- January 31, 2020
- Accounting
- Alexey Kim
How to calculate retained earnings on the balance sheet? You may have often heard the phrase “retained earnings” and wondered what it means? Just as individuals set aside a portion of their salaries to meet future unexpected expenses, companies also do the same. Companies set aside a portion of their profits for various purposes, such as paying off debts, providing an emergency fund, or reinvesting in the core business for expansion. Such savings are called “retained earnings” in accounting terminology.
Introduction
Retained earnings are earnings that have not been distributed to shareholders. This is why these funds are called “retained” rather than distributed. Retained earnings are a cumulative figure. This means that the amount of retained earnings shows the sum of all the profits that a company has retained up to a certain date. Therefore, it does not apply to just one financial year but applies to all financial years up to the above date.
Reflection of retained earnings in the balance sheet of the enterprise is carried out in the 3rd section of liabilities. Its value decreases when losses occur, and increases as a result of profit. This indicator is also called “accumulated profit”, “accumulated income” or “indivisible profit”.
The amount of the balance of retained earnings for previous years can be calculated as the amount of the credit turnover of account 84. As a result of the factors that determined the receipt of a retained loss by a company in the current year, this company can compensate for it at the expense of the residual value of retained earnings accumulated over previous years.
What is retained earnings and how is it formed?
Retained earnings are the balance of net profit for the previous reporting years of the company's activities. Retained earnings, as its own source of financing, can grow annually and ensure business development. From the point of view of balance sheet items, this means that the annual increase in equity capital is accompanied by a movement between balance sheet asset items. To distribute profits, a decision of the general meeting of participants is required (see also about corporate income tax).
Download and use it
:
Accounting policy The document regulates the rules for reflecting the company’s income and expenses, long-term and current assets, advances from customers, loans, as well as taxes payable
The procedure for accounting for profits and losses in management reporting If it is necessary to consolidate the classification of income and expenses, as well as the rules and procedure for accounting in management accounting, this document can be used as a sample.
Retained earnings: formula
Generally speaking, this measure measures the total amount of profit a company has earned since its inception, minus any losses incurred and the amount of profit distributed to shareholders. Retained earnings can also be a negative number. This occurs when total losses up to date increase profits. Such accumulated losses are also called “accumulated deficit.”
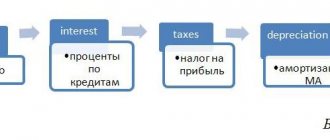
The formula for retained earnings for a given period looks like the picture below.
The amount shown on the balance sheet as "retained earnings" is referred to as "Ending Retained Earnings" (ERE).
As can be seen from the formula, retained earnings are equal to the difference in the amount of net income and dividends paid, summed with the previous value of retained earnings itself, in accordance with the definition and economic meaning of the indicator.
What should funds from retained earnings be spent on?
Retained earnings refer to the company's liabilities - that is, to the totality of debts and obligations. Some economists argue that, ideally, the entire amount of funds remaining in a company's account as retained earnings should be divided between investors and shareholders.
However, there are some nuances to this issue. Of course, shareholders are interested in paying significant dividends and will be happy with bonuses in the form of additional income . At the same time, it is important for the company’s owners that the enterprise in which they have invested develops and generates even more income in the future. That is, theoretically, they may agree to use retained earnings for the development of the company, rather than divide them among themselves .
Planning for spending retained earnings must necessarily take place with the participation of investors. What is it reasonable to propose using these funds for?
- Purchase of new equipment.
- Renting new premises and expanding the network of companies.
- Hiring new employees.
- Organization of franchising.
- Repayment of debts and credit obligations.
- Replenishment of the company's working capital.
- Encouragement of high-quality employees of the company.
- Reserve fund.
Shareholders are interested in paying significant dividends and will be pleased with bonuses in the form of additional income
The procedure for recording the indicator
Retained earnings in the balance sheet is the total of account 84 of the balance sheet liability. Its value represents the accumulated amount of the company's net profit since its inception. Therefore, the amount of accumulated earnings can be a positive or negative number.
If the company did not have retained earnings or retained losses reflected in account 84, the financial result for the year will be equal to the net profit from the corresponding report.
