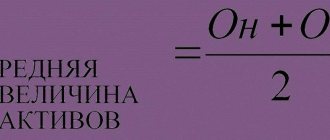What determines the size of net assets on the balance sheet
Net assets (NA) include those funds that will remain in the ownership of the enterprise after the repayment of all current liabilities.
Defined as the difference between the value of assets (inventory, intangible assets, cash and investments, etc.) and debts (to counterparties, personnel, budget and extra-budgetary funds, banks, etc.) with the necessary adjustments applied. The calculation of the value of net assets on the balance sheet is carried out based on the results of the reporting period (calendar year) in order to obtain reliable information about the financial condition of the company, analyze and plan further operating principles, pay dividends received or actually evaluate the business in connection with a partial/full sale.
- When filling out annual reports.
- When a participant leaves the company.
- At the request of interested parties - creditors, investors, owners.
- In case of increasing the amount of the authorized capital due to property contributions.
- When issuing dividends.
What is included in the structure of the HA
In its simplest sense, this indicator indicates the size of the company’s owners’ net worth. That is, this is what will remain with them after paying all their debts to partners, government agencies and other persons to whom the company owes.
In other words, we can express the essence of this concept as the difference between the figure of absolutely all the assets of the enterprise, as well as its liabilities. It is these indicators that make up the structure of this indicator. All assets are compiled from certain lines of one of the most important accounting documents, the balance sheet:
- a group consisting of elements of non-current property of an enterprise;
- assets that are in circulation during the main activity of the company.
The first group is data from the first part of the balance sheet.
This includes:
- property of an intangible nature;
- fixed assets;
- construction work that has not yet been completed;
- investments in material assets, which are investments with the aim of obtaining maximum income;
- investments for a long period.
The second group of structural elements for calculating this indicator should be found in the next part of the main reporting document of accountants. Financiers classify the following data on the company’s activities as assets in circulation:
- inventories, as well as VAT on acquired property, debtor obligations;
- short-term investments;
- monetary resources, as well as other funds in circulation.
The structure of the private equity does not include real expenses that occurred during the repurchase of shares into one’s own possession for planned resale or destruction. In addition, the share funds of shareholders that have not been contributed to the authorized capital should not be classified as current assets.
Liabilities that reduce net assets include:
- amounts of debt on short-term loans;
- amounts required to repay long-term loans;
- accounts payable;
- unpaid profits of investors and shareholders;
- reserve amounts of income;
- other obligations received for a short period of time.
Calculation of the accounting value of NAV: assets as equity capital
The term “accounting value” (or “accounting unit”) is used as a certain parameter, which is one of the accounting characteristics of an economic object or process. For example, the key rate is the accounting value of the interest rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation.
In turn, the accounting value of net assets is, if you follow the general definition of their essence, the value of the organization’s property, reduced by the amount of debts and expressed in rubles or foreign currency, sometimes in an alternative monetary unit (for example, in bitcoins). However, in official accounting, as a rule, assets in generally recognized fiat currency are taken into account.
There are several approaches to calculating the value of net assets. The most popular among Russian experts are:
- an approach according to which the value of net assets is defined as identical to the size of the company’s equity capital;
- an approach according to which the value of net assets is determined as the difference between the total value of the organization's assets and liabilities.
Let's study their specifics in more detail.
The identification of net assets and equity capital of a company is a tradition that has been consolidated not only among economists, but also at the level of some legal acts issued in the Russian Federation. For example, in the provisions of paragraph 3 of Art. 35 of the Federal Law “On Joint-Stock Companies” dated December 26, 1995 No. 208-FZ states that in credit structures, instead of the value of net assets, it is precisely the equity capital indicator that is calculated.
In turn, economists traditionally include the following components in equity capital:
- authorized, additional and reserve capital of the company;
- its retained earnings;
- the amount of increase in the value of non-current assets after revaluation;
- the cost of shares purchased by the company from the owners.
In order to calculate the SC, it is necessary to add up the numbers reflecting the indicators noted above. It is quite simple for a Russian financier to do this: the terms will be indicators that generally correspond to lines from 1310 to 1370 of the balance sheet, the form of which was approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n.
NA = Page 1310 Page 1320 Page 1340 Page 1350 Page 1360 Page 1370.
Let's study another popular and at the same time somewhat more complex approach to calculating the value of net assets.
