The authorized capital is an estimate of the contributions made by the founders at the time of creation of the LLC. The funds are stored in account 40. But the amount of the total capital is determined in conjunction with the unpaid share.
The authorized capital in the balance sheet is not fixed assets, but only the part that was contributed in advance by the owners. It is reflected in the charter and other documents of the company.
Dear readers! The article talks about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is individual. If you want to find out how to solve your particular problem , contact a consultant:
+7 (499) 110-43-85 (Moscow)
+7 (812) 317-60-09 (Saint Petersburg)
8 (800) 222-69-48 (Regions)
APPLICATIONS AND CALLS ARE ACCEPTED 24/7 and 7 days a week.
It's fast and FREE !
Capital formation has some features that may vary depending on the legal form and type of ownership.
Based on the shares contributed, each founder receives certain rights to the company. The amount of funds also determines the net profit.
What is it and where does it come from?
Authorized capital on the balance sheet is required when creating an enterprise. At this moment, the owners do not have any common funds other than their own. Therefore, the founders invest certain shares in the company.
The authorized capital is expressed not only in monetary terms. It can be contributed by property, copyright. After the transfer of funds, each owner receives a certain number of shares.
The amount of capital is negotiated by the owners. The transferred amount is specified in the charter, therefore the capital is defined as authorized capital.
When creating an OJSC or CJSC, all funds are determined in the form of shares. They can later be exchanged for money or property. In this case, most often the shares are simply displayed in documents, but do not have a material expression to exclude counterfeits.
You can take into account the number of shares using a special register. It is a table in which data for each shareholder is recorded. Maintenance is carried out by special organizations, where accounting is based on tracking purchases and sales of shares.
When forming an LLC, no shares are issued. The owners fix their shares in the charter. Division can be done into equal parts.
https://youtu.be/SMvt7MaMjw0
Online magazine for accountants
- account No. 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” in connection with prepayments made for the upcoming execution of work, provision of services, delivery of goods or materials;
- account No. 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” in connection with the shipment of goods, performance of services and work overdue for payment by customers and customers;
- account No. 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees”, where there is a surplus of the amount transferred to the tax authority from the calculation of taxes and fees;
- account No. 69 “Calculations for social insurance and security” in connection with the surplus paid to the Social Insurance Fund;
- account No. 70 “Settlements with personnel for wages” in terms of overpaid wages;
- account No. 71 “Settlements with accountable persons” in connection with funds paid to employees of the organization;
- account No. 73 “Settlements with personnel for other transactions” in connection with credits, borrowings and advances issued to the organization’s personnel, or for compensation of material damage to the company;
- account No. 75 “Settlements with founders” in connection with the debt of the founders for contributions to the authorized capital of the organization;
- account No. 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors” in connection with accrued income from joint activities, sanctions recognized by debtors for failure to fulfill contractual terms, debts of other persons on transactions, dividends that must be paid by other companies.
We recommend reading: Public cadastral map of Saransk
Highlights
In order to correctly form the authorized capital, it is important to remember several features. They are related to basic operations, posting, balance sheet balancing.
Basic Operations
Nowadays, founders often sell their own share of capital. Alienation can be accomplished in several ways. In the first case, the share is transferred to other participants. This allows you to maintain the amount of capital by changing the distribution of parts.
The option of transferring funds to a person who is not related to the founding board is also available. Then the authorized capital becomes smaller.
Any transactions are considered valid after appropriate corrections are made to the Unified State Register. All transactions are reflected in accounting. To understand the nature of the changes being made, it is necessary to consider an example.
One of the owners buys a share at par value. Then it is necessary to enter into the accounting record D 75 about the settlement with the founder, K 91-1 about other income to reflect the proceeds received from the sale of the share. It is also necessary to write down D 91-2 on other expenses and K 81 on own shares to reflect the write-off of the nominal value of the company’s share.
In addition to selling the share, the starting cost of capital can be increased. This is necessary to increase working capital and comply with licensing requirements.
Capital transactions entries
You can increase capital using your own property or additional contributions from new participants.