Changes in retained earnings in the current reporting period compared to the previous reporting period are not directly reflected in the balance sheet. However, you can calculate retained earnings in the balance sheet by subtracting the value of the indicator of previous years from the corresponding value of the current year. If there is any change in the accounting policies or practices adopted by the company in the current financial year, the company may also restate opening retained earnings. The purpose of this practice is to report changes in retained earnings in the current accounting cycle due to a change in policy.
Formula for calculating net profit on balance sheet
In the standard form of the balance sheet, approved by the order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia “On forms of financial statements of organizations” dated 07/02/2010 No. 66n, there is no net profit indicator. But in Section III “Capital and Reserves” of the balance sheet, line 1370 reflects retained earnings (uncovered loss), part of which is the net profit (loss) of the current period.
balance sheet and learn about the composition of its lines you can from the article
Having data from line 1370 of the balance sheet, net profit can be calculated using the formula:
PE = NP (at the end of the current year) - NP (at the end of last year),
where NP is retained earnings.
This formula is valid in the case where the company did not pay dividends. If dividends (D) were paid, net profit is calculated as follows:
PE = NP (at the end of the current year) - NP (at the end of last year) + D.
You can avoid calculating net profit using data from the balance sheet by studying another important accounting report - the financial results. In it, net profit is reflected in line 2400 “Net profit (loss)”. This indicator is used by financiers and accountants in their further calculations, reports and analyses. The formula for calculating net profit may be required only in cases where there is no access to other forms of accounting and financial reporting other than the balance sheet.
Despite the fact that net profit is calculated in the income statement, most assets and liabilities reflected in the balance sheet have an impact on the value of this indicator. We'll talk about this in the following sections.
Capitalization of retained earnings
The company may also capitalize its retained earnings by issuing bonus shares. The remainder of retained earnings can be distributed as dividends or carried forward as retained earnings into the next accounting cycle. How to calculate the nominal price of bonus shares that need to be issued in order to capitalize retained earnings on the balance sheet? It's simple - you need to divide the amount of retained earnings subject to capitalization by the number of shares, resulting in the nominal price of the share.
Movement of funds through the organization's accounts
Part of the profit aimed at paying dividends to shareholders is reflected in the financial statements as a debit to account 84 and a credit to accounts 75, 70 (“Settlements with founders”, “Settlements with personnel for wages”). Payment of interim interest is processed in exactly the same way. A loss in the balance sheet is most often reflected in the credit of account 84 in correspondence with the following accounts: 80 (“Authorized capital”) - when the authorized capital is transferred to the net assets of the organization; 82 (“Reserve capital”) - in the process of paying off losses using reserve funds; 75 (“Settlements with founders”) - repayment of losses at the expense of the funds of the organization’s participants. Revenue tracking and analytics are carried out in a certain way. This provides clear information about their use. In some cases of accounting for receipts of retained earnings, you can find a division of funds already used (for example, aimed at the development of the organization through the acquisition of additional basic income) and those still remaining on the balance sheet of the enterprise.
Factors influencing profit retention
- Age of the company: The longer the life of the company, the higher the retained earnings. A company will have more retained earnings if it has been around for a long time since it has more time to collect accumulated earnings.
- Dividend Policy: A company having a generous dividend policy will have lesser retained earnings. Such a company distributes dividends more frequently than a company with a conservative dividend distribution policy.
- Profitability: Businesses with higher profit margins will usually have higher retained earnings as these companies earn more and therefore can save higher amounts as retained earnings.
Indicator for investors
Retained earnings are a very convenient indicator for investors of the success of an enterprise. There may be several options, and from each a certain conclusion is drawn. Here are some examples:
- A situation when a company accumulates retained earnings without launching development projects. If the business is stable and does not require further progress, this is a good option that allows you to receive dividends.
- If modernization or further advancement in the market is needed, such conservatism can lead to stagnation and then a drop in income.
***
Retained earnings in the balance sheet are determined according to an established formula and show how much business owners can distribute in different directions. In addition, this indicator gives investors an idea of the company's success.
Similar articles
- How to calculate income tax on an accrual basis?
- How to calculate income tax: example
- How to show a loss on the balance sheet
- What is book profit?
- The ratio of penalties and losses
Report on this indicator
To calculate retained earnings in the balance sheet of an enterprise, first of all you should pay attention to correspondent accounts and accounting entries that are made on account 84.