This method involves determining the size of net assets based on:
- from the total indicator of all assets, reduced by amounts reflecting the debts of the founders and shareholders on transactions into fixed capital;
- the total indicator of all obligations, reduced by amounts reflecting the amount of government assistance, as well as gratuitous receipt of property and forming expenses of future periods.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the Law on Personal Data, an overview of changes.
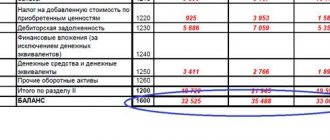
The total amount of the organization’s assets is recorded in line 1600 of the balance sheet, the organization’s liabilities are in its lines 1400 (long-term liabilities) and 1500 (short-term liabilities). The debt of the founders of the company to contribute funds to the authorized capital is recorded in the debit of account 75 and the credit of account 80.
How are the indicated indicators used to determine the amount of net assets?
The fact is that they all correlate with those indicated as elements of the formula for calculating the financial indicator that we are considering, recommended by the Ministry of Finance of Russia in order No. 84n dated August 28, 2014. The Department believes it is correct to determine the size of net assets through the following set of transactions:
- adding numbers corresponding to lines 1400 and 1500;
- subtracting from the resulting result indicators for the credit of account 98 and subaccounts reflecting future income (or DBP);
- subtracting from the figure corresponding to line 1600 the one that is recorded on the debit of account 75 and the credit of account 80 and reflects the debts of the founders of the company for contributing funds to the authorized capital (DUO);
- subtracting from the resulting result the figure defined in paragraph 2.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytcopyrightru
NA = (Page 1600 – DUO) – (Page 1400 Page 1500 – DBP).
In what cases should you choose the 1st or 2nd method of calculating the size of net assets?
Correct calculation of NA using an example
To calculate net assets, it is necessary to evaluate one of the cases using an example.
| Assets | Amount, rub. |
| 1. Non-negotiable: | |
| — residual value of fixed assets | 1,000 thousand |
| — capital investments in unfinished construction | 500 thousand |
| — long-term investment | 300 thousand |
| 2. Negotiable: | |
| - reserves | 100 thousand |
| - accounts receivable | 400 thousand |
| incl. Unpaid amounts by the founders for replenishment of the management company | 50 thousand |
| Liability balance | |
| 3. Capital and reserves | |
| — UK | 100 thousand |
| — Retained income | 900 thousand |
| 4. Long-term debt: | |
| - long-term loans | 500 thousand |
| 5. Loans for a short period: | |
| — short-term loans | 200 thousand |
| - debt to the budget | 100 thousand |
| — other short-term liabilities | 800 thousand |
Net assets - formula
To determine the indicator, the calculation includes assets, except for the receivables of the participants/founders of the organization, and liabilities from the liabilities section, with the exception of those deferred income that arose due to the receipt of government assistance or donated property.
NA = (Non-current assets Current assets – Debt of founders – Debt of shareholders in connection with the repurchase of shares) – (Long-term liabilities Short-term liabilities – Income attributable to future periods)
NA = (line 1600 – ZU) – (line 1400 line 1500 – DBP)
The calculation must be drawn up in an understandable form using a self-developed form, which is approved by the manager. It is allowed to use the previously valid document for determining the NA (Order No. 10n of the Ministry of Finance). This form contains all required lines to be filled out.
NA = Capital/reserves (line 1300) DBP (line 1530) – Debts of the founders
The key procedure for calculating the value of net assets on the balance sheet is determined by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation and is presented in a separate order No. 84n dated August 28, 2014. Please note that previously a different procedure was in effect, but it is not currently used.
This formula for net assets on the balance sheet is applicable to the following range of economic entities:
- public or non-public joint stock companies;
- state or municipal unitary enterprises;
- limited liability companies;
- production cooperatives or housing cooperatives;
- business partnerships.
- JSC - the amount of non-current and current assets of an economic entity as of the reporting date;
- DE - debt of the founder incurred to the enterprise for the formation of the authorized capital;
- FOR - debt on own shares generated upon issue;
- OB - the sum of the company's short-term and long-term liabilities;
- DBP - future income in the form of state financial support or gratuitous transfer of property assets.
How to calculate net assets according to balance sheet lines?
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Money Laundering
Calculating the amount of net assets in the balance sheet (the lines indicated above) using a pencil calculator is not enough. This calculation must be documented. However, a unified form for reflecting calculated data is not provided for in Order No. 84n. Organizations are required to independently develop a form and regulate it in their accounting policies.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytcreatorsru
Note that before the approval of Order No. 84n, the old form was in force (Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 10 and the Federal Commission for the Securities Market of Russia dated January 29, 2003 No. 03-6/pz). In the new instructions, the Russian Ministry of Finance has not prohibited the use of this form, therefore, firms can use it to prepare calculations of net assets in the balance sheet (the document lines contain all the necessary information).
