A company or individual entrepreneur, if they pay VAT, can, as they say, deduct “input” VAT. The “input” tax is the VAT that is included in the price of purchased goods, works or services. However, sometimes it is necessary to restore the “input” VAT accepted for deduction, that is, pay it to the budget. It turns out that the restoration of VAT leads to an increase in the tax payable, and the restored VAT is the money by which the VAT will increase, which must be paid to the budget.
If, when purchasing goods, works, VAT was absent (for example, due to the purchase of goods from a simplifier) or was not accepted for deduction (for example, due to the absence of an invoice), then there cannot be an obligation to restore VAT.
VAT restoration – what is it in simple words
A popular question is what VAT restoration is, in what situations it may be required, and what it means. In simple words for dummies - when purchasing a product, the buyer - the payer of the contribution - can take it as a deduction. But the entrance fee sometimes needs to be returned for payment. What does it mean.
Restoring a tax that was previously accepted for deduction is a procedure during which the tax accepted for deduction must be paid to the budget. There are some cases regulated by law when it is required to return deductions.
The amount of tax to be contributed to the budget is established based on the results of the tax period, deductions are excluded from it, but the indicator increases by the amount of the restored deduction. How the amount payable to the budget is calculated: the amount of the deduction is subtracted from the calculated indicator and the amount of the restored deductions is added.
In what situations is it necessary to make this payment to the budget:
- Property or intangible assets are transferred as a contribution to the authorized capital of business companies.
- Goods are used, including fixed assets and intangible assets, to perform the operations reflected in the second paragraph of Article 170 of the Tax Code.
- The buyer transfers the payment amount towards the planned delivery.
- Adjustments have been made to the price of shipped goods.
- The payer, according to the laws, received subsidies to reimburse the costs of paying for goods, taking into account the fee.
An example of a situation when it is required to return the fee - the buyer transferred an advance payment under the contract to the supplier in the amount of 118 thousand, incl. deductions of 18 thousand in April. In August, the supplier brought products for this amount, including tax.
The buyer sets the fee independently. For example, he applies a deduction for a payment in the amount of 18 thousand. In August, a deduction of 18 thousand was applied for purchased products. In the same month, deductions should be restored.
Including recovered VAT in income tax expenses
Having sold a product or service with VAT included, the company takes this amount into account according to the rules of Art. Such operations, by virtue of clause. The taxpayer must directly weigh for himself this or that opportunity, taking into account the emerging risks and obligations to prove his position in a dispute with the fiscal:. Let’s say an organization sold its goods for rubles.
Dear readers! Our articles talk about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is unique.
If you want to find out how to solve your particular problem, please use the online consultant form on the right or call the numbers provided on the website. It's fast and free!
- Recovered VAT should be included in other expenses
- How to reflect VAT in accounting and tax accounting
- “Profit-expenditure” VAT
- Input VAT in income tax expenses
- Accounting for “input” VAT as part of expenses: permitted cases and nuances
- The relationship between VAT and income tax
- VAT restoration: simple about complex things
Recovered VAT should be included in other expenses
The organization was provided with a subsidy from the federal budget. In the course of its activities, the organization incurred expenses for the services of third-party organizations, the purchase of inventory and fixed assets. Tax officials explained to the company that in this case, VAT amounts are not deductible.
https://youtu.be/aTQkOyQuYq0
But are VAT amounts included in the cost of goods, works and services purchased from the federal budget? The taxpayer asked this question to the Ministry of Finance.
Officials explained that in the case when subsidies are received as payment for goods, works, services sold by the taxpayer, which are subject to taxation, then VAT in respect of such subsidies is calculated in the generally established manner.
If subsidies are received to reimburse costs associated with payment for purchased goods, works, services, then such funds are not included in the VAT tax base, since these funds are not associated with payment for goods, works, services sold by this taxpayer.
It is necessary to take into account that since the deduction of VAT paid from the federal budget will lead to a repeated refund of the tax from the budget, the amounts of VAT paid from the funds of this budget are not subject to deduction.
Thus, the amounts of VAT previously accepted for deduction on goods, works, services, paid from the federal budget should be restored on the basis of subparagraph 6. In this case, the tax amounts subject to restoration are not included in the cost of these goods, works, services, and are taken into account as part of other expenses in accordance with the article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
My profile Favorites Clerk. Business Personal blog. State Report platform. User Agreement Rules for the use of materials.
How to reflect VAT in accounting and tax accounting
Amounts of input VAT previously accepted for deduction and restored on assets that began to be used in activities not subject to VAT, sub. When calculating income tax, take into account the restored amounts of VAT as part of other expenses associated with the production and sale of paragraph.
When calculating income tax, do not take into account tax amounts recovered in the following cases:. Previously restored VAT amounts cannot be reclaimed for deduction.
In particular, a repeated deduction is not possible if the property for which the input tax was restored again began to be used in transactions subject to VAT.
The organization was provided with a subsidy from the federal budget. In the course of its activities, the organization incurred expenses for the services of third-party organizations, the purchase of inventory and fixed assets.
