Profit is the monetary expression of the main part of cash savings created by enterprises of any form of ownership. It characterizes the financial result of the enterprise's entrepreneurial activity. Profit is an indicator that most fully reflects production efficiency, the volume and quality of products produced, the state of labor productivity, and the level of costs. Profit is one of the main financial indicators of the plan and assessment of the economic activities of enterprises. Profits are used to finance activities for the scientific, technical and socio-economic development of enterprises and to increase the wage fund for their employees. It is not only a source of meeting the intra-economic needs of the enterprise, but is becoming increasingly important in the formation of budgetary resources, extra-budgetary and charitable funds.
In conditions of market relations, an enterprise must strive to obtain maximum profit, that is, to such a volume that would allow the enterprise not only to firmly maintain a sales position in the market for its products, but also to ensure the dynamic development of its production in a competitive environment.
Therefore, each enterprise, before starting production, determines what profit, what income it can receive. Hence, profit is the main goal of entrepreneurial activity, its final result.
The important task of every business entity is to get more profit at the lowest cost by observing a strict regime of economy in spending funds and using them most efficiently.
The main source of cash savings for an enterprise is revenue from sales of products, namely that part of it that remains after deduction for the production and sale of these products.
Content
- The essence and functionality that makes a profit
- What affects profit levels
- Typology
- Formation and distribution of profits
- Optimal profit distribution
- Profit distribution management
- The procedure for distributing profits at enterprises of various forms of ownership
- Distribution of profits in LLC
- Peculiarities of the procedure in a company with one founder
- Distribution of profits in a joint stock company
- Distribution of profits in a production cooperative
- Distribution of profits in a limited partnership
- Procedure for distribution of profit of a unitary enterprise (unitary enterprise)
- Distribution of profits by property
- Terms of profit distribution
- How is profit distributed under the simplified tax system?
- Conclusion
https://youtu.be/GP2xfnwYxa0
The essence and functionality that makes a profit
In economic terms, profit is the difference between income and costs incurred by production. When can we say that an enterprise or company is making a profit? In order to identify the financial result, the revenue received is compared with the costs incurred for production and sales, which will take the form of cost.
If the revenue received exceeds the cost, it is concluded that a profit has been made. If costs exceed revenue, this indicates losses.
Profit performs a number of functions:
- Gives a description of the economic effect obtained by a company or manufacturing enterprise;
- Has the effect of stimulating all activities as a whole;
- Allows you to create different types of budgets;
- Summarizes the entire result of the company's activities.
How is revenue reflected on the balance sheet?
The method of accounting for revenue is strictly prescribed in the accounting policy of the enterprise. In the first paragraph, the calculation formula looks like this: TR = OGPn + GP - OGPk, where:
- OGPN – balance of finished products as of the first day of the reporting period;
- GP – finished products produced during this time and intended for sale;
- OGPk – balance of finished products as of the last date of the reporting period.
But in the current turbulent times, an increasing number of entrepreneurs and organizations prefer the cash method of accounting for revenue.
The formula for determining revenue according to point two looks like this: TR=P*Q, where:
- TR – revenue;
- P – price per piece of goods;
- Q – volume of goods sold.
As you can see, nothing complicated. Example.
Instruction 1 Cost analysis is one of the most important aspects of economic analysis. It shows how much it cost the company to produce a certain volume of products.
When setting the price, these expenses must be taken into account as a minimum cost. To increase profits without increasing the price of a popular product, you should explore opportunities to reduce costs without losing product quality.
Attention
To find the cost, add up all the costs associated with the production and sale of products. They can be divided into two large groups: variable and fixed costs.
Note that the former grow in proportion to the volume of output. These include: costs for the purchase of raw materials, wages, purchase or rental of special equipment, creation or purchase of containers and personal packaging.
What affects profit levels
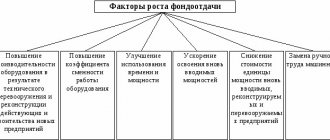
Experts divide factors influencing profit into several groups:
- Internal factors - affect profit through output volumes, by improving the quality characteristics of products;
- External factors do not depend on the activities carried out by an enterprise or company, but they have an impact on the level of profit.
When an enterprise carries out economic activities, the entire complex of these factors is dependent and interconnected with each other.