Calculation of net assets by balance sheet lines
To begin with, we will provide a sample balance sheet form to make it easier to navigate the numbers and line names:
We calculate the amount of net assets using the lines in the balance sheet:
Please note that from line 1530 “Deferred income” we take only gratuitously received income (for example, through government subsidies), and from line 1230 – only the debt of participants.
The size of the NAV shows the efficiency of the enterprise. That is, if it is easier to describe the above calculations, NAV is the difference between what the organization has and what it owes.
Subscribe to our newsletter
Read us on Yandex.Zen Read us on Telegram
A positive value indicates the profitability of the activity: after settling all its obligations, the company will have assets left.
A negative NAV value indicates that the enterprise does not have enough assets to pay all its obligations, that is, its activities are unprofitable.
Analysis of indicators
Having completed the arithmetic calculations, we move on to analyzing the result obtained. With a positive amount of net assets in the balance sheet, we can conclude that the company is profitable and has high solvency. And, accordingly, the higher the indicator, the more profitable the enterprise.
Negative net assets are an indicator of the low solvency of an enterprise. In other words, a company with a negative NAV will most likely go bankrupt soon; the company will simply have nothing to pay off its debts. However, in such a situation, exceptional circumstances must be taken into account. For example, the company has just been formed and has not yet covered its costs, or the company received a large loan for expansion.
An increase in net assets can be achieved by increasing the authorized, reserve or additional capital or by reducing the founder’s debts to the enterprise.
The size of Net Assets (NA) is one of the main economic and investment indicators of the performance of any enterprise. The success, stability and reliability of a business is characterized by positive values. A negative value shows the unprofitability of the company, possible insolvency in the near future, and probable risks of bankruptcy.
Based on the results of settlement actions, the value of net assets is estimated over time, which should not be less than the amount of the authorized capital (AC) of the company. If the reduction does occur, according to the legislation of the Russian Federation, the enterprise is obliged to reduce its capital and officially register the changes made in the Unified Register (Law No. 14-FZ, Article 20, paragraph 3).
Additionally, there is a relationship between the value of the NAV and the payment of required dividends to participants/shareholders. If, after accrual of income/dividends, the value of net assets decreases to a critical level, it is necessary to reduce the amount of accruals to the founders or completely cancel the operation until the normatively designated ratios are achieved.
How to calculate the assets of an enterprise on the balance sheet?
As you know, by the end of March 2020, Rosstat and the tax authority must receive the enterprise’s annual statements, which must include a balance sheet. This means it’s time to use the formula for calculating net assets for the 2016 balance sheet . Moreover, it is established by law.
What are net assets called?
Successful conduct of economic and entrepreneurial activities is impossible without analyzing its key financial characteristics. One of the main values among them is the value of the organization's net assets .
In general terms, the value of net assets is the difference between the value of all the assets of the company and the sum of all its debts and obligations.
Please note that net assets are calculated by:
- integrally annually and reflected in the annual report;
- if necessary, obtain data on the current economic state of the company, issue dividends or the value of a share in the business.
Place of the enterprise's net assets in the balance sheet
To see where net assets are on the balance sheet , you need to look at the eponymous Section 3 of the Statement of Changes in Equity. It looks like this:
As you can see, net assets on the balance sheet are a special separate indicator. According to the order of the Ministry of Finance dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n, the code for the line of net assets in the balance sheet is 3600.
How to calculate net assets on a balance sheet
To understand how to calculate net assets on a balance sheet, an example of a proper approach is reflected in the order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation under number 84n of 2014. It provides the correct procedure for calculating them.
It is suitable for organizations of most forms of ownership:
- CJSC and PJSC;
- OOO;
- State unitary enterprises and municipal unitary enterprises;
- Cooperatives;
- business partnerships.
As stated in the order, in order to calculate net assets on the balance sheet, you need to subtract the value of liabilities from the value of assets. To do this, use the following formula for calculating net assets on the balance sheet :
| NA = (AK – Zuch – Zwak) – (O – Db) |
NA – net assets; AK – assets (current + non-current); Zuch – the debt of the founders to the company to pay for their shares in the management company; Zvak – debt obligations to repurchase their shares; О – existing obligations (with long and short terms of fulfillment); Db – income that is planned to be received (aid from the state, free receipt of property).