It must be remembered that in the balance sheet of the enterprise, the account of retained earnings corresponds with the above accounts. This means that accounting entries in this account can be carried out by transferring money from the enterprise according to settlement transactions with partners, stakeholders, personnel, increasing or decreasing all types of capital of the enterprise.
Since there is no accurate information about changes in the balance sheet of retained earnings, how to calculate this indicator, companies can make a decision on their own. For example, prepare a separate report called “Statement of Retained Earnings.” The purpose of this report is to describe changes in retained earnings for a given reporting period. This report has been prepared in accordance with applicable accounting standards such as GAAP, IND AS or IFRS.
This report reconciles beginning and ending retained earnings for the period. This report uses information such as net income for the current accounting period, opening balance of retained earnings, dividends distributed in the current period, etc.
The income statement may be published as a separate report or supplemented by a balance sheet or income statement.
The concept of retained earnings and its display on the balance sheet
For any commercial organization, the main goal is to extract maximum profit from its activities, but not everyone who is going to engage in this business knows how to correctly take it into account and what indicators to pay attention to.
Any company manager is always interested in ensuring the optimal value of the retained earnings ratio, that is, providing himself with funds that can be distributed among the founders or left on the company’s accounts for the purpose of its further development.
At the same time, you need to correctly understand how retained earnings are reflected correctly and how to maintain a balance sheet taking this indicator into account.
Definition
Retained earnings on the balance sheet is a certain amount of cash that is in the accounts of an organization after it has fully paid taxes to the state budget. In other words, it is simply “net profit” that can be distributed at the discretion of members of the company's management team.
In the vast majority of cases, this amount of funds is used to purchase new physical assets or expand the proposed list of commercial products.
Asset or liability
Retained earnings on the balance sheet are a liability, since the value of this indicator shows the presence of the organization’s direct debt to its founders, since ideally this amount is fully distributed among members of the management team and invested in the further development of the business. In fact, the company does not have the right to dispose of its retained earnings until the owners of the organization make an appropriate decision.
It is worth noting that the loss that is reflected in line 1370 should also be located on the passive side of the balance sheet, but in this case we are talking about a negative value, and therefore the number will need to be placed in parentheses.
Formation and what it includes
Any result obtained from the sale of any product or the provision of its own services by the company must be reflected in the active-passive account 90, and the debit of this account indicates the cost, value added tax and other expenses, while the credit indicates the received revenue, and the final balance should subsequently be transferred to account 99.
In this case, only two entries will need to be made in the accounting book: Dt 90, Kt 90 – receipt of income; Dt 99, Kt 90 – receipt of expenses. All operations of the company related to non-operating and operational must be reflected in account 91.
In particular, this applies to:
- sale or temporary lease of any company assets;
- revaluation or depreciation of non-current assets;
- any operations that involved foreign currency;
- investments in the business of other organizations;
- donation or liquidation of any property;
- profit and costs received from transactions with securities.
In this case, only two entries are also indicated: Dt 91, Kt 99 – receipt of income; Dt 99, Kt 91 – receipt of expenses. This procedure in the professional environment is usually called balance reformation.
Retained earnings can expand if any errors are discovered in the accounting statements that cause expenses to be overstated, and also if shareholders do not claim their own dividends within three years from the date they were accrued. Likewise, any errors that result in overstated profits will ultimately reduce the amount of funds accumulated.
The components of retained earnings do not always represent direct cash in the form of an amount in a current account or cash, and this also must be taken into account in the process of conducting economic analysis.
During the last days of the reporting year, the accountant will also need to write off the final balance from account 99 to account 84, making two more entries in parallel: Dt 99, Kt 84 - receipt of income; Dt 84, Kt 99 – receipt of expenses.
Ultimately, account 99 is reset, and no further operations will be carried out on it until the end of the current year. In this case, account 84 refers to active-passive, and before entering the total amount of undistributed funds into it, you need to subtract the amount of tax from it.
Formation of retained earnings
Calculation formula
The formula used to calculate retained earnings provides for the addition of net profit to the initial amount of accumulated funds, with the further deduction of dividends paid to shareholders.
In other words, the formula itself will look like this: NNP + PE-D.
Previous reporting years
Retained earnings saved from previous years can be seen in accounting account 84.
At the same time, it is worth noting the fact that the balance on the credit of this account must always be transferred to balance sheet line 1370, and during the year there should be no movement on the credit of this account, since profit in the organization is traditionally distributed only after the results of the annual meeting of founders.
