kt 99.
- The loss from sales will be reflected by the posting Dt 99 Kt 90. 9.
- IMPORTANT! In some accounting programs, subaccount numbers may differ from the Chart of Accounts approved by the Ministry of Finance. In addition, the organization can change, delete or introduce additional sub-accounts independently if required by the specifics of its activity. The amount of the posting in correspondence with account 99 will be equal to the profit or loss received from the sale. That is, the amount of revenue minus cost, VAT and excise taxes, if any. If the calculation is correct, the collapsed (without analytics) balance of account 90 should become zero at the end of the period.
Revenue from product sales is adjusted (increased or decreased) for amount differences. Paragraph 12 of PBU 9/99 establishes the following conditions under which revenue is recognized: - the organization has the right to receive this revenue (such a right can be confirmed by a specific agreement); — the amount of revenue can be determined; — there is confidence that this or that business transaction will improve the financial and economic position of the organization; — ownership of the product has passed to the buyer or the work has been accepted by the customer; — the costs incurred in connection with this operation can be determined.
If all these conditions are met, then the revenue is reflected in the subaccount “Revenue of account 90 “Sales”. In this case, the following entry is made in accounting: Dt 62 Kt 90 subaccount “Revenue” - revenue from the sale of products, works, services is reflected (including VAT, excise taxes, sales tax).
Revenue from Sales of Goods Which Line in the Balance Sheet
- acquisition and creation of fixed assets;
- acquisition of intangible assets and other non-current assets;
- contributions to the capital of other organizations;
- purchasing shares and other securities that are not intended to be resold in current transactions;
- transfers of funds under intermediary agreements;
- repayment of loans and borrowings;
- advance payment, advances issued, deposits towards payment.
In the economic activities of organizations, there are often cases when the buyer of products, goods, works and services does not fully repay his debt to the supplier. In cases where the amount of receipts and (or) receivables only partially covers revenue, revenue in the supplier’s accounting is defined as the sum of receipts and receivables not covered by receipts. Let's consider the line used in the balance sheet to reflect the output of products when it comes to completing the production process and posting the finished product to the warehouse. Let us remind you that accounting for the output of finished products can be kept both using account 40 “Output of products (works, services)”, and without its use, when the cost of finished products is reflected directly in account 43 “Finished products (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated 10/31/2011). 2000 No. 94n). We talked about what accounting entries are made in this case in our separate section.
To summarize information on income and expenses associated with the ordinary activities of the organization, the Chart of Accounts for accounting the financial and economic activities of the organization and instructions for its application, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n, account 90 “Sales” is intended. This account reflects, in particular, the revenue and cost of providing for a fee for temporary use (temporary possession and use) of its assets under a lease agreement (when this is the subject of the organization’s activities). – in organizations engaged in industrial and other production activities – packaging and transportation costs (between individual types of shipped products on a monthly basis based on their weight, volume, production cost or other relevant indicators); – in organizations engaged in trading and other intermediary activities – transportation costs (between the goods sold and the balance of goods at the end of each month); – in organizations that procure and process agricultural products – to the debit of accounts 15 “Procurement and acquisition of material assets (expenses for the procurement of agricultural raw materials) and (or) 11 “Animals for growing and fattening (expenses for the procurement of livestock and poultry”).
It should be noted that the cash method of accounting for income and expenses is best used by small businesses with a small number of business transactions, since it reduces the reliability of accounting. The fact is that when using this method, all expenses are reflected only after they have been paid. Therefore, if the actual expenses incurred are not paid, with a large number of business transactions it is difficult to track which of the actual expenses incurred are not reflected in the accounting records.
How to calculate?
Every owner of an enterprise, its potential or actual investor, is interested in obtaining information about how efficiently it operates. Financial analysis helps us evaluate business performance. With its help, you can get an idea of the current activities of the company, or you can make a forecast.
Profitability is a relative measure of profitability. This is not a single indicator, but a whole system, a set of indicators. The main ones are return on sales, assets, equity, and product profitability. We will talk about the latter in this article.
Read about return on equity in the article “Determining return on equity (formula).”