It is important to take into account some conditions:
- it is necessary to repay the debts of the participants to the company in full;
- the increased amount should not be greater than the difference between assets and debts;
- the net asset must be greater than the authorized capital.
Reflection of share capital is carried out similarly to the authorized capital. It is necessary to account for the company's profits.
Nuances of formation
The formation of the authorized capital is carried out depending on the type of property. The size is determined by the participants who contribute to the development of the enterprise.
When depositing not cash, but property, it is assessed. An independent person participates in it. The cost cannot be reduced after the documents reflect what assessment was made by the invited expert.
Responsibility for the procedure carried out lies with both the appraiser and the participants of the company themselves. If less property is contributed, additional subsidies will be made. The rule is considered valid for five years after the company is registered or changes are made to the charter.
This requirement does not apply to organizations that have privatized state or municipal unitary enterprises.
Payment for valuation services must be included in the initial cost of the transferred property, which includes:
- intangible assets;
- fixed assets;
- materials;
- goods.
If another organization acts as the founders, then when making a contribution, the amount of input VAT is restored. It is important that it is accepted for deduction earlier.
Tax restoration on property that has depreciation is carried out on the basis of its residual value. If other values are used, then the actual cost is taken into account.
If the tax is not recognized as part of the deposit, the amount is reflected in line 19 with account 83. In another situation, account 19 is used and account credit 75.
When contributing property less than the nominal share value, the founders' debt on deposits is formed. Otherwise, the difference is reflected in additional capital.
The profitability threshold shows the sales volume at which the LLC can cover all its expenses without making a profit. The types of business activities for which UTII is introduced are listed here.
The property that is a contribution to the authorized capital is allowed to be transferred into production, sold or transferred free of charge. At the same time, the size of the authorized capital should not decrease.
https://youtu.be/QPzWmJ-GJXU
Order and wiring
The company's funds are formed on the basis of share capital. It is required to carry out the activities of a company of an economic nature to make a profit.
The starting capital is reflected in the charter and is the nominal value of the company's shares (when forming an OJSC, CJSC) with a minimum amount of 1000 or 100 minimum wages. If an LLC is created, then the size is regulated at the legislative level and should not be less than 10,000 rubles.
Investments can be made using:
- Money;
- securities of value;
- copyright;
- other property.
You can contribute start-up capital in several parts. In this case, the first must be at least 50%. The outstanding debt must be repaid within the first year of operation of the firm. If the obligations are not fulfilled, the founder must reduce the size of his share. If the authorized capital is reduced to a level below that established by law, the company will be liquidated.
When transferring property against the authorized capital, it is important to take into account some features:
- Participants must evaluate the property. At the same time, they can determine its value higher than that established by the appraiser.
- When transferring a natural share, a transfer and acceptance certificate is drawn up.
- The charter may contain information about restrictions on the use of this or that property as authorized capital.
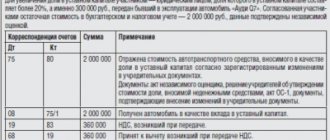
- The amount of capital is reflected not only in the charter, but also in the balance sheet. It is accounted for in passive account 80. After fixing, posting D75 is made on settlements with the founders and K80, which shows the size of the authorized capital. Using this information, you can confirm the availability of funds from the company based on the charter and track the amount of unpaid amounts by the founders.
- In the balance sheet, capital is reflected in line 1310 (Authorized capital). It includes the full amount even if partial payment is made. The debt is formed on account 1230 (Accounts receivable).
Receipt transactions are entered into specific accounts.
They can be expressed as follows:
| Cash | Dt 50, 51, 52 Kt 75 |
| Intangible assets | Dt 08 Kt 75 |
| Materials | Dt 10 Kt 75 |
| Securities | Dt 58 Kt 75 |
The importance of balance
Each company must have an equal number of assets and liabilities, expressed in ruble equivalent. This is why a balance sheet is maintained. It is a kind of scale with bowls in balance.