How to make a payment
It should be taken into account that calculating net assets using the formula is not enough. This fact needs to be documented. Meanwhile, there is currently no legally approved document form for these purposes. Therefore, firms are required to develop their own form and adopt it as an addition to their accounting policies.
However, previously there was an order of the Ministry of Finance No. 10n and the Federal Commission for the Securities Market of the Russian Federation No. 03-6/pz dated January 29, 2003 with a similar form for joint-stock companies. Although it is no longer valid, any business can use it as a guide when developing their own uniform.
How to calculate net assets on a balance sheet
To obtain the necessary information, you can use not only the net assets formula, but also calculate them line by line when the balance sheet has already been compiled.
Here's how to calculate net assets based on balance sheet lines :
| Option 1 | Line 1300 + Line 1530 – Line 1170 (debts of participants on deposits in the management company) |
| Option 2 | Line 1600 – (Line 1400 + Line 1500) + Line 1530 – Line 1170 (debts of participants on deposits in the management company) |
Analysis of the result
Obviously, after calculating the net asset value, it is desirable to obtain a positive result. Negative net assets will indicate that:
- the company does not make a profit;
- with a high probability of becoming bankrupt in the near future.
The only exception is a company that has not been open for a very long time, since during its existence the invested resources have not yet had time to pay for themselves due to understandable circumstances.
So after calculating net assets according to the lines of the balance sheet , we can talk about the economic condition of the enterprise.
Note that when calculating and assessing the net assets of an enterprise, the authorized capital of the organization occupies a significant place in the balance sheet (see table).
| № | Situation | Analysis |
| 1 | The amount of the organization's net assets is greater than the authorized capital | This indicates the good health of the organization |
| 2 | Net assets are less than the authorized capital | The company is unprofitable |
Let us emphasize: situation No. 2 is acceptable only for the first year of the company’s operation. If, after time, the situation does not change in a positive direction, management should reduce the volume of capital down to the value of net assets.
You should consider closing a business if the size of your net assets is equal to or less than the minimum required by law.
Conclusion
As a general rule , net assets are one of the main characteristics on the balance sheet that indicate the economic viability of the company. The larger they are, the more efficient the enterprise, and the more interesting it is for investment.
Only an organization with significant net assets can guarantee the interests of its lenders and investors. Therefore, one should take a very careful approach to assessing the value of net assets.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Definition
Net assets are a value determined by subtracting the amount of its liabilities from the total assets of the organization. Net assets are the amount that will remain to the founders (shareholders) of an organization after the sale of all its assets and the repayment of all debts.
The net asset indicator is one of the few financial indicators, the calculation of which is clearly defined by the legislation of the Russian Federation. The procedure for calculating net assets was approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 28, 2014 N 84n “On approval of the Procedure for determining the value of net assets.” This procedure is used by joint-stock companies, limited liability companies, state unitary enterprises, municipal unitary enterprises, production cooperatives, housing savings cooperatives, and economic partnerships.
Calculation (formula)
The calculation comes down to determining the difference between assets and liabilities (liabilities), which are determined as follows.
The assets accepted for calculation include all assets of the organization, with the exception of receivables of the founders (participants, shareholders, owners, members) for contributions (contributions) to the authorized capital (authorized fund, mutual fund, share capital), for payment of shares.
The liabilities accepted for calculation include all liabilities, except for deferred income.
.
But not all future income, but those recognized by the organization in connection with the receipt of government assistance, as well as in connection with the gratuitous receipt of property
. These incomes are actually the organization's own capital, therefore, for the purposes of calculating the value of net assets, they are excluded from the short-term liabilities section of the balance sheet (line 1530).
Those. The formula for calculating net assets on the Balance Sheet of an enterprise is as follows:
Net assets = (line 1600 – ZU) – (line 1400 + line 1500 – DBP)
where ZU is the debt of the founders for contributions to the authorized capital (it is not separately allocated in the Balance Sheet and is reflected as part of short-term receivables);
DBP – deferred income recognized by the organization in connection with the receipt of government assistance, as well as in connection with the gratuitous receipt of property.
An alternative way to calculate the net asset value, giving exactly the same result as the formula above would be:
Net assets = line 1300 – ZU + DBP
Normal value
The net asset indicator, known in Western practice as net assets or net worth, is a key indicator of the activity of any commercial organization. The organization's net assets must be at least positive. Negative net assets are a sign of the insolvency of an organization, indicating that the company is completely dependent on creditors and does not have its own funds.