They calculate both the profitability of products for the company as a whole, and the profitability of individual types of products.
Rpr = Pr / Ss × 100,
We suggest you familiarize yourself with How to draw up an agreement for the assignment of the right to an apartment
Rpr - product profitability;
Pr - profit;
CC - cost price.
However, taking into account the purposes of the analysis, product profitability can be considered:
- by net profit or profit from sales;
- the full cost of production or only production.
Depending on this, the final calculation formula will differ.
Tracking the current state of an enterprise and monitoring the profitability of its activities is a common practice throughout the world.
For successful business development, it is not enough just to have an intuitive understanding that a project will bring profit; it is also necessary to conduct a mathematical analysis of the objective state of the market, calculating the return on the implementation of the project (product) and its payback period.
The current level of product profitability is calculated based on real data, which is reflected every month in the accounting documentation of the enterprise, as well as quarterly reports.
Calculating profitability is of interest to a wide range of people:
- business owners who evaluate the correctness of the “laid course”;
- creditors who monitor the economic situation of the enterprise.
The profitability of the enterprise is considered as an absolute value, thus it is easy to represent it in the form of cash (in the accounting report).
When using relative profitability indicators (ratios of absolute values that are expressed as a percentage of each other), it is necessary to give some explanations. Relative indicators are not so demonstrative.
The product profitability ratio (in its general form) demonstrates how many units of profit a businessman will receive from a unit of production costs.
The profitability ratio is written as a fraction, where the numerator is the profit earned in the process of selling the product, and the denominator is the total costs related to both commercial promotion and the technological production cycle.
The calculated coefficient must be multiplied by 100. Thus, the proportion shows the ratio of profit to total cost (full production costs).
It is important to understand that a single calculation of product profitability cannot reflect the real state of the enterprise. When conducting a comprehensive analysis, the following points should be taken into account:
- the difference between the actual and planned profitability of products sold;
- comparison of the data obtained during profitability calculations with competing firms for similar products;
- analysis of the company's product ratings over the past few years.
There are two main concepts in searching for the profitability of an enterprise's products.
Very often, profitability is calculated only for a unit of a product, then the costs of its production and the profit received from sales from the general structure are separated.
This concept is used primarily by analysts to make forecasts. The second concept for calculating profitability is to analyze the global situation. A study of the total amounts for the reporting period is carried out.
The profitability of goods production is always considered as a percentage. This makes it possible to simplify the further use of calculated indicators for conducting a comprehensive analysis of the enterprise in the long term.
Profitability of products sold (ROM - from English Return on Margin) is an indicator that shows the efficiency of product sales in the form of the ratio between income and costs for the production of goods and their sale.
To know the final benefit that a business entity receives from the sale of products, you should know the exact amount of revenue and the size of the final costs of producing goods. Thus, the final benefit is the amount remaining after costs have been subtracted from revenue.
After the concept of net income and the process of calculating it has become clear, a logical question arises - how to calculate the cost of production? It is the sum of the costs of work and services, commercial and coordination expenses.
It should also be noted that if a company produces different types of items, then it makes economic sense to calculate the profitability of each position separately, and not all the profitability in the aggregate.
Let's consider how to find such an important indicator as production profitability. To do this, you should display RO TC or the so-called return on cost. It is this that is the key option for determining the company’s performance, showing how well the production process is organized and whether it can be improved to achieve market average values.
ROTC is defined as the ratio (PR/TC)*100%, where PR is the profit received from the sale of goods or services, and TC is the total cost of production. To determine the profit from sales of services or goods, it is necessary to subtract expenses from the income received, that is, PR is equal to the difference between TR and TC, where Tr denotes revenue and TC is the company’s expenses.
If you measure ROTC as a percentage, it becomes clear how efficient the company is not so much as the use of its resources. Moreover, ROTC can be counted for the entire company as a whole, and for each department or production unit. Moreover, you can calculate profitability even for specific products or services produced.
Which line is profit from sales reflected in the balance sheet?