Assets are values owned by an enterprise. Liabilities reflect debt obligations. Thus, when paying off debts, the company has a zero balance.
When completing a balance sheet, the value of assets exceeds the value of liabilities. This does not indicate an increase in funds for the enterprise. Often accountants make mistakes, so the balance is upset.
At first glance, it may seem that balance is only required on paper. But it helps to find errors when inequality appears.
Accounting for settlements with founders and shareholders
At the time of state registration of the company, a standard entry is generated for the amount of the authorized/share capital. The same entries are made with a further increase in the amount of capital. At the same time, the credit balance of the account. 80 is equal to the amount of the authorized capital reflected in the constituent documentation. Primary documents are decisions, constituent/payment documents, acceptance certificates, cash orders, appraisers’ opinions, etc.
Related publications
Page 1230, which displays accounts receivable to the organization, includes the account balance. 75.1 on unpaid contributions to the authorized capital. At the same time, the “charter” itself is fully included in the liability side of the balance sheet on page 1310.
We recommend reading: Husband Took Child By Force And Won’t Give It Back
Nowadays, founders often sell their own share of capital. Alienation can be accomplished in several ways. In the first case, the share is transferred to other participants. This allows you to maintain the amount of capital by changing the distribution of parts.
How to reflect the authorized capital on the balance sheet
Every accountant must be able to reflect the authorized capital in the initial balance sheet and documentation of a legal entity.
To carry out the procedure, it is important to follow certain instructions:
- The constituent documentation must indicate the nominal value of the authorized capital in ruble equivalent. When property is listed at a value of more than 200 minimum wages, independent appraisers are invited.
- The balance sheet contains information about the authorized capital in line 410 of passive funds. If an LLC is registered, the tax service requires repayment of capital by at least 50%. In the case of creating a joint stock company, 50% is paid within three months after registration, and the remaining part - during the year of existence.
- When paying capital in cash, entries D 50, 51 and Kt 75 are made. Debts are formed using D 75 Kt 80.
- If fixed assets are made as a contribution, then account 08 is selected. This is due to the fact that the owners contribute both the cost of the property and the costs of its maintenance, registration, input and evaluation.
- When paying with raw materials or materials, a posting of D 10 Kt 75 is drawn up if their cost is taken into account, or D 10 Kt 76 when additional expenses are included. The decision is made based on the company's policy.
- If the founder fails to contribute the balance of funds, it is possible to return the contributed share or distribute the part among other owners or sell it to an outsider. In this case, liquidation will be used.
We fill out the balance sheet using a simplified form
Small businesses actively use simplified reporting forms when drawing up a balance sheet and financial statements for the past year. It would seem much simpler: the simplified balance sheet has only 5 items in its assets, and 6 items in its liabilities. However, even under these “three pines” there are hummocks. In this article we will talk about them.
Let me remind you that simplified reporting forms were approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated August 17, 2012. No. 113n. First, a few words about which assets and liabilities fall into which lines of the simplified balance sheet:
1. Tangible non-current assets: fixed assets, unfinished capital investments (accounts 01, 03 minus 02, accounts 07, 08).
2. Intangible, financial and other non-current assets: intangible assets (account 04 minus 05), long-term financial investments (corresponding subaccount 58, subaccount 55/3, possibly 73), unfinished investments in intangible assets, results of research and development (corresponding subaccounts accounts 08, 04)
3. Inventories: raw materials and materials, work in progress, finished goods, goods (accounts 10, 20, 23, 41, 43, 45, etc.)
4. Cash and cash equivalents: money in cash and in accounts (accounts 50, 51, 52, 55 except deposits, 57)
5. Financial and other current assets: short-term financial investments (corresponding subaccount of account 58), VAT (account 19), accounts receivable and other assets (accounts 60, 62, 68, 69, 70, 71, 73, 75, 76).