Net assets must not only be positive, but also exceed the authorized capital of the organization. This means that in the course of its activities, the organization not only did not waste the funds initially contributed by the owner, but also ensured their growth. Net assets less than the authorized capital are permissible only in the first year of operation of newly created enterprises. In subsequent years, if net assets become less than the authorized capital, the civil code and legislation on joint stock companies require that the authorized capital be reduced to the amount of net assets. If the organization's authorized capital is already at a minimum level, the question of its further existence is raised.
Net asset method
In valuation activities, the net asset method is used as one of the methods for assessing the value of a business. With this method, the appraiser uses data on the organization's net assets according to the financial statements, previously adjusted based on its own estimated values of the market value of property and liabilities.
Net assets (NA) are the real value of all company property, fixed assets and cash. In simpler terms, they represent the residual amount of own assets unencumbered by liabilities.
The indicator is calculated every year by enterprises of all organizational and legal forms. NA are calculated when organizing and running a business and are the main criterion for financial well-being, solvency, and the degree of risk of ruin of the company.
Calculation procedure and examples
The procedure for calculating the value is approved by legal documents and instructions. The calculation is made quarterly and annually on the reporting date with the results obtained being recorded in the relevant documents.
The following are used in the calculations:
- Non-current assets are fixed and intangible assets, long-term financial investments.
- Current assets are cash, accounts receivable, securities, production, inventory, etc.
When adding up assets, the company's costs for purchasing its own shares from co-owners of the business and the debt of participants for investments in the authorized capital are excluded.
Liabilities involved in the calculation include:
- debt to co-owners for payment of dividends;
- targeted funding and revenues;
- other long-term liabilities, including deferred tax payments;
- loans, loans, etc.
When adding up liabilities, future income is not taken into account. Moreover, only those that are recognized by the company in connection with the receipt of gratuitous property or assistance from the state.
The formula looks like this:
NA = (A - ZU - ZVA) - (P - DBP) , where:
- NA - net assets;
- A - assets;
- ZU - debt of business participants on contributions to the authorized capital;
- ZBA - costs of purchasing the company's own shares from co-owners;
- P - liabilities;
- DBP - deferred income.
The amounts for calculation are taken from the enterprise’s balance sheet, where liabilities are accounted for in lines 1400 and 1500, assets - in line 1600. You will also need the debit value of account 75, reflecting the debts of participants on contributions to the authorized capital, and the data in line 1530 - deferred income.
The calculation algorithm for the balance sheet looks like this:
NA = (line 1600 - line 75) - (line 1400 + line 1500 - line 1530)
Example
The balance sheet of Sibiryak LLC as of November 1, 2015 is presented in the following table:
| Balance indicators | Balance data |
| ASSETS | |
| 1. Non-current assets (1st part) | 1 599 500 |
| residual value of fixed assets | 999 300 |
| capital investments in unfinished construction | 455 150 |
| long-term financial investments | |
| 2. Current assets (2nd part) | |
| stocks | 145 200 |
| accounts receivable | 525 600 |
| including debts of co-owners in the authorized capital | 35 850 |
| cash | 630 250 |
| PASSIVE | |
| 3. Capital and reserves (3rd part) | |
| authorized capital | 125 300 |
| retained earnings | 1 250 300 |
| 4. Long-term liabilities (4th part) | |
| long-term loans | 745 300 |
| 5. Short-term liabilities (5th part) | |
| short-term loans | 268 300 |
| debts to the budget | 95 600 |
| other current liabilities | 1 520 600 |
- Value of assets: 3,919,150 = 1,599,500 + 999,300 + 455,150 + 145,200 + 525,600 + 630,250 - 35850.
- The amount of liabilities: 2,629,800 = 745,300 + 268,300 + 95,600 + 1,520,600, the calculation does not include data from the 3rd part of the report.
- NA = 3,919,150 – 2,629,800 = 1,289,350.
Based on the calculation, the net asset value of Sibiryak LLC as of November 1, 2015 is 1,289,350 rubles.
You can get detailed information about this indicator from the following video:
Analysis of the results obtained
The resulting value determines the organization's solvency, profitability, and sometimes further development.
The indicator should be used to judge the company’s ability to pay off its obligations, invest in expanding production, or open new directions. Therefore, the normal value of net assets must be positive . When the NAV value is negative, the firm is considered insolvent, dependent on loans and has no income of its own. The higher the indicator, the more solvent and attractive the company is to investors.