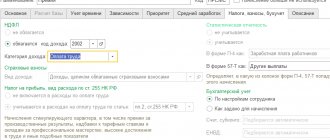
Production volume, what line in the balance sheet or where to look?)
It is this formula that should be used when analyzing external financial statements. The cost of products sold is determined by formula (8.2.1). Remains of shipped products - according to Form 1 “Balance Sheet”, line 216 “Goods shipped”.
The volume of shipped products is calculated only at cost, since the balances of shipped products in the balance sheet are taken into account only at cost.
Commodity products - the number of products, the volume of work, services intended for sale, fully completed in production. Typically, products are considered complete after their final acceptance by the inspection service.
The volumes of shipped and marketable products are related by the following relationship:
STP = SOP + SGPk - SGPn (8.2.3)
where SOP is the cost of products shipped in the reporting period, p; STP is the cost of marketable products produced in this period, p; SGPn, SGPk - balances of marketable products, respectively, at the beginning and end of the reporting period (at cost), rub.
Go to page: 1 23
>Proceeds from net sales in the balance sheet are a line
Typology
Profit comes in various forms. Let us briefly describe some of them.
| Profit type | Brief description of the type |
| Balance sheet | Final result for the reporting period |
| Gross | The difference between revenue and cost, excluding selling expenses |
| Clean | Which remains after deducting all expenses |
| Marginal | It turns out when revenue exceeds production costs |
| Normal | Allows you to maintain your position in this market |
| Capitalized | Used to increase assets |
| Nominal | Corresponding balance sheet reflected in financial documents |
How to determine revenue from sales of goods, services or products
With a deeper and more detailed analysis, the indicators of capital turnover and return on equity are determined. Calculation of revenue in formulas and examples Let's return to the definition of revenue and look at what types of revenue exist:
- Gross (or “dirty”, total, gross) is all the funds received as a result of the sale (both “cash” at the cash desk and “non-cash” paid by bank card);
- Net (net) - there is revenue without taxes (if you pay excise taxes and VAT, in retail gross and net revenue are equal).
In accounting, there are two ways to calculate revenue:
- The accrual method (in other words, in accounting slang, “by shipment”) is used in large holdings, where products are shipped in large volumes and over considerable distances;
- Cash method (i.e.
Analytical accounting for the subaccount should ensure that each type of cost is broken down into separate accounts in such a way that it is possible to isolate the amounts for commercial expenses (packaging, storage, transportation and sales) of each type of product and administrative expenses (maintenance of the administrative and managerial apparatus). Where is sales profit used in mandatory reporting forms? In mandatory reporting forms, the indicator is reflected as follows:
- profit from sales in the balance sheet - there is no line with this name;
- profit from sales in the income statement - line 2200.
The absence of a separate line (indicator) of sales profit in the balance sheet is due to the fact that the task of the balance sheet is to group the liabilities and assets of the organization according to the principle of their urgency.
Formation and distribution of profits
There are several methods for generating profit. Let's look at each of them, analyzing the pros and cons.
- Direct counting method : in this method, profit is determined by the output of goods and the volume of products sold by the enterprise. The main advantage of this technique is its accuracy, but the disadvantage is that it is too labor-intensive and sometimes impossible to apply;
- Standard method: one of the positive aspects is the high accuracy in calculations, but at the same time it can be used only if production is stable. This method has shown its effectiveness in justifying various economic plans;
- Analytical method: used to establish the planned profit of an enterprise. The essence of the method is to analyze the influence that internal and external factors have on the results of the activities carried out by the enterprise.
The algorithm consists of the following stages : analysis of the profit received for a specific period of time, determination of production volumes, establishment of what part profit occupies in all income received, and the planned profit is determined.
There is also a combined calculation method, which combines the direct counting method and the analytical method.
As for the distribution of profits, this is the most important process, which not only ensures that the various needs of entrepreneurs are covered, but also takes part in the formation of the country’s budget.
The profit distribution system at any enterprise should be built in such a way that production efficiency increases, not decreases.
The principles of distribution are formulated as follows:
- The resulting profit must be distributed between the state and the company;
- The state receives part of the profit through taxation and fees, the size of which cannot be arbitrarily changed;
- The profit remaining with the enterprise should not have a negative impact on increasing production volumes;
- The remaining profit, first of all, goes to the savings part; the remainder can be used at the discretion of the company.