The amount of the posting in correspondence with account 99 will be equal to the profit or loss received from the sale. That is, the amount of revenue minus cost, VAT and excise taxes, if any. If the calculation is correct, the collapsed (without analytics) balance of account 90 should become zero at the end of the period.
The presence of a balance will mean that the formation of the entry for writing off profit (loss) was made with an error.
- Revenue is reflected by posting Dt 62 Kt 90. 1. But in retail trade, the posting will look like Dt 50 Kt 90. 1 or Dt 57 Kt 90. 1.
- The cost of services and work is written off with such entries as Dt 90. 2 Kt 20 (23, 26, 25, etc.). In wholesale trade, the cost of goods will be written off by operation Dt 90. 2 Kt 41, and sales expenses - Dt 90. 2 Kt 44. In retail, you additionally need to take into account the markup Dt 90. 2 Kt 42. And in production, the cost of finished products will be written off by recording Dt 90. 2 Kt 43.
- VAT for any type of activity will be charged by posting Dt 90. 3 Kt 68.
- Profit from sales will be reflected in the accounting record Dt 90. 9 Kt 99.
- The loss from sales will be reflected by the posting Dt 99 Kt 90. 9.
As mentioned above, it is impossible to directly see in the balance sheet how much profit from sales was for the reporting period. In order to discover this indicator, you will have to look at line 2200 of the income statement. A positive amount will indicate a profit, and a negative amount will indicate a loss. Negative indicators in financial statements are usually enclosed in parentheses without a minus sign. If the profit from sales in the total amount of net profit is an insignificant share, and the main influence on the net profit is exerted by other activities, then you should think about whether it’s time to change the profile of the company.
Or even decide to close it altogether, since often large profits from other activities can mean the sale of the company’s assets, which sometimes indicates its unstable position.
Accountant's Directory
Analytical accounting for the subaccount should ensure that each type of cost is broken down into separate accounts in such a way that it is possible to isolate the amounts for commercial expenses (packaging, storage, transportation and sales) of each type of product and administrative expenses (maintenance of the administrative and managerial apparatus). Where is profit from sales used in mandatory reporting forms? In mandatory reporting forms, the indicator is reflected as follows: BALANCE OF COMMODITY SUPPLY OF RETAIL TRADE TURNOVER - a system of indicators characterizing the connections and proportions between the wholesale supply of market stock goods and retail turnover. It has an annual periodicity broken down by quarters. It considers the growth of inventory as a form of resource use, and the reduction as the involvement of additional resources in trade turnover.
It is an integral part of a comprehensive econometric model of a market economy. Retail turnover is one of the main indicators by which the activities of enterprises and trade organizations are assessed. The main goal of trading enterprises is to obtain maximum profit and trade turnover acts as the most important and necessary condition, without which this goal cannot be achieved. Since a trading enterprise receives a certain amount of income from each ruble of goods sold, the task of maximizing profits necessitates a constant increase in the volume of trade turnover as the main factor in the growth of income and profits, a relative reduction in distribution costs and labor costs.
The article “Administrative expenses” (line 040) of the profit and loss statement reflects the general business expenses of the organization, which are collected on account 26 of the same name, in the case when these expenses are written off directly from account 26 to account 90. 2 “Cost”, if provided accounting policy of the organization. In the case when general business expenses are distributed to manufactured finished products (to production cost accounts - 20, 23, 29), these costs are included in the amount on line 020 “Cost”, and do not fall into line 040.
Methods for estimating volumes of produced and sold products
Products sold - the number of products (works, services) in payment for which the company received cash or other means of payment. This definition corresponds to the “on payment” method of accounting for sales. In addition to this, the method of accounting for sales “by shipment” is allowed, when the products for which documents for payment are issued are classified as sold.
The current external accounting reports contain information on the volume of products sold. They are presented in the form of the “Profit and Loss Statement”. This:
a) revenue (net) from the sale of goods, works, services (less value added tax, excise taxes and similar mandatory payments). Revenue is shown as a separate line 010;
b) total cost of goods sold. It can be calculated as the sum of the following components:
PSA = SP + SK + SU (8.2.1)
where SP - production cost (cost of sales of goods, products, work, services - line 020 of form 2), rub.; SK - commercial expenses (line 030 of form 2), rub.; SU - administrative expenses (line 040 of form 2), rub.