1. Capital and reserves: authorized capital (account 80), additional and reserve capital (if any, accounts 83 and 82), retained earnings (uncovered loss, account 84), revaluation of fixed assets (intangible assets), if such is carried out in organizations (account 83). This line also reflects own shares purchased from shareholders for cancellation (account 81). 2. Long-term borrowed funds: borrowed funds received under long-term loans and borrowings (account 67). 3. Other long-term liabilities (account 77, 96) 4. Short-term borrowed funds: borrowed funds received under short-term loans and borrowings (account 66). 5. Accounts payable: debt to creditors on accounts 70, 71, 68, 69, 76, etc. 6. Other short-term liabilities (account 96)
For each balance line, you need to enter the corresponding code in the column. What code to put if a line includes several indicators, each of which has its own code? Clause 5 of Order No. 66n of the Ministry of Finance “On Forms of Accounting Reports of Organizations” states that the code corresponding to the largest share is assigned.
For example, let Romashka LLC include in the line “Intangible, financial and other non-current assets”:
— intangible assets – 80 thousand rubles.
— long-term financial investments – 200 thousand rubles.
— results of research and development – 150 thousand rubles.
Total: 430 thousand rubles.
Financial investments have the greatest share. They correspond to code 1170. It is this code that will be entered in the simplified balance sheet in the line “Intangible, financial and other non-current assets” with the amount of 430 thousand rubles.
Question - what to do if there is nothing to write in a certain line? Those. There are no assets or liabilities that match the line. In this case, the string is simply not given.
A common situation is that a company has only recently been formed and is not yet active. A common question is: how to create a zero (empty) balance?
Despite the lack of activity, the balance will still not be completely empty. Not only the header will be filled in, but also some lines of liabilities and, possibly, assets.
If an organization is created, then at least it has formed an authorized capital:
Debit 75/1 – Credit 80
If the founders have not yet contributed the authorized capital in the form of property (money, goods, fixed assets, etc.), then there is a debt of the founders, which is a receivable.
Most often, founders contribute their capital in the form of cash to a current account:
Debit 51 – Credit 75/1
As a result, you will have the following lines filled in your balance sheet:
Capital and reserves (account balance 80)
Cash and cash equivalents (account balance 51).
Usually, even in the absence of activity, the bank debits funds from the current account for banking services. As a result, the funds in the account “melt”, and the balance sheet asset tends to zero.
In this case, the organization has an uncovered loss at the end of the year, the negative value of which “eats up” the authorized capital and the liability becomes equal to zero.
In this case, it is better to use the general form of the balance sheet to show the authorized capital and uncovered loss in brackets in separate liability lines. Or provide explanations for the balance.
If you do not have time to prepare “zero reporting” yourself and waste time on trips to the tax office, then contact us for help here:
Another common situation for young organizations is that uncovered losses exceed the amount of the authorized capital, due to which the Capital and reserves line becomes negative.
Let LLC “Forget-Me-Not” have an authorized capital of 10 thousand rubles, an uncovered loss of 30 thousand rubles. Then, when filling out a simplified balance sheet in the Capital and reserves line, it will show the value (20) and line code 1300.
A situation close to this begins with the words: we are trying to draw up a balance sheet, the asset turns out to be less than the liability. In principle, this cannot happen. Options: something was not reflected in the asset, or more likely, there are uncovered losses in excess of the authorized capital.
Example of a simplified balance sheet
Romashka LLC is a small business entity and fills out the balance sheet in a simplified form based on the results of 2014.
As of December 31, 2014, the company has the following assets:
The balance sheet of Romashka LLC is filled out in thousands of rubles and looks like this:
SCREENSHOT
The company began operations in February 2014, so it does not have data for 12/31/13 and 12/31/12, so dashes are placed in the columns dedicated to previous years.
We discussed the problems that arise when preparing a statement of financial results in an abbreviated form in this article.
>Systematization of accounting
Articles, reviews, expert comments
Cases of increase
The authorized capital may change during the course of the company's activities. This is possible by attracting new investors.
You can do this in several ways:
- When increasing the authorized capital, funds must be received no later than 2 months after the decision is made. After the money is received, the results of the increase are summed up at the meeting.