Enterprises distribute the so-called “net profit”, which remains after making all mandatory payments. Distribution of net profits is partly an area related to planning. Taking this indicator into account, expense estimates are drawn up.
The profit that remains at the disposal of the enterprise itself can be used to develop and improve its activities. The state and regulatory authorities should not interfere with the procedure for using these funds.
Along with financing production, it can be used to pay benefits, bonuses, incentives for employees who retire, and so on. These same funds can be used to finance competitions, cultural events, etc.
We also clarify that profits can be used to pay off penalties.
All profits remaining at the disposal of the enterprise or company are divided into 2 parts. The first can be considered accumulative, and the second can be used in the process of consumption. If there is profit that has not been distributed in previous years, this characterizes the enterprise as stable and financially sound.
The question naturally arises: Who makes the decision on the distribution of profits? This depends on the organizational form of the enterprise, which will be discussed further.
Optimal profit distribution
As already mentioned, net profit can be directed to a variety of expense items, or it can be capitalized, which allows you not to attract third-party assets and expand the functionality of the enterprise using your own funds.
One example of thoughtful distribution of profits is the allocation of some of it to the needs of staff. After all, the human factor, people can be called the most important asset of any enterprise.
To make a reasonable distribution, each component of the profit must be carefully analyzed. It is also important to do this in order to identify the weaknesses of the enterprise in a timely manner.
Profit distribution management
When a category such as profit is considered, not only its types are taken into account, but also the management methodology. To manage rationally, it is enough to follow simple rules:
- Before making management decisions, you need to approach them carefully and comprehensively;
- Apply different approaches to managing the enterprise as a whole;
- Respect the interests of not only the owners of the enterprise, but also the state and employees;
- Carefully analyze risks;
- Increase competitiveness.
All procedures around this indicator should be aimed at increasing positive indicators and reducing possible risks.
Revenue from sales of products which line in the balance sheet
Having false information is worse than not having it. Therefore, it is important that financial statements are prepared correctly.
Unfortunately, even accountants make mistakes. The use of technical means allows you to avoid arithmetic errors, but not methodological ones. Also, reporting may be distorted due to the low skills of a specialist. Therefore, reporting is always done “with a reserve”. In the registers you can always find costs that will reduce the profitability indicator. For example, write off more inventory, non-current assets or bad debts. After all, it is always easier to lose profit than to increase it.
So, what can revenue tell us at first glance:
- Is our product (service) in general demand;
- Analysis of revenue for a single product item at different retail outlets will help make a decision on moving certain groups of goods from one retail outlet to another (where it is sold faster);
- Which product should be purchased or produced in larger volumes;
- Comparing revenue indicators for past and current periods allows you to assess how quickly the enterprise is developing, or maybe, on the contrary, there has been a decline and urgent measures need to be taken;
- Having data on the current revenue of the enterprise, an entrepreneur can intelligently redistribute funds to pay bills, taxes, wages, and purchase a new batch of goods.
In the economic analysis of an enterprise, the revenue indicator is also used.
The procedure for distributing profits at enterprises of various forms of ownership
As already mentioned, the distribution of profits is based on certain principles. Distribution itself includes its use in accordance with the requirements of the legislator, the goals and objectives set by the enterprise, taking into account the interests of the owners.
Distribution of profits in LLC
The procedure for distributing profits in a limited liability company is subject to taxation and is distributed in the manner prescribed for legal entities. persons In addition, the entire procedure is regulated by current legislation.
Let us immediately make a reservation that only that part of the profit that remains after all taxes have been paid and other obligations have been fulfilled (to creditors, etc.) is subject to distribution.
The distribution of net profit occurs after the accounting is compiled. reporting for a specific period of time. The decision on distribution is made through voting. If the company's participants have not made a unanimous decision, the meeting is postponed to the next date.
The constituent documents do not always reflect information about when and where payments can be sent.
The distribution of profits between the company's participants also takes into account the financial statements.
Important information: there are times when profits are not subject to distribution.
As an example, here are a few of them:
- When the amounts of the authorized capital are not paid in full;
- The company is bankrupt or has all the signs of bankruptcy.
Other cases are given in the legislation.
What part of the profit will be distributed is decided by the meeting of founders. The decision that was made is documented in the form of a protocol.