The indicator analysis includes:
- Monitoring changes in the size of the net assets; for this purpose, they are compared at the beginning and end date of the reporting period. And based on the results obtained, the reasons that contribute to the increase or decrease of own funds are identified.
- An assessment of the reality of the dynamics of the net asset value is used to calculate the proportion of net and total assets at the beginning and end of the reporting period. A large increase in the indicator at the end date is associated with an increase in total funds, and the increase in the NAV is actually insignificant.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of use. Determined by calculating and studying turnover and profitability ratios.
Since during the analysis this value is compared with data on revenue and net profit for the year, when making calculations it is more correct to use not a fixed figure of net assets as of the end date, but the average value for this period.
Comparison with authorized capital
In addition to dynamic analysis, after the first year of operation, the company is obliged to regularly compare the value of net assets and the authorized capital. The law establishes that the size of the private equity must be greater than the authorized capital .
If the calculations reveal a reverse trend, this greatly increases the risk of bankruptcy of the company, and legal documents prescribe reducing the authorized capital to the size of the private equity. If its monetary volume is already minimal, the enterprise is obliged to announce its liquidation. However, the current legislative document defines the following:
- Even in cases where the value of net assets is actually less than the authorized capital, the company can maintain solvency, conduct financial activities for a certain time and strictly fulfill debt obligations.
- Requirements to reduce the size of the authorized capital or liquidate the organization are considered interference in its activities; in addition, the enterprise can be declared bankrupt, which will serve to protect the interests of creditors.
Find out what the absolute liquidity ratio shows here.
Ways to increase the indicator
Regular and thorough study of NA allows you to find ways to increase them, such as:
- improving the composition of fixed assets;
- sale or destruction of unused property and equipment;
- increasing the volume of goods sold by improving product quality, expanding sales channels, changing pricing policies, and using new ideas and solutions;
- increasing the efficiency of control over the company's inventories, debts and investments.
Net assets are the most important indicator of a company's performance. The main goal of competent and timely analysis of financial data is the ability to prevent and avoid undesirable situations in the activities of any organization.
General concept of net assets
Assessing the performance efficiency and successfully planning the work of modern companies is impossible without analyzing their economic indicators. One of the most important values among such indicators is the value of net assets (NA).
The value of net assets is the difference between the value of all the organization’s assets (property, land, cash, etc.) and the sum of all its liabilities (debts for taxes and payments to the budget, loans, etc.). To put it simply, net assets are those company funds that will remain after repaying debts to creditors.
The calculation of net assets is mandatory once a year and is reflected in the annual financial statements on line 3600 of Section 3 of the Statement of Changes in Capital. It is also done when necessary to obtain information about the current financial situation, to pay interim dividends or the actual value of the share to the participant.
How to calculate the net asset value according to the balance sheet 2019-2020 (formula)
To find out this, let us turn to the order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 28, 2014 No. 84n, which provides the procedure for calculating net assets.
What is the difference between this procedure and the one that was in effect previously, read in the material “A new procedure for calculating net assets has been approved .
It is valid for companies of the following forms of ownership:
- joint stock companies (public and non-public);
- limited liability companies;
- state and municipal unitary enterprises;
- cooperatives (industrial and housing savings);
- business partnerships.
According to Order No. 84n, to calculate the company’s net assets, the value of liabilities must be subtracted from the value of assets. The formula used for this is:
NA = (VAO + OJSC – ZU – ZVA) – (DO + KO – DBP),
NA - net assets;
VAO - non-current assets of the organization;
OJSC - current assets of the organization;
ZU - the debt of the founders to the organization to fill shares in the authorized capital;
ZBA - debt incurred during the repurchase of own shares;
DO - long-term obligations;
KO - liabilities of a short-term nature;
DBP - future income (in the form of government assistance and gratuitous receipt of property).
To calculate net assets, you can also use the data contained in the company's balance sheet. To calculate the value of net assets on the balance sheet, the formula can be modified:
NA = (line 1600 – ZU) – (line 1400 + line 1500 – DBP).
For more information about the values given in this formula, read the article “Net assets - what is it in the balance sheet (nuances)?” .
Please note that it is not enough to simply do the calculation on a calculator; it must also be formalized. There is currently no approved form. Companies must develop a form for calculating net assets for 2019–2020 independently and approve it as an annex to their accounting policies. However, earlier, before the publication of Order No. 84n of the Ministry of Finance dated August 28, 2014, the form given in the appendix to Order No. 10 of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation and the Federal Commission for the Securities Market of Russia dated January 29, 2003 No. 03-6/pz was used to calculate net assets. The form of this form lists all the indicators that are required to calculate net assets even now, therefore we consider its use acceptable (after its approval in the accounting policies of the organization).