- If a person is not a member of the company, but wants to receive a share, he will need to draw up an application. It specifies the amount of the deposit, the term and method of transferring the contribution. When his candidacy is approved, changes are made to the charter and they are registered with the tax service.
- In the balance sheet, these changes are reflected using entries D 50, 51 K 75, and D 75 K 80. They are not reflected in tax accounting, even if the amount is greater than the nominal amount. Companies use a simplified version of reflection.
- If you want to increase capital by revaluing the value of existing property, the shares of each participant are increased. Revaluation is carried out no more than once a year. In this case, postings D 01 K 83 and D 83 K 02, D 83 K 80 are issued.
- An increase in capital can be made at the expense of profits that were not subject to distribution. This is written as D 84 K 80. Tax accounting provides for the recognition of an increase as non-operating.
Capital and reserves: lines
Section III “Capital and Reserves” is intended to reflect the organization’s own sources of financing the activities and includes the following indicators (clause 66 of Order of the Ministry of Finance dated July 29, 1998 No. 34n, Order of the Ministry of Finance dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n):
| Indicator name | Code |
| Authorized capital (share capital, authorized capital, contributions of partners) | 1310 |
| Own shares purchased from shareholders | 1320 |
| Revaluation of non-current assets | 1340 |
| Additional capital (without revaluation) | 1350 |
| Reserve capital | 1360 |
| Retained earnings (uncovered loss) | 1370 |
Let us recall that organizations that have the right to use simplified accounting have the right to prepare simplified reporting, in which the “Capital and Reserves” section is shown rolled up in one amount, without a breakdown by type of capital and reserves.
Reserve capital. Line 1360
This line reflects the amount of the organization’s reserve capital, formed both in accordance with the constituent documents and in accordance with the law (clause 20 of PBU 4/99).
What is included in reserve capital?
As part of the reserve capital on account 82 “Reserve capital” in limited liability companies the following may be taken into account:
— reserve fund;
- other funds created in the manner and amounts established by the company’s charter (clause 1, article 30 of Law No. 14-FZ).
The reserve capital in joint stock companies may include:
— reserve fund (clause 1, article 35 of the Federal Law of December 26, 1995 N 208-FZ “On Joint-Stock Companies”);
— a special fund for the corporatization of employees (clause 2 of article 35 of Law N 208-FZ, clause 1 of article 7 of Federal Law of July 19, 1998 N 115-FZ “On the peculiarities of the legal status of joint-stock companies of employees (national enterprises)”);
— special funds for the payment of dividends on preferred shares (clause 2 of Article 42 of Law No. 208-FZ);
— other funds created in accordance with the company’s charter, for example, a fund for the redemption of own shares at the request of shareholders (Articles 75, 76 of Law No. 208-FZ).
The reserve capital in unitary enterprises may include:
— reserve fund (clause 1 of article 16 of the Law of November 14, 2002 N 161-FZ “On state and municipal unitary enterprises”);
- other funds provided for by the charter of a unitary enterprise (clause 2 of article 16 of Law No. 161-FZ).
Attention!
The organization has the right to organize the accounting of its special funds (for the payment of dividends on preferred shares, for the corporatization of employees, etc.) in account 84 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)” separately (Instructions for using the Chart of Accounts). But regardless of the account in which these funds are accounted for, in the Balance Sheet they are shown on line 1360 “Reserve capital”.
Attention!
The distribution of profit (including for the formation of reserve capital) based on the results of the year falls into the category of events after the reporting date, indicating the economic conditions in which the organization conducts its activities that arose after the reporting date. At the same time, in the reporting period for which the organization distributes profits, no entries are made in accounting (synthetic and analytical) accounting. And when an event occurs after the reporting date in the accounting of the period following the reporting date, in general order an entry is made reflecting this event (clauses 3, 5, 10 of the Accounting Regulations “Events after the reporting date” (PBU 7/98 ), approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 25, 1998 N 56n). Consequently, data on account 82 in the reporting year is formed taking into account the decision made in the reporting year on the distribution of profit received based on the results of the previous year.
What accounting data is used when filling out line 1360 “Reserve capital”?