Typically, profits are distributed in proportion to the shares that participants contributed to the authorized capital. But there may also be a disproportionate distribution of profits in the LLC.
The law does not prohibit such distribution if this procedure is fixed in the Charter.
Peculiarities of the procedure in a company with one founder
This procedure has its own characteristics. It is worth saying that if a company has only one founder, he makes all decisions himself.
In this case, there is no need to hold a meeting; a written execution of the said decision, certified by the signature of the founder, is sufficient.
A sample is shown below.
Distribution of profits in a joint stock company
The distribution of profits in a joint-stock company has the most complex mechanism. Usually it is spelled out in the Charter in some detail.
A distinctive feature is the need to form a reserve, the size of which is at least 10% of the total capital. In addition, some share of profits should be used to increase the capital.
The distribution of profits among shareholders of the company also has its own nuances. Dividends on preferred shares are paid at specific rates, while on ordinary ones they are based on the decision of management, which is approved or not by the meeting of shareholders.
When planning a distribution, you need to take into account what types of shares are issued. The future development of joint stock companies largely depends on the correct distribution of profits.
If dividends are unreasonably high, this will hinder the company's development. But if they are not paid at all, this is also fraught with negative consequences for the business, since the interests of shareholders will be infringed.
Distribution of profits in a production cooperative
A production cooperative is a commercial organization in which people are united by membership, created to carry out economic or production activities jointly.
Only that part of the profit that remains after making all payments is also distributed. If members of the cooperative made a labor contribution to its activities, then the process of profit distribution will proceed in accordance with this contribution and share contributions, and if there was no labor participation, then in accordance with the contribution. The statutory documents contain all the information about the distribution procedure in this case.
Production cooperatives, as a form of doing business, are rare in Russia. This is explained by the fact that in this case, more contributions made by labor are combined, rather than cash. And the presence of liability, which is subsidiary, does not add to the popularity of this form.
Distribution of profits in a limited partnership
In a limited partnership, before distributing profits, taxes are paid, the necessary contributions to the budget are made, and only then income is paid to investors. These investors do not take any part in the daily activities of the partnership and are not responsible for the results obtained. They are only making their contributions.
Profits are divided among the partners of the partnership in accordance with the shares they contributed to the capital. And the remaining part is distributed among full comrades.
If there is no profit at all, or it is much less than planned, the following scenarios are possible:
- The members of the partnership give their share to the investors through the sale of property that belongs to the partnership;
- A decision is made not to pay shareholders their share of the profits.
Procedure for distribution of profit of a unitary enterprise (unitary enterprise)
The UE itself is characterized by the fact that it does not have ownership rights to the property that is assigned to it. The UE can dispose of property only if the owner agrees, that is, the Russian Federation itself.
Based on the developed documentation, the profit that was received by the unitary enterprise from work or services, or sold products will be directed to production, to social services. service according to standards. All standards are developed by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation.
The remainder of the profit will be withdrawn in favor of the federal budget.
Where can I find the amount of revenue in the financial statements?
No such line exists. To reflect revenue, another important accounting report is used - financial results. However, revenue and balance sheet are related, although this connection is not clearly visible. Let's trace it using the example of individual balance sheet lines. Revenue and the 1st section of the balance sheet Almost every line of the first section of the balance sheet is associated with a revenue indicator. For example, if the residual value of fixed assets or intangible assets decreased sharply during the reporting period, it is possible that some of them were sold. In this case, we can talk about the company’s possible revenue from their sale. If information appears on the balance sheet about profitable investments in material assets, you can expect to receive revenue from an activity such as renting out property. Add to favoritesSend by email Revenue in the balance sheet - in which line can you see it? Such a question can only arise from someone who is far from accounting, since there is simply no specific line in the balance sheet in which revenue is presented. Yet revenue and balance sheet are interconnected. Where to find revenue in the balance sheet Revenue and the 1st section of the balance sheet Revenue and current assets 3rd section of the balance sheet and revenue Revenue and borrowed funds Results Where to find revenue in the balance sheet When the company has operated for a year, everyone is interested in knowing what its revenue is for this period and what part of it is expenses.
It is by these indicators that one can judge the profitability or unprofitability of its activities. According to all accounting laws, the balance sheet is a snapshot of the company’s performance indicators at a certain reporting date.
Searching the balance sheet for a line that would show revenue is useless.