Volume indicators are indicated for the reporting period from the beginning of the current year.
The volume of product sales reflected in Form 2 does not accurately characterize the production capacity of the enterprise. It includes the sale of not only main products, but also goods purchased for resale.
Shipped products include products sent to consumers, but not counted as sold. It includes the following types of products:
· the payment due date has not arrived;
· not paid on time;
· located in the custody of consumers.
The debt to pay for shipped products forms the principal amount of the enterprise's receivables. Therefore, at present, this indicator should be under the special control of managers.
The cost of sold and shipped products is related to the following relationship:
SOP = SRP + SOPk - SOPn (8.2.2)
where SOP is the cost of products shipped in the reporting period, p; SOPn, SOPk - balances of shipped products at the beginning and end of the period (at cost), rub.
Which line shows profit from sales in the balance sheet? all about taxes
If an organization uses account 40 “Output of products (works, services)” to account for production costs, the amount of excess of the actual production cost of manufactured products, completed works and rendered services over their standard (planned) cost is included in the article “Cost of goods sold, products, works, services." In the case when the actual production cost is lower than the standard (planned) cost, the amount of this deviation reduces the data for the specified item.
- amounts of VAT, excise taxes, export duties and other similar mandatory payments;
- amounts received under commission agreements, agency agreements and other similar agreements in favor of the principal, principal, etc.;
- amounts of advances received as advance payment for products, goods, works, services;
- receipts as collateral, if the agreement provides for the transfer of the pledged property to the pledgee;
- amounts received to repay a loan provided to the borrower.
- administrative and management expenses;
- maintenance of general business personnel not related to the production process;
- depreciation charges and expenses for repairs of fixed assets for management and general economic purposes;
- rent for general business premises;
- expenses for payment of information, audit, consulting and other similar services;
- other administrative expenses similar in purpose.
- the organization has the right to receive the specified revenue according to the contract, or this right is confirmed in another way;
- the amount of revenue can be determined;
- there is confidence that as a result of a specific transaction there will be an increase in the economic benefits of the organization, that is, when the organization received an asset in payment or there is no uncertainty regarding the receipt of this asset;
- the right of ownership (possession, use and disposal) of the product (goods) has passed from the organization to the buyer or the work has been accepted by the customer (service provided);
- the expenses that have been or will be incurred in connection with this operation can be determined.
- VAT for any type of activity will be charged by posting Dt 90. 3 Kt 68.
- Profit from sales will be reflected in the accounting record Dt 90. 9 Kt 99.
- The loss from sales will be reflected by the posting Dt 99 Kt 90. 9.
- IMPORTANT! In some accounting programs, subaccount numbers may differ from the Chart of Accounts approved by the Ministry of Finance. In addition, the organization can change, delete or introduce additional sub-accounts independently if required by the specifics of its activity. The amount of the posting in correspondence with account 99 will be equal to the profit or loss received from the sale. That is, the amount of revenue minus cost, VAT and excise taxes, if any. If the calculation is correct, the collapsed (without analytics) balance of account 90 should become zero at the end of the period.
Income recognized in accounting as income from ordinary activities, if it is significant or without knowledge of which it is impossible for interested users to assess the financial results of the organization's activities, must be reflected separately in the form of a transcript to line 010 or in an appendix to the profit and loss statement (in if it is developed and adopted by the organization independently).
Sales profitability analysis
Analyze correctly
- With sales of competing companies
- With previous indicators and dynamics in general
- Compliance with previously drawn up forecasts and plans
The second indicator, which would expediently complement the first calculation, should be the productivity of the product at its full intrinsic value.
Analysis of these two figures will help to fully reveal both the efficiency and ergonomics of the enterprise’s technological base, and the profitability of selling products.
Indicators below the threshold indicate the required updating of one or another component of the business.