From the city We have restored VAT on the balance. Can we take the amount of restored VAT as income tax expenses and what entry should we make in accounting? In tax accounting, take into account the restored VAT amounts as part of other expenses associated with the production and or sale of paragraph.
“Profit-expenditure” VAT
VAT and income tax raise the most questions among companies and often lead to disputes with inspectors. Let us consider the main important aspects of tax accounting for them, as well as the relationship between these taxes. VAT is the most complex tax. And even experienced specialists cannot figure out all the nuances on their own.
Article on the topic: Income tax in the year: new rates, table. When calculating income tax, VAT is not taken into account as expenses, as are the amounts of other taxes paid. But in some cases, the VAT that the company paid in the purchase price is not deducted, but is attributed to expenses. And these expenses reduce income taxes.
Input VAT in income tax expenses
Any accountant knows that submitted VAT can be deducted under certain conditions. However, there are cases when, due to legislation or the current situation, this is impossible.
When is it permissible to take into account paid VAT as part of expenses that reduce the income tax base? How do tax authorities interpret its provisions, and is their point of view always supported by judicial practice?
. Over the 10 years of its existence, the Academy has made a name for itself in the consulting and audit market: conducting thematic seminars and trainings both for those who are taking their first steps in creating a business, and for specialists and managers of the highest level.
We will review them and analyze whether there is a risk of a dispute with the inspectors.
Please note that we will only consider situations where an organization takes VAT into account as an independent expense, and does not simply include it in the cost of purchased assets according to the rules of paragraph.
The Ministry of Finance adheres to the same position and Letter from the Ministry of Finance from But there is one thing: if the zero VAT rate is confirmed, the tax calculated on the 1st day can be deducted in the future.
Accounting for “input” VAT as part of expenses: permitted cases and nuances
Reflect the VAT restoration in accounting with the following entries: An exception to this procedure is provided for the restoration of VAT on advances issued, when transferring property as a contribution to the authorized capital of another organization. Losses of inventory items are recognized as economically justified only within the limits of the norms of natural loss subclause.
WATCH THE VIDEO ON THE TOPIC: Lesson No. 10. Income tax
.
The relationship between VAT and income tax
.
On the possibility of including the amount of VAT (its equivalent) in expenses. Recovered amounts of VAT when calculating income tax.
.
We restore VAT correctly, how to restore a tax previously accepted for deduction, clause 8, article 145
The specifics of the restoration of VAT previously accepted for deduction are reflected in Article 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Previously, there was no such obligation, as a result of which controversial situations often arose on questions of how to restore VAT and when.
This article establishes the peculiarity of the procedure for releasing payers to make a payment. In paragraph 8 of Art. 145 states that collection amounts accepted for deduction in the VAT return are subject to restoration before exercising the right to exemption.
It may be necessary to restore VAT in several situations. According to Article 145, for persons who do not apply the exemption from the beginning of the quarter, an additional period is established for the purpose of restoration when the exemption began to be applied.
Restoring payment may be necessary if the payment terms have changed. Such an operation may be required in the event of exemption from deductions, a change in regime, when non-taxable transactions appear, or when working with a zero tariff.
Restoration may be required when property is contributed to the management company, the terms of advances are changed, the purchase price of an earlier purchase is reduced, or in the event of compensation for cash costs.
In case of restoration, you must correctly calculate the amount of payment and provide the necessary list of documentation. The procedure is not carried out if the fee was not accepted for deduction.
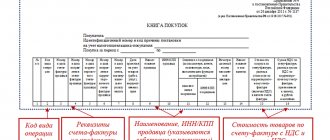
The returned payment must be entered into the sales ledger. This action is performed by registering the required amount with reference to information from the invoice, a certificate from the accounting department in the absence of a primary document.
If restoration is required as a result of a change in the terms of taxation of payments, then it may be necessary to organize separate accounting and distribute the tax in the future. Deductions will be taken for those portions of contributions that correspond to taxable activities.
If there has been an exemption in accordance with Article 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, a transition to a special regime or only to non-taxable activities has been made, there are special rules for reinstatement. The entire tax is fully restored, the amount of deductions for fixed assets is calculated in proportion to their residual price.
If there has been a partial transition to a special regime, taxable and non-taxable activities are combined, and restoration occurs partially. The fee that applies to direct expenses is fully refundable. The fee attributable to the residual price of the fixed asset is determined. For expenses that are not classified as taxable or non-taxable activities, the fee is distributed in accordance with Article 170 of the Tax Code.
Restoration with a complete change in tax conditions
Here we will talk about the following situations:
- exemption under Art. 145 and 145.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- full transition to a special regime - simplified tax system, UTII or PSN; when switching to the unified agricultural tax, there is no need to restore the tax (subclause 2, clause 3, article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- transition to conducting only non-taxable activities (exempt from tax, not recognized as an object of taxation or carried out outside the Russian Federation).
The period intended for restoration may vary:
- in the quarter preceding the start of work under new conditions, restoration is done in the event of a transition to a special regime, upon release under Art. 145 (if applied from the beginning of the quarter) and Art. 145.1 Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- in the quarter of commencement of work under new conditions, restoration is carried out upon transition to non-taxable operations and upon exemption under Art. 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, if the exemption does not begin to apply from the first month of the quarter.