Distribution of profits by property
Quite often questions arise as to whether it is possible to pay profits with property. Typically, these situations arise among LLC participants. The law does not limit the form of profit distribution in any way. This means that it is permissible to distribute profits in non-monetary form. This is confirmed by the presence of judicial practice on this issue.
The charter can stipulate the type of property with which profit is planned to be paid. It is clear that such a decision must be supported by the meeting of shareholders. If the general meeting does not make such a decision, then the distribution is made only in money.
Legal experts recommend making and documenting the decision of the shareholders’ meeting for each type of property, if it is planned to distribute profits using the property, so as not to have legal problems later.
Net revenue
Net revenue
Net revenue is the amount of money that a business entity is guaranteed to receive for products, goods or services sold to counterparties, excluding the tax on added construction on the amount of sales. Net revenue is not taken into account in the accounting accounts, but is calculated by calculation. Displayed in line 10 of Form No. 2 of the financial statements (profit and loss statement).
Find what Net Revenue is in the Yandex search engine...
Find what Net Revenue is in the Google search engine...
services, accountant, goods, counterparty, revenue, rib, accounting, accounting, cash, products, loss services, accountant, goods, counterparty, revenue, rib, accounting, accounting, cash, products, loss
See also terms related to “Net Revenue”:
Accountant Accounting Revenue Cash Counterparty Products RIB Goods Loss Services Accounting
comments powered by Disqus
Other definitions starting with "B":
Vacancy Vacant position Vacant position gross domestic product currency balance sheet currency contract currency currency pair Foreign exchange transactions Foreign exchange bank account Foreign exchange deposit Foreign exchange spread shift method GDP Salary statement Promissory note Venture Venture financing Venture capital Venture fund Related companies Deposit Deposit in currency Depositor Signature key certificate owner Implementation of 1c Non-current assets External audit External report External processing Internal audit internal labor regulations Volatility Upward trend Temporary disability World Trade Organization World Bank WTO Selective default Benefit Bargain purchase Bargain purchase Issuance of funds “on account” Bank statement Payment of wages Payment of wages Paid wages fee Revenue Gross revenue Highly liquid asset Highly paid job
You have learned what Net Revenue is. There are 1,195 accounting terms and definitions in our Accountant's Dictionary. If you have not found an accounting term that interests you, you can send us a request for its inclusion in our dictionary! We would also like to note that the dictionary is constantly being updated... and if you have not found what you are looking for today, there is a chance that you will find the information you are looking for later!
How is profit distributed under the simplified tax system?
Profit under the simplified tax system is most often distributed in order to pay dividends. Taxpayers under the simplified tax system are most often LLCs, this is already an established fact.
Let us remind you that you can distribute profits under the simplified tax system once a year, or every quarter. This requires only a decision of the meeting of shareholders or a single participant.
There are also joint-stock companies working on the simplified tax system. In this case, payments are made based on the results of the quarter, 6 months and year.
Net profit under the simplified tax system is calculated based on accounting data. accounting. This will not be difficult if all the information is reflected on time and reliably.
The amount of net profit here is the difference between the assets and liabilities of the balance sheet. At the same time, future income is not included in liabilities, but accounts payable are included in them.
If the balance sheet is not compiled, it is impossible to determine net profit and, accordingly, to pay dividends.
Finished products in the balance sheet
The organization may have other unforeseen expenses (p. 2350) and income (p. 2340). This way you can calculate net profit or net sales in the balance sheet: Line 2400 = 2110 – (2120 + 2210 + 2220) + 2340 – 2350 – 2410, where 2410 is the amount of income tax.
Net sales on the balance sheet can be calculated by subtracting retained earnings (uncovered loss) at the end of the period from the value at the beginning of the period. A positive difference indicates a net profit, and a negative difference indicates losses.
General business expenses include:
- administrative and management expenses;
- maintenance of general business personnel not related to the production process;
- depreciation charges and expenses for repairs of fixed assets for management and general economic purposes;
- rent for general business premises;
- expenses for payment of information, audit, consulting and other similar services;
- other administrative expenses similar in purpose.
An organization that is a professional participant in the securities market reflects the amount of costs associated with its activities under the item “Administrative expenses”. The amount on line 040 is equal to the amount of costs written off in the reporting period from the credit of account 26 to the debit of account 90.2 “Cost”.