Difference from net profit
Net profit must be reproduced in the company's financial statements, and in itself it is characteristic of any modern organization.
At the same time, retained earnings must be reproduced in the balance sheet, taking into account the payment of dividends to the owners of the organization.
Thus, in some cases, given the right circumstances, these two types of income may be exactly the same, and sometimes they may differ by the amount of deferred tax payments.
How is retained earnings displayed on the balance sheet (account 1370)
Net profit is always indicated on the balance sheet of account 99 at the end of the reporting period, and this indicator serves as a demonstration of the final economic result of the organization’s financial activities over a certain period of time.
Balance sheet entries made on account 84
The first question that may arise is: is retained earnings on the balance sheet an asset or a liability? As noted above, this indicator is reflected in the 84th liability account of the balance sheet.
The postings made at the end of the relevant periods are shown below.
In accordance with these transactions, correspondent accounts are credited and debited, as a result of which the balance sheet value of the enterprise's retained earnings is calculated.
It is obvious that as a result of the above entries, both profit and loss from the activities of the enterprise for the reporting period are taken into account; accordingly, the numerical value of account 84 can either increase or decrease.
Retained earnings (uncovered loss) in the balance sheet
Uncovered loss or retained earnings on the balance sheet is an indicator that demonstrates the company's performance over the entire period of its existence. It is calculated on an accrual basis at the end of each specific reporting period. How retained earnings are formed , where it is reflected in the balance sheet and what mechanisms are involved in its calculation is the topic of this publication.
Retained earnings: asset or liability?
Retained earnings (uncovered loss) on the balance sheet is, of course, a liability, since it represents a share of the owners’ capital - profit generated and not yet directed to various needs. Being an internal source of finance, the company's profit in terms of economic content relates to a free reserve, which is distributed at the discretion of the founders and shareholders. This is what retained earnings (RE) means. Traditionally it is directed to:
- Investing in production development;
- Acquisition of assets;
- Payment of dividends;
- Creation (replenishment) of reserves.
The company can dispose of this liability only after a decision on the allocation of funds is made at a general meeting of owners, recorded in the minutes. Retained earnings are reflected in the balance sheet in line 1370 of the “Capital” section. The uncovered loss is also recorded there (if costs are higher than income), enclosing it in parentheses, and the overall result for the section is reduced by the amount of the loss.
Reflection of the indicator of previous years
Retained earnings from previous years are reflected in account 84 in accordance with the above formula. In order to reflect on the balance sheet entries with account 84 for previous years, the accounting entries shown in the table below are used.
As a result of making all the necessary entries at the end of the reporting period, the enterprise’s balance sheet on account 84 displays the total result regarding retained earnings (uncovered loss) for the reporting and all previous periods using the cumulative (accumulative) method. Thus, it is always possible to analyze the activities of the enterprise, the results of which take into account the payment of all mandatory payments and dividends, based on the numerical value of this account.
Regarding balance
Retained earnings of the reporting year are formed on the balance sheet of the enterprise as an active-passive account. It is shared by the owners of the company, but they have the right to use it only as specified in the charter. Money cannot be allocated for purposes that are not provided for in this document.
Here is a clear example of this accounting concept. The company earned 1,000,000 rubles in a year, from which it paid income tax in the amount of 200 thousand rubles. The amount of 800 thousand rubles should appear in the passive balance sheet, which is the net profit of the company’s reporting year. In the balance sheet, the line number is 1370, and the uncovered loss is recorded in it.
Such profits from previous years can be reflected on the balance of account 99. By the way, accounting distinguishes between non-return income and net profit. They are created on different accounts and have different meanings. The accounting documentation of the reporting period remains in the archives of the company. This is the legal procedure and should be followed by the accounting department.
Features of the Reformation
This process within the existing chart of accounts is carried out as follows. The accountant in account 99 (“Profits and losses”) displays, depending on the profitability or unprofitability of the organization, the ending balance. It must be transferred to account 84. In this case, this entry must be the final entry for the reporting period in the general ledger. Reformation of the balance sheet, according to established and approved generally accepted practice, is carried out only in the year following the reporting period, after the redistribution of retained earnings by the meeting of shareholders. At the same time, the accountant begins to carry out this activity by writing off amounts according to the instructions of the owner from account 84.