Recovery in all these situations will occur in the same order:
- restore in full the entire tax related to those expenses that will form costs already under the new taxation system;
- the amount of tax related to fixed assets and intangible assets is calculated in proportion to their residual value (subclause 2, clause 3, article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- They use special restoration rules for real estate (Article 171.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), which at the date of transition to the new regime is depreciated at partial cost or has been used by the payer for less than 15 years.
Real estate should also include the costs of construction and installation works and the acquisition of vessels (sea, river and air). The restoration of such VAT is done at 1/10 of its total amount related to the object for 10 years, counted from the year of depreciation (clause 4 of Article 171.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The full amount of tax is formed not only by the VAT of suppliers, but also by the tax applied for deduction for construction and installation work carried out on a business basis. If the use of an object in a non-taxable activity began later than the year in which depreciation began, then the actual recovery period will be less than 10 years. The estimated amount must be restored in the last quarter of each year. In the case of reconstruction, the amount of the restored tax and the restoration period are adjusted taking into account the features contained in clauses 6 and 8 of Art. 171.1 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The restored amount is taken into account as an expense in the calculation of income tax or special tax of the simplified tax system (subclause 2, clause 3, article 170, clause 5, clause 7, clause 9, article 171.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Current VAT, received already in the process of applying the new regime, is included in the cost of acquisitions (clause 4 of article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Features of restoring VAT amounts for some fixed assets
Payment amounts previously accepted for deduction for fixed assets need to be restored not for all fixed assets, but only for those that were used in some transactions.
Cases when VAT restoration is required:
- Major construction was underway.
- Real estate was purchased.
- Ships or engines from them were purchased from the Russian Federation or imported into the Russian Federation.
- Objects used for construction and installation work were purchased.
- Construction and installation work was carried out for our own needs.
Recovered VAT is not required to be paid on fixed assets that have a depreciation rate of 100%, or more than 15 years have passed since they began to be used. The amount of the restored payment is reflected in the declaration. Each year, the amount of the recovery fee is set as 1/10 of the amount of tax accepted for deduction, in the corresponding share.
Restoration when applying 0% rate
The reasons for the restoration when an activity appears for which a 0% rate is applied lie in the difference in determining the moment of making a deduction at a rate of 18 (10)% and at a rate of 0% (clause 9 of Article 167, clause 3 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) . In the first case, the deduction is made immediately, and in the second - at a certain moment, sometimes much later. This necessitates separate accounting of taxes related to activities at different rates.
A one-time recovery during the commencement period of a 0% rate operation, whether all or part of it is converted to the 0% rate, will be required in respect of the tax attributable to the direct and allocable costs that would be included in the 0% rate costs. Restoration of VAT on fixed assets and intangible assets that begin to be used in such activities is not required from 2020.
In the future, VAT on direct expenses (including on fixed assets and intangible assets acquired during the period of application of the 0% rate and used only in this activity) will be taken into account separately, and tax on distributed expenses related to the 0% rate at the end of the quarter will have to be restored regularly.
The procedure for the first VAT recovery will be as follows:
- The tax on all direct expenses related to transactions at a 0% rate is fully restored.
- VAT on expenses that, at the time of the establishment of activity at a rate of 0%, cannot be unambiguously attributed to the rate of 0% or 18 (10)% (except for VAT on existing fixed assets and intangible assets), at the end of the tax period are distributed in the manner that the taxpayer establishes in his accounting policy, and restore the part related to the 0% rate.
In subsequent tax periods, the tax will be restored:
- periodically - for direct expenses that were supposed to be used in activities at a rate of 18 (10)%, but in fact they turned out to be used at a rate of 0% (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated August 28, 2015 No. 03-07-08/49710);
- regularly - for distributed expenses in the part related to the 0% rate, including for fixed assets and intangible assets acquired during the period of application of the 0% rate and used in both types of activities.
Accounting entries for VAT restoration
Recoverable VAT, according to the existing Tax Code in Russia, must be reflected in accounting entries. When switching to the simplified tax system, the following transactions will be used:
- DT 19 CT 68.02 – value added tax, previously deductible, has been restored.
- DT 20 CT 19 - the restored indicator is included in other expenses.
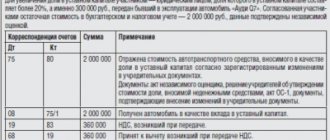
The procedure for VAT restoration includes the mandatory preparation of accounting entries when transferring assets. When the restored value is offset against the primary value of the share in the authorized capital, the posting will be DT 58.01 CT 19.
When do you need to restore VAT?
There is a list of cases when it is necessary to restore VAT. One of the situations when the payer must return the tax fee is when property is transferred as a contribution to the management company.
Deductions are also returned if the further use of goods and fixed assets is used in non-taxable transactions. Payment is also returned upon shipment of goods if the seller has previously received advance payment amounts and the tax on the advance payment has been deducted.
The same action is performed when the price of shipped products is reduced and subsidies are issued to reimburse costs. No other refunds are provided.