You can download this form on our website:
Net Asset Value Analysis
It is easy to conclude that when analyzing net assets, the output should be positive. A negative one will indicate that the company is unprofitable and with a high degree of probability in the near future may become completely insolvent, that is, insolvent. The only exception can be a recently opened company, since during its existence the invested funds did not have time to justify themselves and did not generate income for objective reasons. Thus, the dynamics of calculating net assets is one of the key indicators of the company’s financial condition.
Note that when calculating and assessing net assets, the authorized capital of the company plays an important role. If the amount of net assets exceeds the amount of the authorized capital, this indicates the well-being of the company. If the net assets at some stage become less than the amount of the authorized capital, this indicates the opposite: the organization is operating at a loss.
What consequences await the company if net assets are less than the authorized capital, read here.
Let us repeat: this situation is acceptable only for the 1st year of the company’s operation. However, if after this period the situation does not change in a positive direction, the company’s management is obliged to reduce the size of the authorized capital to the amount of net assets. If this figure is equal to or less than the minimum indicators established by law, the issue of closing the enterprise should be raised (clause 4, article 30 of the Law “On LLC” dated 02/08/1998 No. 14-FZ).
Read more about the consequences of negative NAV values in the material “What are the consequences of negative net assets?” .
Results
The amount of net assets is one of the most important indicators of the financial viability of an organization. The higher it is, the more successful the organization and the more attractive it is for investment. Only an organization with high net assets can guarantee the interests of its creditors. This is why it is necessary to be very careful when assessing the value of a company's net assets.
General concepts
Successful business conduct is impossible without a detailed analysis of the financial and economic indicators of the economic activity of an economic entity. In order to assess the property and financial position of an organization and make the right management decisions in a timely manner, it is necessary to determine important solvency and profitability ratios. One of the key calculation indicators is the calculation of the value of net assets on the balance sheet.
The organization's net assets (NA) are the amount of funds of an economic entity, determined by calculation, which will remain at the disposal of the company after full repayment of debt obligations. In other words, the value of net assets is calculated as the arithmetic difference between the total indicators of the company’s property, material and financial assets and assumed liabilities.
Note that calculating the value of net assets on the balance sheet is mandatory for organizations. The indicator is calculated once a year based on accounting data. Indicators are reflected in the third section of the report on changes (movements) of capital; net assets are (in the balance sheet) line 360 of this reporting form.
Formula for calculating net assets
The key procedure for calculating the value of net assets on the balance sheet is determined by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation and is presented in a separate order No. 84n dated August 28, 2014. Please note that previously a different procedure was in effect, but it is not currently used.
This formula for net assets on the balance sheet is applicable to the following range of economic entities:
- public or non-public joint stock companies;
- state or municipal unitary enterprises;
- limited liability companies;
- production cooperatives or housing cooperatives;
- business partnerships.
Net assets formula:
- JSC - the amount of non-current and current assets of an economic entity as of the reporting date;
- DE - debt of the founder incurred to the enterprise for the formation of the authorized capital;
- FOR - debt on own shares generated upon issue;
- OB - the sum of the company's short-term and long-term liabilities;
- DBP - future income in the form of state financial support or gratuitous transfer of property assets.
How to calculate net assets according to balance sheet lines?
To calculate the net asset value on the balance sheet, the calculation lines use the following:
Calculating the amount of net assets in the balance sheet (the lines indicated above) using a pencil calculator is not enough. This calculation must be documented. However, a unified form for reflecting calculated data is not provided for in Order No. 84n. Organizations are required to independently develop a form and regulate it in their accounting policies.
Note that before the approval of Order No. 84n, the old form was in force (Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 10 and the Federal Commission for the Securities Market of Russia dated January 29, 2003 No. 03-6/pz). In the new instructions, the Russian Ministry of Finance has not prohibited the use of this form, therefore, firms can use it to prepare calculations of net assets in the balance sheet (the document lines contain all the necessary information).
How to calculate net assets on a balance sheet, example
Let's look at a specific example of how to calculate net assets on a balance sheet.
Vesna LLC prepared annual financial statements, including a balance sheet in the OKUD form 0710001.
Based on the balance sheet data, the following calculations were made:
NA = (13,800 +19,283 – 0) – (12,930 – 0) = 20,153 rubles.