Possible ways to improve disappointing indicators are to reduce the cost of goods and search for additional opportunities for the sale of produced volumes. When using them, you need to be careful, since a risky move can result in business regression and decline.
Consequently, the higher the profitability indicator, the more rationally resources and capital are spent. High profitability indicators of the company's products are directly dependent on the sustainability and competitiveness of the enterprise.
The decisive role is played by the analysis of all factors affecting the net profit of the enterprise. It is important to correctly assess the financial result of the enterprise, which should be reflected in the accounting records. This is justified by the fact that it is important for an accountant to correctly calculate the tax contributions that must be paid on profits.
The main parameter is the gross profit received as a result of sales.
Its size is influenced by the following factors:
- revenue amount;
- cost of goods sold;
- cost size 1 in physical terms (tons, pieces, l, m2 l, etc.);
- fluctuations in demand for the range of products sold.
Vp = Orp = C - C, where Orp is the volume of products sold; C is revenue; C is the cost of products sold.
It is necessary to note that the main parameters affecting the amount of gross profit are revenue indicators, cost and changes in the range of products sold.
Tags: balance sheet, profit, products, sales, formula
« Previous entry
Finished products in balance
It is impossible to give a resigning employee a copy of SZV-M. According to the law on personal accounting, when dismissing an employee, the employer is obliged to give him copies of personalized reports (in particular, SZV-M and SZV-STAZH). However, these reporting forms are list-based, i.e. they contain data about all employees. This means transferring a copy of such a report to one employee means disclosing the personal data of other employees.
Volume of production in the balance sheet
Income recognized in accounting as income from ordinary activities, if it is significant or without knowledge of which it is impossible for interested users to assess the financial results of the organization's activities, must be reflected separately in the form of a transcript to line 010 or in an appendix to the profit and loss statement (in if it is developed and adopted by the organization independently). Every year, companies prepare financial statements. Using data from the balance sheet and profit and loss report, you can determine the effectiveness of the organization’s activities, as well as calculate the main planned indicators. Provided that management and the finance department understand the meaning of terms such as profit, revenue and sales on the balance sheet.
Terminology The volume of product sales on the balance sheet is the amount of revenue received for the sale of goods in the reporting period.
- administrative and management expenses;
- maintenance of general business personnel not related to the production process;
- depreciation charges and expenses for repairs of fixed assets for management and general economic purposes;
- rent for general business premises;
- expenses for payment of information, audit, consulting and other similar services;
- other administrative expenses similar in purpose.
The corresponding composition of gross output depends on the sectoral affiliation of the enterprise (production). For example, at machine-building enterprises, most often the gross output does not include work in progress and semi-finished products due to their small volume. In such situations, gross and marketable products are the same in composition, but may differ in price. Revenue from Sales of Goods Which Line in the Balance Sheet
Balance sheet profit of the enterprise in reporting
Accounting statements reflect all performance indicators of companies. It allows you to assess the degree of success of a business project, calculate its profitability and prospects. The line in the balance sheet for book profit is not highlighted. The report shows the value of the profit remaining after deducting from it all types of costs and tax liabilities.
The reason for the impossibility of identifying the value of balance sheet profit according to the balance sheet reporting form is the different approach to reflecting the results of operations. The balance sheet is compiled on the basis of the ending account balances. Balance sheet profit must be calculated based on information generated cumulatively. The calculation can be made based on the balance and data from accounting registers. To do this, the amount of income tax paid during the year must be added to the retained earnings from the balance sheet line under code 1370.
Balance sheet profit is a line in Form 2, corresponding to the code designation 2300. If the company has a loss instead of a profit, then in the column with code 2300 its value is indicated without a minus, but the number is taken in parentheses.
Balance sheet profit is the profit (loss) before tax received by an enterprise from all types of business activities (both from ordinary activities and from other income) for a certain period and reflected in the financial statements.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytdevru
Balance sheet profit (hereinafter referred to as BP) is an indicator that, along with gross profit and net profit, is used to assess the financial and economic activity (FEA) of an organization.
BP has this name because it is calculated based on accounting indicators and analysis of balance sheet items.