When filling out this line of the Balance Sheet, data on the credit balance of accounts 82 and 84 (in terms of special funds) as of the reporting date is used (clause 69 of the Regulations on Accounting and Financial Reporting).
Line 1360 “Reserve capital” = Credit balance on account 82 + Credit balance on account 84 (in terms of special funds)
The indicators in line 1360 “Reserve capital” as of December 31 of the previous year and as of December 31 of the year preceding the previous year are transferred from the Balance Sheet for the previous year.
Example of filling out line 1360 “Reserve capital”
Indicators for account 82 (there are no indicators for account 84 regarding special funds): rub.
| Index | As of the reporting date (December 31, 2014) |
| 1 | 2 |
| 1. On the credit of account 82 | 8 990 000 |
Fragment of the Balance Sheet for 2013
| Explanations | Indicator name | Code | As of December 31, 2013 | As of December 31, 2012 | As of December 31, 2011 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Reserve capital | 1360 | 5000 | 3000 | 2500 |
Solution
The amount of reserve capital is:
The optimal amount of the organization's equity capital
The amount of capital required for the effective operation of an organization depends on the direction of activity and the volume of transactions performed within one year. To determine the level of financial stability for a specific legal entity, insurance utilization ratios are used. Such indicators indicate the economic component of operations and do not affect accounting and tax accounting.
The agility coefficient shows the company’s ability to maintain the size of the capital stock and replenish working capital from internal sources. The indicator is calculated as the ratio of own working capital to the amount of capital insurance. The amount of working capital is determined based on the results of the second section of the balance sheet. In a financially stable company, the coefficient is at least 0.2.
The independence of a legal entity from creditors is determined by the autonomy coefficient. It is calculated as the ratio of the capital account to the balance sheet currency. If the indicator is more than 0.3, the company will have the necessary funds to pay off its obligations.
The financial stability ratio is characterized by the share of the company's assets that are financed by long-term borrowings. The indicator is defined as the ratio of the sum of capital assets and long-term liabilities to the balance sheet currency. For stable operations, the level of financial stability of the company must be 0.6 or higher. At this level, a legal entity has the ability to financially plan taking into account long-term financing of activities.
Changes and personal income tax
When a company is created by an individual and the size of the authorized capital changes, personal income tax also changes. In this case, the company is considered a tax agent.
Based on the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (Article 217), personal income tax is not taken into account when revaluing the fund’s assets due to additional attraction of shares or the difference between the original and new value of shares or shares of the authorized capital.
Article 217. Income not subject to taxation (exempt from taxation)
If the amount of capital increases with retained earnings, then personal income tax is charged. The amount is calculated based on all income of a certain tax period. The countdown starts from the date of the decision that the authorized capital and shares of each founder are increased.
In the absence of receipt of funds by the founders, personal income tax is not accrued. Each owner pays off his debt independently without using the tax agent's money.
If the authorized capital is reduced by the decision of the founders, additional income appears when the nominal value is reduced. It is taken as a basis when calculating personal income tax. When decreasing according to the law, no benefit is observed. Therefore no tax is paid.
It is important to correctly reflect the authorized capital in the accounting and tax balance sheets. This will make it possible to evaluate the company's funds, taking into account increases and decreases in the amount.
R&D expenses are written off from account 08 to the debit of account 04 “Intangible assets”.
We will describe in this article what IT outsourcing gives a company.
How analytical accounting of settlements for loans and borrowings is carried out - read
What is an organization's equity
Equity capital (EC) is the amount of cash and property that will remain at the disposal of the company when all obligations are paid. From an economic point of view, this indicator determines the efficiency of the company, because one of its elements is retained earnings (loss). The final financial result can either increase the well-being of the company or worsen it if a loss occurs.
The insurance company ensures the continuity of the company's activities, ensuring financial security during unfavorable periods. At the same time, the indicator has a guarantee function, ensuring payment of obligations to creditors. The structure determines the share of income received by each owner of the legal entity, and also makes it possible to make decisions that affect operational and strategic activities.