Analysis of indicators
Having completed the arithmetic calculations, we move on to analyzing the result obtained. With a positive amount of net assets in the balance sheet, we can conclude that the company is profitable and has high solvency. And, accordingly, the higher the indicator, the more profitable the enterprise.
Negative net assets are an indicator of the low solvency of an enterprise. In other words, a company with a negative NAV will most likely go bankrupt soon; the company will simply have nothing to pay off its debts. However, in such a situation, exceptional circumstances must be taken into account. For example, the company has just been formed and has not yet covered its costs, or the company received a large loan for expansion.
An increase in net assets can be achieved by increasing the authorized, reserve or additional capital or by reducing the founder’s debts to the enterprise.
Which method of calculating the NA to choose
First of all, it is worth paying attention to the fact that the first of the methods we examined, in principle, can hardly be called the most popular among economists. It is used only due to the permissible identity of the concepts “equity capital” and “net assets” - based on certain provisions of economic theory, as well as the norms of the legislation of the Russian Federation. The fact is that most experts are still inclined to consider net assets as an indicator that involves deducting the company's liabilities.
The approach that uses indicators on lines 1310-1370 will actually be valid only in one scenario: the company has no liabilities that could be deducted from equity. This state of affairs is possible, for example, if the individual entrepreneur works for himself, has no loans and does not hire employees.
In this case, it is legitimate to talk about one-sided identity, when any net assets should be considered as equity capital, but not all equity capital should be considered as net assets.
Read more about the correlation between the concepts of “net assets” and “equity capital” in the article “What is included in the equity capital of an enterprise (formula)?”
Thus, in general, the financier will use the 2nd method. Let's call it the Ministry of Finance method.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the Calculation of compensation upon dismissal at your own request.
But if, for example, a company, due to the ideality of its business model, does not have short-term and long-term obligations, the debts of the founders for contributions to the authorized capital have been paid, and deferred income is not recorded in accounting, it is quite possible to get by with a simpler formula for determining the value of net assets, and names: based on the total indicators on lines from 1310 to 1370 of the balance sheet.
Calculation formula
The economic formula for net worth is quite simple. It boils down to the fact that the indicator under consideration characterizes the activities of the company, and also establishes whether it has certain property in personal ownership.
If there are no NAs at all, and are there any creditors’ funds, then this indicator of the company is negative.
It is important to deal with it as quickly as possible. This way you can minimize problems with the tax service.
It is important to work out all the main points in advance. This is the only way to avoid standard problems.
An important point is the ratio of two indicators - net assets and authorized capital. The following situations exist:
| The value of the private equity has a positive value and at the same time it is higher than the volume of the authorized capital | In this case, the meaning comes down to determining that the enterprise during its activities not only did not spend capital, but was able to increase its quantity |
| If the situation is reverse | When the average is less than the capital, this situation is extremely negative |
The second option is excusable at the second stage of the company’s activities.
How to calculate a company's net assets?
The procedure for calculating the amount of net assets for joint-stock companies is established by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia N 10n, FCSM of Russia N 03-6/pz dated January 29, 2003*
*According to the Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated January 26, 2007. N 03-03-06/1/39 limited liability companies can use the rules developed for joint stock companies.
The value of a company's net assets is understood as a value determined by subtracting the amount of its liabilities from the amount of the company's assets.
Net assets are calculated based on balance sheet data. At the same time, not all balance sheet indicators are included in the calculation.
If net assets are less than authorized capital
If your company's net assets have become less than its authorized capital, then you are obliged to reduce the authorized capital to the level of net assets and register such a decrease in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities (Clause 3, Article 20 of the Law of 02/08/98 N 14-FZ). That is, at least after drawing up the annual financial statements, you need to compare the authorized capital and net assets.
In addition, the following rule applies. If an LLC decides to pay dividends to participants, but as a result of accrual of dividends, the value of net assets becomes less than required, then dividends cannot be accrued in the planned amount. It is necessary to reduce the profit distributed on dividends to an amount at which the above ratio will be satisfied.
At the same time, no liability has been established for violation of the requirement for the ratio of authorized capital and net assets.
An example of calculating the value of a company's net assets
Sometimes the appraiser needs to conduct a “quick” analysis of the general condition of the companies. To do this, you can use information about the company's net assets, which can be highlighted from the balance sheet.
Net assets reflect the real value of a company's assets excluding its debts.
Thus, net assets are the difference between the book value of all the company's assets and the amount of the company's debt obligations.